---
tags: vaje, rg, dcel, subdivizije
hackmd: https://hackmd.io/nnM_pT7WTfGWW_iVZpbmbg
plugins: mathjax
---
# Computational geometry - Tutorial 28.4.2021
---
## DCEL
DCEL: doubly connected edge list
* vertex $v$
- `edge`: an incident semi-edge originating in $v$
- coordinates
* semi-edge $e$:
- `origin`: the origin vertex
- `twin`: the opposite semi-edge corresponding to the same edge
- `next`: the next semi-edge on the same face
- `prev`: the previous semi-edge on the same face
- `face`: the incident face
* face $f$:
- `outer_component`: an incident semi-edge from the outer boundary of $f$
- `inner_components`: a list containing one incident semi-edge for each inner boundary of $f$
---
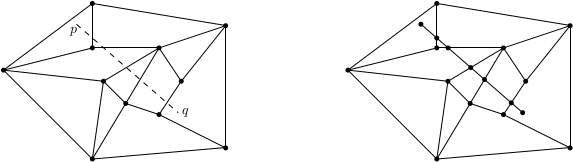
### Exercise 1
We are given a DCEL of a connected subdivision in a plane. Each face of the subdivision, except for the outer face, is convex. Give an efficient pseudocode for the following tasks.
1. Given a face $f$, list the vertices of $f$.
2. Given a face $f$, determine whether $f$ is the outer face.
3. Given a vertex $v$, find the faces incident to $v$.
4. Given a vertex $v$, find the vertex of the DCEL with the smallest $x$-coordinate.
5. Given a face $f$, list the faces with at least one vertex in common with $f$.
6. Given a line $\overline{pq}$ intersecting the edges of the DCEL (but not its vertices) and a face $f$ containing $p$, update the DCEL to represent a new subdivision which includes $\overline{pq}$.
----
1. ```python
def vertices(f):
if f.outer_component is None:
e0 = f.inner_components[0]
else:
e0 = f.outer_component
vcs = [e0.origin]
e = e0
while e.next != e0:
e = e.next
vcs.append(e.origin)
return vcs
```
2. ```python
def outer_face(f):
return f.outer_component is None
```
3. ```python
def faces(v):
e0 = v.edge
fcs = [e0.face]
e = e0
while e.twin.next != e0:
e = e.twin.next
fcs.append(e.face)
return fcs
```
4. * let $f$ be a face incident to $v$ (`f = v.edge.face`)
* if $f$ is the outer face, return its leftmost vertex
* find the semi-edge $e$ originating in the leftmost vertex of $f$
* set `f = e.twin.face` and repeat
5. ```python
def common_vertex(f):
if f.outer_component is None:
e0 = f.inner_components[0]
else:
e0 = f.outer_component
fcs = set()
e = e0
fcs.union(faces(e.origin))
while e.next != e0:
e = e.next
fcs.union(faces(e.origin))
fcs.remove(f)
return fcs
```
6. ```python
def add_segment(f, p, q):
find semi-edge e incident to f such that pq intersects e in a point v
p.edge = Edge()
v.edge = Edge()
v.edge.origin = v
v.edge.face = f
v.edge.next = e.next
v.edge.prev = p.edge
v.edge.twin = e.twin
e.next.prev = v.edge
e.next = Edge()
e.twin.twin = v.edge
e.twin = Edge()
e.twin.origin = v
e.twin.face = v.edge.twin.face
e.twin.next = v.edge.twin.next
e.twin.prev = v.edge.twin
e.twin.twin = e
e.twin.next.prev = e.twin
e.twin.prev.next = e.twin
e.next.origin = v
e.next.face = f
e.next.next = v.edge.prev
e.next.prev = e
e.next.twin = v.edge.prev
p.edge.origin = p
p.edge.face = f
p.edge.next = v.edge
p.edge.prev = e.next
p.edge.twin = e.next
f = e.twin.face
while pq has another intersection u with the boundary of f:
split the face f with uv
f = face on the other side of the edge split by u
v = u
add the segment vq
```

---
### Exercise 2
We are given a DCEL representing a subdivision of the plane and a face $f$ of this subdivision. Assume that each face of the subdivision is defined by a cycle of edges without repetitions. We want to delete all edges incident to $f$, i.e., we delete the edges from the set $D = \lbrace e \mid e \text{ is an edge of } f \rbrace$. Assume that the subdivision remains connected after $D$ is deleted. Write the pseudocode for deleting the edges of $D$ and updates the DCEL. What is the time complexity of the algorithm?

---
## Arrangements
### Exercise 3
Let $H$ be a set of $n$ lines in the plane which intersect in the same point $p$, and let $H'$ be a set of $m$ lines in the plane which intersect in another point $p' \ne p$. The lines of $H$ do not contain $p'$ and the lines of $H'$ do not contain $p$.
1. How many vertices, edges and faces does the arrangement $\mathcal{A}(H)$ have?
2. How many vertices, edges and faces does the arrangement $\mathcal{A}(H \cup H')$ have?
3. Let $R$ be a set of $n$ planes in $\mathbb{R}^3$. Each plane of $R$ contains the point $(0, 0, 0)$, and no triple of planes intersects in a line. How many vertices, edges, faces and cells does the arrangement $\mathcal{A}(R)$ have?
----
$v - e + f = 1$ (since we have a connected arrangement with infinite edges)
1. $v = 1$, $e = 2n$, $f = 2n$

---
### Exercise 4
Let ${L_h}$ and ${L_v}$ be sets of $n$ horizontal lines and $n$ vertical lines in a plane, respectively. Let ${L_p}$ be a set of $n$ lines in a plane intersecting in a point $p$. No line of ${L_p}$ is horizontal or vertical and no line from ${L_h}$ or ${L_v}$ contains the point $p$. Furthermore, no three lines ${\ell_h} \in {L_h}, {\ell_v} \in {L_v}, {\ell_p} \in {L_p}$ intersect in the same point.
1. How many vertices, edges and faces does the arrangement $\mathcal{A}({L_h} \cup {L_v} \cup L_p)$ have?
2. Describe the points dual to ${L_h} \cup {L_p}$.
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

