# 重新理解數值
主講人: [jserv](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/User/jserv) / 課程討論區: [2016 年系統軟體課程](https://www.facebook.com/groups/system.software2016/)
## 數字背後的道理
* `0.1 - 0.3 + 0.2` 的結果竟然不等於 0 ?!
* 1985 年,IEEE 發佈 [IEEE 754](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_floating_point)
* 在 KTV 唱歌時,若唱不上去,我們常會「低八度」,這時雖然聲音低多了,但與原唱並不衝突,與伴奏也依然和諧。為什麼「八度」如此特別呢?更明確來說,差了八度的聲音聽起來如此相似呢?
* 差距八度的兩個音的頻率正好差 2 倍!
* 中音 do (記作 c’) 是 261.6Hz; 高音 do (記作 c’’) 是 523.3Hz
* 訊號處理 (signal proccessing)
## 二進位
* George Boolean 在1800年介紹「邏輯代數」,後來成為「布林代數」(Boolean Algebra)
* Claude E. Shannon 於 1938 年發表布林代數對於二進制函數的應用
## Integer Overflow
* [神一樣的進度條](https://www.facebook.com/JservFans/photos/a.743333619126308.1073741828.638604962932508/908325589293776/)
* [波音 787 不再「夢幻」](https://www.facebook.com/JservFans/posts/907938812665787)
* 波音 787 的電力控制系統在 248 天電力沒中斷的狀況下,會自動關機,為此 FAA (美國聯邦航空管理局) 告知應每 120 天重開機,看來「重開機治百病」放諸四海都通用?這當然是飛安的治標辦法,我們工程人員當然要探究治本議題。
* 任教於美國 [Carnegie Mellon University](https://www.facebook.com/carnegiemellonu/) (CMU) 的 Phil Koopman 教授指出,這其實就是 integer overflow,再次驗證「失之毫釐,差之千里」的道理。
* 我們先將 248 天換成秒數:
* 248 days * 24 hours/day * 60 minute/hour * 60 seconds/minute = 21,427,200
* 這個數字若乘上 100,繼續觀察:
* 0x7FFFFFFF (32-bit 有號數最大值) = 2147483647 / (24 * 60 * 60) = 24855 / 100 = 248.55 days.
* 看出來了嗎?每 1/100 秒紀錄在 32-bit signed integer,然後遇到 overflow
* [Counter Rollover Bites Boeing](http://betterembsw.blogspot.tw/2015/05/counter-rollover-bites-boeing-787.html)[ ](http://betterembsw.blogspot.tw/2015/05/counter-rollover-bites-boeing-787.html)[ 787](http://betterembsw.blogspot.tw/2015/05/counter-rollover-bites-boeing-787.html)
* 飛行控制系統和軟體工程/編譯器的[關聯](https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=10153481990772389)
* [航空太空科技是科技發展的火車頭](https://www.facebook.com/JservFans/posts/907381016054900)
* [Deep Impact ](https://www.facebook.com/JservFans/posts/904562523003416)(2005)
* [Ariane 5](https://www.facebook.com/JservFans/posts/904552413004427) (1996)
* [detail report](https://www.ima.umn.edu/~arnold/disasters/ariane5rep.html) : a data conversion from 64-bit floating point to 16-bit signed integer value
其他 integer overflow 案例:
* [Openssh 2002 security hole](http://www.openssh.com/txt/preauth.adv)
* [Year 2038 problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Year_2038_problem)
* [Youtube Gangnam Style overflows](http://arstechnica.com/business/2014/12/gangnam-style-overflows-int_max-forces-youtube-to-go-64-bit/)
* [Diablo III Real Money Action House integer overflow](http://gamasutra.com/blogs/MaxWoolf/20130508/191959/Diablo_III_Economy_Broken_by_an_Integer_Overflow_Bug.php)
* [Lempel-Ziv-Oberhumer (LZO) algorithm](http://thehackernews.com/2014/06/20-years-old-vulnerability-in-lzo.html)
* [OpenSSL integer underflow leading to buffer overflow in base64 decoding](https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1202395)
* [Trend Micro Discovers Vulnerability That Renders Android Devices Silent](http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/trend-micro-discovers-vulnerability-that-renders-android-devices-silent/)
* [IPv4 address ](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4_address_exhaustion)[L](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4_address_exhaustion)[exhaustion](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4_address_exhaustion) , [A bug and a crash --- The explosion of Ariane 5 rocket](http://www.around.com/ariane.html)
* [Integer overflow in Mozilla Firefox 3.5.x before 3.5.11 and 3.6.x before 3.6.7](http://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2010-2753)
* [CVE-2015-1593 - Linux ASLR integer overflow: Reducing stack entropy by four](http://hmarco.org/bugs/linux-ASLR-integer-overflow.html)
* [Integer overflow in Bitcoin software](http://cve.circl.lu/cve/CVE-2010-5139), [Bitcoinwiki - Value overflow incident](https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Value_overflow_incident)
* [SSH CRC32 attack detection code contains remote integer overflow](http://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/945216)
* [.NET Framework EncoderParameter integer overflow vulnerability](http://www.akitasecurity.nl/advisory/AK20110801/_net_framework_encoderparameter_integer_overflow_vulnerability.html)
* [The classic videogame Donkey Kong has an infamous ’kill screen’, where the game stops working. But why? =>integer overflow](http://mentalfloss.com/uk/games/31376/why-does-donkey-kong-break-on-level-22)
* [Adobe Flash Player casi32 Integer Overflow](http://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/exploit/windows/browser/adobe_flash_casi32_int_overflow)
* [ngx_http_close_connection integer overflow](http://www.oschina.net/news/39973/ngx_http_close_connection-integer-overflow)
* [愛國者飛彈系統軟體問題](http://sydney.edu.au/engineering/it/~alum/patriot_bug.html)
* [PHP Integer Overflow Affects Tenable’s Security Center](https://www.tenable.com/security/tns-2014-10)
* [Therac-25 radiation overdose](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Professionalism/Therac-25#cite_note-medical-devices-1)
* [CVE-2014-3669: Integer overflow in unserialize() PHP function](https://www.htbridge.com/blog/cve_2014_3669_integer_overflow_in_unserialize_php_function.html)
* [MS15-034 – Range Header Integer Overflow](https://sathisharthars.wordpress.com/tag/range-header-integer-overflow/)
* [PID控制器設計上的一些考量 避免發生overflow](http://www.ledin.com/integer-algorithms-implementation-and-issues/)
* [Oracle Issues Fix for Oracle Linux) Python Integer Overflow in ’bufferobject.c’ Lets Users Obtain Potentially Sensitive Information](http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1033118)
* [Super Mario Bros life](https://www.reddit.com/r/programming/comments/1aigv9/integer_overflow_in_an_rpg_defeat_a_boss_by/)
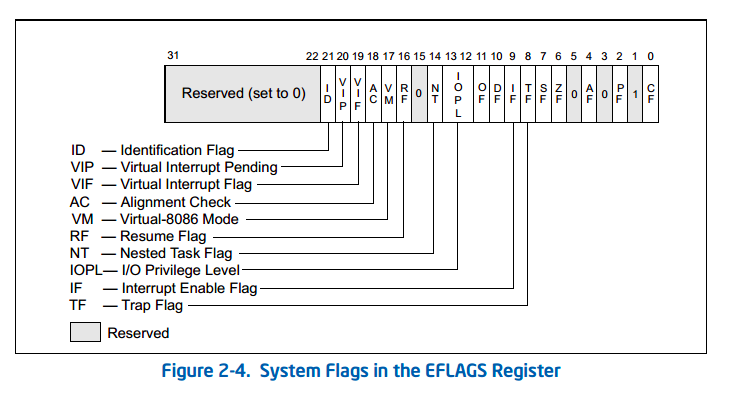
[gdb 顯示 FLAGS register](http://louieluhbt.blogspot.tw/2016/09/gdb-flags-register.html)
## 邏輯和算術的差異
**When exactly do side-effects take place in C and C++?**
```C=
int a = 41; a++; printf("%d\n", a); 42
int a = 41; a++ & printf("%d\n", a); undefined
int a = 41; a++ && printf("%d\n", a); 42
int a = 41; if (a++ < 42) printf("%d\n", a); 42
int a = 41; a = a++; printf("%d\n", a); undefined
```
* 以下的差異呢?
* int a=41; a++ & printf("%d\n", a);
* int a=41; a++ && printf("%d\n", a);
* int a=41; a=a++; printf("%d\n", a);
* 語法/語意分析
* `Left & Right` 中 (位元運算),關於是先對 `Left` 還是 `Right` 取值,沒有明確順序
* 但對於 `Left && Right` 來說 (邏輯運算),一定是先確保 `Left` 成立,才會作 `Right`
以下程式碼中:
```C=
a++ && printf();
```
左邊先運算 `a++`,倘若為真,接著才會作右邊的 `printf()`
# 運用 bit-wise operator
* C 語言中,`x & (x - 1) == 0` 的數學意義
* power of two
* signed v.s. unsigned
* C 語言中,`x | (x + 1)` 又表示什麼?
* x with lowest cleared bit set
* 以下 C 語言程式的 DETECT 巨集能做什麼?
```C=
#if LONG_MAX == 2147483647L
#define DETECT(X) \
(((X) - 0x01010101) & ~(X) & 0x80808080)
#else
#if LONG_MAX == 9223372036854775807L
#define DETECT(X) \
(((X) - 0x0101010101010101) & ~(X) & 0x8080808080808080)
#else
#error long int is not a 32bit or 64bit type.
#endif
#endif
```
* 巨集 `DETECT` 在偵測什麼?
* Detect NULL
測試這程式時,要注意到由於 **LONG_MAX** 定義在 `<limits.h>` 裡面,因此要記得作 `#include`
這個巨集的用途是在偵測是否為 0 或者說是否為 NULL char ’\0’,也因此,我們可以在 iOS 的原始程式碼 [strlen](http://opensource.apple.com/source/Libc/Libc-583/arm/string/strlen.s) 的實作中看到這一段。那,為什麼這一段程式碼可以用來偵測 NULL char ?
我們先思考 strlen() 該怎麼實做,以下實作一個簡單的版本
```C=
unsigned int strlen(const char *s)
{
char *p = s;
while (*p != ’\0’) p++;
return (p - s);
}
```
這樣的版本有什麼問題?雖然看起來精簡,但是因為他一次只檢查 1byte,所以一旦字串很長,他就會處理很久。另外一個問題是,假設是在 32-bit 的 CPU 上,一次是處理 4-byte (32-bit) 大小的資訊,不覺得這樣很浪費嗎?
為了可以思考這樣的程式,我們由已知的計算方式來逆推原作者可能的思考流程,首先先將計算再簡化一點點,將他從 **(((X) - 0x01010101) & ~(X) & 0x80808080)** 變成
```
((X) - 0x01) & ~(X) & 0x80
```
還是看不懂,將以前學過的笛摩根定理套用上去,於是這個式子就變成了
```
~( ~(X - 0x01) | X ) & 0x80
```
再稍微調整一下順序
```
~( X | ~(X - 0x01) ) & 0x80
```
所以我們就可進行分析
* `X | ~(X - 0x01)` => 取得最低位元是否為 0 ,並將其他位元設為 1
* X = 0000 0011 => 1111 1111
* X = 0000 0010 => 1111 1110
* 想想 0x80 是什麼? 0x80 是 1000 0000 ,也就是 1-byte 的最高位元
上面這兩組組合起來,我們可以得到以下結果
* X = 0 => 1000 0000 => 0x80
* X = 1 => 0000 0000 => 0
* X = 2 => 0000 0000 => 0
* .......
* X = 255 => 0000 0000 => 0
於是我們知道,原來這樣的運算,如果一個 byte 是 0,那經由這個運算得到的結果會是 0x80,反之為 0。
再將這個想法擴展到 32-bit,是不是可以想到說在 32bit 的情況下,0 會得到 0x80808080 這樣的答案?我們只要判斷這個數值是不是存在,就可以找到 ’\0’ 在哪了!
參考資料:
* [Hacker’s Delight](http://www.amazon.com/Hackers-Delight-Edition-Henry-Warren/dp/0321842685)
* [](http://www.hackersdelight.org/corres.txt)[http://www.hackersdelight.org/corres.txt](http://www.hackersdelight.org/corres.txt)
* [FreeBSD 的 strlen(3)](https://blog.delphij.net/2012/04/freebsd-strlen3.html)
* [Bug 60538 - [SH] improve support for cmp/str insn ](https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=60538)
應用:
* [newlib 的 strlen](https://github.com/eblot/newlib/blob/master/newlib/libc/string/strlen.c)
* [newlib 的 strcpy](https://github.com/eblot/newlib/blob/master/newlib/libc/string/strcpy.c)
* SSE 4.2 最佳化版本: [Implementing strcmp, strlen, and strstr using SSE 4.2 instructions](https://www.strchr.com/strcmp_and_strlen_using_sse_4.2)
## 算術完全可用數位邏輯實做
只能使用位元運算子和遞迴,在C程式中實做兩個整數的加法,可行嗎?
先回顧[加法器](http://www.gauss.com.tw/logic/ch6/index6.htm) 的實做,思考以下程式碼:
```C
int add(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0) return a;
int sum = a ^ b; /* 相加但不進位 */
int carry = (a & b) << 1; /* 進位但不相加 */
return add(sum, carry);
}
```
延伸閱讀: [How to simulate a 4-bit binary adder in C](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14695051/how-to-simulate-a-4-bit-binary-adder-in-c)
## Count Leading Zero
當我們計算 log2 (以2為底的對數) 時, 其實只要算高位有幾個 0's bits. 再用 31 減掉即可。
```C
BITS = 31;
for (; i < 32; --BITS) {
if (N & 0x80000000) break;
N <<= 1;
}
```
LOG(N) is BITS
當要算 log10 時, 因為 32-bit unsigned integer 最大只能顯示 4294967295U,所以 32-bit LOG10() 的值只有可能是 0 ~ 9.
這時可透過查表法,以省去除法的成本。
```C
unsigned int vals[] = {
0UL,
10UL,
100UL,
1000UL,
10000UL,
100000UL,
1000000UL,
10000000UL,
100000000UL,
1000000000UL,
};
for (i = 0; i < (nr - 1); ++i) { // 9
if (N >= vals[i] && N < vals[i + 1]) { // 8
break; // 1
}
}
```
換句話說,計算 log2 時,知道「高位開頭有幾個 0」就成為計算的關鍵操作。
延伸閱讀: [Fast computing of log2 for 64-bit integers](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11376288/fast-computing-of-log2-for-64-bit-integers)
* 類似 De Bruijn 演算法
* 64-bit version
```C
const int tab64[64] = {
63, 0, 58, 1, 59, 47, 53, 2,
60, 39, 48, 27, 54, 33, 42, 3,
61, 51, 37, 40, 49, 18, 28, 20,
55, 30, 34, 11, 43, 14, 22, 4,
62, 57, 46, 52, 38, 26, 32, 41,
50, 36, 17, 19, 29, 10, 13, 21,
56, 45, 25, 31, 35, 16, 9, 12,
44, 24, 15, 8, 23, 7, 6, 5
};
int log2_64 (uint64_t value)
{
value |= value >> 1;
value |= value >> 2;
value |= value >> 4;
value |= value >> 8;
value |= value >> 16;
value |= value >> 32;
return tab64[((uint64_t)((value - (value >> 1 ))*0x07EDD5E59A4E28C2)) >> 58];
}
```
* 32-bit version
```C
const int tab32[32] = {
0, 9, 1, 10, 13, 21, 2, 29,
11, 14, 16, 18, 22, 25, 3, 30,
8, 12, 20, 28, 15, 17, 24, 7,
19, 27, 23, 6, 26, 5, 4, 31
};
int log2_32 (uint32_t value)
{
value |= value >> 1;
value |= value >> 2;
value |= value >> 4;
value |= value >> 8;
value |= value >> 16;
return tab32[(uint32_t)(value*0x07C4ACDD) >> 27];
}
```
gcc 提供 built-in Function:
* [int __builtin_clz (unsigned int x)](http://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Other-Builtins.html)
* Returns the number of leading 0-bits in x, starting at the most significant bit position.
* If x is 0, the result is undefined.
可用來實做 log2:
```C
#define LOG2(X) ((unsigned) \
(8 * sizeof (unsigned long long) -
__builtin_clzll((X)) - 1))
```
那該如何實做 clz 呢?
- [ ] iteration version
```C
int clz(uint32_t x) {
int n = 32, c = 16;
do {
uint32_t y = x >> c;
if (y) { n -= c; x = y; }
c >>= 1;
} while (c);
return (n - x);
}
```
- [ ] binary search technique
```C
int clz(uint32_t x) {
if (x == 0) return 32;
int n = 0;
if (x <= 0x0000FFFF) { n += 16; x <<= 16; }
if (x <= 0x00FFFFFF) { n += 8; x <<= 8; }
if (x <= 0x0FFFFFFF) { n += 4; x <<= 4; }
if (x <= 0x3FFFFFFF) { n += 2; x <<= 2; }
if (x <= 0x7FFFFFFF) { n += 1; x <<= 1; }
return n;
}
```
- [ ] byte-shift version
```C
int clz(uint32_t x) {
if (x == 0) return 32;
int n = 1;
if ((x >> 16) == 0) { n += 16; x <<= 16; }
if ((x >> 24) == 0) { n += 8; x <<= 8; }
if ((x >> 28) == 0) { n += 4; x <<= 4; }
if ((x >> 30) == 0) { n += 2; x <<= 2; }
n = n - (x >> 31);
return n;
}
```
* [ffs](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/ffs.3.html)() 會回傳給定數值的 first bit set 的位置
* 例如 128 在 32-bit 表示為 `0x10000000`,ffs(128)會回傳 8
* 129 在 32bit 表示為 `0x10000001,`ffs(129) 會回傳 1
延伸閱讀: [Bit scanning equivalencies](https://fgiesen.wordpress.com/2013/10/18/bit-scanning-equivalencies/)
## 省去迴圈
考慮以下 C 程式,解說在 32-bit 架構下具體作用(不是逐行註解),以及能否避開用迴圈?
```c
int func(unsigned int x) {
int val = 0; int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
val = (val << 1) | (x & 0x1);
x >>= 1;
}
return val;
}
```
簡單來說這段程式碼就是拿來顛倒輸入數字的位元順序,如下面測試所示,顛倒後位元不足 32bit 者,全部補 0
```txt
------input number 99--------
2bit= 1100011
val = 11000110000000000000000000000000
------output number -973078528--------
------input number 198--------
2bit= 11000110
val = 1100011000000000000000000000000
------output number 1660944384--------
------input number 297--------
2bit= 100101001
val = 10010100100000000000000000000000
------output number -1803550720--------
------input number 396--------
2bit= 110001100
val = 110001100000000000000000000000
------output number 830472192--------
------input number 4294967281--------
2-bit= 11111111111111111111111111110001
val = 10001111111111111111111111111111
------output number -1879048193--------
```
參考 [Reverse integer bitwise without using loop](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21511533/reverse-integer-bitwise-without-using-loop),將原本的 for 迴圈變更為 bit-wise 操作:
```
new = num;
new = ((new & 0xffff0000) >> 16) | ((new & 0x0000ffff) << 16);
new = ((new & 0xff00ff00) >> 8) | ((new & 0x00ff00ff) << 8);
new = ((new & 0xf0f0f0f0) >> 4) | ((new & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4);
new = ((new & 0xcccccccc) >> 2) | ((new & 0x33333333) << 2);
new = ((new & 0xaaaaaaaa) >> 1) | ((new & 0x55555555) << 1);
```
在不使用迴圈的情況下,可以做到一樣的功能。
## 加解密的應用
- [ ] Caesar shift cipher
* 把 A-Z 這 26 個字母表示成 A=0, B=1, ..., Z=25,然後給任意一個 KEY,把訊息的字母加上 KEY 之後 mod 26 就會得到加密之後的訊息。假設 KEY=19,那麼原本的訊息例如 HELLO (7 4 11 11 14) 經過 cipher 後 (26 23 30 30 33) mod 26 => (0 23 4 4 7) 會變成 AXEEH 的加密訊息。
- [ ] XOR
* 假設有一張黑白的相片是由很多個0~255的pixel組成(0是黑色,255是白色),這時候可以用任意的 KEY (00000000~2~ - 11111111~2~) 跟原本的每個 pixel 做運算,如果使用 AND (每個bit 有75% 機率會變成 0),所以圖會變暗。如果使用 OR (每個 bit有 75% 機率會變 1),圖就會變亮。這兩種幾乎都還是看的出原本的圖片,但若是用 XOR 的話,每個 bit 變成 0 或 1 的機率都是 50%,所以圖片就會變成看不出東西的雜訊。

上圖左 1 是原圖,左 2 是用 AND 做運算之後,右 2 是用 OR 做運算之後,右 1 是用 XOR,可見使用 XOR 的加密效果最好。
參考資料:[Ciphers vs. codes
](https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/cryptography/ciphers/a/ciphers-vs-codes)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet