---
slideOptions:
transition: slide
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
# 基礎排序
by 南天門日月卦長
---
## 預備知識
1. 陣列
2. 迴圈
3. 函數
4. 時間複雜度
----
## 你知道這些代表神麼意思嗎?
``` cpp=
int s[] = {7,1,2,2,9,4,8,7};
int a[10000005] = {1}; //想清楚!!
int b = s[8]; //b是什麼呢?
```
----
## 你知道這些代表神麼意思嗎?
``` cpp=
int s[] = {7,1,2,2,9,4,8,7};
int b=0;
for(int i=0;i<8;++i) b += s[i];
for(;b--;){
cout<<7122<<'\n';
}
```
----
## 這個函數的時間複雜度?
``` cpp=
int MAX(int s[], int n){
int res = s[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
if(s[i]>res) res = s[i];
return res;
}
```
----
## 常見的時間複雜度
* 找n個數裡的最大值?
* 掃過所有數字選出最大的 $\longrightarrow \mathcal{O}(n)$
* 判斷一個數字n是不是質數?
* 掃過 $2\sim n \longrightarrow \mathcal{O}(n)$
* 掃過 $2\sim \sqrt{n} \longrightarrow \mathcal{O}(\sqrt{n})$
---
## 交換兩變數
在接下來的課程中
我們會經常需要交換兩變數的值
因此我們先來複習一下
----
## 交換兩變數
``` cpp=
int a = 7122, b = 9487;
//交換a,b
int tmd = a;
a = b;
b = tmd;
cout << a << ' ' << b << '\n';
```
----
## std::swap()
需要 ```#include<algorithm>```
可以用更簡單的寫法交換兩個變數
更詳細用法會在之後STL的課程告訴你
----
## 交換兩變數
``` cpp=
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
int main(){
int a = 7122, b = 9487;
//交換a,b
std::swap(a,b);
std::cout << a << ' ' << b << '\n';
return 0;
}
```
----
## 交換兩變數
``` cpp=
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; //這樣可以省略 std::
int main(){
int a = 7122, b = 9487;
//交換a,b
swap(a,b);
cout << a << ' ' << b << '\n';
return 0;
}
```
---
## 排序基本想法
給你一個大小為n的陣列
你要把裡面的元素由小到大排好順序
----
## 範例
``` cpp
int s[105] = {7, 1, 2, 2, 7, 1, 2, 2};
```
<span>將s前8項排序---><!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1" --></span>
<span>s[0]~s[7]分別為1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 7, 7<!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="2" --></span>
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## 基於交換的排序
---
## 基本想法
對於一個排序好長度為n的陣列s
對於任何的 0 $<$ i $<$ n
一定滿足 s[i] $\ge$ s[i-1]
----
所以說
如果我發現 s[i] < s[i-1]
那就表示s是沒有排序好的
----
這個性質可以幫助我們在$\mathcal O (n)$的時間
判斷陣列有沒有按順序排
``` cpp=
bool sorted(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
if(s[i]<s[i-1]) return false;
return true;
}
```
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## very stupid sort
超級蠢的排序
---
既然只要存在 s[i] < s[i-1] 就是沒有排序好
----
那我們就在陣列裡面一直找 s[i] < s[i-1]
只要遇到了就把 s[i], s[i-1]做交換就行啦!
----
一直找直到陣列裡面沒有 s[i] < s[i-1] 為止
----
## 讓我們來看程式碼
``` cpp=
void veryStupidSort(int s[], int n){
while(!sorted(s,n)){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
if(s[i]<s[i-1]){
swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
break;
}
}
}
}
```
----
## 更好的寫法
``` cpp=
void veryStupidSort(int s[], int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
if(s[i]<s[i-1]){
swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
i = 0; //注意等一下會++i
}
}
}
```
----
## 蠢在哪裡?
----
## 時間複雜度
不要以為只有一個for時間複雜度就是$\mathcal O(n)$喔
----
仔細看
每次發現 s[i] < s[i-1] 就會把 i 歸 0
意思是每次交換後會重新掃描陣列一次!
----
重新掃描陣列大約花$\mathcal O(n)$的時間
因此總複雜度是:
$\mathcal O(n)\times$交換次數
----
## 交換次數
稍微思考一下
會發現在陣列「倒著排序」的情況下
需要最多的交換次數
``` cpp=
int s[]={5,4,3,2,1};
```
----
仔細算會發現
對長度n「倒著排序」的陣列來說
用我們的排序法需要進行
$(n-1)(n-2)/2=\mathcal O(n^2)$次交換
----
## 總複雜度
因此我們演算法的複雜度是$\mathcal O(n) \times \mathcal O(n^2)=\mathcal O(n^3)$
----
但是排序最快可以做到$\mathcal O(n \;log \;n)$,這方法太蠢了
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## bubble sort
氣泡排序
---
剛剛的第一份code裡面有一個break
``` cpp=
void veryStupidSort(int s[], int n){
while(!sorted(s,n)){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
if(s[i]<s[i-1]){
swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
break;//拿掉會發生什麼事呢?
}
}
}
}
```
----
拿掉break就變成所謂的bubble sort了
``` cpp=
void bubbleSort(int s[], int n){
while(!sorted(s,n)){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
if(s[i]<s[i-1]) swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
}
}
}
```
----
## 複雜度有變好嗎?
----
當然有!變$\mathcal O(n^2)$
我們現在要來證明外層的while最多只會執行n次!
----
我們要來證明,不管陣列的元素排列順序
執行一次底下這個程式碼之後
最大的元素一定會被放在s[n-1]的位置!
```cpp=
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
if(s[i]<s[i-1]) swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
}
```
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 假設陣列長這樣
* 當前i=2
* 此時s[i-1]為最大值(99)
| | i-1 | i | | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 99 | 71 | 22 | 87 |
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 因為 s[i]<s[i-1]
* 所以會執行swap的操作
* 執行完後會得到以下的結果
| | i-1 | i | | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 99 | 22 | 87 |
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 接著會執行for的++i
* 執行完後會得到以下的結果
* 你會發現現在s[i-1]又變成最大值了(99)
| | | i-1 | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 99 | 22 | 87 |
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 最大值一定比其他所有元素大,如此不斷重複
* 直到i==n-1為止
* 你會發現最後最大值就會跑到s[n-1]的位置
| | | i-1 | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 22 | 99 | 87 |
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 最大值一定比其他所有元素大,如此不斷重複
* 直到i==n-1為止
* 你會發現最後最大值就會跑到s[n-1]的位置
| | | | i-1 | i |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 22 | 99 | 87 |
----
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
* 最大值一定比其他所有元素大,如此不斷重複
* 直到i==n-1為止
* 你會發現最後最大值就會跑到s[n-1]的位置
| | | | i-1 | i |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 22 | 87 | 99 |
----
只要最大值在某個 i-1 的位置
他最後一定會被交換到 s[n-1] 去
----
除非最大值本身就在 s[n-1]
否則他一定會在某個 i-1 的位置
因此執行一次for之後最大值一定會被放到s[n-1]
----
那如果最大值已經在 s[n-1]了
執行for迴圈之後會發生什麼事呢?
----
稍微想一下
你會發現第2大值就一定會被放在s[n-2]的位置
----
準確來說
執行第k次for迴圈後
第k大值就會被放在s[n-k]的位置
(這也是被稱為bubble sort的原因)
----
因此最多只要執行n-1次迴圈就可以完成排序
故總複雜度為$\mathcal O(n(n-1))=\mathcal O(n^2)$
----
因為已經知道最多只會執行n-1次while
可以把code寫得更短
```cpp=
void bubbleSort(int s[], int n){
for(int t=0; t<n-1; ++t)
for(int i=1; i<n-t; ++i)
if(s[i]<s[i-1]) swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
}
```
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## selection sort
選擇排序
---
## 基本想法
把最小的元素找出來,和s[0]交換位置
接著找第二小的,和s[1]交換位置
接著找第三小的...
最後所有s[0]~s[n-1]都會是排序好的
----
再找第k小的元素時
由於前k-1小的元素都已經被放在s[0]~s[k-2]了
故s[k-1]~s[n-1]中最小元素就是原本陣列中的第k小
----
## 從s[k]~s[n-1]中找最小的index
```cpp=
int find_index_of_min_element(int s[],int k,int n){
int res = k++;
for(; k<n; ++k)
if(s[k]<s[res]) res = k;
return res;
}
```
----
## selection sort
```cpp=
void selectionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
int min_id = find_index_of_min_element(s,i,n);
swap(s[i],s[min_id]);
}
}
```
----
## 複雜度
顯然 find_index_of_min_element 是$\mathcal O(n)$
總共會執行$n$次
故總複雜度為$n \times \mathcal O(n)=\mathcal O(n^2)$
----
## 只用一個函數的寫法
```cpp=
void selectionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
int min_id=i;
for(int j=i+1; j<n; ++j)
if(s[j]<s[min_id]) min_id = j;
swap(s[i],s[min_id]);
}
}
```
----
## 補充
可以利用一種叫做[Heap](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure))的資料結構幫陣列做預處理
這樣的話 find_index_of_min_element 就可以做到$\mathcal
O(log\;n)$
總複雜度就會是$\mathcal
O(n \;log\;n)$,稱為[heap sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heapsort)
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## insertion sort
插入排序
---
## 基本想法
1. 把陣列分成排序好(左半)和沒有排序好(右半)
2. 將(右半)的最左邊元素加入(左半)中
3. (左半)的部分一直向左邊比,如果順序不對就交換
4. 重複2,3直到排序完成
----
## 下一步會發生什麼事呢?
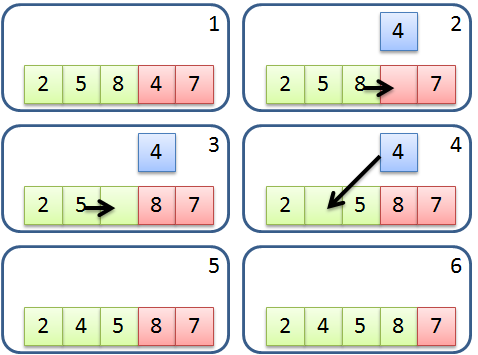
----
## 很短的code
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | i | | | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| j-1 | j | | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 99 | 22 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | i | | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | j-1 | j | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 99 | 22 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | | j-1 | j | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 99 | 22 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | | j-1 | j | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 22 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | j-1 | j | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 71 | 22 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | j-1 | j | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 22 | 71 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| j-1 | j | | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 50 | 22 | 71 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| j-1 | j | | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 22 | 50 | 71 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | i | |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| j | | | | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 22 | 50 | 71 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | | i |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | | | j-1 | j |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 22 | 50 | 71 | 99 | 87 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | | i |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | | | j-1 | j |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 22 | 50 | 71 | 87 | 99 |
----
## 模擬操作
<!-- .slide: data-transition="none" -->
```cpp=
void insertionSort(int s[],int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i)// 小於i的都是已經排序好的(左半)
for(int j=i; j && s[j]<s[j-1]; --j)
swap(s[j],s[j-1]);
}
```
| | | | | i |
| ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| | | j-1 | j | |
| s[0] | s[1] | s[2] | s[3] | s[4] |
| 22 | 50 | 71 | 87 | 99 |
----
## 複雜度分析
顯然裡面的for是$\mathcal O(n)$
而且每執行一次,(左半)的元素就會增加一個
----
## 複雜度分析
因此裡面的for最多執行$n$次就排好序了
故總複雜度是$n\times \mathcal O(n)=\mathcal O(n^2)$
----
## 好處
1. 常數很小
2. 當陣列很接近排序完成的情況
會花比較少的時間$\simeq \mathcal O(n)$
3. 當n很小( <= 15 )的時候
在一般電腦上是跑最快的排序(我自己測的)
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="fade-in convex-out" -->
## 其他有趣的排序
---
## gnome sort
侏儒排序
----
其實就是insertion sort只用一個迴圈的寫法
但是常數比較大
仔細一看有點像 very stupid sort
```cpp=
void gnomeSort(int s[], int n){
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
if(i && s[i]<s[i-1]){
swap(s[i],s[i-1]);
i -= 2;
}
}
}
```
----
## 複雜度
和insertion sort一樣$\mathcal O(n^2)$
---
## stooge sort
臭皮匠排序
----
取名來自於三個臭皮匠
是我看過最優美的排序方法
不用任何迴圈
```cpp=
void stoogeSort(int s[], int L, int R){
if(s[R]<s[L]) swap(s[L],s[R]);
if(R-L<=1) return;
int p = (R-L+1) / 3;
stoogeSort(s, L, R-p);
stoogeSort(s, L+p, R);
stoogeSort(s, L, R-p);
}
```
----
## 使用方法
假設你要對長度為n的陣列s做排序
```cpp=
stoogeSort(s,0,n-1);
```
----
## 複雜度
* 遞推關係式
* $T(n) = 3T(\frac{2}{3}n)+\mathcal O(1)$
* by [master theorem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_theorem_(analysis_of_algorithms)), $T(n) = \mathcal O(n^{log_{1.5}3})=\mathcal O(n^{log 3/log 1.5}) \simeq \mathcal O(n^{2.71})$
---
<!-- .slide: data-transition="zoom" -->
## 補充 - 高效的排序法
以下的排序法都是$\mathcal O(n\;log\;n)$
* [merge sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort)
* [heap sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heapsort)
* [introsort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Introsort)([quick sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort)改良版)
---
## 有趣的影片
{%youtube kPRA0W1kECg %}
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

