# Leetcode刷題學習筆記 -- Disjoint set/Union Find
## 教學
參考leetcode官方的Exlort card。強力推薦。
[Detailed Explanation of Graph](https://leetcode.com/explore/learn/card/graph/)
### 使用時機
+ union-find是==用來判斷node之間,是否有相連在一起。== 。可以根據root的相同與否來判斷。
+ 只要問題是判斷連通問題,都可以使用union-find。
+ 有些變形的題目是會限制連通路徑的條件。
### Code Snippets
1. 宣告兩個vector來儲存root和rank,2D的情況就是全部element的總和。
```cpp
// case 1 : 1D
vector<int> nums;
int sz = nums.size();
vector<int> root(sz), rank(sz);
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0); // 初始化root成0, 1, 2...
// case 2 : 2D vector
vector<vector<int>> grid;
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
int sz = m * n;
vetor<int> root(sz), rank(sz);
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0);
```
2. find root function
尋找真的root,必且把所有經過的路經都update成最後找到的root。
```cpp
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
```
3. union function
連結兩個node成一個,就是把root設定為一樣。
```cpp
void union(int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if(rootx == rooty) return; // root已經一樣不需要union
if(rank[rootx] > rank[rooty])
root[rooty] = rootx;
else if(rank[rooty] > rank[rootx])
root[rootx] = rooty;
else {
root[rooty] = rootx;
rank[rootx]++;
}
}
```
這邊rank可以用來統計group的數量。必須先init每個rank到1。
```cpp=
vector<int> rank(n, 1);
// union的時候,大的rank(比較多)合併小的rank(比較少)
int union(int a, int b) {
int a = find(a);
int b = find(b);
if(a == b) return 0; // 代表不用合併
if(rank[a] > rank[b]) {
root[b] = a;
return rank[a] += rank[b]; // 回傳合併後的大小
} else {
root[a] = b;
return rank[b] += rank[a];// 回傳合併後的大小
}
}
```
### 使用virtual vertex
某些題目,使用virtual vertex可以大幅簡化問題的複雜度。
例如:
+ [1970. Last Day Where You Can Still Cross](https://hackmd.io/wU2PrLOpSZmcgiu64UYnRQ#1970-Last-Day-Where-You-Can-Still-Cross)
+ [1168. Optimize Water Distribution in a Village](https://hackmd.io/wU2PrLOpSZmcgiu64UYnRQ#1168-Optimize-Water-Distribution-in-a-Village)
### Reset node
把某個node從Union Find中移除?
把某個idx從root[idx]中設為idx。
```cpp=
root[idx] = idx;
```
例如:
+ [2092. Find All People With Secret]()
## Example
### [547. Number of Provinces(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-provinces/)
給你一個vector<vector<int> isConnected,如果isConnected[i][j] = 1,代表city i到city j是連通的。provinces是表示全部連在一起的城市,返回有多少個provinces。
> 1. 這題是標準的Union Find問題,用disjoint set來統計有多少個相同的root node。
> 2. 使用path compress和union by rank技巧,可以讓time complexity更好。
> 3. 每連結一個新的node就把count-1,可以避免之後統計root的數量。
```cpp=
class Solution {
int find(int x) { // path compress
if(x == root[x]) return x;
return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void un(int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if(rootx == rooty) return;
if(rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) // union by rank
root[rooty] = rootx;
else if(rank[rootx] < rank[rooty])
root[rootx] = rooty;
else {
root[rooty] = rootx;
rank[rootx] += 1;
}
count--;
}
vector<int> root, rank;
int count;
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
auto n = isConnected.size();
if(n == 1) return 1;
root.resize(n);
rank.resize(n, 1);
count = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
root[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if(isConnected[i][j]) un(i, j);
return count;
}
};
```
### [200. Number of Islands](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/)
給你一個2D vector<vector<char>> 其中grid[y][x] = '1'為island,四個方向視為連接再一起,請問有多少個獨立的island。
> 1. 把每個'1'都視為是一個獨立的island
> 2. 連起來後就把island數減一
> 3. 一定要是用rank來判斷root,避免會來連上來的node會有兩個以上的root。
> 4. 一定要判斷四個方向? 因為有可能從下面連到上面的node。
```cpp
class Solution {
int m, n, sz, ans;
vector<int> root, rank;
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void un(int y, int x) {
int rooty = find(y);
int rootx = find(x);
if(rooty == rootx) return;
if(rank[rooty] > rank[rootx])
root[rootx] = rooty;
else if(rank[rootx] > rank[rooty])
root[rooty] = rootx;
else {
root[rootx] = rooty;
rank[rooty]++;
}
ans--;
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
m = grid.size();
n = grid[0].size();
sz = ans = m * n;
root.resize(sz);
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0);
rank.resize(sz);
for(int y = 0; y < m; ++y) {
for(int x = 0; x < n; ++x) {
if(grid[y][x] == '0') ans--;
else {
int prev = y * n + x;
for(auto& d : dirs) {
int ny = y + d[0];
int nx = x + d[1];
if(ny < 0 || nx < 0 || ny == m || nx == n || grid[ny][nx] == '0') continue;
un(prev, ny * n + nx);
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
### [2421. Number of Good Paths](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-good-paths/)
找出tree中所有Good path的數目。其中good path的定義是兩個端點的值是一樣的,且node越往中間數值越小(小於等於)。
> 1. why union-find? 因為我們想知道兩個點是否連在一起,形成一個good path。
> 2. 因為good path的定義,我們決定了連結node的順序和方法。也就是從小的值開始連,慢慢往大的數值。
> 3. 計算good path的個數,就是看每個相同root的group中有多少個element,就可以用$cnt*(cnt - 1)/2$的方法來計算。
```cpp
class uf{
vector<int> root, rank;
public:
uf(int sz) : root(sz), rank(sz) {
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void un(int x, int y) {
cout << "un : " << x << "," << y << endl;
x = find(x); y = find(y);
if(x == y) return;
if(rank[x] > rank[y]) root[y] = x;
else if(rank[y] > rank[x]) root[x] = y;
else {
root[y] = x;
rank[x]++;
}
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int numberOfGoodPaths(vector<int>& vals, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> adj;
for(auto& e : edges) {
if(vals[e[0]] >= vals[e[1]]) adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
if(vals[e[1]] >= vals[e[0]]) adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
map<int, vector<int>> sameVal;
for(int i = 0; i < vals.size(); ++i) sameVal[vals[i]].push_back(i);
int ans{0};
uf _uf(vals.size());
for(auto& [v, nodes] : sameVal) {
// connect the node from samve value group to the adjust node
for(auto& n : nodes)
for(auto& j : adj[n])
_uf.un(n, j);
unordered_map<int, int> g; // value, count
for(auto& n : nodes) {
g[_uf.find(n)]++;
}
ans += nodes.size();
for(auto& [_, cnt] : g)
ans += cnt * (cnt - 1) / 2;
}
return ans;
}
};
```
### [1697. Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths](https://leetcode.com/problems/checking-existence-of-edge-length-limited-paths/description/)
找出graphic中,兩個點的任一個path其中每個edge上的weight都小於limit。
> 1. 因為每個edge都有數值,其中query的要求是兩個node之間,所有的edge都要小於 limit。
> 2. 所以先對limit排序,把小於limit的edge都連結起來,再判斷這兩個node是否連接再一起。
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<bool> distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
map<int, vector<vector<int>>> m; // weight, list of nodes
for(auto& e : edgeList) {
m[e[2]].push_back({e[0], e[1]});
}
vector<int> idx(queries.size(), 0);
iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 0);
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](int& a, int& b){
return queries[a][2] < queries[b][2];
});
vector<bool> rtn(queries.size());
uf _uf(n);
auto it = m.begin();
for(auto& i : idx) {
while(it != m.end() && it->first < queries[i][2]) {
for(auto& nodes : it->second) {
_uf.un(nodes[0], nodes[1]);
}
it++;
}
rtn[i] = _uf.connect(queries[i][0], queries[i][1]);
}
return rtn;
}
};
```
2023/04/29 daily challenge
一開始我會錯意了,limit是每個edge的最小值,不是路徑的總和,本來以為是要做BFS,又看了一下N最大是$10^5$應該會TLE。
後來又仔細的看了一下,limit是每個路徑的最小值,所以等於是把小於limit的node都連接起來。
```cpp=
class Solution {
vector<int> root, rank;
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void connect(int a, int b) {
int roota = find(a);
int rootb = find(b);
if(roota == rootb) return;
if(rank[roota] > rank[rootb]) root[rootb] = roota;
else if(rank[rootb] > rank[roota]) root[roota] = rootb;
else {
root[rootb] = roota;
rank[roota]++;
}
}
bool isConnect(int a, int b) {
int roota = find(a);
int rootb = find(b);
return roota == rootb;
}
public:
vector<bool> distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
int sz = queries.size();
vector<bool> rtn(sz);
vector<int> idx(sz);
iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 0);
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](auto& a, auto& b){
return queries[a][2] < queries[b][2];
});
sort(edgeList.begin(), edgeList.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b){
return a[2] < b[2];
});
root.resize(n);
rank.resize(n);
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
int j = 0;
for(auto& i : idx) {
int from = queries[i][0];
int to = queries[i][1];
int limit = queries[i][2];
while(j < edgeList.size() &&
edgeList[j][2] < limit) {
connect(edgeList[j][0], edgeList[j][1]);
j++;
}
rtn[i] = isConnect(from, to);
}
return rtn;
}
};
```
### [1724. Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths II](https://leetcode.com/problems/checking-existence-of-edge-length-limited-paths-ii/description/)
> 1. 和[1697-Checking-Existence-of-Edge-Length-Limited-Paths](https://hackmd.io/wU2PrLOpSZmcgiu64UYnRQ#1697-Checking-Existence-of-Edge-Length-Limited-Paths) 類似,只是query的時候不能先排序,所以把每個階段的root都存起來。
```cpp
map<int, vector<int>> rootList; // 把每個階段的root都存起來
```
> 2. 這樣就可以使用lower_bound來找limit。
```cpp
class DistanceLimitedPathsExist {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> edges;
map<int, vector<vector<int>>> m;
uf _uf;
map<int, vector<int>> rootList;
public:
DistanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList) : _uf(n) {
this->n = n;
edges = move(edgeList);
for(auto& e : edges)
m[e[2]].push_back({e[0], e[1]});
for(auto& ref : m) {
for(auto& e : ref.second) {
_uf.un(e[0], e[1]);
}
rootList[ref.first] = _uf.getRoot();
}
}
int find(vector<int>& root, int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root, root[x]);
}
bool connect(vector<int>& root, int x, int y) {
return find(root, x) == find(root, y);
}
bool query(int p, int q, int limit) {
auto it = rootList.lower_bound(limit);
if(it == rootList.begin()) return false;
return connect(prev(it)->second, p, q);
}
};
```
### [1579. Remove Max Number of Edges to Keep Graph Fully Traversable](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-max-number-of-edges-to-keep-graph-fully-traversable/description/)
> 1. 參考官方答案
> 2. 定義一個UnionFind class,必須注意node是從1開始,所以root和rank的大小為n + 1。
> 3. 以前寫un()都沒return value。可以返回是否把這兩個node連在一起,可以藉此判斷是否使用此node。
> 4. 這邊的rank定義為此group中有多少個node。
```cpp=
class UnionFind {
vector<int> root, rank;
int n;
public:
UnionFind(int n) : root(n + 1), rank(n + 1, 1), n(n){
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x) {
if (root[x] == x) return x;
return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
int un(int x, int y) {
x = find(x); y = find(y);
if (x == y) return 0;
if (rank[x] > rank[y]) {
rank[x] += rank[y];
root[y] = x;
} else {
rank[y] += rank[x];
root[x] = y;
}
n--;
return 1;
}
bool isTraversable() {
return n == 1;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maxNumEdgesToRemove(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
UnionFind alice(n), bob(n);
int need = 0;
for (auto& e : edges) {
if (e[0] == 3)
// 這邊有個重點,不能使用 ||
// 因為如果前面成立,就不會執行後面。
// 必須使用bitwise or,
// 因為只要一個成立,這個edge就需要。
need += (alice.un(e[1], e[2]) |
bob.un(e[1], e[2])
);
}
for (auto& e : edges) {
if (e[0] == 1) need += alice.un(e[1], e[2]);
else if (e[0] == 2) need += bob.un(e[1], e[2]);
}
if (alice.isTraversable() && bob.isTraversable()) return edges.size() - need;
else return -1;
}
};
```
### [2685. Count the Number of Complete Components](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-the-number-of-complete-components/description/)
題目要求數complete connected components的數目。
> 1. 這題是2023/5/14週賽第四題,我沒有答出來。原因是對complete connected components的定義不懂。
> 2. 題目給了定義是在complete connected components內的任何頂點,都可用不同的path走到group中其他頂點。也就是每個頂點都有專屬的path到group的其他頂點。這樣的path樹目會是
$nodeCount * (nodeCount - 1) / 2$
> 3. 所以除了用union-find之外,還要==計算每個group的node個數和path個數。==
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> root, edgeCount, nodeCount;
int find(int x){
if(x == root[x]) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void un(int x, int y){
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
// 為了避免判斷式過多,一律把nodeCount[x]換為最大值
if(nodeCount[y] > nodeCount[x]) swap(x, y);
// 計算edge的數目必須在return前+1。
// 避免有少數的情況。
edgeCount[x]++;
if(x == y) return;
root[y] = x;
edgeCount[x] += edgeCount[y];
nodeCount[x] += nodeCount[y];
}
int countCompleteComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int ans = 0;
root.resize(n);
edgeCount.resize(n, 0);
nodeCount.resize(n, 1);
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
for(auto e: edges) un(e[0], e[1]);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(nodeCount[i] && i == find(i) &&
(nodeCount[i] * (nodeCount[i] - 1) / 2 == edgeCount[i]))
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
};
```
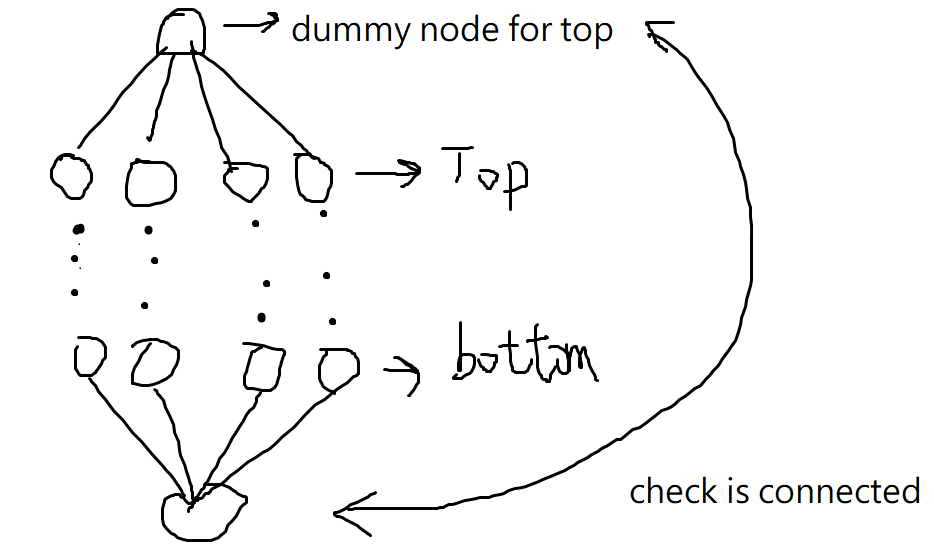
### [1970. Last Day Where You Can Still Cross](https://leetcode.com/problems/last-day-where-you-can-still-cross/description/)
給你一個vector<vector<int>> cells,每天把一個land挖成water,傳回可以從top到bottom的天數。
> 1. 因為一開始是聯通的,如果要檢查是否不通,而且要刪除連通的點有反union-find的規則。
> 2. 所以從後面traverse cells,就是蓋路的觀念,看哪時候蓋出來的路可以讓上下互通。
> 3. 如何檢查top和bottom是互通的?
> 4. 一開始我用以下的code會TLE。
```cpp=
for(int top = 0; top < col; ++top) {
for(int bottom = 0; bottom < col; ++bottom) {
if(isConnected({0, top}, {row - 1, bottom}))
return true;
}
}
return false;
```
> 5. 看了解答發現網友的解法是,創造dummy node最後檢查top bottom的dummy node是否相連。
```cpp=
class Solution {
int row, col, n, top, bottom;
vector<int> root, rank;
vector<vector<int>> map;
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
bool isInBoard(int y, int x) {
if(y < 0 || x < 0 || y == row || x == col) return false;
return true;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> adjust(const vector<int>& pos) {
vector<pair<int, int>> rtn;
for(auto& d : dirs) {
int ny = d[0] + pos[0];
int nx = d[1] + pos[1];
if(!isInBoard(ny, nx)) continue;
rtn.push_back({ny, nx});
}
return rtn;
}
int find(const vector<int>& p) {
return find(p[0] * col + p[1]);
}
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void un(const vector<int>& x, const vector<int>& y) {
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if(rootx == rooty) return;
if(rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) {
root[rooty] = rootx;
rank[rootx] += rank[rooty];
} else {
root[rootx] = rooty;
rank[rooty] += rank[rootx];
}
}
bool isConnected(const vector<int>& p, const vector<int>& q) {
int rootp = find(p);
int rootq = find(q);
return rootp == rootq;
}
bool checkConnected() {
return isConnected({row - 1, col}, {row - 1, col + 1});
}
public:
int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& cells) {
this->row = row;
this->col = col;
this->n = cells.size();
top = n;
bottom = n + 1;
root.resize(n + 2);
iota(root.begin(), root.end(), 0);
rank.resize(n + 2, 1);
// 多兩個dummy node
// 把top dummy node和{0, x}相連
// 把bottom dummy node和{row - 1, x}相連
for(int x = 0; x < col; ++x) {
un({0, x}, {row - 1, col});
un({row - 1, x}, {row - 1, col + 1});
}
map.resize(row, vector<int>(col));
for(int i = cells.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
vector<int>& cell = cells[i];
int y = cell[0] - 1;
int x = cell[1] - 1;
map[y][x] = 1;
for(auto [ny, nx] : adjust({y, x})) {
if(map[ny][nx] == 1) {
un({y, x}, {ny, nx});
if(checkConnected()) return i;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
```
### [1489. Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-critical-and-pseudo-critical-edges-in-minimum-spanning-tree/description/)
> 1. Minimal Spanning Tree(MST) 以前我學的時候是把edges放進priority_queue然後從最小的weights一個一個拿出來。但是使用priority_queue的成本太高,目的只是為了從小到大拿出weight所以可以對weight排序即可。
> 2. 使用union find的union function可以返回bool來表示是否有做union的動作。
> 3. 在union find中同時統計最大group中element的數量(maxGroup),來檢查是否所有的edge都連接在一起了。
> 4. 一開始我沒搞清楚 critical edge和 pseudo-critical的定義。
critical edge : 沒了這個edge還是可以組成MST,但是weights會變大
pseudo-critical edge : 可以出現在其他MST,也就是沒了他MST的weight和有了他MST的weight都會是minWeight
```cpp=
class UnionFind {
vector<int> root;
vector<int> rank;
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
int maxGroup{}; // 紀錄最大group中的數目
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
root.resize(n);
rank.resize(n, 1);
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0);
}
bool un(int a, int b) { //返回是否有做連結
int ra = find(a);
int rb = find(b);
if(ra == rb) return false;
if(rank[ra] > rank[rb]) {
root[rb] = ra;
rank[ra] += rank[rb];
maxGroup = max(maxGroup, rank[ra]);
} else {
root[ra] = rb;
rank[rb] += rank[ra];
maxGroup = max(maxGroup, rank[rb]);
}
return true;
}
int getMaxGroup() {
return maxGroup;
}
};
class Solution {
enum st{a, b, w, idx};
public:
vector<vector<int>> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// add index to edges {a, b, weight, idx}
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i)
edges[i].push_back(i);
// sort by weight
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [](auto& x, auto& y){
return x[w] < y[w];
});
// get minimal weight of MST
UnionFind minUF(n);
int minWeights{};
for(auto& e : edges) {
if(minUF.un(e[a], e[b]))
minWeights += e[w];
}
// get the result
vector<vector<int>> rtn(2, vector<int>());
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) {
UnionFind rmUF(n); // remove ith edge
int weights{};
for(int j = 0; j < edges.size(); ++j) {
vector<int>& e = edges[j];
if(i != j && rmUF.un(e[a], e[b]))
weights += e[w];
}
// 不能組成MST 或是 移除後weights變大
if(rmUF.getMaxGroup() < n or weights > minWeights) {
rtn[0].push_back(edges[i][idx]);
} else {
UnionFind addUF(n); // 有這個edge後,可以組成另一個MST
addUF.un(edges[i][a], edges[i][b]);
int weights{edges[i][w]};
for(int j = 0; j < edges.size(); ++j) {
if(i == j) continue;
vector<int>& e = edges[j];
if(addUF.un(e[a], e[b]))
weights += e[w];
}
if(addUF.getMaxGroup() == n and weights == minWeights)
rtn[1].push_back(edges[i][idx]);
}
}
return rtn;
}
};
```
### [1168. Optimize Water Distribution in a Village](https://leetcode.com/problems/optimize-water-distribution-in-a-village/description/)
> 1. 參考[官方解答](https://leetcode.com/problems/optimize-water-distribution-in-a-village/editorial)
> 2. 這題是變形的Minimal Spainning Tree(MST),重點是怎麼看待well。
> 3. 這邊使用一個virtual vertex 0,0:代表水源,挖井的意思是從0送水給某個點。這樣就是標準的MST問題。

```cpp=
class Solution {
// 使用rank來統計數量
vector<int> root, rank;
int find(int x) {
if(root[x] == x) return x;
else return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
int un(int a, int b) {
int roota = find(a);
int rootb = find(b);
if(roota == rootb) return 0;
if(rank[roota] > rank[rootb]) {
root[rootb] = roota;
return rank[roota] += rank[rootb];
} else {
root[roota] = rootb;
return rank[rootb] += rank[roota];
}
}
public:
int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, vector<int>& wells, vector<vector<int>>& pipes) {
root.resize(n + 1);
rank.resize(n + 1, 1);
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0);
for(int i = 0; i < wells.size(); ++i)
pipes.push_back({0, i + 1, wells[i]});
sort(begin(pipes), end(pipes), [](auto& a, auto& b){
return a[2] < b[2];
});
int ans{};
for(auto& p : pipes) {
if(int rtn = un(p[0], p[1])) {
ans += p[2];
// 達到數量就可以返回
// 使用virtual vertex 0另一個好處是
// 可以有單獨well的狀況。
if(rtn == n + 1) break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
### [2092. Find All People With Secret](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-people-with-secret/description/)
> 1. 參考[答案](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-people-with-secret/description/)
> 2. 這題的重點是,時間一樣的時候,怎麼找出目前的group和person 0是否有連結
> 3. 先把時間t內連結起來,如果沒有和person 0連結再一起,再進行reset
> 4. union find的reset就是把root[x] = x,再把root設為原本
> 5. 因為有reset,rank不在適用。
```cpp=
class UnionFind {
vector<int> root, rank;
public:
UnionFind(int n) : root(n), rank(n, 1) {
iota(begin(root), end(root), 0);
}
void connect(int a, int b) {
root[find(b)] = find(a);
}
int find(int a) {
if(root[a] == a) return a;
else return root[a] = find(root[a]);
}
bool isConnected(int a, int b) {
return find(a) == find(b);
}
void reset(int a) { root[a] = a; }
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findAllPeople(int n, vector<vector<int>>& A, int firstPerson) {
int sz = A.size();
sort(begin(A), end(A), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[2] < b[2];
}); // Sort the meetings in ascending order of meeting time
UnionFind uf(n);
uf.connect(0, firstPerson); // Connect person 0 with the first person
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ) {
vector<int> ppl;
int time = A[i][2];
for (; i < sz && A[i][2] == time; ++i) { // For all the meetings happening at the same time
uf.connect(A[i][0], A[i][1]); // Connect the two persons
ppl.push_back(A[i][0]); // Add both persons into the pool
ppl.push_back(A[i][1]);
}
for (int n : ppl) { // For each person in the pool, check if he/she's connected with person 0.
if (!uf.isConnected(0, n))
uf.reset(n); // If not, this person doesn't have secret, reset it.
}
}
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (uf.isConnected(0, i))
ans.push_back(i); // Push all the persons who are connected with person 0 into answer array
}
return ans;
}
};
```
###### tags: `leetcode` `刷題`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet