---
tags: vaje, ds, grafi
hackmd: https://hackmd.io/zJTrYDZCTO-6ZggIIHW1xQ
plugins: mathjax, viz.js
---
# Diskretne strukture (FiM) - vaje 9.12.2020
---
## Urejenosti
Delna urejenost <i>$(A, \le)$</i>
* $x$ infimum množice <i>$B \subseteq A$</i>:
$$
x = \inf B \iff \forall y \in B: x \le y \land \forall z \in A: (\forall y \in B: z \le y \Rightarrow z \le x)
$$
* $x$ supremum množice <i>$B \subseteq A$</i>:
$$
x = \sup B \iff \forall y \in B: y \le x \land \forall z \in A: (\forall y \in B: y \le z \Rightarrow x \le z)
$$
---
### Naloga 1
Na <i>$\mathbb{R}^2$</i> definiramo relacijo <i>$\preceq$</i> takole:
$$
(x_1,y_1)\preceq(x_2,y_2) \Leftrightarrow
x_1 \leq x_2 {\rm\;in\;} y_1 \leq y_2.
$$
1. Pokaži, da je <i>$(\mathbb{R}^2, \preceq)$</i> delna urejenost.
2. Določi supremum in infimum elementov <i>$(1,3)$</i> in <i>$(2,4)$</i> ter supremum in infimum elementov <i>$(3,2)$</i> in <i>$(4,1)$</i>.
----
1. * refleksivnost: <i>$(x_1, y_1) \preceq (x_1, y_1) \iff x_1 \le x_1 \land y_1 \le y_1$</i> velja
* antisimetričnost:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(x_1, y_1) \preceq (x_2, y_2) \land (x_2, y_2) \preceq (x_1, y_1)
&\Rightarrow x_1 \le x_2 \land y_1 \le y_2 \land x_2 \le x_1 \land y_2 \le y_1 \\
&\Rightarrow x_1 = x_2 \land y_1 = y_2 \\
&\Rightarrow (x_1, y_1) = (x_2, y_2)
\end{aligned}
$$
* tranzitivnost:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(x_1, y_1) \preceq (x_2, y_2) \land (x_2, y_2) \preceq (x_3, y_3)
&\Rightarrow x_1 \le x_2 \land y_1 \le y_2 \land x_2 \le x_3 \land y_2 \le y_3 \\
&\Rightarrow x_1 \le x_3 \land y_1 \le y_3 \\
&\Rightarrow (x_1, y_1) \preceq (x_3, y_3)
\end{aligned}
$$
2. * <i>$\sup\lbrace (1, 3), (2, 4) \rbrace = (2, 4)$</i>
* <i>$\inf\lbrace (1, 3), (2, 4) \rbrace = (1, 3)$</i>
* <i>$\sup\lbrace (3, 2), (4, 1) \rbrace = (4, 2)$</i>
* <i>$\inf\lbrace (3, 2), (4, 1) \rbrace = (3, 1)$</i>
* <i>$\sup\lbrace (x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2) \rbrace = (\max\lbrace x_1, x_2 \rbrace, \max\lbrace y_1, y_2 \rbrace)$</i>
* <i>$\inf\lbrace (x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2) \rbrace = (\min\lbrace x_1, x_2 \rbrace, \min\lbrace y_1, y_2 \rbrace)$</i>
---
## Teorija grafov
(Neusmerjen) graf <i>$G = (V, E)$</i>
* <i>$V$</i> je množica vozlišč
* <i>$E \subseteq {V \choose 2} = \lbrace \lbrace u, v \rbrace \mid u, v \in V, u \ne v \rbrace$</i> je množica povezav
```graphviz
graph G {
a -- b
a -- c
b -- d
c -- e
d -- e
c -- f
b -- f
f -- g
d -- g
e -- g
}
```
* Stopnja vozlišča <i>$u \in V$: $d_G(u) = d(u) = |\lbrace e \in E \mid u \in e \rbrace|$</i>
* Maksimalna stopnja grafa <i>$\Delta(G) = \max_{u \in V} d_G(u)$</i>
* Minimalna stopnja grafa <i>$\delta(G) = \min_{u \in V} d_G(u)$</i>
* Graf je *dvodelen*, če lahko zapišemo <i>$V = A + B$</i>, tako da za vsako povezavo <i>$\lbrace u, v \rbrace \in E$</i> velja <i>$u \in A$, $v \in B$</i>
* Grafa <i>$G_1 = (V_1, E_1)$</i> in <i>$G_2 = (V_2, E_2)$</i> sta *izomorfna*, če obstaja bijektivna preslikava <i>$f : V_1 \to V_2$</i>, tako da velja
$$
\forall u, v \in V_1: (\{u, v\} \in E_1 \iff \{f(u), f(v)\} \in E_2)
$$
---
### Naloga 2
Dan je graf $G=(V,E)$, kjer je $V = \lbrace 1,2,3,4,5 \rbrace$ in $E = \lbrace \lbrace 1,2 \rbrace, \lbrace 1,4 \rbrace, \lbrace 1,5 \rbrace, \lbrace 2,3 \rbrace, \lbrace 2,4 \rbrace, \lbrace 3,4 \rbrace, \lbrace 4,5 \rbrace \rbrace$.
1. Čim lepše nariši graf $G$.
2. Poišči stopnje vseh vozlišč ter minimalno in maksimalno stopnjo grafa $G$. Ali je graf regularen?
3. Ali je graf dvodelen?
----
1. ```graphviz
graph G {
1 -- 2
1 -- 4
1 -- 5
2 -- 3
2 -- 4
3 -- 4
4 -- 5
}
```
2. * $\delta(G) = 2$
* $\Delta(G) = 4$
* zaporedje stopenj: $2, 2, 3, 3, 4$
* graf ni regularen
3. Graf **ni** dvodelen, saj vsebuje lihe cikle (trikotniki, petkotnik).
---
### Naloga 3
Na zabavi se je zbralo $13$ ljudi. Vsak je s seboj prinesel $3$ darila, ki bi jih rad izmenjal s tremi drugimi udeleženci zabave. Ali je to izvedljivo? Predstavi kot problem iz teorije grafov in ga reši.
----
* <i>$G = (V, E)$</i>
* <i>$V$</i> ... udeleženci zabave, <i>$|V| = 13$</i>
* <i>$\lbrace u, v \rbrace \in E$</i> ... <i>$u$</i> in <i>$v$</i> si izmenjata darilo
* <i>$d_G(u) = 3$</i> za vse <i>$u \in V$</i>
**Lema o rokovanju**: <i>$\sum_{u \in V} d_G(u) = 2 |E|$</i>
* <i>$39 = \sum_{u \in V} d_G(u) = 2 |E|$</i>
* <i>$|E| = 19.5$</i> protislovje
To torej **ni izvedljivo**.
---
### Naloga 4
Ali sta spodnja grafa izomorfna?
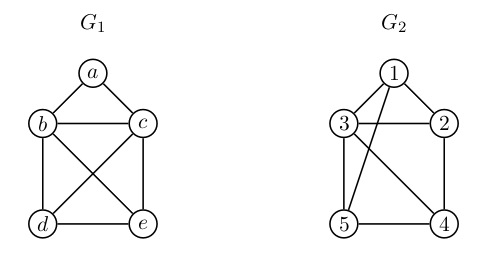
* <i>$|V_1| = |V_2| = 5$</i>
* <i>$|E_1| = |E_2| = 8$</i>
* stopnje vozlišč - zaporedje stopenj:
- <i>$G_1$</i>: 2, 3, 3, 4, 4
- <i>$G_2$</i>: 3, 3, 3, 3, 4
- grafa **nista izomorfna**
---
### Naloga 5
Ali sta spodnja grafa izomorfna?
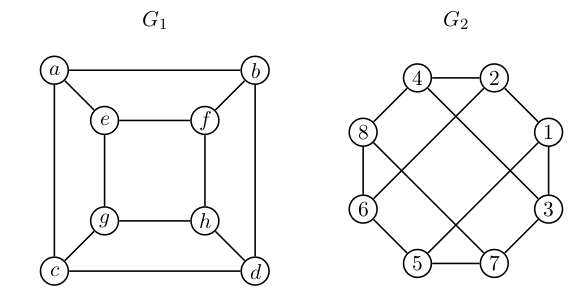
* <i>$|V_1| = |V_2| = 8$</i>
* <i>$|E_1| = |E_2| = 12$</i>
* oba grafa sta $3$-regularna
* izomorfizem:
- $a \to 1$
- $b \to 2$
- $c \to 3$
- $e \to 5$
- $f \to 6$
- $g \to 7$
- $d \to 4$
- $h \to 8$
* grafa **sta izomorfna**
---
### Naloga 6
Ali sta spodnja grafa izomorfna? Nasvet: v vsakem od grafov preštej cikle dolžine $4$.
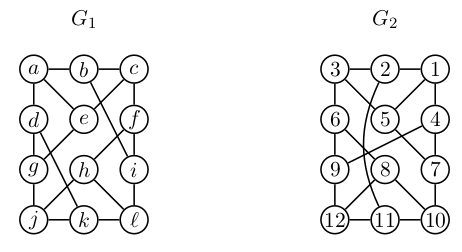
----
* <i>$|V_1| = |V_2| = 12$</i>
* oba grafa sta $3$-regularna
* cikli dolžine $4$:
+ <i>$G_1$</i>: 6 ciklov dolžine 4
- abce
- adge
- bcfi
- dgjk
- fhli
- hjkl
+ <i>$G_2$</i>: 4 cikli dolžine 4
- 1, 2, 3, 5
- 1, 4, 7, 5
- 6, 8, 12, 9
- 8, 10, 11, 12
+ grafa **nista izomorfna**
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

