# 2016q3 Homework2 (phonebook-concurrent)
contributed <`nekoneko`>
# 資料閱讀
- [ ] Toward Concurrency
- [ ] 軟體開發現狀
- [x] The Free Lunch Is Over: A Fundamental Turn Toward Concurrency in Software
- [x] An Introduction to Lock-Free Programming
- [x] Acquire and Release Semantics
- [x] Weak vs. Strong Memory Models
- [ ] Concurrency Kit
- [ ] Functional Programming
- [x] Why are functional languages considered a boon for multi threaded environments?
- [x] It’s Time to Get Good at Functional Programming
- [x] Don’t Be Scared Of Functional Programming
- [x] Functional programming in C
- [x] Concurrency (並行) vs. Parallelism (平行)
- [ ] Concurrency 系列文章 (繁體中文)
- [x] Concurrency系列一到五
- [ ] 冼鏡光投影片
- [ ] Process vs. Thread vs. Coroutines
- [ ] SMT (Simultaneous Multithreading), VMT(Vertical Multithreading)
- [x] setjmp, longjmp
- [ ] switch case
- [ ] POSIX Threads
- [x] [POSIX Threads Programming(point 1 ~8)](https://computing.llnl.gov/tutorials/pthreads/)
- [x] condition variable
- [x] thread pool
- [ ] sorting link list
## 軟體開發現狀
### The Free Lunch Is Over
- 隨著CPU邁向多核和hyper threading等增加效能的性能,這兩種技術已經普遍於大多的CPU。然而,CPU的頻率因為物理現象造成的瓶頸已經到達上限。
- Past 30 years
- clock speed
- execution optimization
- cache
- near-term future
- hyperthreading
- multicore
- cache
### An Introduction to Lock-Free Programming
- What is Lock Free Program ?
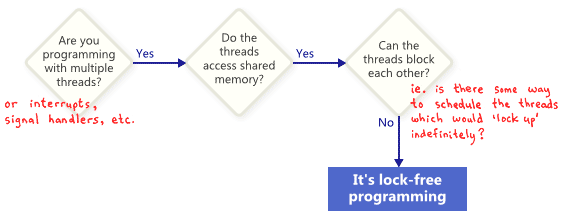
- Lock-Free Programming Techniques
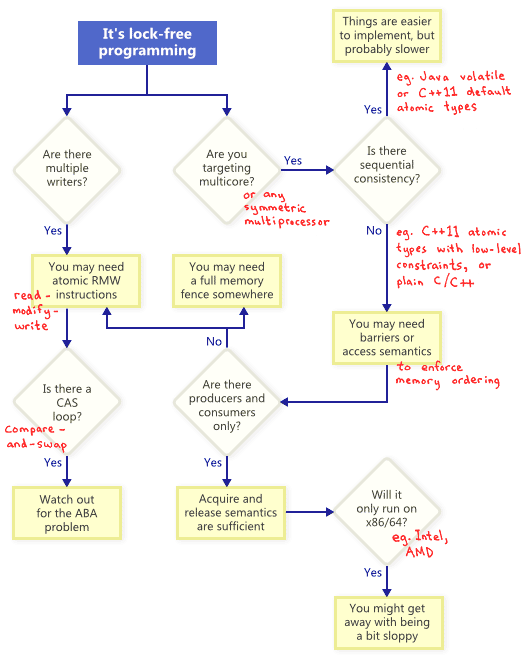
> 不懂的詞: ABA Problem, ~~CAS, Lock~~MUTEX
- Atomic Read-Modify-Write
在多執行序的情況下,對資料的讀寫使用atomic操作,保證資料的一致性
- Compare And Swap
atomic的實做有不同的方式,在恐龍本中提到test-and-set和compare-and-swap,兩種都是為了在多執行序的情況下,只讓一個執行序進入critical session。以下是恐龍本書中程式碼。
```clike=
int compare_and_swap(int *value, int expected, int new_value) {
int temp = *value;
if (*value == expected)
*value = new_value;
return tempt;
}
some_other_atomic (...) {
do {
while (compare_and_swap(&lock,0,1) != 0) ;
/* critical section */
lock = 0;
/* remainder section */
} while (true);
}
```
- ABA Problem
這邊可以參考[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ABA_problem)和[tundegrod大大的筆記](/s/rk5IVI0a),寫的很清楚。
- Sequential Consistency & Memory Ordering
編譯器的優化和CPU本身亂序執行,會導致指令執行的順序與原先程式碼不同(Memory Ordering)。
>> 搭配看影片: [Memory Ordering Intro - Georgia Tech](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5L5CheUeSnw) [name=jserv]
> - [ ] 有提到三種防止memory Ordering的方式。目前沒看懂之後再補。[name=cheng hung lin]
- Different Processors Have Different Memory Models
如標題,各個cpu對於自家的亂序執行都有其不同的方式。
- 參考資料
[atomic](http://www.makelinux.net/books/lkd2/ch09lev1sec1) , [read-modify-write](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Read-modify-write), [恐龍本(OS) 6.4章](https://www.amazon.com/Operating-System-Concepts-Abraham-Silberschatz-ebook/dp/B00APSZCEQ), [tundergod的筆記](/s/rk5IVI0a)
### Acquire and Release Semantics

- [Memory Ordering at Compile Time](http://preshing.com/20120710/memory-barriers-are-like-source-control-operations/)
- 四種指主要的barrier: LoadLoad, LoadStore, StoreLoad, StoreStore。
- 本篇以兩個end-user對應一個central repository來介紹四種主要的memory barrier。
- 文章提到四種有barrier功能的函式
- Certain inline assembly directives in GCC, such as the PowerPC-specific `asm volatile("lwsync" ::: "memory")`
- Any `Win32 Interlocked` operation, except on Xbox 360
- Many operations on C++11 atomic types, such as `load(std::memory_order_acquire)`
- Operations on POSIX mutexes, such as `pthread_mutex_lock`
- [Memory Barriers Are Like Source Control Operations](http://preshing.com/20120710/memory-barriers-are-like-source-control-operations/)
- fense instruction, barrier instruction
### Weak vs. Strong Memory Models
### Concurrency Kit
- [Slides](http://concurrencykit.org/slides.html):
- [Introduction to Concurrency](http://concurrencykit.org/presentations/ck-pt.pdf)
- [ ] [Fast Bounded-Concurrency Hash Tables](http://concurrencykit.org/presentations/lpc2015.pdf)(未讀)
## Functional Programming
### Why are functional languages considered a boon for multi threaded environments?
- ++"there's no **share state**"++
- ++"The absence of shared state makes multithreading safe."++
> **share state**不懂,之後再補
### It's Time to Get Good at Functional Programming
- 隨著Moore's Law遇到物理上的瓶頸(熱能產生),中央處理器轉向多核的趨勢。而FP在平行運算上的優勢因多核被受到重視。
- 簡單介紹幾種FP語言: Scala, F#, Erlang, Haskell
- Scala: Java語言支援,為hydrid式FP(OOP/FP)
- F#: .Net 系列,為hydrid
- Erlang, Haskell: 都為純FP程式語言
### Don’t Be Scared Of Functional Programming
- 以javascript為例,撰寫一份FP的programe
### Functional programming in C
> 有看沒有懂,之後在研究[name=cheng hung lin]
> 這篇的下一篇為FP in C的實做,[Functional programming in C – Implementation](https://lucabolognese.wordpress.com/2013/01/11/functional-programming-in-c-implementation/)
## Concurrency (並行) vs. Parallelism (平行)
- parallelism: 像是一個工作請兩個工人來做。
- concurrency: 像是一個工作切很多子工作,請一個工人來做。假如工人交錯每做一部份子工作,就換下一個子工作,這樣的情況就類似平行(time slicing),但絕對不是平行。
> 英文太差,中文表達不好,還是沒有佷讀透其中道理。
> - [ ] Concurrency (並行) vs. Parallelism (平行)
> [name=cheng hung lin]
### Concurrency 系列文章 (繁體中文)
- 一到三篇key word: `Sequential-before` ,`happen-before`
- 第五篇對在ReadRead, ReadWrite, WriteRead, WriteWrite中不遵守Sequential Consistency的情況舉例。另外還簡單提到`Cache Coherence`
- Cache Coherence: 確保同一份資料在不同處理器的cache上保持一致,包括讀寫順序。
### 並行計算投影片
> 尾聲的部份跟主題沒關,但可以先看一下[name=cheng hung lin]
## Process vs. Thread vs. Coroutines
- [Coroutines](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coroutine#Comparison_with_subroutines)
`Coroutines are computer program components that generalize subroutines for --nonpreemptive multitasking, by allowing multiple entry points for suspending and resuming execution at certain locations.`
- [ ]SMT, VMT
### coroutines
#### setjmp, longjmp
直接看`man setjmp`和`man longjmp`,與參考瞿同學的[筆記](https://hackmd.io/s/BJwe5Upa)和[程式碼](https://github.com/kevinbird61/Fun-part-of-C/blob/master/setjmp/setjmp_test.c)
- `setjmp`:
- `save stack context for nonlocal goto`
- `setjmp() and sigsetjmp() return 0 if returning directly, and nonzero when returning from longjmp(3) or siglongjmp(3) using the saved context.`
- `longjmp`:
- `nonlocal jump to a saved stack context`
- `longjmp() restores the environment saved by the last call of setjmp(3) with the corresponding env argument.`
- `longjmp() cannot cause 0 to be returned. If longjmp() is invoked with a second argument of 0, 1 will be returned instead.`
`longjmp(jump_buff_*, val)`是跳回最後一次呼叫`setjmp(jump_buffer_*)`的位置,所以說這也是為什麼會加`if (r == 0) /* call other function */`,避免一直回覆呼叫同一個函式後又跳回原呼叫的`setjmp(jump_buff_*)`,此外,`longjmp`是禁止以0為參數的,若傳0進去,則會在setjmp回傳1。
例如以下就會一直循環不停。
```clike=
int count;
void bufferA() {
printf("bufferA incremnet count: %d\n", ++count);
sleep(1);
longjmp(bufferMain, 1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
count = 0;
setjmp(bufferMain) && printf("setjmp bufferMain!!\n");
bufferA();
return 0;
}
```
#### switch case
> 目前先跳過[name=cheng hung lin]
## POSIX Threads
### POSIX Thread 實例: 光線追蹤
> 先略[name=cheng hung lin]
### POSIX thread
- 有些pthread函式的manual找不到的話,可能是沒有裝glibc的manual
```txt
$ sudo apt-get install glibc-doc
```
- Common thread modules:
- manager/worker
- pipeline
- peer
- Thread Safe
函式庫也要保證thread safe
- - [ ]Condiction variable
- Discussion on calling `pthread_exit()` `from main()`:
- `By having main() explicitly call pthread_exit() as the last thing it does, main() will block and be kept alive to support the threads it created until they are done.`
- `man pthread_exit()`的Notes也有提到:
` To allow other threads to continue execution, the main thread should terminate by calling pthread_exit() rather than exit(3).`
- main直接回傳(return)時,會呼叫`exit()`,連帶整個task都會結束(die)。若是呼叫`pthread_exit()`,則是把main當作task裡的其中一個thread,只會把main thread關掉,整個task仍然存在,其他衍生的thread也得以繼續執行。
- Reference: [CS360 Lecture notes -- Thread #1](http://web.eecs.utk.edu/~huangj/cs360/360/notes/Thread1/lecture.html)
- `pthread_exit()`
- `void pthread_exit(void *retval)`
- 在man pthread_exit\(\)的Notes提到:
The value pointed to by retval should not be located on the calling thread's stack, since the contents of that stack are undefined after the thread terminates.
- stack management:
- 使用`pthread_attr_setstack/pthread_attr_getstack`做stack調整,而非`pthread_attr_setstackattr/pthread_attr_getstackattr`。
- `man pthread_attr_setstackattr`裡提到,這函式的攜帶性(portable)不足。
### condition variable:
- 恐龍本6.8章的mintor,是有加上condition variable。
- 將thread放入condition variable `x` 的waiting queue,當其他thread有符合`x`這個condition時,喚醒`x`waiting queue裡的thread。~~condition variable使得thread之間可以依照condition做先後相依有順序的執行,當condition符合時,可以喚醒再waiting queue裡的thread。~~
- 可以避免對所有thread做**輪尋(polling)**檢查condition是否符合
## thread pool
- 何謂`thread pool`?
- [thread pool from wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thread_pool)
## Lock free thread pool
- [ring buffer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_buffer)
# 作業
## refactoring
## clz 的應用: 加速記憶體管理
- SuperMalloc
- `LD_PRELOAD`
- [What is the LD_PRELOAD trick?](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/426230/what-is-the-ld-preload-trick)
If you set LD_PRELOAD to the path of a shared object, that file will be loaded before any other library (including the C runtime, `libc.so`).
- - [ ][`man ld.so`](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ld.so.8.html)
## 程式分析
### 程式檔案
- main.c ( * )
- calculate.c
- file.c ( * )
- file_align.c
- phonebook_org.c ( * )
- phonebook_org.h ( * )
- phonebook_opt.c ( * )
- phonebook_opt.h ( * )
- debug.h ( * )
- Makefile ( * )
打星號的部份,是編譯產生`phonebook_*`會使用到的檔案
# 其他關鍵字
- `violate`
- `register`
- `first-class objects`
# 參考資料
-
###### tags: `nekoneko`