# ZTNBD
[Opracowanie z hurtownii danych, które ktoś kiedyś popełnił.](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1vwh1HF_IwT66qAn5txmXJOotBhUdWBGUP_nYqGrZHVw/edit) Raczej tylko szczątkowo przydatne.
## 1. Definicje podstawowych pojęć z hurtowni danych (fakt, wymiar, tabela wymiaru, tabela faktu, miara, kostka)
Najprościej wytłumaczyć to w następujący sposób: wymiary to rzeczy/obiekty. To, że w sklepie nie sprzedaliśmy jeszcze konkretnego produktu nie znaczy, że ta rzecz nie istnieje! Wymiar więc to jest jakiś rzeczownik, coś, co może istnieć niezależnie od zdarzeń biznesowych. Produkty, sprzedawcy, sprzęt, itd. to są rzeczy które istnieją. Wymiar albo coś robi, albo coś na nim się dzieje.
Sprzedawcy sprzedają, klienci kupują. Sprzedawcy i klienci to przykłady wymiarów.
Produkty są sprzedawane --- też są wymiarem, ponieważ coś się z nimi dzieje.
Fakty są czasownikami. Wpis w tabeli faktów oznacza pewno zdarzenie, które stało się rzeczy z tabeli wymiaru. Sprzedaż produktu byłaby wpisem w tabeli faktów. Zdarzenie sprzedaży byłoby zanotowane z informacją jaki produkt został sprzedany, który pracownik go sprzedał i który klient go kupił. Produkt, Sprzedawca i Klient to wymiary zdarzenia (sprzedaży).
Dodatkowo tabela faktów zazwyczaj też ma jakieś mierzalne dane, np. ilość sprzedanych rzeczy, cena za rzecz, łączna cena i tak dalej.
Teraz z czystych definicji:
* fakt: pewne zdarzenie powiązane z procesem biznesowym, zawiera pewne dane mierzalne (miary) powiązane ze zdarzeniem
* tabela faktów: tabela zawierająca fakty (kto by pomyślał)
* wymiar: opisuje obiekty istniejące w procesie biznesowym, np. klienta, sprzedawcę, produkt
* tabela wymiarów: tabela zawierająca detale pewnego typu obiektu w procesie biznesowym, np. tabela wymiarów produktów zawierałaby informacje o wszystkich produktach sprzedawanych w sklepie, takie jak cena, dostawca, kolor, rozmiar i tym podobne
Tabela faktów i tabela wymiarów są ze sobą powiązane, w przykładzie wyżej na przykład tabela faktów o transakcjach klientów zawierałaby referencję (przez klucz zewnętrzny) do tabeli wymiarów produktów.
* kostka: wielowymiarowa tablica danych (jeśli liczba wymiarów jest większa niż 3, jest czasami nazywana hiperkostką). Można sobie trochę wyobrazić jak rozszerzona wersja arkusza kalkulacyjnego, gdzie możemy grupować pomiary po pewnych wymiarach (odpowiednik excelowy: po kolumnie/wierszu)

---
## 2. Porównanie schematu gwiazdy i schematu płatka śniegu.
Na dobrą sprawę schematy te są bardzo podobne: mamy jakąś centralną tabelę faktów otoczoną przez tabele wymiarów. Różnią się jednak w wymiarach. W schemacie gwiazdy każdy wymiar jest "denormalizowany" w jedną tabelę, z kolei w płatku śniegu przynajmniej niektóre wymiary są znormalizowane. Innymi słowy, w schemacie płatka śniegu wymiary mają jeszcze klucze zewnętrzne do kolejnych tabel wymiarów.
- model gwiazdy

- model płatka śniegu

---
## 3. Charakterystyka modelu wielowymiarowego.
| | OLTP | OLAP |
| ---------------- | ----------------- | ------ |
| Volume | From small to big | Large |
| History | Sometimes | Always |
| Number of users | Big | Small |
| Query complexity | Small or medium | Big |
| Normalization | Yes | No |
| Addition | Yes | No |
| Removal | Yes | No |
| Updates | Yes | Rarely |
| Transactions | Yes | No |
Źródło: ze slajdów
Właściwie to nie mam pojęcia. Cały [wykład 2](https://enauczanie.pg.edu.pl/moodle/pluginfile.php/420050/mod_resource/content/1/DW_02_L_2_BI.pdf)?
Też nie mam pojęcia o co chodzi w tym pytaniu
---
## 4. Narzędzie Hive jako nakładka na system plików Hadoop.

Hive nie jest przeznaczony do przetwarzania danych w czasie rzeczywistym! Używa się go raczej do typowych zadań związanych z hurtowniami danych.
Hive zapewnia interfejs podobny do SQL (nazywa się Hive Query Language, HQL), którym można odpytywać dane zawarte w Hadoopie w sposób tabelaryczny. Hive sam pod spodem kompiluje sobie odpowiednie wywołania Hadoopa.
> Some of the key points about Hive:
> * The major difference between HQL and SQL is that Hive query executes on Hadoop's infrastructure rather than the traditional database.
> * The Hive query execution is going to be like series of automatically generated map reduce Jobs.
[Źródło](https://www.guru99.com/introduction-hive.html)
---
## 5. Transakcyjność w narzędziu Hive.
> HIVE ACID tables
> - if delete, update and write required then ORC format is required (managed and transactional)
> - if only insert is required then ACID is in any format
> // managed and transactional in ORC format but without delete and update
> CREATE TABLE T2(a int, b int) STORED AS ORC TBLPROPERTIES ('transactional'='true', 'transactional_properties'='insert_only');
Źródło: pdf, *Instruction - partitioning*
[Podobny materiał do tego co mieliśmy na zjęciach](http://shzhangji.com/blog/2019/06/10/understanding-hive-acid-transactional-table/)
---
## 6. Rola komponentu Metastore w architekturze narzędzia Hive.
> HIVE Metastore
> * central repositoryfor HIVE metadata –a backing database to store the metadata
> * services to which the client connects and queries the metastore.
>
> Metadata:
> * table and database definitions
> * mapping to the data in HDFS.
(ze slajdów)
Metastore zawiera informacje potrzebne do tworzenia i obsługi zapytań.

---
## 7. Charakterystyka, podobieństwa i różnice tabel zewnętrznych (ang. external) i wewnętrznych (ang. managed).
> This document lists some of the differences between the two but the fundamental difference is that Hive assumes that it owns the data for managed tables. That means that the data, its properties and data layout will and can only be changed via Hive command. The data still lives in a normal file system and nothing is stopping you from changing it without telling Hive about it. If you do though it violates invariants and expectations of Hive and you might see undefined behavior.
>
>Another consequence is that data is attached to the Hive entities. So, whenever you change an entity (e.g. drop a table) the data is also changed (in this case the data is deleted). This is very much like with traditional RDBMS where you would also not manage the data files on your own but use a SQL-based access to do so.
>
>For external tables Hive assumes that it does not manage the data.
>
>Managed or external tables can be identified using the DESCRIBE FORMATTED table_name command, which will display either MANAGED_TABLE or EXTERNAL_TABLE depending on table type.
[Źródło](https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Managed+vs.+External+Tables)
Wg. mnie prościej opisane - [tutaj](https://data-flair.training/forums/topic/difference-between-external-table-and-managed-table-in-hive/)
---
## 8. Partycjonowanie i bucketing w narzędziu Hive.
src: https://github.com/vaquarkhan/Apache-Kafka-poc-and-notes/wiki/What-is-the-difference-between-partitioning-and-bucketing-a-table-in-Hive-%3F
>### Partitioning
>
> Partitioning data is often used for distributing load horizontally, this has performance benefit, and helps in organizing data in a logical fashion. Example: if we are dealing with a large employee table and often run queries with WHERE clauses that restrict the results to a particular country or department . For a faster query response Hive table can be PARTITIONED BY (country STRING, DEPT STRING). Partitioning tables changes how Hive structures the data storage and Hive will now create subdirectories reflecting the partitioning structure like
>
> .../employees/country=ABC/DEPT=XYZ.
>
> If query limits for employee from country=ABC, it will only scan the contents of one directory country=ABC. This can dramatically improve query performance, but only if the partitioning scheme reflects common filtering. Partitioning feature is very useful in Hive, however, a design that creates too many partitions may optimize some queries, but be detrimental for other important queries. Other drawback is having too many partitions is the large number of Hadoop files and directories that are created unnecessarily and overhead to NameNode since it must keep all metadata for the file system in memory.
> ### Bucketing
>
> Bucketing is another technique for decomposing data sets into more manageable parts. For example, suppose a table using date as the top-level partition and employee_id as the second-level partition leads to too many small partitions. Instead, if we bucket the employee table and use employee_id as the bucketing column, the value of this column will be hashed by a user-defined number into buckets. Records with the same employee_id will always be stored in the same bucket. Assuming the number of employee_id is much greater than the number of buckets, each bucket will have many employee_id. While creating table you can specify like CLUSTERED BY (employee_id) INTO XX BUCKETS; where XX is the number of buckets . Bucketing has several advantages. The number of buckets is fixed so it does not fluctuate with data. If two tables are bucketed by employee_id, Hive can create a logically correct sampling. Bucketing also aids in doing efficient map-side joins etc.
> ### Hive Partitioning:
>
> Partition divides large amount of data into multiple slices based on value of a table column(s).
>
> Assume that you are storing information of people in entire world spread across 196+ countries spanning around 500 crores of entries. If you want to query people from a particular country (Vatican city), in absence of partitioning, you have to scan all 500 crores of entries even to fetch thousand entries of a country. If you partition the table based on country, you can fine tune querying process by just checking the data for only one country partition. Hive partition creates a separate directory for a column(s) value.
>
> Pros:
>
> - Distribute execution load horizontally
> - Faster execution of queries in case of partition with low volume of data. e.g. Get the population from "Vatican city" - - returns very fast instead of searching entire population of world.
>
> Cons:
>
> - Possibility of too many small partition creations too many directories. Effective for low volume data for a given partition. But some queries like group by on high volume of data still take long time to execute. e.g. Grouping of population of China will take long time compared to grouping of population in Vatican city. Partition is not solving responsiveness problem in case of data skewing towards a particular partition value.
>
> ### Hive Bucketing
>
> Bucketing decomposes data into more manageable or equal parts.
>
> With partitioning, there is a possibility that you can create multiple small partitions based on column values. If you go for bucketing, you are restricting number of buckets to store the data. This number is defined during table creation scripts.
> Pros
>
> - Due to equal volumes of data in each partition, joins at Map side will be quicker.
> - Faster query response like partitioning
>
> Cons
>
> - You can define number of buckets during table creation but loading of equal volume of data has to be done manually by programmers.
A jeśli ktoś nie chce czytać tej ściany tekstu, TL;DR:
* partycjonowanie: dzielenie danych na podstawie jednego (lub więcej) pola w tabeli. Fizycznie w Hive tworzone są po prostu podkatalogi. Dobry wybór, jeśli nasze dane mogą przyjąć w polu tylko kilka wartości. Nie ma jednak gwarancji równego rozdzielenia danych pomiędzy partycje, więc jeśli mamy dane, które mogą przyjąć bardzo wiele wartości pewnego pola, to partycjonowanie może być złym wyborem.
* kubełkowanie (bucketing): dzielenie na podstawie hasha JEDNEGO pola. Wtedy elementy o tej samej wartości pola są zawsze razem (ponieważ hash będzie ten sam). Możemy z góry określić ilość kubełków. Fizycznie w Hive jeden kubełek = jeden plik.
Możemy łączyć jedno z drugim, wtedy Hive tworzy katalog zgodnie z definicją partycjonowania, a w katalogu pliki kubełków (tyle, ile określiliśmy w konfiguracji).
---
## 9. Charakterystyka narzędzia Kylin.
> What is Kylin?
>
>Apache Kylin is an open source distributed analytical engine that provides SQL interface and multidimensional analysis (**OLAP**) on Hadoop **supporting extremely large datasets**. It pre-calculates OLAP cubes with a horizontal scalable computation framework (**MR**, Spark) and stores the cubes into a reliable and scalable datastore (**HBase**).
> [...]
>
> Below are the steps on how Kylin fetches the data and saves the results:
> * First, syncs the input source table. In most of the cases, it reads data from Hive
> * Next, it runs MapReduce/Spark jobs (based on the engine you select) to pre-calculate and generate each level of cuboids with all possible combinations of dimensions and calculate all the metrics at different levels
> * Finally, it stores cube data in HBase where the dimensions are rowkeys and measures are column family
>

[Źródło](https://www.tigeranalytics.com/blog/apache-kylin-architecture/)
---
## 10. Integracja narzędzia Kafka z narzędziem Hive
> Load needed libraries. To do that load to $HIVE_HOME1/lib the following library:
> wget https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.hive/kafka-handler/3.1.0.3.1.0.0-78
Definicja w Hive'ie
> CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE kafkaEvents (msg string) STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.kafka.KafkaStorageHandler' TBLPROPERTIES ("kafka.topic"="Hello-Kafka","kafka.bootstrap.servers"="sandbox-hdp.hortonworks.com:6667");
[Źródło](https://enauczanie.pg.edu.pl/moodle/pluginfile.php/440250/mod_resource/content/1/KafkaLab.pdf)
Z tego co jeszcze pamiętam to na zajęciach pytała się co się dzieje z wiadomościami, dla których w JSONie nie ma pola, którego zdefiniowaliśmy.
Odpowiedź na to pytanie brzmi: pole jest wtedy NULLem.
[Tu jest na poważnie od Cloudery.](https://blog.cloudera.com/introducing-hive-kafka-sql/)
---
## 11. Wyjaśnij pojęcia Producent, Log, Partycja w narzędziu Kafka.
Zacznijmy od podstaw.
* broker: serwer obsługujący wiadomości Kafki
* temat (topic): kategoria wiadomości/po prostu jakaś nazwa informująca, że wiadomości są ze sobą powiązane. Tematy w Kafce zawsze wspierają wielu klientów, tzn. pewien temat może mieć zero, jeden lub więcej klientów subskrybujących temat.
* log: najprostszy sposób abstrakcji, jest to po prostu sekwencja rekordów, jeden po drugim, posortowane po czasie. Wiadomości dopisywane są na końcu, a odczyt jest od lewej do prawej. Temat w Kafce jest takim logiem.
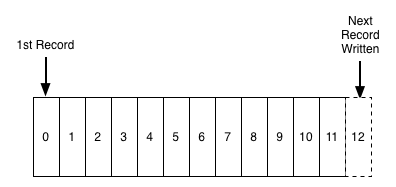
* partycje: każdy temat jest podzielony na pewną liczbę partycji. Jest to fizycznie jednostka przechowywania danych w Kafce (to właśnie partycja jest przechowywana na dysku). Partycje pozwalają na zrównoleglenie tematu poprzez rozłożenie go na wiele brokerów --- każda partycja może być umieszczona na osobnej maszynie, aby pozwolić wielu klientom na równoległy odczyt wiadomości z tematu. Dodatkowo, każda wiadomość w Kafce ma identyfikator (*offset*). Offset jest informacją o kolejności wiadomości, Kafka sama dba o dobre ustawienie wiadomości w kolejności. Klienci mogą zaczą czytać od jakiegokolwiek offsetu, więc mogą też dołączać kiedy chcą. Łącząc to wszystko, wiadomość w klastrze Kafki można zidentyfikować po temacie, partycji i offsecie.
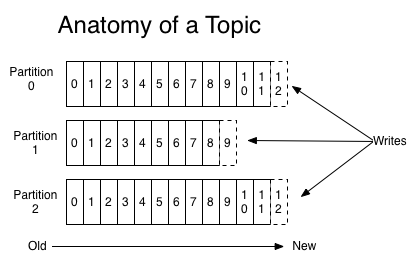
* producent: coś, co dokłada wiadomości do jednego lub więcej tematu Kafki
---
## 12. Wyjaśnij pojęcia Konsument, Grupa Konsumentów, Partycja w narzędziu Kafka.
* partycja: wytłumaczona w pytaniu wyżej
* konsument: aplikacja, która czyta dane z tematu Kafki.
* grupa konsumentów: możemy pogrupować konsumentów razem, aby mogli oni dzielić między sobą partycje pewnego tematu Kafki. Dla przykładu: jeśli mamy 4 partycje tematu i 4 konsumentów w grupie konsumentów i grupa subskrybuje temat, to każdy konsument będzie czytał dane z jednej partycji tematu.
> Consumers label themselves with a consumer group name, and each record published to a topic is delivered to one consumer instance within each subscribing consumer group. Consumer instances can be in separate processes or on separate machines.
> If all the consumer instances have the same consumer group, then the records will effectively be load balanced over the consumer instances.
> If all the consumer instances have different consumer groups, then each record will be broadcast to all the consumer processes.
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/

---
## 13. Zadania Map, Combine i Reduce w systemie Hadoop.
>src: https://data-flair.training/blogs/hadoop-combiner-tutorial/

- map
> The map or mapper’s job is to process the input data. Generally the input data is in the form of file or directory and is stored in the Hadoop file system (HDFS). The input file is passed to the mapper function line by line. The mapper processes the data and creates several small chunks of data.
- combine
> The combiner in MapReduce is also known as ‘Mini-reducer’. The primary job of Combiner is to process the output data from the Mapper, before passing it to Reducer. It runs after the mapper and before the Reducer and its use is optional.
- reduce
> This stage is the combination of the Shuffle stage and the Reduce stage. The Reducer’s job is to process the data that comes from the mapper/combiner. After processing, it produces a new set of output, which will be stored in the HDFS.
---
## 14. Operacje relacyjne w narzędziu Pig.
### Selekcja
> FILTER aliasBY expression, np. recs2 = FILTER recs BY $1 < 1990
### Projekcja
> FOREACH can be used to:
> * projection, by leaving only the selected columns, [...]
### Połączenie (Iloczyn kartenzjański)
> To perform joins we use JOIN operation
> Joins are similar to their SQL counterparts,
> [...] JOIN r1 BY $1, r2 BY $0 [...]
> Outer joins can also be performed, but in that case JOIN can be used only on two relational variables, and the type of the join has to be specified in the first part of the command
> JOIN r1 BY $1 FULL OUTER, r2 BY $0;
### Suma
> The UNION operator of Pig Latin is used to merge the content of two relations. To perform UNION operation on two relations, their columns and domains must be identical.
> `grunt> Relation_name3 = UNION Relation_name1, Relation_name2;`
[Źródło](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/apache_pig/apache_pig_union_operator.html)
### Część wspólna
JOIN
### Różnica
> The SUBTRACT() function of Pig Latin is used to subtract two bags. It takes two bags as inputs and returns a bag which contains the tuples of the first bag that are not in the second bag.
> grunt> SUBTRACT(expression, expression)
[Źródło](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/apache_pig/apache_pig_subtract.html)
---
## 15. Model danych HBase. Rola klucza i rodzin kolumn.
> ### klucz:
> src: https://enauczanie.pg.edu.pl/moodle/pluginfile.php/435597/mod_resource/content/0/HBase2.pdf
> 
> Keys and cell values are simply treated as sequences of bytes
> Keys are sorted lexicographically, i.e. 1, 10, 2, 20, 3...
> There are two basic forms of accesing data:
> - Get( key_value) returns the value of the record for the given key value
> - Scan( key_value) returns something like a cursor which traverses data in the direction of increasing key values. The initial position of the cursor is the record with the give key value, if sucha record exists, or the record with the „next” closest value of the key otherwise
>
> Keeping that in mind we can assemble our key in a way that it will sort records by type/date/whatever by itself as in our beloved example: 
>
>### rodzina kolumn:
> src: https://www.dummies.com/programming/big-data/hadoop/column-families-in-the-hbase-data-model/
> In the HBase data model columns are grouped into column families, which must be defined up front during table creation. Column families are stored together on disk, which is why HBase is referred to as a column-oriented data store.
>
> Logical View of Customer Contact Information in HBase
> | Row Key | Column Family: {Column Qualifier:Version:Value} |
> | -------- | -------- |
> | 00001 | CustomerName: {‘FN’:1383859182496:‘John’,‘LN’: 1383859182858:‘Smith’,‘MN’: 383859183001:’Timothy’,‘MN’: 1383859182915:’T’}ContactInfo: {‘EA’:1383859183030:‘John.Smith@xyz.com’,’SA’: 383859183073:’1 Hadoop Lane, NY11111’}|
> |0002|CustomerName: {‘FN’:1383859183103:‘Jane’,‘LN’: 1383859183163:‘Doe’,ContactInfo: {’SA’: 1383859185577:’7 HBase Ave, CA22222’}|
>
> The table shows two column families: CustomerName and ContactInfo. When creating a table in HBase, the developer or administrator is required to define one or more column families using printable characters.
>
> Generally, column families remain fixed throughout the lifetime of an HBase table but new column families can be added by using administrative commands. The official recommendation for the number of column families per table is three or less. (See the Apache HBase online documentation.)
>
> In addition, you should store data with similar access patterns in the same column family — you wouldn’t want a customer’s middle name stored in a separate column family from the first or last name because you generally access all name data at the same time.
>
---
## 16. Operacje dostępu do danych w HBase.
> - Get( key_value) returns the value of the record for the given key value
> - Scan( key_value) returns something like a cursor which traverses data in the direction of increasing key values. The initial position of the cursor is the record with the give key value, if sucha record exists, or the record with the „next” closest value of the key otherwise
---
## 17. Charakterystyka kolumnowych baz danych.

> OLAP servers are column-oriented databases. Red arrows indicate how data is stored
> The data in the relational database is stored row by row.
> The column database stores datacolumn by column. This means that all patientids are stored first, then all hospitalids, admission dates etc.
>
> To perform an analytical query, the relational database engine must read the entire content of the table when in fact (for the sample query) only the values of the patient_idand no_of_procedurescolumnsare needed. Due to the fact that fact tables are very large, reading entire rows is inefficient. Thus OLAP servers store data in column-orientedorganization.

---
## 18. Rola optymalizatora zapytań w bazach danych.
> src: https://enauczanie.pg.edu.pl/moodle/pluginfile.php/435596/mod_resource/content/0/HBase1.pdf
> Query optimization aims at determining the optimal query execution plan (logical and physical). It often involves changing relational operations to their counterparts or changing the order of their execution for better performance
---
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

