# 2017q3 Homework2 (prefix-search)
contributed by<`kevin550029`>
## Ternary Search Tree 基本介紹
:::danger
1. 用「自己理解的認知」,改寫以下描述
2. 技術報告的訓練,就是強化思考和資料彙整的能力,日後才可有基礎做研究
:notes: jserv
:::
* 不同於 trie 的結構, 每個 node 只有三個 pointer
* TST 的 1 個 node 中有包含 5 個 component, 如圖所示
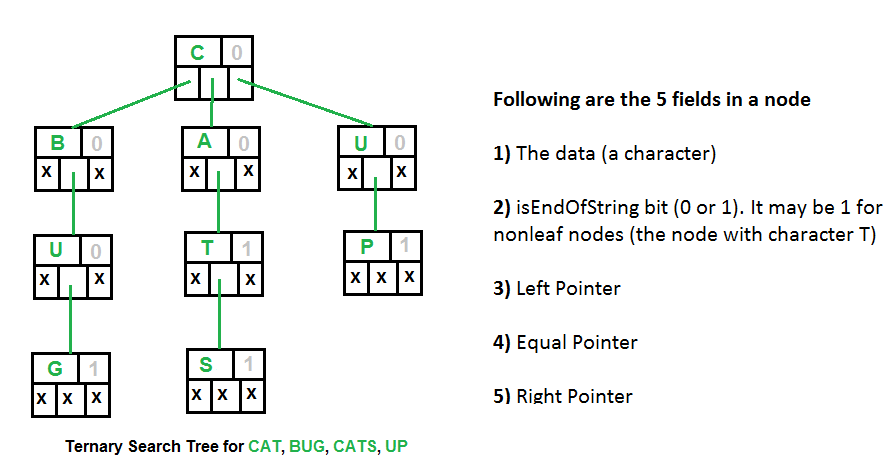
1. data field: 儲存 node 的內容
1. EndOfString field: 用來指出該 node 是否為一個字串的最後一個元字元
1. Left Pointer: 指向值小於自己的 child
1. Equal Pointer: 指向值等於自己的 child
1. Right pointer: 指向值大於自己的 child
## 測試環境
```
Linux version 4.4.0-96-generic
Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 6144K
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 4
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 4
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 94
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-6400 CPU @ 2.70GHz
```
## 測試 prefix-search 程式碼
```
Commands:
a add word to the tree
f find word in tree
s search words matching prefix
d delete word from the tree
q quit, freeing all data
```
* Insertion
a 可以將字元加入樹中
```
choice: a
enter word to add: test_city_kevin
test_city_kevin - inserted in 0.000008 sec. (259113 words in tree)
```
* Find
f 可判斷某個字元是否在樹中
```
choice: f
find word in tree: test_city_kevin
found test_city_kevin in 0.000006 sec.
find word in tree: xxxxx_ooooo
xxxxx_ooooo not found.
```
* Search prefix
s 將含有指定開頭字串的字元找出來
```
choice: s
find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): Taiw
Taiw - searched prefix in 0.000009 sec
suggest[0] : Taiwala,
suggest[1] : Taiwan
```
這邊觀察到有些城市名中會帶有逗號
舉例來說,若直接輸入Taiwala, 而不是 `Taiwala,`
會回傳 Taiwala not found
* delete
刪除功能要在 refcnt 為零的時候才能成功刪除
```
choice: d
enter word to del: Taiwan
deleting Taiwan
Taiwan (refcnt: 18) not removed.
delete failed.
```
## 修改 test_ref.c
開始針對 test_ref.c 中 `FIXME` 的部分作修改
```clike=
/* FIXME: insert reference to each string */
res = tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, CPY);
```
將原本使用的 CPY 改為 REF, 並使用 s 搜尋 prefix: `Amer`, 結果如下
```
choice: s
find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): Amer
Amer - searched prefix in 0.000018 sec
suggest[0] : Amer
suggest[1] : Amer
suggest[2] : Amer
suggest[3] : Amer
suggest[4] : Amer
```
合理結果應該是要列出以 `Amer` 為 prefix 的所有字元
但這邊都輸出成 Amer, 推測原因可能是所有 node 都存取到同一個記憶體位置
使用 q 時, 也會發生錯誤
```
choice: q
*** Error in `./test_ref': free(): invalid pointer: 0x00007ffebbfe5dd0 ***
```
* 觀察 tst_ins_del()
```clike=
/* Place nodes until end of the string, at end of stign allocate
* space for data, copy data as final eqkid, and return.
*/
if (*p++ == 0) {
if (cpy) { /* allocate storage for 's' */
const char *eqdata = strdup(*s);
if (!eqdata)
return NULL;
curr->eqkid = (tst_node *) eqdata;
return (void *) eqdata;
} else { /* save pointer to 's' (allocated elsewhere) */
curr->eqkid = (tst_node *) *s;
return (void *) *s;
}
}
pcurr = &(curr->eqkid);
```
發現使用 cpy 時,會執先行 strdup()
strdup()會先用maolloc()配置和 s 字符串相同的空間大小
然後將參數 s 字符串的内容複製到該地址,然后把該地址回傳
而使用 ref 的話, 則直接將 curr->eqkid 指到 s 指到的 address
但是 s 指到的位址內容應該要隨著每次讀的 word 而改變
* 修改方法
在 test_ref.c 分配位置給 word 時, 使用 strdup()
```clike=
char *p = strdup(word);
/* FIXME: insert reference to each string */
if (!tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, REF)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: memory exhausted, tst_insert.\n");
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
```
* 重新執行
同樣使用 s 搜尋 prefix: `Amer`, 發現已可正常執行
```
choice: s
find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): Amer
Amer - searched prefix in 0.000022 sec
suggest[0] : Amerang,
suggest[1] : Amerdingen,
suggest[2] : America,
suggest[3] : American
suggest[4] : Americana,
suggest[5] : Americus,
suggest[6] : Amerongen,
suggest[7] : Amersfoort,
suggest[8] : Amersham
suggest[9] : Amersham,
suggest[10] : Amery,
```
* 修改後 q 一樣可正常執行, 因為 strdup() 用 maolloc() 來配置記憶體, 可以使用 free() 來釋放
## 效能評估&比較
參考 [st9007a](https://hackmd.io/s/SkeKQEq3Z) & [tina0405](https://hackmd.io/JwDhDMAYHYGMBYC0sDMliPgNgIa0QEbgBMKiWkWF4KWArBQIxA==#分析資料) 同學的共筆設計測試方法
* 設計bench_test Function
```clike=
char word[SAMPLES][WRDMAX]; //儲存要拿來做搜尋的 prefix
char prefix[3] = "";
char *sgl[LMAX] = {NULL};
int sidx=0, count=0;
//從 cities.txt 中取出一些城市名稱, 拿來做搜尋的 prefix
//SAMPLES 可以指定要拿出多少筆, 這邊設成 30000
FILE *prefixF = fopen(IN_FILE,"r");
for (int i=0; i < SAMPLES; i++)
{
fscanf(prefixF, "%s", word[i]);
}
fclose(prefixF);
double t1, t2;
FILE *fp = fopen(output_file,"w"); //輸出時間結果用的檔案
for (int i=0; i < SAMPLES; i++)
{
//取出在word中, 每個城市的前三個字元, 當作準備要搜尋的 prefix
if (strlen(word[i]) < 3) continue;
strncpy(prefix, word[i], 3);
// 執行 prefix search 並計算時間
t1 = tvgetf();
tst_search_prefix(root, prefix, sgl, &sidx, LMAX);
t2 = tvgetf();
fprintf(fp, "%d %.6f sec\n", count, t2 - t1);
count++; //紀錄第幾筆 search
}
fclose(fp);
```
* 利用gnuplot繪圖
關於gnuplot語法, 參考以下幾個網站
[GT Chen's Blog: Gnuplot](http://gtchen.pixnet.net/blog/post/5873441-gnuplot-%28part-i%29), [Gnuplot 簡單數據繪圖](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10158860)
用 3000 個長度為 3 的 prefix 來做搜尋得到的結果

縮小圖的範圍,在輸出一次

光看上圖很難看出明顯的分別
所以再去計算個別的平均值和標準差
可以發現在平均搜尋時間上, CPY 花的時間較少
```
CPY Version
Mean: 0.000067
Standard Deviation:0.000076
```
```
REF version
Mean: 0.000072
Standard Deviation:0.000083
```
兩個方法的cache-misses的情況相差不多
```
CPY Version
Performance counter stats for 'sudo chrt -f 99 taskset -c 0 ./test_cpy --bench' (100 runs):
2080 cache-misses # 33.556 % of all cache refs ( +- 1.44% )
6197 cache-references ( +- 0.78% )
3,5200 instructions # 0.42 insns per cycle ( +- 0.48% )
8,4727 cycles ( +- 1.30% )
0.852326170 seconds time elapsed ( +- 0.93% )
```
```
REF Version
Performance counter stats for 'sudo chrt -f 99 taskset -c 0 ./test_ref --bench' (100 runs):
2082 cache-misses # 33.628 % of all cache refs ( +- 1.36% )
6192 cache-references ( +- 0.86% )
3,5289 instructions # 0.42 insns per cycle ( +- 0.48% )
8,3771 cycles ( +- 0.96% )
0.863542987 seconds time elapsed ( +- 0.28% )
```
* 引入 Memory pool 方法
## 作業要求
> 「作業要求」放在超連結就好,不需要先貼出來,這樣是拿不到 P 幣的。
> Show me the code!
> [name=jserv"][color=red]
> got it
> 先貼在這邊方便自己查看, 完成後會移除
> [name="kevin550029"]
* 在 GitHub 上 fork [prefix-search](https://github.com/sysprog21/prefix-search),並修改 `Makefile` 以允許 `$ make bench` 時,可對 ternary search tree 的實作做出效能評比,涵蓋建立 tst 和 prefix search 的時間,應比照 [clz](https://hackmd.io/s/Hyl9-PrjW) 透過統計模型,取出 95% 信賴區間
* 測試程式碼應該接受 `--bench` 的執行參數,得以在沒有使用者輸入的前題下,對 tst 程式碼進行效能分析,應涵蓋 `cpy` 和 `ref` 兩種途徑 (詳情參閱 `tst.h` 的程式碼註解)
* 解釋 tst 的優點和引入 tst 到電話簿或戶政管理系統的適用性
* 修改 [test_ref.c](https://github.com/sysprog21/prefix-search/blob/master/test_ref.c),參照裡頭標註 `TODO` 的部分,替換成真正有效的 API 和對應的程式碼,這裡要求你學習分析現有的程式碼並得以擴充
* 分析 `test_cpy` 和 `test_ref` 兩種方式 (copy/reference) 的效能,並且針對現代處理器架構,提出效能改善機制
* 指出目前實作中,針對各國城市的 prefix search 有無缺陷呢?比方說無法區分城市和國家,並提出具體程式碼的修正
* 引入 [phonebook](https://hackmd.io/s/HJJUmdXsZ) 的基礎工作,透過 [ternary search tree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ternary_search_tree) 讓電話簿程式得以更符合人性,當使用者新增資料時,可以在居住地透過 prefix search 找出最接近的城市並避免輸入錯誤
* 詳細觀察 `tst.h` 和 `tst.c` 為何要 forward declaration 呢?分離介面和實作有何好處呢?這樣的思維又該如何運用於 [phonebook](https://hackmd.io/s/HJJUmdXsZ) 呢?提出想法並且實作
* 研究程式碼的 `tst_traverse_fn` 函式,並思考如何運用這個實作,注意到 [callback function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Callback_(computer_programming)) 的程式開發技巧/模式
* 將你的觀察、上述要求的解說、應用場合探討,以及各式效能改善過程,善用 gnuplot 製圖,紀錄於「[作業區](https://hackmd.io/s/HkVvxOD2-)」
## 參考資料
[Ternary Search Tree](http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ternary-search-tree/)
[Ternary Search Tree (Deletion)](http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ternary-search-tree-deletion/)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet