# 2025q1 Homework1 (lab0)
contributed by < `Eric-0522` >
### Reviewed by `Andrushika`
在你的筆記中,提及你參考他人的筆記後,在 `update_statistics` 中加上了以下程式碼:
```diff
static void update_statistics(const int64_t *exec_times, uint8_t *classes)
{
- for (size_t i = 0; i < N_MEASURES; i++) {
+ for (size_t i = 10; i < N_MEASURES; i++) {
```
這看起來是無條件丟棄前十筆數值,和百分位數的過濾無關,有點好奇這樣做的目的是什麼呢?採取該實作的用意應該註明。
{%hackmd NrmQUGbRQWemgwPfhzXj6g %}
## 開發環境
```shell
$ gcc --version
gcc (Ubuntu 13.3.0-6ubuntu2~24.04) 13.3.0
$ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Address sizes: 39 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
Model name: 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-12100F
CPU family: 6
Model: 151
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 4
Socket(s): 1
Stepping: 5
CPU(s) scaling MHz: 19%
CPU max MHz: 4300.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 6604.80
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d: 192 KiB (4 instances)
L1i: 128 KiB (4 instances)
L2: 5 MiB (4 instances)
L3: 12 MiB (1 instance)
NUMA node(s): 1
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
```
## 針對佇列操作的程式碼實作
### `q_new`
使用 malloc 分配記憶體後,由於其返回 `void *`,必須強制轉型成 `struct list_head *` 才能正確操作。接著,以 `INIT_LIST_HEAD` 將該指標初始化為空列表。
```c
struct list_head *q_new()
{
struct list_head *new = (struct list_head *)malloc(sizeof(struct list_head));
if (!new)
return NULL;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(new);
return new;
}
```
### `q_free`
原本想透過 `list_for_each_entry_safe` 巨集來走訪並釋放每個元素。但在進行`git pre-commit hook`檢查時,卻出現了以下錯誤訊息:
> error: There is an unknown macro here somewhere. Configuration is required. If list_for_each_entry_safe is a macro then please configure it. [unknownMacro]
上述錯誤訊息,已經在 commit [00b37f4](https://github.com/sysprog21/lab0-c/pull/211/commits/00b37f4b1f7acb8586f94e0dbeab9c9f8dbb5b30) 被 [lumynou5](https://hackmd.io/@lumynou5/linux2025-homework1) 給修正。
```c
/* Free all storage used by queue */
void q_free(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head)
return;
element_t *entry, *tmp;
list_for_each_entry_safe (entry, tmp, head, list)
q_release_element(entry);
free(head);
}
```
於是我參考了老師提供的「[2023 年 Linux 核心設計/實作課程第一次作業檢討](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux2023-lab0-review)」(包含其解說影片),在影片第[42:43](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pB0YOqkNk4Y)處老師提到 `list_entry` 這個巨集,它利用 `container_of` 將 `list_head *` 轉換成對應的 `element_t *`的記憶體位址。因此將程式碼修改成:
```c
/* Free all storage used by queue */
void q_free(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head)
return;
struct list_head *pos, *q;
list_for_each_safe (pos, q, head) {
element_t *entry = list_entry(pos, element_t, list);
q_release_element(entry);
}
free(head);
}
```
### `q_insert_head`
在實作 `q_insert_head` 時,首先檢查 `head` 是否為 `NULL`,若是則回傳 `false`;否則,建立一個 `element_t *` 節點 `new`,若建立失敗則回傳 `false`。接著,使用 `harness.h` 中定義的 `strdup` 巨集來複製字串 s,並將結果賦值給 `new->value`。如果 `new->value` 為 `NULL`,則釋放 `new` 並回傳 `false`;否則,使用 `list_add` 巨集將 `new` 插入 `queue` 的頭部。
> commit [3328406](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/33284061223afe0e8e14ba779958298c25ca32ee)
### `q_insert_tail`
在實作 `q_insert_tail` 前,參考了老師提供的「[2023 年 Linux 核心設計/實作課程第一次作業檢討](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux2023-lab0-review)」(包含其解說影片),其中提到程式碼重用性問題。我發現 `q_insert_tail` 跟 `q_insert_head` 實作幾乎相同(參考 commit [3328406](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/33284061223afe0e8e14ba779958298c25ca32ee)),其差別只在於傳入的第一個參數不同,因此我的想法是先判斷 `head` 是否為`NULL` 若是則回傳 `false`;否則將 `head` 改成 `head->prev` 帶入 `q_insert_head` 即可。
```c
/* Insert an element at tail of queue */
bool q_insert_tail(struct list_head *head, char *s)
{
if (!head)
return false;
return q_insert_head(head->prev, s);
}
```
### `q_remove_head`
在實作 `q_remove_head` 前,我先釐清需求,我的想法使用 `list_first_entry` 來取得第一個節點,再利用 `strncpy` 根據提供的字串大小複製字串,這樣能有效避免 `buffer overflow`,最後使用 `list_del` 將該節點從鏈節串列中移除。
> commit [d03c293](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/d03c2936ad1f435e9a36229036027874d77da7e1)
對於這種實作方式,我也在思考是否能有其他方法,讓使用 `strncpy` 後不必額外補 `NULL` 結尾。
此外,在查閱 [The Linux Kernel API](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/core-api/kernel-api.html) 網頁時,我發現[I-HSIN Cheng](https://hackmd.io/@vax-r/linux2024-homework1#q_delete_mid)所提的 `list_del` 描述問題仍存在。
> void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
> deletes entry from list.
### `q_remove_tail`
在實作 `q_remove_tail` 時,也需考慮程式碼重用性。因此,我的想法是將 `head->prev->prev` 放到 `q_remove_head` 第一個參數中,這樣即可正確指向鏈節串列的尾部節點。
```c
/* Remove an element from tail of queue */
element_t *q_remove_tail(struct list_head *head, char *sp, size_t bufsize)
{
if (!head || list_empty(head))
return NULL;
return q_remove_head(head->prev->prev, sp, bufsize);
}
```
### `q_delete_mid`
在實作 `q_delete_mid` 時,原本打算用快慢指標,但後來發現,由於 `list_head` 是環狀雙向鏈節串列,可直接令 `right` 指向 `head->prev`,`left` 指向 `head->next`,並同時移動它們,直到兩者相遇,此時即為中間節點,然後刪除該元素。
> commit [a9131f1](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/a9131f147a2bf0f6ac278b397ca52cbc451cf323)
### `q_delete_dup`
在實作 `q_delete_dup` 時,使用 `list_for_each_safe` 走訪鏈節串列,並為當前元素設定一個 `next` 指標指向下一個節點。接著利用 `while` 迴圈搭配 `strcmp` 比較當前元素與其後續節點的 `value`,若相同則刪除後者。
> commit [8e0d264](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/8e0d264bbe47805fafb377f88e427cdf75a063c9)
在測試`trace-06-ops.cmd` 時,當執行到 `dedup` 命令時,遇到這個錯誤:
> Segmentation fault occurred. You dereferenced a NULL or invalid pointerAborted (core dumped)
運用了 `Valgrind` 後,發現問題如下:
```
==40897== Invalid read of size 8
==40897== at 0x1101B9: q_delete_dup (queue.c:125)
==40897== by 0x10C396: do_dedup (qtest.c:467)
==40897== by 0x10E74D: interpret_cmda (console.c:181)
==40897== by 0x10ED12: interpret_cmd (console.c:201)
==40897== by 0x10F7FC: run_console (console.c:659)
==40897== by 0x10DB3C: main (qtest.c:1444)
==40897== Address 0x555555555555555d is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd
==40897==
Segmentation fault occurred. You dereferenced a NULL or invalid pointer==40897== 6 bytes in 1 blocks are still reachable in loss record 1 of 54
```
因此將原先實作的版本進行修改,先將佇列中的內容先排序,並改成使用單層迴圈。
> commit [0fc608e](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/0fc608e12f7bd9a645b022de31e6f4ec728d7964)
### `q_swap`
本來想使用 `list_for_each` 搭配 `list_swap` 來實作 `q_swap`。結果在執行 `make test` 遇到了以下錯誤:
> error: implicit declaration of function ‘list_swap’ [-Werror=implicit-function-declaration]
查看 `list.h` 後,我發現其中並沒有 `list_swap` 函式,但在 [The Linux Kernel API](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/core-api/kernel-api.html) 中卻有,故推測該函式可能已被老師移除。
在完成 `q_reversek` 後,回去看 `q_swap` 的實作,我發現 `q_swap` 僅涉及兩元素間彼此做反轉而已,因此決定重用 `q_reversek`,所以做了以下修改:
```diff
@@ -139,14 +139,7 @@
// https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
if (!head || list_empty(head))
return;
- struct list_head *pos;
- list_for_each (pos, head) {
- element_t *entry = list_entry(pos, element_t, list);
- if (pos->next != head) {
- element_t *next_entry = list_entry(pos->next, element_t, list);
- list_swap(&entry->list, &next_entry->list);
- }
- }
+ q_reverseK(head, 2);
}
```
### `q_reverse`
在實作 `q_reverse` 時,我想法是使用 `list_for_each_safe` 搭配 `list_move`來完成實作。使用這兩個的目的是,`list_for_each_safe` 會保存下一個節點,這樣再做 `list_move` 時,順序才不會跑掉。
> commit [f024a46](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/f024a46dc0098aaab969178f5f76a94cc990de88)
### `q_reversek`
使用變數 `count` 記錄已走訪的節點數,當 `count` 等於 `k` 時,利用 `list_cut_position` 將包含當前節點 `pos` 但不含下一個節點 `next` 的區段(即 `[pos, next)`)切下。接著對切下的子列表使用先前實作的 `q_reverse` 進行反轉,最後再用 `list_splice` 將剩餘的部分(從 `next` 開始)接回 `head`。
> commit [5dc28f6](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/5dc28f67286038cfe17d9ccbea1d040a7aa8c2ad)
在進行 `make test`時,測試到 `trace-04-ops.cmd` 這個檔案時,遇到了這個錯誤:
> ERROR: Removed value gerbil != expected value bear
因此我透過 `qtest` 手動測試,發現執行 `swap` 後,佇列由原本的三個元素減少到只剩一個。因此,我檢查了 `q_reversek`(因 `swap` 重用了它的程式碼)的實作,發現呼叫 `list_cut_position` 時,第一個參數必須設為 `empty`,否則會導致資料遺失。
修改後的版本:
> commit [9490842](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/9490842e47f5a7125becbcc15dc5978717bda806)
### `q_descend`
`q_descend` 的實作方式與 `q_delete_dup` 類似,不同之處在於它使用 `strcmp` 比較當前元素的 `value` 與後續節點的 `value`,若當前值較小,則刪除此元素。
> commit [b6819b5](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/b6819b542bae722ec23c1fd699e509720e0da36f)
### `q_ascend`
`q_ascend` 的實作方式跟 `q_descend`很像,差別在於`<`改成`>`。不確定是否可以直接重用 `q_descend` 函式。
> commit [4a805be](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/4a805be16f34fa67fd5bb2af0a0b1573f6f15850)
### `q_merge_two`
為了實作 `q_sort` 以及 `q_merge`,我參考[Alan Jian](https://hackmd.io/@alanjian85/lab0-2023#q_merge_two)的方法實作了此函式。合併的方式是每次從輸入的二個串列中,取較小的,放到一個暫存串列中 `tmp` ,之後再把串列接回 `first` 。
> commit [63b74db](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/63b74dbe1f79a444cade5bed3a43ff6a954dd935)
但在實作 `q_sort` 時,我發現多了一個 `descend` 參數,用於判斷排序方式(升序或降序)。因此,我修改了 `q_merge_two` 的實作以適應這個變化。
> commit [f4b6b68](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/f4b6b68ff07497cc405f97d6c73abfdb306f40d3)
在測試 `trace-04-ops.cmd` 這個檔案時,遇到 `Not stable sort` 的問題,經過分析錯誤的原因,是當 `q_merge_two` 比較兩字串相等時,會導致該問題發生。原本的邏輯是當兩字串相等時,會選擇來自第二個子序列的元素,而不是保持它們在原序列中的順序。因此進行以下修改:
```diff
@@ -188,11 +188,11 @@ static int q_merge_two(struct list_head *first,
element_t *second_entry = list_first_entry(second, element_t, list);
element_t *cmp_value;
if (!descend)
- cmp_value = strcmp(first_entry->value, second_entry->value) < 0
+ cmp_value = strcmp(first_entry->value, second_entry->value) <= 0
? first_entry
: second_entry;
else
- cmp_value = strcmp(first_entry->value, second_entry->value) > 0
+ cmp_value = strcmp(first_entry->value, second_entry->value) >= 0
? first_entry
: second_entry;
list_move_tail(&cmp_value->list, &tmp);
```
### `q_sort`
採用分治法實作 `q_sort`:首先利用雙向鏈節串列的特性從頭尾向中間尋找中點,將列表分割為 `head` 與 `second` 兩部分,再對這兩個子列表分別遞迴排序,最後用 `q_merge_two` 合併排序結果。
> commit [1e75b8d](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/1e75b8d52d59ffa0a205832b4cb9b2d3d49fbdcc)
### `q_merge`
`q_merge`實作方式一樣採用分治法,並搭配 `q_merge_two` 函式,它會根據 `descend`是否為 `true` 來實作升序/降序的合併,並回傳合併後的大小。其餘部份則是參考[Alan Jian](https://hackmd.io/@alanjian85/lab0-2023#q_merge)的實作。
> commit [9af6bc0](https://github.com/Eric-0522/lab0-c/commit/9af6bc07c54c155f21252d31976739e06abf986a)
在進行 `make test`時,測試到 `trace-03-ops.cmd` 這個檔案時,遇到了這個錯誤:
> ERROR: Freed queue, but 2 blocks are still allocated
經過分析,我發現 q_merge 的實作存在問題:在執行 `second->q = NULL` 與 `list_move_tail` 後,`context` 被移到鏈節串列尾端,導致多個空的 `queue context` 遺留在列表中,最終在釋放佇列時,這些空 `context` 會被誤認為是已分配的記憶體區塊,導致上述錯誤出現。
因此我將程式碼進行以下修改:
```diff
@@ -285,9 +285,11 @@ int q_merge(struct list_head *head, bool descend)
queue_contex_t *first, *second;
first = list_first_entry(head, queue_contex_t, chain);
second = list_first_entry(head->next, queue_contex_t, chain);
- while (second->q) {
+ queue_contex_t *end = NULL;
+ while (second != end) {
queue_size = q_merge_two(first->q, second->q, descend);
- second->q = NULL;
+ if (!end)
+ end = second;
list_move_tail(&second->chain, head);
second = list_entry(first->chain.next, queue_contex_t, chain);
}
```
## 研讀論文〈Dude, is my code constant time?〉
論文介紹的量測程式碼的方法 [dudect](https://github.com/oreparaz/dudect),用以量測其時間複雜度是否為常數時間 O(1),主要是為了進行 `leakage detection test`。
### 實驗方法
對執行時間進行洩漏檢查,使用 `Welch t-test` 統計方法,來檢測時間分佈是否存在顯著性差異。
1. 測量執行的時間方法:
使用 `fix-vs-random` ,將第一組輸入設為固定,而第二組輸入則會依據每次的測量隨機設定。
2. 進行後處理:
在進行統計分析之前,根據[chiangkd](https://hackmd.io/@chiangkd/dudect-study)撰寫的導讀筆記,有提到:
> 在較長的執行時間中,典型的時間分佈會呈現正偏態 (positive skew)
> 可能的原因為測量誤差 (measurement artifacts),主要的行程被作業系統或其他外部無關的活動 (extraneous activities) 打斷 (interrupt),可藉由過裁切 (crop) 掉大於某個大於、固定,且 class-independent 的閾值 (threshold,也譯作臨界值)。
因此需要對結果進行篩選或取捨,以確保統計分析的準確性。
3. 進行統計測試:
使用 `Welch t-test` 來測試兩組數據的時間分佈是否相等(e.g. 平均數是否相等)。若檢測結果不相同,則可能存在時間洩漏問題。
### 解釋 [Student's t-distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student%27s_t-distribution)
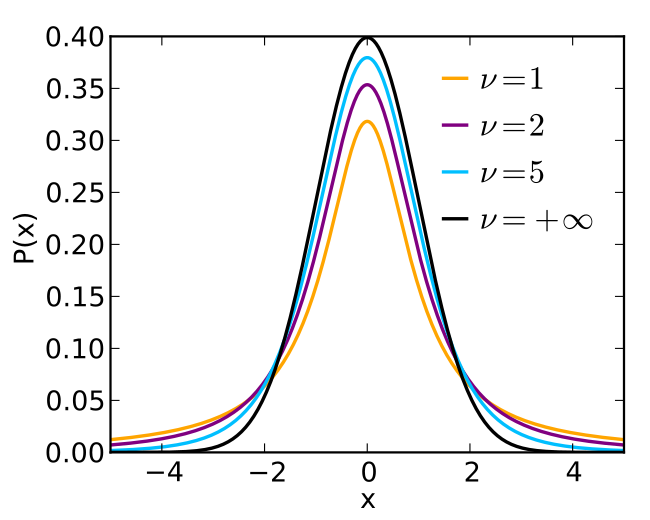
是一種連續機率分佈,其依據小樣本來估計未知標準差的母體期望值。透過自由度 `v` 來控制其分佈的形狀,當 `v` 越小則出現極端值得概率越高。相反地,當 `v` 接近無限大時,分佈越接近常態分佈。
### 修正 lab0-c 專案,使其擁有處理 percentile 的能力
在作業要求中,有提到:
> 在 [oreparaz/dudect](https://github.com/oreparaz/dudect) 的程式碼具備 percentile 的處理,但在 lab0-c 則無。
在參閱[vax-r](https://hackmd.io/@vax-r/linux2024-homework1#%E7%A0%94%E8%AE%80%E8%AB%96%E6%96%87%E3%80%88Dude-is-my-code-constant-time%E3%80%89)筆記後,可以得知 `lab0-c` 專案,實際執行測試 constant time 的函式為 `doit`,而在 [oreparaz/dudect](https://github.com/oreparaz/dudect) 專案對應的是 `dudect_main` 這個函式。接者在根據[vax-r](https://hackmd.io/@vax-r/linux2024-homework1#%E7%A0%94%E8%AE%80%E8%AB%96%E6%96%87%E3%80%88Dude-is-my-code-constant-time%E3%80%89)筆記中的內容,進行對應的實作與修改,即可以完成 `traces/trace-17-complexity.cmd`的測試。
以下是修改的程式碼:
```diff
static void update_statistics(const int64_t *exec_times, uint8_t *classes)
{
- for (size_t i = 0; i < N_MEASURES; i++) {
+ for (size_t i = 10; i < N_MEASURES; i++) {
```
以及在 `update_statistics` 函式前,新增以下程式碼:
```c
static int cmp(const int64_t *a, const int64_t *b)
{
return (int) (*a - *b);
}
static int64_t percentile(int64_t *a_sorted, double which, size_t size) {
size_t array_position = (size_t)((double)size * (double)which);
assert(array_position < size);
return a_sorted[array_position];
}
/*
set different thresholds for cropping measurements.
the exponential tendency is meant to approximately match
the measurements distribution, but there's not more science
than that.
*/
static void prepare_percentiles(int64_t *exec_times) {
qsort(exec_times, N_MEASURES, sizeof(int64_t), (int (*)(const void *, const void *))cmp);
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_MEASURES; i++) {
exec_times[i] = percentile(exec_times, 1 - (pow(0.5, 10 * (double)(i + 1) / N_MEASURES)), N_MEASURES);
}
}
```
### 參考資料
- [<Dude, is my code constant time?>](https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/1123.pdf)
- [dudect](https://github.com/oreparaz/dudect)
- [chiangkd](https://hackmd.io/@chiangkd/dudect-study)以及[Lccgth](https://hackmd.io/@subsidium/linux2024-homework1#%E7%A0%94%E8%AE%80%E8%AB%96%E6%96%87-%E3%80%88-Dude-is-my-code-constant-time-%E3%80%89) 撰寫的導讀筆記
- [vax-r](https://hackmd.io/@vax-r/linux2024-homework1#%E7%A0%94%E8%AE%80%E8%AB%96%E6%96%87%E3%80%88Dude-is-my-code-constant-time%E3%80%89)筆記
## 研讀 lib/list_sort.c 並嘗試改進
在研讀 `lib/list_sort.c` 程式碼時,搭配 [lab0(E)](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux2023-lab0/%2F%40sysprog%2Flinux2023-lab0-e#%E7%A0%94%E8%AE%80-Linux-%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83%E5%8E%9F%E5%A7%8B%E7%A8%8B%E5%BC%8F%E7%A2%BC%E7%9A%84-liblist_sortc) 一起閱讀,對於 `lab0(E)` 提到的合併方式不懂,不懂的點在於:
> 因為只要 $3 * 2^k$ 可以放得進 L1 cache,可以避免 cache thrashing。
為什麼這樣做可以避免 `cache thrashing`?
## 整合網頁伺服器
## 開啟 Address Sanitizer,修正 qtest 執行過程中的錯誤
## 實作 `shuffle` 命令
## 疑惑的內容
### 針對lab0-c/CONTRIBUTING.md中的Initialization標題所寫的內容
> Do not initialize static and global variables to 0; the compiler will do this.
- 為什麼compiler會對static和global變數做初始化?
### 什麼是Just-in-time編譯技術?
### 為什麼需要用到callback function?
- 以linenoise.h中的程式碼為列:
```c
typedef void(line_completion_callback_t)(const char *, line_completions_t *);
typedef char *(line_hints_callback_t)(const char *, int *color, int *bold);
typedef void(line_free_hints_callback_t)(void *);
typedef int(line_eventmux_callback_t)(char *);
void line_set_completion_callback(line_completion_callback_t *);
void line_set_hints_callback(line_hints_callback_t *);
void line_set_free_hints_callback(line_free_hints_callback_t *);
void line_set_eventmux_callback(line_eventmux_callback_t *);
```
- 這樣設計是有什麼實際的考量嗎?
## 啟發的內容
### lvalue
- C99[6.3.2.1]的備註
> (53) The name ‘‘lvalue’’ comes originally from the assignment expression E1 = E2, in which the left operand E1 is required to be a (modifiable) lvalue. It is perhaps better considered as representing an object ‘‘locator value’’.
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet