# [compute-pi](https://hackmd.io/s/rJARexQT)
[github](https://github.com/diana0651/compute-pi) contributed by <`Diana Ho`>
###### tags: `d0651` `sys`
## 案例分析
### 學習目標
- [ ]學習透過離散微積分求圓周率
* [Leibniz formula for π](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leibniz_formula_for_%CF%80)
* [積分計算圓周率π](http://book.51cto.com/art/201506/480985.htm)
* [Function](http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/Function2.html)
- [ ]著手透過 SIMD 指令作效能最佳化
### 開發環境
Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
---
## Wall-clock time vs. CPU time
* clock(), clock_gettime() 的使用
* clock()
returns an approximation of processor time used by the program.
```clike=
clock_t begin = clock();
compute_pi;
clock_t end = clock();
double time = (double)(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
```
* clock_gettime()
retrieves the time of the specified clock clk_id.
```clike=
struct timespec {
time_t tv_sec; // seconds
long tv_nsec; //nanoseconds
}
struct timespec start,end;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW,&start);
compute_pi;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW,&end);
double time = (double)((end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec)+(end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec)/1000000000);
```
* time(), gettimeofday() 的使用
* time()
returns the wall-clock time from the OS, with precision in seconds.
* gettimeofday()
returns the wall-clock time with nominally µs precision.
* 為什麼 clock_gettime() 結果飄忽不定?
* function的執行時間單位以nanoseconds來決定,執行時間很短時並無法排除Linux背景處理其他事情,導致額外的cache miss,所以需要很多針對某一筆參數作累積再平均,才能避免飄忽不定
* 為什麼 time() 和 gettimeofday() 不適合拿來作 benchmark ?
* clock_gettime()是monotonic,而time() 和 gettimeofday()的精準度較低,所以不適合
>>[參考概念](https://embedded2015.hackpad.com/HW1-Mj4fZIhTKVH)
---
## 效能分析比較圖表
預期執行 `$ make plot` 後,可透過 gnuplot 產生效能分析比較圖表
- 舊電腦:
每當執行到 avxunroll 時, 就會發生不合法命令的錯誤
```clike=
$ make check
make: *** [check] Error 132
$ make gencsv
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
make: *** [gencsv] Error 132
$ time ./time_test_avxunroll
不合法的命令 (core dumped)
real 0m1.219s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.000s
```
:::warning
> [參考](https://hackmd.io/KwUwLCAmBsYIwFoAcwCGBjBZICYDMyOkSCADEqgOwBmSIAnAEak5hA==)
如果在跑make check時發現下面的回應Illegal instruction (core dumped)代表電腦不支援AVX SIMD
不知道是什麼原因造成無法順利執行
舊電腦的開發環境:
- `$ cat /etc/issue`
Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS \n \l
- `$ cat /proc/version`
Linux version 4.4.0-53-generic (buildd@lgw01-54) (gcc version 4.8.4 (Ubuntu 4.8.4-2ubuntu1~14.04.3) )
:::
- 新電腦:
```clike=
gcc -c -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.c -o computepi.o
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DBASELINE -o time_test_baseline
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DOPENMP_2 -o time_test_openmp_2
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DOPENMP_4 -o time_test_openmp_4
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DAVX -o time_test_avx
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DAVXUNROLL -o time_test_avxunroll
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o benchmark_clock_gettime.c -o benchmark_clock_gettime
time ./time_test_baseline
N = 400000000 , pi = 3.141593
4.90user 0.00system 0:04.90elapsed 99%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 1760maxresident)k
0inputs+0outputs (0major+85minor)pagefaults 0swaps
time ./time_test_openmp_2
N = 400000000 , pi = 3.141593
5.04user 0.00system 0:02.52elapsed 199%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 1780maxresident)k
0inputs+0outputs (0major+87minor)pagefaults 0swaps
time ./time_test_openmp_4
N = 400000000 , pi = 3.141593
5.54user 0.00system 0:01.49elapsed 370%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 1784maxresident)k
0inputs+0outputs (0major+95minor)pagefaults 0swaps
time ./time_test_avx
N = 400000000 , pi = 3.141593
1.57user 0.00system 0:01.58elapsed 99%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 1768maxresident)k
0inputs+0outputs (0major+86minor)pagefaults 0swaps
time ./time_test_avxunroll
N = 400000000 , pi = 3.141593
1.70user 0.00system 0:01.70elapsed 99%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 1688maxresident)k
0inputs+0outputs (0major+85minor)pagefaults 0swaps
```
```clike=
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DBASELINE -o time_test_baseline
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DOPENMP_2 -o time_test_openmp_2
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DOPENMP_4 -o time_test_openmp_4
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DAVX -o time_test_avx
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o time_test.c -DAVXUNROLL -o time_test_avxunroll
gcc -O0 -std=gnu99 -Wall -fopenmp -mavx computepi.o benchmark_clock_gettime.c -o benchmark_clock_gettime
for i in `seq 100 5000 25000`; do \
printf "%d," $i;\
./benchmark_clock_gettime $i; \
done > result_clock_gettime.csv
```
:::info
#### AVX
[Introduction to Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions](https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/introduction-to-intel-advanced-vector-extensions)
The hardware supporting Intel® AVX (and FMA) consists of the 16 256-bit YMM registers YMM0-YMM15 and a 32-bit control/status register called MXCSR.
:::
### 使用 gnuplot 製圖
- 在 `runtime.gp` 中編輯繪圖語法
- 在 `Makefile` 中定義製圖的 rule
```clike=
plot: default
gnuplot runtime.gp
```
- 執行 `$ make plot` 產生`runtime.png`
- 執行 `$ eog runtime.png` 看到圖像
### 測量時間的函式
> [實作參考](https://hackmd.io/KwUwLCAmBsYIwFoAcwCGBjBZICYDMyOkSCADEqgOwBmSIAnAEak5hA==)
原來程式碼輸出的圖形(25倍時間),明顯看出資料分佈抖動的很厲害
clock 疊代了25次,所以應將程式改為取25次運算時間之平均
```clike=
clock_gettime(CLOCK_ID, &start);
for(i = 0; i < loop; i++){
compute_pi_baseline(N);
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_ID, &end);
printf("%lf",(double)((end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec)+(end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec)/ONE_SEC))/loop);
```
#### 解法:
用信賴區間消去極端值
再將X軸取logscale
:::info
#### 信賴區間(Confidence interval)
由樣本資料定義一段數值區間,宣稱有多少信心以估計母體的參數包含於此區間內。
該數值區間上、下限稱為信賴界限(confidence limit)。
用以估計的信心程度稱為信賴(心)水準(confidence level)。
##### 標準差

* 一般常以 95% 或 99% 為信賴水準指標;相對應的 Z分數(相差幾個標準差) 分別為 1.96 與 2.58。
* 可表示為:
有 95% 信心估計母群體平均數,在樣本平均數 ± 1.96 * (母群體標準差 / 樣本數 n 的平方根) 的範圍內。
而 99% 信心估計母群體平均數,則在樣本平均數 ± 2.58 * (母群體標準差 / 樣本數 n 的平方根) 的範圍內。
科學符號表示方式:
μ 之 95% CI = X ± 1.96 * ( σ / √n )
μ 之 99% CI = X ± 2.58 * ( σ / √n )
:::
- `clock()`

- `clock_gettime()`

- data 飄動, 嘗試增加 Makefile 定義 data 的資料數量:
```clike=
for i in `seq 100 100 25000`; do \
printf "%d " $$i;\
./benchmark_clock_gettime $$i; \
done > result_clock_gettime.csv
```

### Error Rate
:::info
The higher the error rate, the less reliable the connection or data transfer will be.
:::
* references:
* [廖健富學長的筆記](https://hackpad.com/Hw1-Extcompute_pi-geXUeYjdv1I)
- error rate的計算:
利用定義在`<math.h>`中的M_PI與computepi中的計算結果對比
---
## baseline 版本
* pi 的公式

* 黎曼積分原理
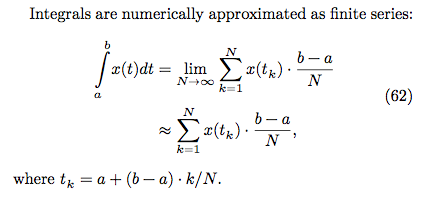
* 程式碼:
```clike=
double compute_pi_baseline(size_t N)
{
double pi = 0.0;
double dt = 1.0 / N; // dt = (b-a)/N, b = 1, a = 0
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = (double) i / N; // x = ti = a+(b-a)*i/N = i/N
pi += dt / (1.0 + x * x); // integrate 1/(1+x^2), i = 0....N
}
return pi * 4.0;
}
```
## Leibniz 版本

### 實作
```clike=
double compute_pi_leibniz(size_t N)
{
double pi = 0.0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
int temp = (i%2) ? -1 : 1;
pi += (double) temp / (2*i+1);
}
return pi * 4.0;
}
```
### 測試程式效能

#### 測量 error rate
### 優化方向
...
- OpenMP
- AVX
- AVX + loop unrolling
>>[實作參考](https://hackmd.io/GYZgRgnALAhgHAJgLRgCYIkqBWMMlwgwhIAMMA7AGzbBSkKpQRA=)
## Euler 版本

### 實作
```clike=
double compute_pi_euler(size_t N)
{
double pi = 0.0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
pi += (double)(1 / pow(i, 2));
pi *= 6;
return sqrt(pi);
}
```
>>[實作參考](https://hackmd.io/GYZgRgnALAhgHAJgLRgCYIkqBWMMlwgwhIAMMA7AGzbBSkKpQRA=)
### 測試程式效能

若呼叫 `#include <math.h>` 的函式, 需要花的時間更長
#### 測量 error rate
### 優化方向
...
- OpenMP
- AVX
- AVX + loop unrolling
## Monte Carlo 版本
...
### 實作
```clike=
int main()
{
double x,y;
int count=0; /* # of points in the 1st quadrant of unit circle */
double z;
double pi;
count=0;
for(size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
x = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;
y = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;
z = x*x+y*y;
if (z<=1) count++;
}
printf("pi = %lf \n",(double)count/n*4);
return 0;
}
```
>>[實作參考](https://hackmd.io/MYFgHAJgDAjBCcBaAbAIwKZkeESzoHZhEBDYE9ECAJnjHAGYg===)
...
---
## SIMD
### 閱讀資料
[SIMD](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1LeVe7EAmZvqD3KN7p4Wynbd36xPOk9biBCFrdmsqzKs/edit#slide=id.p3)
SIMD = Single Instruction Multiple Data,主要把原本一個指令中的數值分成多個部份,分配給多個執行緒執行完後再統整程最後結果,加速執行速度
#### SIMD 優化方式
- Auto/Semi-Auto method
- 讓compiler做vectorization處理(ex: `#pragma`)
- 把原本serial的執行變成平行化處理的方式
- [IR Optimization](https://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs143/cs143.1128/lectures/14/Slides14.pdf): 對中間語言(intermediate representation)的優化
- 在從高階語言轉換產生IR後,時常會有一些冗餘的計算,應該優化
- 使用者會使用for loop來做一些型式類似並且多次的運算,減少所寫的code數量,所以compiler做loop unrolling達到優化
- Compiler Intrinsics
- 利用intrinsics讓compiler編譯時,會被直接編譯成組合語言
- Specific Framework/Infrastructure
- 為了平行化
- 直接利用data Parallel Framework,或是透過SIMD優化過的library
- Coding in Assembly
- 最極致的最佳化的方式
#### SIMD 困難的地方
- Finding Parallelism in Algorithm
- 找出原本程式中可以做平行運算的部份
- Portability between different intrinsics
- 不同架構中的轉換
- sse -> neon
- neon -> sse
- 在不同平台上就要使用不同的intrinscis,可攜性是一個問題
- Boundary handling
- 資料邊界的對齊與填充
- ==Divergence==
- Register Spilling
- 電腦中register數量有限,所以變數會對應到register或memory上
- 編譯產生組合語言時,所使用的variable數量 > register的數量的情況發生
- ==Non-Regular Access/Processing Pattern/Dependency==
- Unsupported Operations
- 比較高階的函數
- Floating-Point
- 浮點數運算跨裝置上的相容性問題
>>[參考概念](https://hackmd.io/BwVgxmCMBMYJwFoCmYAmBDBAWExgOA0XSQDYkRUR1TUB2MIA?both)
>>[參考概念](https://hackmd.io/KYQwbMBMkAxgtAVgOwE5LwCwmAY3qogIwBm8kywAzIhCCDLrkA==?both)
### implement 效能最佳化
---
<style>
h2.part {color: red;}
h3.part {color: green;}
h4.part {color: blue;}
h5.part {color: black;}
</style>
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet