# [phonebook-concurrent](https://hackmd.io/s/rJsgh0na)
[github](https://github.com/diana0651/phonebook-concurrent) contributed by <`Diana Ho`>
###### tags: `d0651` `sys`
## 案例分析
* [phonebook](https://hackmd.io/KzDMBYFME4CMHYC00BmLiPAE1gNkQBzTj4CM4ADAIYDGpBpa9QA=)
### 預期目標
* 學習第二週提及的 [concurrency](/s/H10MXXoT) 程式設計
* 學習 POSIX Thread
* 學習效能分析工具
* code refactoring 練習
* 探索 clz 的應用
### 作業要求
* [phonebook-concurrent](https://github.com/sysprog21/phonebook-concurrent)
* 適度修改 `phonebook_opt.c` 和相關的檔案
* 程式正確性驗證
* 效能分析實驗 (必須要有圖表)
* 說明你如何改善效能
* 透過 POSIX Thread 縮減 `alloc()` 的時間成本
* 建立 thread pool 管理 worker thread
* 學習 [concurrent-ll](https://github.com/jserv/concurrent-ll) (concurrent linked-list 實作) 的 scalability 分析方式
* 透過 gnuplot 製圖比較 list 操作的效能
* 嘗試重構 (refactor) 給定的程式碼
---
## Toward Concurrency
### Concurrency (並行) vs. Parallelism (平行)
* 名詞解釋
* Sequential (順序):一件做完再做另一件
* Concurrency (並行):兩件同時進行
* Parallelism (平行):兩件交錯進行&平行
* [Concurrency is not Parallelism](https://blog.golang.org/concurrency-is-not-parallelism)
* concurrency provides a way to structure a solution to solve a problem that may be parallelizable
* different concurrent designs enable different ways to parallelize
* 比較
* 單核心 CPU:multi-threading 無法達到 parallelism,而只有 concurrency
* 多核心 CPU:concurrency 通常具有 parrallel 特性
* [Concurrency 系列文章](http://opass.logdown.com/posts/)
* sequeced-before:
對同一個 thread 下,求值順序關係的描述
同一個 thread 內的 happens-before
* happens-before:
前一個操作的效果在後一個操作執行之前必須要可見
強調可見,而不是實際執行的順序
* synchronized-with:
跨 thread 版本的 happens-before
兩個不同 thread 間的同步行為
* Memory Consistency Models:
系統保證正確的情況,盡可能最佳化
* Sequential Consistency:
兩個觀點
1. 對於每個獨立的處理單元,執行時都維持程式的順序(Program Order)
2. 整個程式以某種順序在所有處理器上執行
* concurrency 問題:
1. 多執行序競爭同一個資源
2. thread 之間的不同步行為
* 使用 mutex 或 semephore 改善
* 確保在寫入或讀取共享記憶體資源之操作是 atomic 的
* 必要時取消編譯器優化,因為可能發生 memory reordering 的不同步行為
* lock 與 lock-free programming
核心目標:使程序間互相溝通順利
* lock:包含 mutex 與 semephore 等,防止程序競爭同一記憶資源
* lock-free:沒有使用 mutex 與 semephore 等,但能達到 lock 者
* 未來的效能效能提昇方向:
1. hyperthread (多執行序並行處理task)
2. multicore (核心多自然處理的快)
3. cache (cache大小的增加與速度的提昇對效能影響顯著)
>>[參考整理](https://hackmd.io/IwIxBYDMDZYWgEwA5oHY7gMwGNtxAKyQCGcAJgKYLgLBnSQEIhA=?both)
>>[參考整理](https://hackmd.io/GwEwZgRgHArGAMBaAxgUwgdkQFgEwEZhEBOAQ2WMTAGYRr5VsYZGIg==?both)
## POSIX Threads
>[POSIX Threads Programming](https://computing.llnl.gov/tutorials/pthreads/)
### Thread
* Thread : 輕量級的行程(Lightweight process;LWP)
* Mach microkernel 作業系統中同一個 task 的所有 thread 共享該 task 所擁有的系統資源。
* UNIX 的一個 process 可以看成是一個只有一個 thread 的 Mach task。
* 對 CPU 而言,產生一個 thread 是一件相對簡單的工作。
* 共享系統資源的 thread 跟獨佔系統資源的 process 比起來,thread 是也是相當節省記憶體的。
#### Synchronization
...
:::info
Thread 同步問題:**mutex** 和 **condition variable**
* POSIX 提供了兩組用來使 thread 同步的基本指令: mutex 和 condition variable。
* mutex :
* 一組控制共享資源存取的函數
* 一般用在解決 race condition 問題
* mutex 並不是一個很強的機制,因為他只有兩個狀態:locked 和 unlocked
* condition variable :
* 將 mutex 的功能加以延伸,能夠做到讓某一個 thread 暫停,並等待另一個 thread 的 signal
* 總是搭配 mutex lock 使用

>>[參考觀念](https://hackmd.io/JwDgzMCMAmAMCGBaYAmaSAsA2ARpRIArAGbSLSGFbzogbTA5A===?both)
:::
#### Process vs. Thread vs. Coroutines
### 使用注意事項
* 編譯使用 pthread 的程式
* 引入相關的標頭檔 `<pthread.h>`
* 連結 pthread library `-lpthread`
```clike=
pthread_t a_thread;
pthread_attr_t a_thread_attribute;
void thread_function(void *argument);
char *some_argument;
```
### PThread 函式
#### [pthread_setconcurrency](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/pthread_getconcurrency.3.html)
```clike=
int pthread_setconcurrency(int new_level);
int pthread_getconcurrency(void);
```
>[UNIX環境高級編程:線程屬性之並行度](http://www.bianceng.cn/OS/unix/201408/44151.htm)
#### [pthread_create](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/pthread_create.3.html)
```clike=
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
```
#### [pthread_join](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/pthread_join.3.html)
```clike=
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
```
### Mutex 函式
>[Mutexes](https://computing.llnl.gov/tutorials/pthreads/#Mutexes)
```clike=
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, pthread_mutexattr_default);//定義mutex
pthread_mutex_lock( &mutex );//鎖定共享資源
pthread_mutex_unlock( &mutex );//解所共享資源
pthread_mutex_destroy();//結束mutex
```
### Thread Pool
>>[參考觀念](https://hackmd.io/GYVgLATAbGAmYFpYHYBGsFgMYEZgNRFgA4CBmVMYATmIENYAGLCIA===?both)
- Thread 缺陷
- 建立太多執行緒,會浪費一定資源,並且有些執行緒未被充份使用
- 銷毀太多執行緒,會導致之後浪費時間再次創建它們
- 建立執行緒太慢,導致效能變差
- 銷毀執行緒太慢,導致其它執行緒沒有資源
- Thread Pool 功能
- 管控 Thread 的產生與回收
- 分發 Thread 處理 request
- 處理 request 的 queue
>[C 的 Thread Pool 筆記](http://swind.code-life.info/posts/c-thread-pool.html)
>[github source code](https://github.com/mbrossard/threadpool)
```clike=
typedef struct {
void (*function)(void *);
void *argument;
} threadpool_task_t;
//Thread Pool 需要 job/task 讓 Thread 知道他們要做什麼事情
threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int thread_count, int queue_size, int flags);
//傳入 thread 的數量,queue 的大小,回傳 threadpool 型態是 threadpool_t
int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void (*routine)(void *), void *arg, int flags);
//傳入 threadpool,要執行的 function 位置,要傳入的參數
int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool, int flags);
//傳入 threadpool,會把 threadpool 的空間 free 掉
```
### Lock-free Thread Pool
#### Thread Pool VS Lock-Free Thread Pool
* Thread Pool
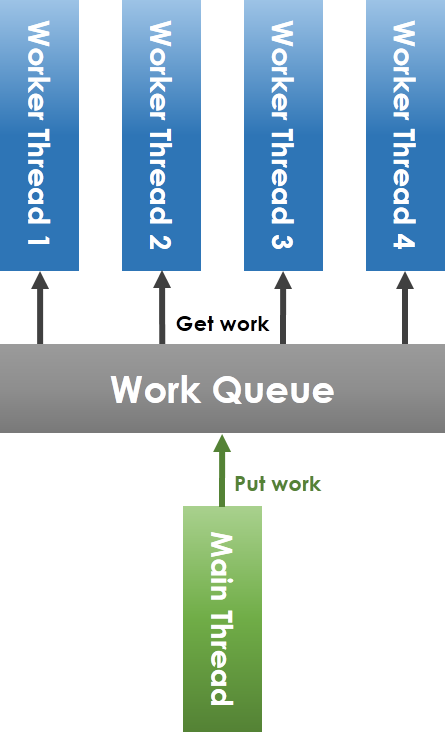
共享 workqueue 的操作必須在 mutex 的保護下安全進行。
* Lock-Free Thread
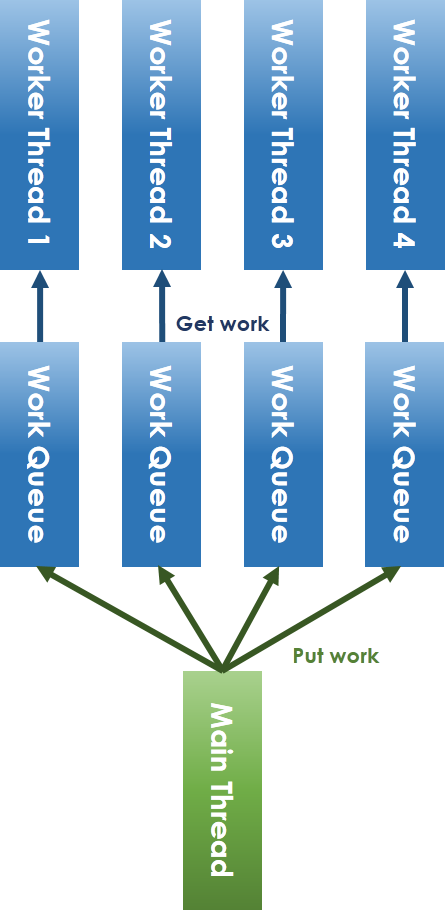
* 解決 lock 機制:
解決 lock-free 必須避免共享資源的競爭,因此將共享 workqueue 拆分成每個 worker thread 一個 workqueue。
對於 main thread 放入工作和 worker thread 取出任務的競爭問題,可以採取 ring-buffer 的方式避免。
* condition variable 問題:
condition variable 解決執行緒之間的通訊。
semaphore 作為一種通信方式,可以代替之。
>[高效線程池之無鎖化實現](http://blog.csdn.net/xhjcehust/article/details/45844901)
```clike=
void *tpool_init(int num_threads)
//初始化時決定要用哪種方式進行 put work,選用 `ring-buffer` 的方式將 worker 加入queue
static int wait_for_thread_registration(int num_expected)
//確保所有執行緒都在準備中
int tpool_add_work(void *pool, void(*routine)(void *), void *arg)
//配合 `dispatch` 加入 task 到 work queue 中
static void *tpool_thread(void *arg)
//給 worker task,沒有用到 mutex_lock
static tpool_work_t *get_work_concurrently(thread_t *thread)
//利用 CAS 讓每個執行緒拿到自己的 task,確保從 work queue 出來時,遞減 `out` 的變數同步
void tpool_destroy(void *pool, int finish);
//判斷所有的 queue 是不是空的,確保所有 worker 完成工作
```
:::info
**CAS**
以具有 atomic 特性的計算操作來達成。
```clike=
bool CAS(T* addr, T exp, T val)
{
if (*addr == exp) {
*addr = val;
return true;
}
return false;
}
```
:::
>[github source code](https://github.com/xhjcehust/LFTPool)
#### 實做測試
```shell
$ git clone https://github.com/xhjcehust/LFTPool
$ cd LFTPool/
$ make
$ ./testtpool
```
## 函式介紹
### MMAP
[SYNOPSIS]((http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/mmap.2.html))
```clike=
#include <sys/mman.h>
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);
```
#### mmap
mmap() 將檔案映射到一個 virtual memory address 上面,藉由直接對 memory address 修改的方式不用經過buffer,減少資料load到緩衝區的overhead,快速的記憶體存取可以提高對檔案 IO 的效率
:::info
**Blocking** VS **Non-blocking I/O**
* Blocking I/O
允許 sleep/awaken 動作的 process,基本動作:
* 當 process 進行 read 動作但是資料尚未就緒時,process 必須被 block 住 (sleep),而當有資料進來時就需要立即被喚醒 (awaken),就算資料仍不完整也是
* 當 process 進行 write 動作但是 buffer 沒有空間時,process 也必須被 block 住,而且必須被放到跟 read 動作不同的 wait queue 中去等待 wake-up (buffer 騰出空間寫入)
* Non-blocking I/O
* 讀不到資料或寫不進 buffer 時,他會送出 retry 的動作,再試一次
>>[參考觀念](https://hackmd.io/AwJgzA7ARgHMCsBaEJjEQFgMYE4uJgFMcA2RXYEiYYmAMxgiA===?both)
:::
>[記憶體映射函數 mmap 的使用方法](http://welkinchen.pixnet.net/blog/post/41312211)
* `addr` : 要 map 到的記憶體位置
* 如果 addr 為 NULL,kernel 將在建立的 mapping 地址中自行選擇,這是建立新的 mapping 最簡單的方法。
* 如果 addr 不是NULL,mapping 會在附近的 page boundary 建立,並將新 mapping 地址傳回。
* `length`: 要 mapping 的長度,它會從 fd + offset 的位置開始 mapping 檔案。
* `prot`: 要保護的記憶體保護 mapping
**不能跟 open mode 衝突**
* PROT_EXEC 可能執行
* PROT_READ 可能讀取
* PROT_WRITE 可能寫入
* PROT_NONE 可能不能存取
* `flags`: 選擇 map file 能不能被其他程式看到
* MAP_SHARED 分享此 mapping
* MAP_PRIVATE 建立一個私有 copy-on-write mapping
* `fd`: 用系統函式 open 打開的檔案位置,open mode 可以選擇檔案的讀寫屬性,不能跟 prot 有衝突。
* `offset`: 從檔案的哪裡開始 mapping,offset 必須是 page size 的倍數,可以用 sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE) 取得。
#### munmap
munmap() 用來取消參數 start 所指的映射記憶體起始地址,參數 length 則是欲取消的記憶體大小。當行程結束或利用 exec 相關函數來執行其他程式時,映射記憶體會自動解除,但關閉對應的文件描述詞時不會解除映射。
>[C語言munmap()函數:解除内存映射](http://c.biancheng.net/cpp/html/139.html)
### dprintf
## Refactoring
* 定義
「在不改變軟體外部行為的前提下,改變其內部結構,使其更容易理解且易於修改」。也就是說,在對外的介面上沒有做改變、介面背後的對應行為也沒有改變的情況下,基於可讀性,以及日後更便於修改的目的之下,來改寫內部的程式碼實作。
* 該執行重構的時機
* 增加新功能
* 修正錯誤
* 程式碼審查
> [Refactoring - Improving the Design of Existing Code](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r95004/Refactoring_improving_the_design_of_existing_code.pdf)
> [什麼是Refactoring](http://teddy-chen-tw.blogspot.tw/2014/04/refactoring.html)
> [對於重構的兩則常見誤解](http://www.ithome.com.tw/node/79813)
---
## 程式碼解析
>>[參考](https://hackmd.io/IwNgZgxgLCAMDsBaMUCmAjRUCGBOEi6AHLGIuBAKzoBM6AJversEA===?both)
>>參考 refactor 部分
### debug.h
* 提供 macro `dprintf`,與 `printf` 的用法一樣,只是會在前面增加 `DEBUG:` 的字樣,透過定義 `DEBUG` macro 啟用。
* 與 c library 提供的 `dprintf` 功能不一樣,c library 的為將輸出寫入指定的 file descriptor
### file_align.c
* 目的:將檔案中每一行的字串長度貼到指定長度
### main.c
1. 將檔案的內容映射到 memory 上,讓每個 thread 可以同時存取。
* `mmap`:將指定檔案的資料映射到 process 的 virtual memory space 上,可以防止 blocking I/O 的發生。
* `munmap` :刪除配給的區塊,在程式結束時,這個區塊會自動被 delete 掉。
* 關閉對應的 file descriptor 不會刪除配給的記憶體
2. 建立足夠的空 entry 給所有 thread 使用,避免因為 `malloc` 造成 waiting。
3. 準備每個 thread 所需要的資訊
* 讀取資料區間的開頭與結尾
* 寫入資料區間的開頭與結尾
5. 創造 thread,開始讓各自的 thread 工作
6. 等待所有 thread 完成之後將每一段 thread 所屬的 entry list 組合起來
## 程式實驗
### original code
```clike=
Performance counter stats for './phonebook_opt' (100 runs):
826,235 cache-misses # 42.230 % of all cache refs
1,986,333 cache-references
231,999,113 instructions # 1.00 insns per cycle
224,334,273 cycles
0.096829776 seconds time elapsed ( +- 1.72% )
```

### Refactor
- 解決 warning
將 `phonebook_opt.h` 中的 `static double diff_in_second` 加入 `#ifdef DEBUG` & `#endif` 確認是否開啟 DEBUG 模式。
如果要使用 DEBUG 需要使用 `$ make DEBUG=1`
```clike=
warning: variable ‘cpu_time’ set but not used [-Wunused-but-set-variable]
double cpu_time;
```
```clike=
#ifdef DEBUG
static double diff_in_second(struct timespec t1, struct timespec t2);
#endif
```
- 將 `main.c` 中 opt 版本需引入的標頭檔集中在 `main.c` 的前面方便閱讀
- 更改 `main.c` 中的 for loop
主要修改
1. 將 i = 0 的情況移出 for loop 減少 branch 的數量
2. 更正程式錯誤
- 原本為連接 `pHead->pNext`,但應連接 `pHead` 才對
```clike=
pHead = pHead->pNext;
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pHead = app[i]->pHead->pNext;
dprintf("Connect %d head string %s %p\n", i,
app[i]->pHead->pNext->lastName, app[i]->ptr);
} else {
etmp->pNext = app[i]->pHead->pNext;
dprintf("Connect %d head string %s %p\n", i,
app[i]->pHead->pNext->lastName, app[i]->ptr);
}
etmp = app[i]->pLast;
dprintf("Connect %d tail string %s %p\n", i,
app[i]->pLast->lastName, app[i]->ptr);
dprintf("round %d\n", i);
}
```
```clike=
pHead = app[0]->pHead;
dprintf("Connect %d head string %s %p\n", 0, app[0]->pHead->pNext->lastName, app[0]->ptr);
etmp = app[0]->pLast;
for (int i = 1; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
etmp->pNext = app[i]->pHead;
dprintf("Connect %d head string %s %p\n", i, app[i]->pHead->pNext->lastName, app[i]->ptr);
etmp = app[i]->pLast;
dprintf("Connect %d tail string %s %p\n", i, app[i]->pLast->lastName, app[i]->ptr);
dprintf("round %d\n", i);
}
```
- 更改 `phonebook_opt.c` 中變數名稱
- DEBUG: find string
- DEBUG: thread i append string
- 出現很多 DEBUG 和 匯流排遺失
>>[參考程式](https://hackmd.io/s/Bk-rtQGR#code-refactoring)
```clike=
Performance counter stats for './phonebook_opt' (100 runs):
789,020 cache-misses # 37.669 % of all cache refs
2,168,562 cache-references
230,179,204 instructions # 1.07 insns per cycle
231,563,707 cycles
0.096281171 seconds time elapsed ( +- 1.38% )
```

### Thread Pool
>[github source code](https://github.com/mbrossard/threadpool)
```clike=
threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int thread_count,
int queue_size,
int flags);
int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool,
void (*routine)(void *),
void *arg, int flags);
int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool, int flags);
```
```clike=
Performance counter stats for './phonebook_opt' (100 runs):
753,916 cache-misses # 35.587 % of all cache refs
2,129,353 cache-references
238,219,831 instructions # 1.03 insns per cycle
223,924,023 cycles
0.095207583 seconds time elapsed ( +- 1.48% )
```

- 執行結果不明顯
#### 各 work queue 和 worker thread 的比較結果圖
### Lock-free Thread Pool
>[github source code](https://github.com/xhjcehust/LFTPool)
##
---
<style>
h2.part {color: red;}
h3.part {color: green;}
h4.part {color: blue;}
h5.part {color: black;}
</style>
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet