# Leetcode刷題學習筆記--Binary Search
## Introduction
binary search的精隨就是在一個排序過的數列裡面,找出所要的值。因為每次都切半,所以可以時間複雜度達到O(logN)。相較於暴力破解法,例如答案在1~N之內,==如果測試函數可以讓你知道數字是往更大或更小的方向,就可以用binary search。==
> 1. remove special case(答案不在可能的範圍內)
> 因為繼續使用binary search,如果答案比範圍內的還大,會得到left = sz。(還可以判斷)
> 如果答案比範圍內的還小,會得到left = 0。(無法判斷)
> 1. 定義出答案可能出現的範圍left和right。
> 因為計算mid的方法,right必須是範圍最大值+1。
> 2. 決定中間點,mid = left + (righ - left) / 2;
> 避免有overflow的問題。
> 3. ==判斷中間點是否超過要搜尋的值==,例如**278**是用isBadVersion(), 668是看有多少數值超過目前的值。
> 4. 更新left, right。==通常right為錯誤的那一邊==。所以判斷完中間點是錯的,需要把區間往下則right = mid,如果是對的,則區間往上,left = mid +1;
> 5. 直到left < right不成立為止。
> 最後left會等於right。
> 6. 最後結果會在上一次的right上。所以要根據題目決定要取目前這一個(left)還是left - 1的結果。
## Code Snippet
```cpp=
int left = 0;
int right = arr.size() - 1; // 或是 right = arr.size(); 端看最後一個值是不是已經確定了
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; // 避免overflow
// 如果要拿mid來計算,
// 值域會超過int(4)則改用long(8)
int val = ...; // 使用mid計算出新的值。
// 如果計算結果會overflow則可改用long(8)
if(val == target) // 依題目需求決定要步要用
else if(val > target) // 或是使用 val >= target
right = mid;
else
left = mid + 1;
}
```
## Corner Case
### 當長度為1
left = mid = right,都會指向同一個element。

### 當長度為2
left = mid, right = mid + 1, 只有left和mid一樣。所以竟可能拿mid和right來判斷。

## Special Case
當使用 while(left<right)的時候,最左邊和最右邊的答案不會檢查。所以當答案有可能在這兩個之外,必須在while之外做額外的檢查。
case 1 : 如果答案比index 0還小,則最後left/right會停在node 0而離開while loop,但是沒檢查node 0。

case 2 : 如果答案比index 5還大,則最後left/right會停在node 5而離開while loop,但是沒檢查node 5。

這種情況必須視題目而定。如果答案一定是在node0~node5之間,那就直接return沒關係。如果除了node0~node5之外還有額外的答案,那就必須檢查left/right使否正確。
## 從答案的範圍,用binary search 猜測是否正確。
另一種binary search的應用。只知道答案的範圍,使用binary search來逼近正確的答案。如下的code:
```cpp
int left = ANS_MAX, right = ANS_MIN;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 根據題目計算由mid得到的結果
// 和題目給的條件去比較,並更新left, right
}
```
### case 1 : 當搜尋範圍就是比較的範圍
例如 : 從已排列好的array中,找出4的數字。

題目:
+ [34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array](/u7dufNJ-SAq7z0WmS-Semw?both#34-Find-First-and-Last-Position-of-Element-in-Sorted-Array)
### case 2 : 當搜尋範圍和比較的範圍不一樣
### case 2-1 : 比較範圍是遞增數列
### case 2-2 : 比較範圍是遞減數列
搜尋的範圍和比較的範圍不一樣,且比較的範圍是遞減數列。

題目:
+ [1760. Minimum Limit of Balls in a Bag](/u7dufNJ-SAq7z0WmS-Semw?both#1760-Minimum-Limit-of-Balls-in-a-Bag)
+ [875. Koko Eating Bananas](/u7dufNJ-SAq7z0WmS-Semw?both#875-Koko-Eating-BananasMedium)
+ [275. H-Index II]()
## Search Range
針對binary search,首先一定要有一個搜尋範圍。通常使用left和right來表示欲搜尋的上下界。
+ 因為我們都是用mid來測試條件是否成立。所以mid要可以達到答案範圍內的每個值。
+ 如果,left = 1, right = 30,且mid = left + (right - left) / 2,則mid的範圍是mid = 1(left = 1, right = 2)..., mid = 29(left = 29, right = 30),mid就無法達到30。
+ 所以要讓mid達到上界,則right = 31。mid = 30(left = 30, right = 31)
+ 因為答案不可能達到(上界+1),所以最後可以判斷這個(left == 上界+1)排除掉。
```cpp=
// setup search range
int left = 1, right = 31;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int result{0};
// test mid
// update the search range
if(result >= k) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
// 因為結果不可能出現31
return left == 31 ? -1 : left;
```
例如:[1870. Minimum Speed to Arrive on Time](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-speed-to-arrive-on-time/)
```cpp=
class Solution {
// speed : 1, 2, 3, [4], 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, ...
// hour : 10, 9, 9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 7, 7, ...
// > <=
public:
int minSpeedOnTime(vector<int>& dist, double hour) {
int sz = dist.size();
if(hour <= sz - 1) return -1;
int left = 1, right = 1e9 + 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int need{0};
for(int i = 0; i < sz - 1; ++i)
need += (dist[i] + (mid - 1)) / mid;
double fneed = need + dist.back() * 1.0 / mid;
if(fneed <= hour) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left == 1e9 + 1 ? -1 : left;
}
};
```
## Update the Search Range
有了search range,就可以得出mid,這時就必須測試mid是否在範圍之內,然後更新left或是right來縮小搜尋範圍。==通常mid得出的結果必須是遞增或是遞減數列==,這樣才有機會使用binary search。
例如, mid的範圍如下,可以得到測試結果rtn為遞減數列。
```cpp
// mid = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
// rtn = 9, 9, 8, 8, 7, 7, 6, 6, 5
```
再根據題目,通常會限制rtn為某個數,假設是7,因為mid通常在前一個,
```cpp
// mid = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
// rtn = 9, 9, 8, 8, [7], 7, 6, 6, 5
// > <=
// mid
```
所以根據上面的圖示可以寫出
```cpp=
int k = 7;
if(rtn <= k) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1
return left;
```
最後答案就是left。
另一種情況是
```cpp
// mid = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
// rtn = 9, 9, 8, 8, 7, [7], 6, 6, 5
// >= <
// mid
```
可以寫成
```cpp
int k = 7;
if(rtn < k) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
return left - 1;
```
必須返回left - 1,因為最後left == right,會是下一個。
## Maximum-Minimum or Minimum-Maximum problem
一個題目要求尋找一個答案的最小值,但是這個值是某個運算的最大值,通常都是binary search的題目。
例如:[2560. House Robber IV](https://leetcode.com/problems/house-robber-iv/description/)
其中,robber的capability的定義是偷過的金額中==最大值==。但是必須返回某個條件下(最少必需偷k個房子)的==最小值==。Minimum capability(which is maximum of all stealed money)
```cpp=
class Solution {
// capability(maximum) 偷的金額中最大的
// [2, 3, 5, 9], k = 2(minimum) 最少要偷兩間
// 回傳 最小(minimum)的capability。 min-max problem --> binary search?
// capability 2 ~ 9
// mid = capability : 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
// k 1 1 [2] 2 (為了符合capability, 最多能偷的house數)
// < >=
public:
int minCapability(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
auto [minv, maxv] = minmax_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int left = *minv, right = *maxv;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if(nums[i] <= mid) {
count++;
i++;
}
}
if(count >= k) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
};
```
## Example
### [278. First Bad Version(Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/first-bad-version/)
找出第一個錯誤的版本。一定會有一個錯誤的版本。
n = 1, [1]:只有一個版本,則一定是錯誤版本。
n = 2, [1,2]:有兩種情況[X,X]都是錯誤版本和[O,X]一對一錯。
n = 3, [1,2,3]:有三種情況[XXX][OXX][OOX]
使用binary search,right一定會錯誤版本。
```cpp=
int firstBadVersion(int n) {
int left = 1, right = n, mid;
while(right > left) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(isBadVersion(mid))
right = mid; // right為錯誤版本
else
left = mid + 1;
}
return right; // 因為是找錯誤版本
}
```
算中間點有兩種算法
```cpp=
mid = (left + right) / 2;
```
或是
```cpp=
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
```
答案都會是一樣,差別在於如果left和right很大,則left + right有可能overflow,但是第二種方法不會。
==right一定是指向錯誤的版本==。所以code才會寫成以下的樣子。而且最後一定是==return right==。
```cpp=
if(isBadVersion(mid))
right = mid; // right為錯誤版本
else
left = mid + 1; // 下一個版本。
```
----
c++的STL有提供binary search的function。
lower_bound和upper_bound,都是用binary search來找目標值,差別在於
> lower_bound : 返回==等於或大於==目標值的最小位置。
> upper_bound : 返回==大於==目標值的最小位置。
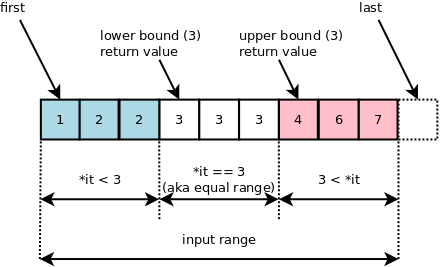
**返回值為iterator**。
所以取值必須用
```cpp=
value = *it;
```
在array中的index必須用
```cpp=
idx = it - nums.begin();
```
### [668. Kth Smallest Number in Multiplication Table(Hard)](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-number-in-multiplication-table/)
在一個乘法表裡面(width(n) x height(m),都是1開頭遞增)找出第k個最小的數字。
例如:n = 3, m = 3, k = 5,其中第5個最小的數字為3。
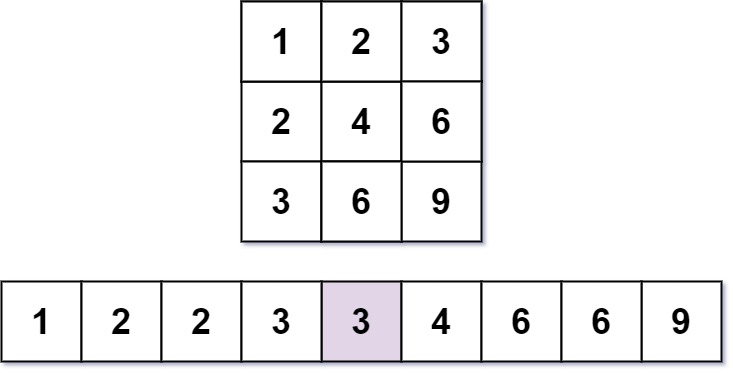
解題思路:
> 1. 在 1 ~ m*n的數字中,找出一個數字,剛好小於這個數字的數量等於k。=> binary search。
> 2. 因為數字都是倍數關係,所以可以用 ==mid / i==來算出小於mid的數量。


```cpp=
int findKthNumber(int m, int n, int k) {
// 第一個和最後一個不用算
if(k == 1 || k == m * n) return k;
int left = 1, right = m * n;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2, cnt = 0;
// 計算比mid小的數值有多少個
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
cnt += (mid > n * i) ? n : (mid / i);
}
// 比較小,區間往上,所以left一定是下一個數
if (cnt < k) left = mid + 1;
// 大於等於,區間往下,所以right = mid
else right = mid;
}
return right;
}
```
### [540. Single Element in a Sorted Array(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/single-element-in-a-sorted-array/)
給你一個排列過的整數數列nums,其中每個數都是兩兩一對,除了一個數只有一個,問你怎麼找出那一個數。題目又說希望執行效率事O(logN)。
例如:
nums = [1,1,2,3,3,4,4,8,8],output = 2。
解題思路
> 1. 一開始看到就想到XOR,這樣就可以找到那個數,但是時間是O(N)。
> 2. 看到O(logN),直覺就想到binary search。但是怎麼判斷範圍要往前還是往後是個問題。
> 3. 先想一下special case。
> 3-1. 題目說長度從1開始,因為兩兩一對只有一個是單獨,所以長度一定是奇數。
> 3-2. 長度 == 1,那不用判斷一定是那一個。
> 3-3. 長度 == 3,那不是第一個,就是最後一個。
> 3-4. 長度 == 7,可以發現要找的數字,和mid和前後關係不太依樣。

> 4. 判斷完mid之後,可以把數列變短,問題又是一樣。
照以上的思緒,程式碼如下:
```cpp=
int singleNonDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
auto n = nums.size();
if(n == 1) return nums[0];
int left = 0, right = n - 1, mid;
while(left < right) {
if(right - left <= 3) {
if(nums[left] != nums[left + 1]) return nums[left];
if(nums[right] != nums[right - 1]) return nums[right];
}
mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if(mid % 2) {
if(nums[mid] == nums[mid + 1])
right = mid - 1;
else
left = mid + 1;
} else {
if(nums[mid] != nums[mid + 1])
right = mid;
else
left = mid;
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### [300. Longest Increasing Subsequence(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
給你一個vector<int> nums找出,這個當中找出最長的strictly increasing subsequence.
+ subsequence的定義是,在nums中的前後順序依樣,但是可以不用連續。
+ strictly increasing,每個數字都比前一個大。
> 1. 一開始的想法是,每看到一個數字就去map找比他還小的數字
> 2. 然後,更新dp[i]和比他還小的數字連起來最長。
> 3. 這個方法效率不好O(NlogN)。
```cpp=
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
auto n = nums.size();
if(n == 1) return 1;
map<int, vector<int>> m;
vector<int> dp(n, 1);
int maxlen{1};
m[nums[0]].push_back(0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(auto& item : m) {
if(item.first >= nums[i]) break;
for(auto& idx : item.second) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[idx] + 1);
}
}
maxlen = max(maxlen, dp[i]);
m[nums[i]].push_back(i);
}
return maxlen;
}
```
> 網路上的解法
> 1. 使用一個vector來記錄走過的subsequence
> 2. 找出lower_bound(大於等於)換掉
> 3. 不然就是推到最後面。
```cpp=
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> v;
for(auto& n : nums) {
auto it = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), n);
if(it == v.end()) v.push_back(n);
else *it = n;
}
return v.size();
}
```
### [875. Koko Eating Bananas(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/koko-eating-bananas/)
請參考原題目。
> 1. 這題思考很久,最後看到題目提示是用binary search才恍然大悟。
> 2. 因為速度k 和最後多少個小時h吃完成線性關係。也就是速度越快,所用的h越少,所以可以用binary search來完成。
> 3. 定義left和right。因為piles最大值為1e9,h最小值為1,所以left = 1, right = 1e9
> 4. 計算k的時候需要無條件進位,等於是(b + mid - 1)/ mid
> 5. 最後是希望最小的k,所以設定right >= h

> 2022/04/25
> 1. 因為吃的速度越快,需要的時間就越短
> 2. 但是koko偏好吃慢一點, 如下圖所示就是2的位置。
> 3. 計算時間使用[無條件進位](https://hackmd.io/3I17t2spT6GDLFRftfEOZA?view#%E7%84%A1%E6%A2%9D%E4%BB%B6%E9%80%B2%E4%BD%8D)。

```cpp=
int minEatingSpeed(vector<int>& piles, int h) {
int left = 1, right = 1e9;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int t = 0;
for(auto& n : piles) t += (n + mid - 1) / mid;
if(t <= h) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
```
### [1539. Kth Missing Positive Number](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-missing-positive-number/)
給你一個vector<int>為嚴格遞增序列(strictly increasing order),找出第k個missing number。
```cpp=
int findKthPositive(vector<int>& arr, int k) {
// 把right設定成arr.size(); 是因為當 k 比最大還大時
// right還可以等於arr.size();
int left = 0, right = arr.size();
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int val = arr[mid] - (mid + 1);
// 等於也要,因為也在arr[mid - 1] ~ arr[mid] 中間的範圍內。
if(val >= k) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return right + k;
}
```
### [1608. Special Array With X Elements Greater Than or Equal X](https://leetcode.com/problems/special-array-with-x-elements-greater-than-or-equal-x/)
找出一個數x,使得在vector<int> nums中,有x個數大於等於x。
ex:
Input: nums = [0,4,3,0,4]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are 3 values that are greater than or equal to 3.
> 1. 因為下面的程式使用了只有當 mid == cnt,才return正確值,反則return -1。所以mid一定要走訪到所有可能的答案[1~sz]。
> 2. 當length = 2的情況,left = mid,所以right必須要等於sz + 1,才可以讓mid走訪所有可能的答案。
```cpp
int specialArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int sz = nums.size();
int left = 1, right = sz + 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int cnt = 0;
int cnt = count_if(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [&](int& a) {
return a >= mid;
});
// 因為用了mid == cnt 才return,
// 所以mid的位置就很重要,因為當length == 2時,mid == left
// 所以right的位置要+1
if(mid == cnt) return mid;
else if(mid > cnt) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
```
### [34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/)
在一個排序的數列中,找出target的左右位置。
> 1. 根據以下的圖,可以得知,在做binary search的比較關係。

> 2. 有兩個special case
> 2-1. 當數字出現在第一個,這個不會影響判斷

> 2-2. 當數字出現在最後一個位置。

> 因為我們都是拿mid來比較,會造成, mid只會停在倒數第二個的位置。

> 所以必須把right的位置往後移一個,讓mid有機會判斷到最後一個位置的數字。

> 並且答案為 left - 1,因為最後會停在 > target的位置。
```cpp
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int sz = nums.size();
if(sz == 0 || target < nums[0] || target > nums[sz - 1]) return {-1, -1};
vector<int> rtn(2);
int left = 0, right = sz - 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] >= target) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
rtn[0] = nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
left = 0, right = sz;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] > target) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
rtn[1] = nums[left - 1] == target ? left - 1 : -1;
return rtn;
}
```
### [1760. Minimum Limit of Balls in a Bag](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-limit-of-balls-in-a-bag/)
operatin的定義是,可以對數字進行切割成兩個。切割的兩個數字可以自己決定。
所有的operation次數不可以超過maxOperations。想辦法讓最大的數字最小化。
> 1. 使用binary serach假設答案是某個數字。因為切割為多次,penalty就會越小。如下圖所示:

```cpp
int minimumSize(vector<int>& nums, int maxOperations) {
int left = 1, right = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int cnt = 0;
for(auto& n : nums) cnt += (n - 1) / mid;
if(cnt <= maxOperations) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
```
2022/11/4
```cpp
// 使用binary search。則mid要搜尋什麼?
// 1. 找penalty?
// 2. 找ops (好像不太容易)
// 把 left , mid, right所表達的意義遞增排序,就可以得到ops為遞減排序
// penalty : 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
// ops : 8, 7, 6, 5, 5, [5], 4
// 假設maxOperations為5,並選到了[5]這一個,
// 因為往左還會有更小的penalty,所以使用小於等於,繼續往左移動
// 相當於是lower_bound的概念。
public:
int minimumSize(vector<int>& nums, int maxOperations) {
int left = 1, right = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
while(left < right) {
// mid 為欲達成的penalty,則所需的ops為?
// 因為ops越多,penalty越少
// ops 1 2 3 4 [5] 6 7 8 <-- 因為這個mid得到的ops次數 = 5
// p 9 8 7 6 [6] 5 4 3 <-- mid
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int ops = 0;
for(auto& n : nums)
ops += (n - 1) / mid;
if(ops <= maxOperations) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
```
### [275. H-Index II](https://leetcode.com/problems/h-index-ii/)
```cpp
int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) {
int sz = citations.size();
int left = 0, right = sz + 1;
// h index : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, ...
// cnt : 8, 7, 7, 6, 6, 5, 5, 4, 3, 2, ...
// >= <
// h-index : h篇論文,每個都被引用至少h次
// 所以h[越小],[越多]論文被引用至少h次
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int cnt = 0;
for(auto& n : citations)
if(n!= 0 && n >= mid) cnt++;
if(cnt < mid) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left - 1;
}
```
2022/11/4
```cpp
// 使用binary search。則mid要搜尋什麼?
// 1. 找penalty?
// 2. 找ops (好像不太容易)
// 把 left , mid, right所表達的意義遞增排序,就可以得到ops為遞減排序
// 因為要找maxOperations,且越大越好,所以等於是找小於等於那一邊
public:
int minimumSize(vector<int>& nums, int maxOperations) {
int left = 1, right = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
while(left < right) {
// mid 為欲達成的penalty,則所需的ops為?
// 因為ops越多,penalty越少
// ops 1 2 3 4 [5] 6 7 8 <-- 因為這個mid得到的ops次數 = 5
// p 9 8 7 6 [6] 5 4 3 <-- mid
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int ops = 0;
for(auto& n : nums)
ops += (n - 1) / mid;
if(ops <= maxOperations) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
```
### [658. Find K Closest Elements](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-closest-elements/)
給以一個排列過的遞增數列,找出K個最接近X的數,結果也要遞增排序。
> 這題一看直覺就是用sort來排序,但是效率比較差O(NlogN + KlogK + K)
> 比較好的解法是使用binary search。只要找出left,則整個數列就會出來。所以使用binary search找出答案array的left在哪裡。
> 所以我們可以列出四種狀況

> case1 : x在left的左邊
> case2 : x在left和right的中間,但是比較靠近left
> case3 : x在left和right的中間,但是比較靠近right
> case4 : x在right的右邊
> 其中,case1和case2必須把array往左邊移動。因為必須讓x在中間,case3和case4必須把array往右邊移動。
> 上面的情況是left和right不一樣的時候,使用兩種判斷式都可以正確的移動array。
> 另外一種情況是數字有重複,則使用abs來判斷就會失效。如下圖。

> 使用abs,三種情況都會是一樣。但是如果是使用
```cpp
if(x - arr[mid] < arr[mid + k] - x) { }
```
或是使用
```cpp
if(arr[mid] - x > x - arr[mid + k]) { }
```
> 因為 x - arr[mid] 和 arr[mid + k] - x,會有==正負的差別==,所以可以判斷出需要往左還是往右移動。
> 相等的時候為什麼是向左移動? 因為我們是使用arr[mid + k]。
> arr[mid + k] 是在k之外的一個數值,如果相等表示需要向左移動。
```cpp
vector<int> findClosestElements(vector<int>& arr, int k, int x) {
int left = 0, right = arr.size() - k;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (x - arr[mid] > arr[mid + k] - x)
left = mid + 1; // 向右移動
else
right = mid; // 向左移動
}
// arr.begin() + left + k 不會取
return vector<int>(arr.begin() + left, arr.begin() + left + k);
}
```
因為binary search只找了N-K的範圍長度。
return的答案占了K長度的vector。
| Time | Space |
| -------- | -------- |
| $O(log(N-K))$ | $O(K)$ |
### [1898. Maximum Number of Removable Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-removable-characters/description/)
給你兩個字串s和p,其中p為s的subsequence。在給你一個vector<int> removeable,表示可以要依序刪除的index。試問最多依序可以刪幾個char還可以保持p為s的subsequence。
> 2022/11/07
> 一開始做這一題完全沒想法,看了答案之後覺得是一題好題目。
```cpp
class Solution {
// 圖1, mid為刪除char的個數,j為s中有p的個數
// mid = 0, 1, [2], 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, ...
// j = 4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 1, ...
// >= <
// 圖2, 說明為什了是map[i] >= mid
// string index 0, 1, 2, [3], 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
// mid = 3, 刪除3個(0, 1, 2), 保留6個(3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
// <--刪除-| |------保留------>
// < >=
// 0, 1, 2
// removable : 3, 1, 0
// 0, 1, 2, [3], 4, 5
// m : 2 1 M 0 M M , M : 表示不會被刪除
public:
int maximumRemovals(string s, string p, vector<int>& removable) {
int sz = s.size();
vector<int> map(sz, INT_MAX);
for(int i = 0; i < removable.size(); ++i) map[removable[i]] = i;
int left = 0, right = removable.size() + 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2, j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size() && j < p.size(); ++i) {
// 圖2
if(map[i] >= mid && s[i] == p[j]) ++j;
}
//圖1
if(j >= p.size()) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return left - 1; // 圖1, 從上圖會選到p.size() - 1那一個,所以要選前一個
}
};
```
### [792. Number of Matching Subsequences](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-matching-subsequences/description/)
找出vector<string> words中,會是s的subsequence的個數。
> 1. 一開始我是用trie結果TLE
> 2. 先建立每個char會出現的index,方便之後尋找。
> 3. 使用 int x = -1, 則使用upper_bound第一次會找到第一個。
> 4. 依序找出每個char會出現的位置。這邊也有Greedy的意味在。因為每次只會找到大於x的最小值。
```cpp
int numMatchingSubseq(string s, vector<string>& words) {
// 建立char和index的對應vector
vector<vector<int>> alpha(26);
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) alpha[s[i] - 'a'].push_back(i);
int rtn = 0;
for(auto& word : words) {
int found = true;
int x = -1; //** 很重要,因為第一次會找到第一個
for(auto& c : word) {
auto it = upper_bound(alpha[c - 'a'].begin(), alpha[c - 'a'].end(), x);
if(it == alpha[c - 'a'].end()) {found = false; break;}
else x = *it;
}
if(found) rtn++;
}
return rtn;
}
```
### [2517. Maximum Tastiness of Candy Basket](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-tastiness-of-candy-basket/description/)
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int maximumTastiness(vector<int>& price, int k) {
sort(price.begin(), price.end());
int left = 0, right = price.back() - price.front() + 1;
while(left < right) {
// 基於這個tastiness之下可以選到最多的candies
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int cnt{1};
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < price.size(); ++i) {
// 因為排序過,所以最小差值只會發生在
// 目前的(i)和選到的candy最大值(j)之間
if(price[i] - price[j] >= mid) {
cnt++;
j = i;
}
}
if(cnt >= k) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return left - 1;
}
};
// [13, 5, 1, 8, 21, 2], k = 3
// [1, 2, 5, 8, 13, 21] after sorting
// search range : 0, 21 - 1
//
// [1, 2, 5, 8, 13, 21]
// t : 10 因為排序過,最小的差值只會出現在鄰近兩個之間。
// tastiness : 0, 1, 2, 3, [4], 5, 6,
// cnt : 5, 4, 4, 3, 3, 2, 1 tastiness越大,可以選的candy越少。
// >= <
```
### [2448. Minimum Cost to Make Array Equal](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-cost-to-make-array-equal/description/)
給你一個vector<int> nums和cost,每對一個數字nums[i]加一或是減一的行為需要cost[i],試問讓nums數字一樣的最小cost。
> 0. 有想到用binary search但是對於二次曲線不知道怎麼用。參考[lee215](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-cost-to-make-array-equal/solutions/2734162/java-c-python-binary-search/)的解答。
> 1. 首先想到讓vector的數字一樣,那個數字一定是在最小值和最大值之間。
```cpp
int left = 0, right = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
```
> 2. 如果x軸是平均數,y軸是cost則會得到一個二次向上凹的曲線。一般的binary search就不適用。
> 3. 必須針對 mid, mid+1來判斷目前在曲線的那個部分。
```cpp=
long long y1 = f(mid), y2 = f(mid + 1);
if(y1 < y2) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
```
+ 完整解答。
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
long long minCost(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& cost) {
long long l = 1, r = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end()), res = LONG_MAX, x;
auto f = [&](int x) {
long long res{};
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
res += 1L * abs(nums[i] - x) * cost[i];
return res;
};
while(l < r) {
x = l + (r - l) / 2;
long long y1 = f(x), y2 = f(x + 1);
res = min({res, y1, y2});
if(y1 < y2) r = x;
else l = x + 1;
}
return res;
}
// time : O(N) + O(logk * (2N)) = O(N + 2NlogK) = O(NlogK)
// N : size of nums
// k : the difference between minimal and maximum value
// space : O(1)
};
```
### [1851. Minimum Interval to Include Each Query](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-interval-to-include-each-query/description/)
> 1. 一開始我也打算使用binary search來解,但是卡住了。因為我用queries來尋找interval,但是這樣會有問題。
> 2. 反過來使用intervals來尋找覆蓋到的queries就簡單多了。
> 3. 先對intervals的長度來排序。
> 4. 從最小的intervals取出來,看看是否有覆蓋的queries,有的話就跟新ans。
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> minInterval(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& queries) {
// O(NlogN)
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b){ // O(NlogN)
return a[1] - a[0] < b[1] - b[0]; // 從短到長排序
});
// O(MlogM)
set<pair<int, int>> st;
for(int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) // O(QlogQ)
st.insert(make_pair(queries[i], i)); // 把queries從小帶大排序
//O(N(logM + MlogM))
vector<int> ans(queries.size(), -1);
for(int i = 0; i < intervals.size() && !st.empty(); ++i) {
int s = intervals[i][0], e = intervals[i][1];
int len = e - s + 1;
auto it = st.lower_bound({s, 0});
while(it != st.end() && it->first <= e) {
ans[it->second] = len;
advance(it, 1);
st.erase(prev(it));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
// time :O(NlogN + MlogM + NMlogM)
// sapce : O(M)
```
### [852. Peak Index in a Mountain Array](https://leetcode.com/problems/peak-index-in-a-mountain-array/description/)
> 0. 根據montain array的定義,arr.front()和arr.back()不會是peak。
> 1. 在peak的右邊一定滿足,arr[i] > arr[i + 1]
> 2. 在peak的左邊一定滿足,arr[i] < arr[i + 1]
> 3. 所以可以使用上面任一個條件來判斷。
+ 使用peak左側來判斷。
```cpp=
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(arr[mid] < arr[mid + 1]) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return left;
```
+ 使用peak右側來判斷
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int peakIndexInMountainArray(vector<int>& arr) {
int sz = arr.size();
if(sz == 3) return 1;
int left = 0, right = sz - 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(arr[mid] > arr[mid + 1]) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
};
// *
// 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
// -------------
// --------------
// arr[i] > arr[i + 1]
// arr[i] < arr[i + 1]
// case1 : 4, 5 , left = mid + 1 = answer
// l/m r
// case2 : 5, 4, right = left = 5 = answer
// l/m r
```
+ 這邊用左邊判斷取left,合理。但是用右邊判斷為什麼不用left - 1?
+ 這邊沒有target,所以之前的分析都不成立?
+ 只和自己的左邊和右邊比較,來更新left和right。
+ 使用arr[mid] > arr[mid + 1] 來判斷會得到以下關係。
```
// 0,10,5,2
// F, T,T,T
```
+ 使用arr[mid] < arr[mid + 1] 來判斷會得到以下關係
```
// 0,10,5,2
// T, F,F,F
```
+ 可以發現不管是使用哪個判斷式,最後會收斂在0,10也就是狀態轉換的邊界,所以答案不用left - 1。
+ 後來想想這種pattern其實和[278-First-Bad-VersionEasy](https://hackmd.io/u7dufNJ-SAq7z0WmS-Semw#278-First-Bad-VersionEasy)一樣,都是TTFFFF,找出TF的交界,答案會是left。
### [2141. Maximum Running Time of N Computers](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-running-time-of-n-computers/)
> 1. 參考官方解答。
> 2. 假設現在可以跑target的時間,則n個computer必須要有 n * target的電量。
> 3. 多少電量可以分配? 大於等於target的電池沒辦法額外使用?
假設n個電腦可以跑到target的時間,那這個電池剩下的電量也就無法使用。所以
```cpp
extra += min(target, batteries[i]);
```
> 4. 判斷式為 extra >= n * target,則可以得到以下的關係
```
target : 1, 2, 3, [4], 5
result : T T T T F
```
> 因為要找出True的最大值,從上面的例子就是4,所以就可以得到以下的判斷式。
```cpp=
if(extra >= n * target)
left = target + 1;
else
right = target;
```
> 5. 從上圖得知,最後結果為 left - 1。
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
long long maxRunTime(int n, vector<int>& batteries) {
long sum = accumulate(batteries.begin(), batteries.end(), 0L); // O(M)
long left = 1, right = sum / n + 1; // K : range from left to right
while(left < right) { // O(logK * M)
long target = left + (right - left) / 2;
long extra{};
for(auto& b : batteries)
extra += min((long)b, target);
if(extra >= (long)(n * target))
left = target + 1;
else
right = target;
}
return left - 1;
}
// time : O(M + MlogK) = O(MlogK)
// space : O(1)
};
// target : 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
// result : T T T T F
```
###### tags: `leetcode` `刷題`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

