# AI大補帖


# 種類

- 分類:這張圖像中有一個氣球。
- 語義分割:這些全是氣球像素。
- 目標檢測:這張圖像中的這些位置上有 7 個氣球。
- 實例分割:這些位置上有 7 個氣球,並且這些像素分別屬於每個氣球。
# 分類
## ResNet 152
### 架構

**其中最重要的兩個部分如下圖**

這樣的一個block叫做一個殘差單元
左邊的單元對應的是淺層ResNet,而右圖則對應深層ResNet。
## VGG16
### 架構

- 13個卷積層、3個全連接層和5個池化層,並全利用3x3的卷積核以產生多層非線性層,如此可增加網絡深度來保證學習更複雜的模式、提升感受野(Receptive Field)以增加參數,即可更好地保持圖像性質。
- 由於使用了更多的參數,VGG會耗費較多計算資源,導致更多的內存佔用
## Inception V3
- 架構

- 一層block就包含1x1卷積,3x3卷積,5x5卷積,3x3池化。這樣,網絡中每一層都能學習到“稀疏”(3x3、5x5)或“不稀疏”(1x1)的特徵,既增加了網絡的寬度,也增加了網絡對尺度的適應性
- 使用1x1的捲積核實現降維操作

- 使用BN層,將每一層的輸出都規範化到一個N(0,1)的正態分佈
- 並行的降維結構(防止bottle neck)


# 語意分割
## Tiramisu
- 架構:

DenseNet + FCN (Fully Convolutional Network)
- 前半段的是Conv+Pooling下採樣,縮小資料長與寬,並增加圖片深度,直到中間 ”U” 的瓶頸,這時開始Deconv反捲積進行上取樣(Upsample、Deconvolution或Transposed convolution)並獲得之前的低層feature map(Skip-connection,灰虛線),一步一步的增加圖片的長寬,直到回到原始的長寬。
- 比較:
- **CNN(Convolutional Neural Networks)**:最後的全連線層,它會將原來二維的矩陣(圖片)壓扁成一維的,從而丟失了空間資訊,最後訓練輸出一個標量,這就是我們的分類標籤。
- **FCN(Fully Convolutional Network)**:丟棄全連線層,換上全卷積層,使輸出為二維而非一維。即上(下)圖後半部。

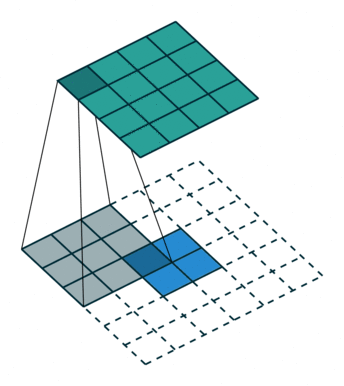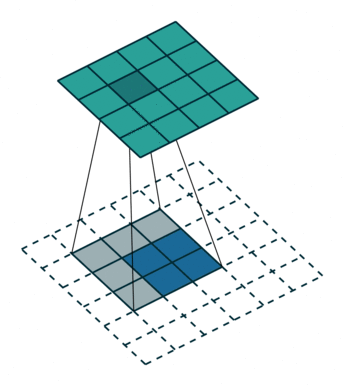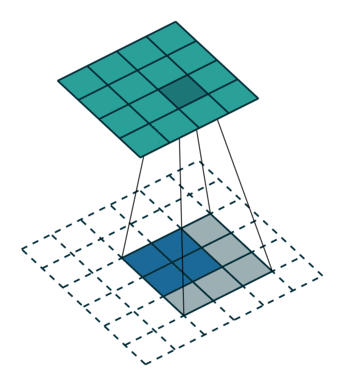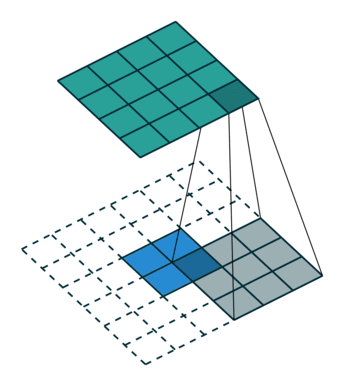
參考:
- [DenseNet:比ResNet更优的CNN模型](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37189203)
- [The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.09326)
- [One-Hundred-Layers-Tiramisu(GitHub)](https://github.com/0bserver07/One-Hundred-Layers-Tiramisu)
- [Convolution animations](https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic#convolution-animations)
## DeepLab
- 架構

- Atrous Convolution(或Dilated Convolution)
- 在本來convolution的kernel中間補上一些零值,讓kernel參數一樣,但是field of view,也就是可見範圍變大,以此取代max pooling,使FOV (field of view)加大,以避免進行pooling時導致的訊息丟失,同時減少參數數量。
- 前幾代的deeplab都是以此方式運作的,並且在deeplab v2的時候加入了ASPP (Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling),減少atrous convolution帶來不連續的破碎問題。然而此方法的問題在於,當output stride (即在feature extrator部分最後feature map與原始圖片的縮小倍率)太大時,會使運記憶體使用量太大。

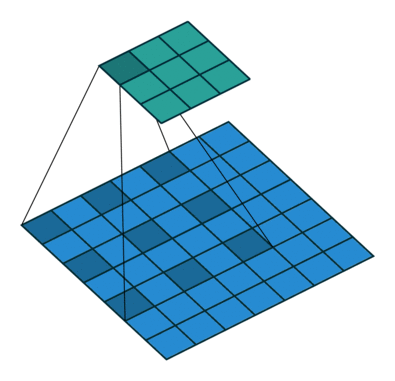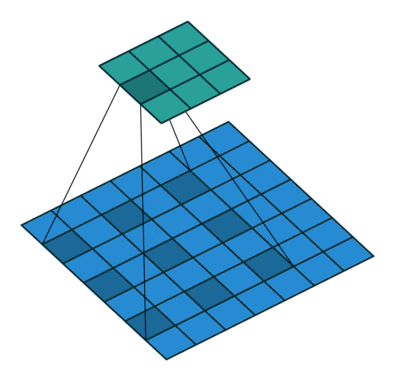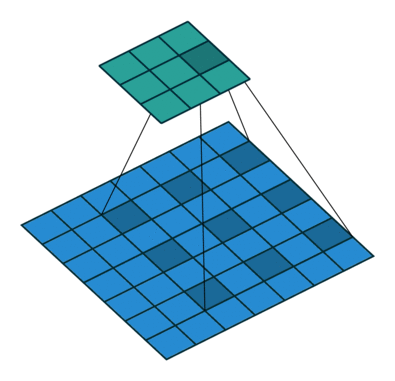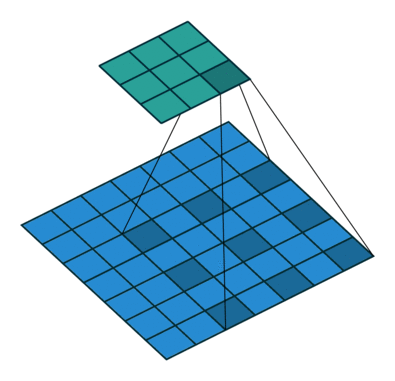
- Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP)
- 以多尺度的信息得到更強健的分割結果
- 將處理後的feature map分別送入幾個dilated rate不同的Atrous Convolution,最後再組合起來(如下圖),以減少atrous convolution帶來不連續的破碎問題。

- 先downsample再upsample的方式,去做影像分割
- 計算量較少,可是在切割細節上卻沒有辦法表現得很好,因為當output stride是32 (一般classification用的網路多是這個倍率)的時候,圖片中pixel小於32的物件,是沒有辦法被decoder復原回來的
- 本來decode部份在deeplab v3只是bilinear的upsample上去而已,而在v3+加入了與encoder中feature map大小一樣的low level feature

參考:
- [Dilated Convolution(带洞卷积)](https://blog.csdn.net/comeontoto/article/details/79983557)
- [Deeplab v3+](https://medium.com/%E8%BD%89%E8%81%B7%E8%B3%87%E5%B7%A5%E8%BF%B7%E9%80%94%E8%A8%98/deeplab-v3-3a105519a0cf)
- [人人必须要知道的语义分割模型:DeepLabv3+](https://www.zybuluo.com/Team/note/1443524)
# 目標檢測
## Faster-R-CNN
- 將 Segment 的結果先各自畫出 bounding box,然後以一個迴圈,每次合併相似度最高的兩個 box,直到整張圖合併成單一個 box 為止。可預先找出圖中目標可能出現的位置,這些box即為即候選區域(Region Proposal),此方法在R-CNN中稱為Selective Search。
- fast rcnn使用spp結構,SPP Net在普通的CNN結構中加入了ROI池化層(Region of Interest Pooling),使得網絡的輸入圖像可以是任意尺寸的,輸出則不變,同樣是一個固定維數的向量。

- ROI池化層一般跟在卷積層後面,此時網絡的輸入可以是任意尺度的,在SPP layer中每一個pooling的filter會根據輸入調整大小,而SPP的輸出則是固定維數的向量,然後給到全連接FC層。
- faster rcnn加入一個提取邊緣的神經網絡,也就說找到候選框的工作也交給神經網絡來做
- 引入Region Proposal Network(RPN)替代Selective Search
- RPN放在最後一個卷積層的後面並直接訓練得到候選區域

### RPN(Region Proposal Network)簡介:
- 接在Feature map和ROI pooling之間的小全捲積網路
- 建一個神經網絡用於物體分類+框位置的回歸
- 一部分判斷判斷框之中有無包含物體的機率(分類),另一部分利用回歸判斷框與ground truth的偏差量(offsets)


參考:
- [關於影像辨識,所有你應該知道的深度學習模型](https://medium.com/cubo-ai/%E7%89%A9%E9%AB%94%E5%81%B5%E6%B8%AC-object-detection-740096ec4540)
- [[物件偵測] S1: R-CNN 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/object-detection-s1-rcnn-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-30091ca8ef36)
- [[物件偵測] S2: Fast R-CNN 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/obeject-detection-s2-fast-rcnn-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-40cfe7b5f605)
- [[物件偵測] S3: Faster R-CNN 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/object-detection-s3-faster-rcnn-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-5f37b13ccdd2)
## YOLO
- 架構
- 
- 利用整張圖作為網絡的輸入,直接在圖像的多個位置上回歸出這個位置的目標邊框,以及目標所屬的類別
- 將物體檢測任務當做一個regression問題來處理,使用一個神經網絡,直接從一整張圖像來預測出bounding box的坐標、box中包含物體的置信度和物體的probabilities 。因為YOLO的物體檢測流程是在一個神經網絡裡完成的,所以可以end to end來優化物體檢測性能。
- 
- 速度快,可達real time
- 因為**YOLO v1**卷積層後面是全連接層。和之前滑動窗口方法的目標檢測相比,因為後面是全連接層,可以整合整張圖片的信息,背景識別錯誤率僅為Fast RCNN的一半
- **YOLO v2**增加drop out與batch normalization,取消了全連接層,而是使用anchor box
- Multi-Scale Training
- **YOLO v3**-Darknet-53基底網路-採用RestNet架構,解決梯度問題-使用 FPN 多層級預測架構以提升小物體預測能力(特徵層從單層 13x13 變成了多層 13x13、26x26 和 52x52單層預測 5 種 bounding box 變成每層 3 種 bounding box (共 9 種))
參考:
- [[物件偵測] S4: YOLO v1簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/object-detection-s4-yolo-v1%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-f3b1c7c91ed)
- [[物件偵測] S5: YOLO v2 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/object-detection-s5-yolo-v2-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-7c160d07e15c)
# 實例分割
## Mask-R-CNN

- 以Faster R-CNN原型,增加了一个分支用於分割任務
- 以一個標準的卷積神經網絡(ResNet50/101)當作主幹網路,作為特徵提取器。
- 將特徵金字塔網絡(FPN)引入主幹網絡,以在多個尺度上更好地表徵目標。以ResNet50/101 5個階段的residual block的Feature map利用插值upsamping後做element-wise的相加。
- 將FPN的輸出進行RPN後再進行ROI Align(而不是ROI Pooling)
- 最後再進行如Faster R-CNN的BBox迴歸及分類與Mask分支進行反卷積(在每一個ROI裡面進行FCN操作)
### ROI Pooling V.S. ROI Align
- ROI Pool的輸入是ROI的坐標和某一層的輸出特徵,不管是ROI Pool還是ROIAlign,目的都是提取輸出特徵圖上該ROI坐標所對應的特徵。
- **ROI Pooling**:
- 由於預選框的位置通常是由模型回歸得到的,一般來講是浮點數,而池化後的特徵圖要求尺寸固定。故ROI Pooling這一操作存在兩次量化的過程。此時的候選框已經和最開始回歸出來的位置有一定的偏差,這個偏差會影響檢測或者分割的準確度,造成不匹配問題(misalignment)。
- 舉例而言:輸入一張800 $\times$ 800的圖片,有一個665 $\times$ 665的框(框中有一隻狗),經stride為32的特徵提取後,800 $\to$ 25、665 $\to$ 20.78,於是ROI Pooling將其量化為20。接著在Pooling過程中要池化為7 $\times$ 7,故20 $\to$ 2.86,ROI Pooling再次量化為2。可見經兩次量化後將產生明顯誤差(feature map上0.1個像素誤差,在原圖上即為3.2個像素誤差)。
- **ROI Align**:
- 主要想法為取消量化操作,使用雙線性內插的方法獲得坐標為浮點數的像素點上的圖像數值(即利用數學方法近似一個單元的值),從而將整個特徵聚集過程轉化為一個連續的操作。
- 同樣舉例:在不進行量化的情況下,進行池化的階段中,每一個單元(bin)中規則置入採樣點(例如4個),這4個點對應的值(浮點數)通過該bin所包含的點插值計算得到,最後對這4個點求均值或最大值作為這個bin的值,然後進行池化操作。

參考:
- [[物件偵測] S9: Mask R-CNN 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/%E7%89%A9%E4%BB%B6%E5%81%B5%E6%B8%AC-s9-mask-r-cnn-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-99370c98de28)
- [[物件偵測] S8: Feature Pyramid Networks 簡介](https://medium.com/@ywchiu84021121/%E7%89%A9%E4%BB%B6%E5%81%B5%E6%B8%AC-s8-feature-pyramid-networks-%E7%B0%A1%E4%BB%8B-99b676245b25)
- [先理解Mask R-CNN的工作原理,然后构建颜色填充器应用](https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/Mask_RCNN-tree-master-samples-balloon)
- [Mask R-CNN 論文筆記](https://www.itread01.com/content/1545670085.html)
- [详解 ROI Align 的基本原理和实现细节](https://blog.csdn.net/Bruce_0712/article/details/80287385)
- [三十分钟理解:线性插值,双线性插值Bilinear Interpolation算法](https://blog.csdn.net/xbinworld/article/details/65660665)
## 一些奇怪的名詞
- AP
- mean AP
- pixel accuracy 標記正確的像素佔總像素比例
- IoU
- freq weighted mean IoU 根據每一類出現的頻率對各個類的IoU進行加權求和
- precision
-  -> G統大佬
- Scikit-Learn
- pillow
# 優化方式
- Batch Normalization(增加準確率與速度)
-- 將每個batch的值做正規化處理
$$
y = \frac{x - \mathrm{E}[x]}{ \sqrt{\mathrm{Var}[x] + \epsilon}} * \gamma + \beta
$$
-- training加速
-- 防止gradient vanishing
-- 幫助 sigmoid 或是 tanh 這種的 activation function
可以讓參數的 initialization 的影響較小
-- 有一些對抗 Overfitting 的效果,但是主要的作用還是用在 training 不好的時候使用,提升 training 的準確率
在tanh上的實現:

- Data Augmentatoin(增加準確率)
## 優化參數
- **Activation Function**
不使用激勵函數的話,神經網絡的每層都只是做線性變換,多層輸入疊加後也還是線性變換。以下三種沒有激勵函數進行平面分割的神經網絡的輸出是線性方程,其用複雜的線性組合來逼近曲線。



明顯線性模型在複雜資料上的表達能力不夠或可能很複雜,因此加入激勵函數以引入非線性因素。
因此激勵函數通常將神經層的輸出進行非線性處理,使最後輸出可以有更多變化。


-- **sigmoid:**
$$\sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}$$

其將輸入值映射到介於0~1的值,缺點為當輸入過大或過小時將進入飽和,使梯度消失,且計算涉及自然指數,運算量較大。
-- **tanh:**
$$tanh\ x=\frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{e^{x} + e^{-x}}$$

映射至-1~1之間,具zero-centered的特性,但同sigmoid,計算較為繁瑣。
-- **ReLU (Rectified Linear Units):**
$$f(x) = max(0, x)$$

為線性整流,CNN中常用。對正數原樣輸出,負數直接置零。在正數不飽和,在負數硬飽和。 relu計算上比sigmoid或者tanh更省計算量,因為不用exp,因而收斂較快。但是還是非zero-centered。其中,在負數區域被kill的現象叫做dead relu。
-- **LeakyReLU:**
$$f(x) = max(0.01x, x)$$

讓負數區域不在飽和區死掉。或可將0.01換成可學習的變數$a$,此為**PReLU(parametric rectifier)**。
-- **ELU (Exponential Linear Units):**
$$f(x) = \left\{ \begin{array} {l} x & \mathrm{if\ x}> \mathrm{0} \\
\alpha (e^x-1) & \mathrm{if\ x \leq 0} \end{array}\right. $$

可以看做是介於relu和LeakyReLU之間的一個東西。當然,這個函數也需要計算自然指數,因此相較計算量上更大一些。
-- **Softmax:**
$$\sigma(z)_i = \frac{e^{z_i}}{\sum_j e^{z_j}}$$

Softmax函數把輸出映射成區間在(0,1)的值,並且做了歸一化,所有輸出的和累加起來等於1。可以直接當作概率對待,選取概率最大的分類作為預測的目標。雖然其中出現指數,但這樣可以讓大的值更大,讓小的更小,增加了區分對比度,學習效率更高。
-- **GELU (Gaussian Error Linerar Units):**
GELUs對於輸入乘以一個0和1組成的mask,而該mask的生成則是由滿足高斯分布的輸入的機率累積函數(Cumulative distribution function)決定,且滿足伯努利分布(Bernoulli distribution)。即$mask = \Phi(x) = P(X \le x)$,因此:
\begin{align}
GELU(x) &= xP(X \le x) \\
&= \Phi(x) \cdot 1 + (1-\Phi(x)) \cdot 0 \\
&=0.5x\left(1+\text{erf}\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\right) \\
&\simeq 0.5x\left(1+\text{tanh}\left(\sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}}(x+0.044715x^3)\right)\right)
\end{align}

因此當輸入x較小的時候,它將有更高的概率被dropout掉,這樣的激活變換就會依賴於輸入x了。所以GELU可以按當前輸入x比其它輸入大多少來縮放x。
參考:
- [神经网络激活函数汇总(Sigmoid、tanh、ReLU、LeakyReLU、pReLU、ELU、maxout)](https://blog.csdn.net/edogawachia/article/details/80043673)
- [通俗理解神经网络之激励函数(Activation Function)](https://blog.csdn.net/hyman_yx/article/details/51789186)
- [常用激活函数(激励函数)理解与总结](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45049692/article/details/90266323)
- [神经网络中的Softmax激活函数](https://blog.csdn.net/dcrmg/article/details/79248571)
- [GELU 激活函数](https://blog.csdn.net/liruihongbob/article/details/86510622)
- [超越ReLU却鲜为人知,3年后被挖掘:BERT、GPT-2等都在用的激活函数](https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/2019-12-30-4)
- [What is GELU activation? StackExchange](https://datascience.stackexchange.com/questions/49522/what-is-gelu-activation)
- **Loss Function**
在一個模型中,預測值與實際值得落差稱為殘差(residual)。通常會希望損失或殘差最小,也就是使
$$loss\ or\ residual = y - \hat{y}$$
盡可能的越小。其中$y$為預測值,$\hat{y}$為實際值。
-- **平均絕對值誤差(Mean absolute error,MAE):**
這裡的誤差(error)指的就是殘差。對於分類問題,預測輸出為一組機率,將其減掉實際值有正有負,因此可用絕對值讓差值變成正數。
$$MAE = \frac{1}{n} \sum^n_{i=1}|y - \hat{y}|$$
-- **均方誤差(Mean square error,MSE):**
由於MAE的梯度始終相同,將使模型權重無法更新至最佳解(在附近來回震盪),因此使用非線性的MSE。
$$MSE = \frac{1}{n} \sum^n_{i=1} (y - \hat{y})^2$$

解決了MAE的問題,但MSE所計算出的誤差較MAE大了許多,可能造成當資料中出現極大偏差值時權重更新過大,導致模型效果較差。
-- **根均方誤差(Root mean square error,RMSE):**
為了解決上述問題,對MSE開根號使不同資料的誤差適當縮小但又不失資訊。
$$RMSE = \sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum^n_{i=1} (y - \hat{y})^2}$$
-- **交叉熵(Cross-entropy):**
對於一機率函數$p(x)$,首先定義訊息量(information gain):
$$I(x) = -log_2(p(x))$$
其意義為「一個事件發生的概率越大,不確定性越小,則它所攜帶的信息量就越小」,例如機率為0.5的隨機性的事件比機率為0.99大(更難預測)。至於熵(Entropy,此處特指Shannon Entropy)則表示為系統的亂度或是系統的不確定性,其公式為:
$$H(x) = \sum_i -p_i log_2(p_i)$$
意即熵為所有事件的期望值。因此信息量用來衡量一個事件的不確定度,熵則用來衡量一個系統(也就是所有事件)的不確定度。若為二分類問題,對上式微分可知熵值最大發生在機率均為0.5的情況(如下圖所示)。若熵等於0,也就是說該事件的發生不會導致任何信息量的增加。

基於以上,交叉熵定義為:
$$H = \sum^c_{c=1} \sum^n_{i=1} -y_{c,i}log_2(p_{c,i})$$
其中,$c$是類別數,$y_{c,i}$為獨熱(one hot,此處有的意義)編碼標籤$p_{c,i}$為第$i$筆資料第$c$類別的機率。
參考:
- [機器/深度學習: 基礎介紹-損失函數(loss function)](https://medium.com/@chih.sheng.huang821/%E6%A9%9F%E5%99%A8-%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%B8%E7%BF%92-%E5%9F%BA%E7%A4%8E%E4%BB%8B%E7%B4%B9-%E6%90%8D%E5%A4%B1%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B8-loss-function-2dcac5ebb6cb)
- [简单谈谈Cross Entropy Loss](https://blog.csdn.net/xg123321123/article/details/80781611)
- [熵与信息增益](https://blog.csdn.net/xg123321123/article/details/52864830)
- [熵 (資訊理論)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%86%B5_(%E4%BF%A1%E6%81%AF%E8%AE%BA))
- **Optimizer**
基本算法:
1. 計算目標函數關於當前參數的梯度:$g_t=\nabla f(\omega_t)$
2. 根據歷史梯度計算一階動量和二階動量:$m_t = \phi(g_1,g_2,\cdots,g_t);V_t = \varphi(g_1,g_2,\cdots,g_t)$
3. 計算當前時刻的下降梯度:$\eta_t = \alpha \cdot\frac{m_t}{\sqrt{V_t} + \epsilon}$
4. 根據下降梯度進行更新:$\omega_{t+1}=\omega_t-\eta_t$
$\omega$為待優化參數,$f(\omega)$為目標函數(誤差函數),$\alpha$為初始學習率,$\epsilon$目的為避免發散並限制更新大小。
-- **SGD (Stochastic gradient descent)**:
在一般的GD中,是一次用**全部**訓練集的數據去計算損失函數的梯度就更新一次參數,而SGD則為一次**跑一個樣本或是小批次(mini-batch)樣本**然後算出一次梯度或是小批次梯度的平均後就更新一次,其改善了GD中內存溢出的問題。缺點為如果學習率太大,容易造成參數更新呈現鋸齒狀的更新,會發生在最後幾步跳不進最佳解。
由於此處不含有動量,因此:
\begin{align}
m_t = \frac{1}{N}\sum_i^Ng_{it} \\
V_t = I^2
\end{align}
帶入3.可得其下降梯度:
$$\eta_t = \alpha \cdot g_t$$

-- **SGD with Momentum(SGDM)**:為了抑制SGD的震盪,SGDM認為梯度下降過程可以加入慣性。下坡的時候,如果發現是陡坡,那就利用慣性跑的快一些。在SGD基礎上引入了一階動量。
$$m_t=\beta_1 \cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1) \cdot g_t$$
-- **Adagrad**:
其算法是在學習過程中對學習率不斷的調整,這種技巧叫做「學習率衰減(Learning rate decay)」,在一開始會用大的學習率,接著在變小的學習率,以避免在SGD中造成的問題。缺點為在訓練中後段時,由3.可知,可能出現梯度接近0。
$$V_t=\sum^n_{t=1} g_t^2$$
-- **Adadelta/RMSProp**:
由於AdaGrad單調遞減的學習率變化過於激進,我們考慮一個改變二階動量計算方法的策略:不累積全部歷史梯度,而只關注過去一段時間窗口的下降梯度。
$$V_t = \beta_2 \cdot V_{t-1} + (1-\beta_2) \cdot g_t^2$$
-- **Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation)**:
把SGDM的一階動量和Adadelta的二階動量結合即為Adam。
\begin{align}
m_t &=\beta_1 \cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1) \cdot g_t \\
V_t &= \beta_2 \cdot V_{t-1} + (1-\beta_2) \cdot g_t^2
\end{align}
$\beta_1$和$\beta_2$分別為一階動量和二階動量的超參數。一般情況下,$\beta_1=0.9,\beta_2=0.99,m_0=0,V_0=0$。另外$m_t$和$V_t$可藉由以下修正以增加在剛開始訓練時的穩定性(參考$\mathrm{An\ intuitive\ understanding\ of\ the\ LAMB\ optimizer}$):
\begin{align}
\hat{m_t} = \frac{m_t}{1 - \beta_1^t} \\
\hat{V_t} = \frac{V_t}{1 - \beta_2^t}
\end{align}
得到:
\begin{align}
\omega_{t+1} = \omega_t - \alpha \cdot \frac{\hat{m_t}}{\sqrt{\hat{V}_{t}} + \epsilon}
\end{align}
-- **LAMB的先備知識 -- LARS (Layerwise Adaptive Rate Scaling):**
隨著batch size的增加,每一個epoch所做的迭代數將減少,若要在相同的次數內達到收斂,勢必要增加學習率,然而學習率的增加反而會造成訓練的不穩定(使用暖身(warm up)有一定程度的幫助但仍有機會發散)。因此可以藉由在每一「層」施以不同的學習率以改善此問題:
\begin{align}
\lambda^l = \alpha \cdot \frac{\| \omega^l \|}{\| g_t^l \|}
\end{align}
其中$\lambda^l$為對應第$l$層的學習率,$\frac{\| \omega^l \|}{\| g_t^l \|}$稱為信任率(trust ratio, the ratio between the norm of the layer weights and norm of gradients update),用來分析訓練時的穩定性。
-- **LAMB (Layer-wise Adaptive Moments optimizer for Batch training):**
基於具衰減的Adam (AdamW)和LARS的方法,其對於$l$層、$t$時刻的權重更新先定義:
\begin{align}
&r_1 = \| \omega^l_{t} \|
\\ &r_2 = \| \frac{\hat{m}_{t}^l}{\sqrt{\hat{V}_{t}^l + \epsilon }} + \lambda \omega^l_{t} \|
\\ &r = \frac{r_1}{r_2}
\\ &\alpha^l = r \cdot \alpha
\end{align}
其中$r$即為信任率,使用$\sqrt{\hat{V}_{t}^l + \epsilon}$而非$\sqrt{\hat{V}_{t}^l} + \epsilon$的原因為前者能獲得更多資訊(如方向)。因此得到:
\begin{align}
\omega_{t+1}^l = \omega_{t}^l - \alpha^l \cdot (\frac{\hat{m}_{t}^l}{\sqrt{\hat{V}_{t}^l + \epsilon }} + \lambda \omega^l_{t} )
\end{align}
其中$\lambda$為AdamW的超參數。
參考:
- [機器/深度學習-基礎數學(三):梯度最佳解相關算法(gradient descent optimization algorithms)](https://medium.com/@chih.sheng.huang821/%E6%A9%9F%E5%99%A8%E5%AD%B8%E7%BF%92-%E5%9F%BA%E7%A4%8E%E6%95%B8%E5%AD%B8-%E4%B8%89-%E6%A2%AF%E5%BA%A6%E6%9C%80%E4%BD%B3%E8%A7%A3%E7%9B%B8%E9%97%9C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95-gradient-descent-optimization-algorithms-b61ed1478bd7)
- [如何理解随机梯度下降(stochastic gradient descent,SGD)?](https://www.zhihu.com/question/264189719)
- [神经网络的优化算法框架](https://blog.csdn.net/ANNILingMo/article/details/80310419)
- [快速神经网络的训练算法LARS/LAMB工作原理 --UC Berkeley在读博士生尤洋](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44107973/article/details/94587766)
- [An intuitive understanding of the LAMB optimizer](https://towardsdatascience.com/an-intuitive-understanding-of-the-lamb-optimizer-46f8c0ae4866)
- [LAMB Optimizer for Large Batch Training (TensorFlow version)](https://github.com/ymcui/LAMB_Optimizer_TF)
- **Regularization**
正則化可用來抑制overfit,其方法是在loss function($f(\omega)$)加上限制(constrain,$\lambda$),使部分的參數歸零(或接近零)。
-- **$L_1$ regularization**
$$f_1(\omega) = f(\omega)+\lambda_1\sum|\omega_i|$$
將其作為新的loss function,取梯度,會得到:
$$\nabla f_1 =
\begin{cases}
\nabla f + \lambda_1, & \text{for $\omega$ > 0} \\
\nabla f - \lambda_1, & \text{for $\omega$ < 0}
\end{cases}
$$
更新參數:
$$\omega_{t+1} =
\begin{cases}
\omega_t - \alpha(\nabla f + \lambda_1), & \text{for $\omega$ > 0} \\
\omega_t + \alpha(\nabla f + \lambda_1), & \text{for $\omega$ < 0}
\end{cases}
$$
可以發現,這樣的操作最終可以使參數歸零。
-- **$L_2$ regularization**
$$f_2(\omega) = f(\omega)+\lambda_2\sum \omega_i^2$$
同樣取梯度,則:
$$\nabla f_2=\nabla f+2\lambda_2 \sum \omega_i$$
得到新參數(為了方便先去除summation):
\begin{align}
\omega_{t+1} &= \omega_t - \alpha(\nabla f+2\lambda_2 \omega_t) \\
&= (1-2\alpha \lambda_2)\omega_t - \alpha \nabla f
\end{align}
由於$\lambda_2$是一個介於0-1的數,因此這樣的操作可以使參數接近零但不等於零。

### 其他:
- **criterion**
-- CrossEntropyLoss
-- L1Loss
-- MSELoss ...
- **Learning Rate**
- **Batch-size**
## 冷知識
- CNN維度計算 $\begin{align}new_{height} = new_{width} = \frac{(W - F + 1)}{S} \end{align}$
## 有用的資料
- [【Python】TensorFlow學習筆記(二):初探 TFRecord](https://dotblogs.com.tw/shaynling/2017/11/20/150241)
- [【Python】TensorFlow學習筆記(三):再探 TFRecord](https://dotblogs.com.tw/shaynling/2017/11/21/162229)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

