---
title: L1 Python 資料型態 + 運算子
description: 中興大學資訊研究社1111學期程式分享會主題社課
tags: Python
---
<style>hr{display:none;}</style>
###### [Python 教學/](/@NCHUIT/py)
## 資料型態 + 運算子
>[name=ZJ][time=110,10,4]
- [colab(線上免安裝直接用)](https://colab.research.google.com/)
[toc]
---
# 什麼是 Python?
Python 是一種高階程式語言,強調程式碼的可讀性、簡潔的語法。
相比於 C++、Java,Python 能讓開發者用更短(簡易)的程式碼做到一樣的結果。
----
## Python優點有哪些?
:heavy_check_mark: 好理解:Python 是一種解釋型語言,瞭解結構之後,非常好理解。
:heavy_check_mark: 好偷懶:Python 可以輕鬆使用各式各樣的函式,短短的程式碼輕鬆搞定。
:heavy_check_mark: 好維護:Python 的架構很明確,非常容易維護。
----
## Python缺點有哪些?
:heavy_check_mark: 速度慢:Python 為了功能,犧牲效能。
:heavy_check_mark: 強制縮排:自有的縮排規則,新手很容易忽略而導致錯誤。
---
#### *[python參考簡介](https://www.blink.com.tw/board/post/78610/)*
## [排名](https://www.tiobe.com/tiobe-index/)

---
## 環境設置
---
先下載[Python本體](https://www.python.org/downloads/),然後選一個IDE安裝,請參閱
- [本體安裝教學](https://medium.com/@ChunYeung/%E7%B5%A6%E8%87%AA%E5%AD%B8%E8%80%85%E7%9A%84python%E6%95%99%E5%AD%B8-1-%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%9Dpython-126f8ce2f967)
- [VS code (python 免費原始碼編輯器,要加本體)](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10212365)
- [Anaconda (python 裝完可以直接用)](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10229662)
- [Pycharm安裝教學 (python 免費原始碼編輯器,要加本體)](https://medium.com/@ChunYeung/%E7%B5%A6%E8%87%AA%E5%AD%B8%E8%80%85%E7%9A%84python%E6%95%99%E5%AD%B8-1-%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%9Dpython-126f8ce2f967)
- [colab(線上免安裝直接用)](https://colab.research.google.com/)
----

---
# Python 語法範例
```python=
# coding = utf-8
a = -1
b = True
c = 'word' #我是註解
d = [a,b,c]
print ("Hello world") # python中 " = '
inputs = input ('Enter sth...')
"""
多行
註解
"""
'''
多行
註解
'''
str = """
多行
字串
"""
```
---
# 資料型態(data type)
###### *詳細參閱: [Python內建資料型態](https://docs.python.org/zh-tw/3/library/stdtypes.html)*
1. Number (數字)
- int (整数), float (浮點數), complex (複數)
2. String (字串)
3. List (串列)
4. Dictionary (字典)
5. Tuple (元组)
6. Set (集合)
----
Python宣告變數時不用像其他程式刻意指定型態,我都說它很隨便
```python=
a = 100
b = True
c = 'word' #注意 Python 的字串用''或""都可以
d = [-1,False,c]
e = {'mon':'mother','dad':'father'}
```
如果你想指定也是可以,指定資料型態會強制轉型
```python=
a = int(7942)
b = bool(0) #同 b = False 另 0,'',None 以外的變數會轉為 True
c = float(True) #同 c = 1.0
```
----
::: spoiler 練習01
```python=
a = "practice1"
print(a)
```
:::
宣告一個字串"practice 1"並列印出來
----
# 輸出和輸入
Python 的輸出和輸入
```python=
print('輸出內容')
a = input ('輸入提示') #input() 在程式中被當作一個字串變數
b = int(input('輸入整數:'))
print('你輸入了:',a)
print('你輸入了:', b)
```
----
使用 print 後都會自動換行,如果不想換行,要指定**結尾字串(end=" ")**
```python=
print('第一個 print', end = '第一個 print 結尾 ') #\n: 換行
print('第二個 print', end = '') #\n: 換行
print(end = '第二2個 print') #\n: 換行
print('第三個 print', end = None) #None 在這邊會換行
print("""
多行字串,前面的內容
""")
```
----
如果想要知道變數為什麼型態,請使用
```python=
a = 100
b=True
print (type(a)) #type(): 用於取得變數資料型態
print (type(b))
```
----
::: spoiler 練習 02
例
```python= [1-3|]
a = int(input('輸入整數:'))
print('你輸入了:\n',a)
print (type(a)) #type(): 用於取得變數資料型態
b = input('輸入整數:')
print('你輸入了:\n',b)
print (type(b))
```
:::
試寫一支程式讓使用者輸入***整數*** 然後輸出它。
----
::: spoiler 練習 03
```python=
a = input('輸入字串:') #input() 是字串
b = float(input('輸入浮點數:'))
print('你輸入了:\n',type(a),a,'\n和\n',type(b),b)
```
:::
試寫一支程式讓使用者輸入***字串*** 與***浮點數*** 然後輸出它們跟它們對應的資料類型。
----
# 運算元(operator)
Python 的運算遵循四則運算,會先乘除後加減
| 算數運算 | 加 | 減 | 乘 | 除 |
| --------| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 符號 | + | - | \* | / |
| 整除 | 取餘 | 次方 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| // | % | ** |
----
| 邏輯運算 | 且 | 或 | 非 | 比較資料類型 |
| -------- | --- | --- | --- | ---- |
| 符號 | and | or | not | is |
| 算數邏輯運算 | 大於 | 小於 | 等於 |
| ------------ | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 符號 | > | < | == |
| 不小於 | 不大於 | 不等於 |
| ------ | ------ | ------ |
| >= | <= | != |
----
## 範例
```python=
a = 3
b = 27
print(a+b, a-b, a*b, a//b, b/a, a%b)
"""
輸出: 30 -24 81 0 9.0 3
"""
print(a>b, a<b, a==b, a>=b, a<=b)
"""
輸出: False True False False True
"""
print((True is "") and (not (a == b)) and (a**a is b))
"""
# True is "" -> False
# not(a == b) -> not(False) -> True
# 3**3 is 27 -> True
# (False) and (True) and (True) -> False
#輸出: False
"""
```
----
# 條件運算
| 語法 | 說明 |
| ------ | --- |
| `if()` | ``()``中條件成立時執行 |
| `elif()` | 上一個`if()`或`elif()`不成立時``()``中條件成立時執行,可無限接續 |
| `else` | 上一個`if()`或`elif()`不成立時執行 |
----
## 範例
```python=
a = input('輸入數字正負: ')
if(int(a)>0):
print (a,'是正數')
elif(int(a)<0):
print (a,'是負數')
else: print (a,'是 0') #如果執行區塊只有一行可以這樣縮寫
```
## 單行簡寫
```python=
c = input('資訊社英文簡寫? ')=='NCHUIT'
print ('正確') if (c) else print('不正確')
x = '喜' if (c) else '怒'
print (x)
```
----
::: spoiler 練習04
例
```python=
w = float(input ('請輸入體重: '))
h = float(input ('請輸入身高: '))
bmi = w/h**2
print ('BMI:', bmi, '體重 ',end='')
if(bmi<18.5): print ('過輕')
elif(bmi<24): print ('正常')
elif(bmi<27): print ('過重')
elif(bmi<30): print ('輕度肥胖')
elif(bmi<35): print ('中度肥胖')
else: print ('重度肥胖')
```
或者...
```python=
bmi = float(input ('請輸入體重(kg): '))/(float(input ('請輸入身高(cm): '))/100)**2
print ('BMI:', bmi, '體重 ',end='')
print ('過輕') if(bmi<18.5) else print ('正常') if(bmi<24) else print ('過重') if(bmi<27) else print ('輕度肥胖') if(bmi<30) else print ('中度肥胖') if(bmi<35) else print ('重度肥胖')
```
:::
試寫一個 BMI 計算器 *[BMI-wiki](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%BA%AB%E9%AB%98%E9%AB%94%E9%87%8D%E6%8C%87%E6%95%B8)*
BMI值計算公式: BMI = 體重(kg) / 身高^2^(m^2^)
例如一個52公斤的人,身高是155公分,則BMI為:
52/1.552^2^ = 21.6 (kg/m^2^)
體重正常範圍為 BMI=18.5~24
----
::: spoiler 練習05
例
```python=
y = int(input ('輸入1個整數讓程式判斷是否為閏年: '))
if(y%4==0 and y%100!=0 or y%400==0): print ('閏年')
else: print ('平年')
```
:::
[閏年](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/闰年)判斷,輸入1個整數讓程式判斷是否為閏年
閏年定義: 4的倍數是閏年,但100的倍數不是閏年,400的倍數是閏年
範例
```
輸入: 1600
輸出: 閏年
```
```
輸入: 1000
輸出: 平年
```
----
## 先這樣
提醒各位,Python 以外的語言(例如C)
字串記得用回 ```""```
---
## 補充
### [f-字串](https://docs.python.org/zh-tw/3/tutorial/inputoutput.html#formatted-string-literals)
```python
>>> name = "Fred"
>>> f"He said his name is {name}." # {} 可以塞變數
"He said his name is Fred."
>>> f"He said his name is {name!r}." # !r 還原
"He said his name is 'Fred'."
>>> value = 12.34567
>>> f"result: {value:10.4}" # 補空白鍵
'result: 12.35'
>>> f"result: {value:010.6}" # 補0
'result: 00012.3457'
>>> number = 1024
>>> f"{number:#0x}" # 格式化字串用修飾符
'0x400'
>>> line = "The mill's closed"
>>> f"{line = }" # 連變數名稱印出來: 變數 = 內容
'line = "The mill\'s closed"'
>>> f"{line = :20}"
"line = The mill's closed "
>>> f"{line = !r:20}"
'line = "The mill\'s closed" '
```
----
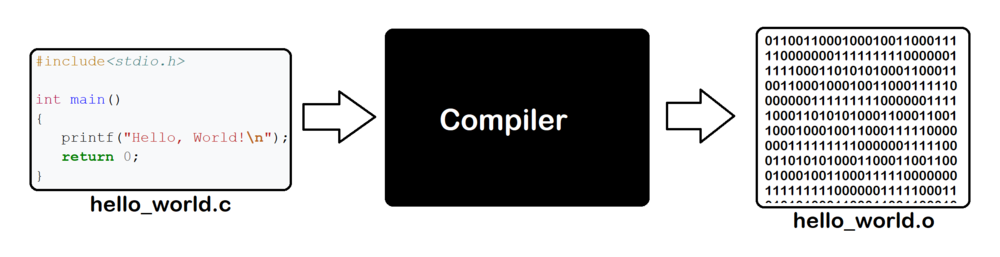
### Python vs. C
每次編譯再執行(直譯機器碼),包很多東西
```python=
print ("Hello world")
```
只會放要用的,編譯後另有檔案專門給機器執行
```cpp=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
printf("Hello world");
return 0;
}
```
----
#### 填個[回饋單](https://forms.gle/vr8panG1mi59t49v7)複習一下吧
[](https://forms.gle/vr8panG1mi59t49v7)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

