---
robots: index, follow
tags: NCTU, CS, 共筆, 密碼學, 陳榮傑
description: 交大資工課程學習筆記
lang: zh-tw
dir: ltr
breaks: true
disqus: calee
GA: UA-100433652-1
---
密碼學概論--陳榮傑
=====
`NCTU` `CS`
[回主頁](https://hackmd.io/s/ByOm-sFue)
# Syllabus
- Course Site: http://people.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~rjchen/Crypto2017/
- Book: Cryptography and Network Security - principles and pracice (5th edition by William Stallings)
- Score
- HW (25%)
- Midterm (35%)
- Final (40%)
# Course
## Ch0
3 related research areas in CS and EE
1. Information Theory
2. Coding Theory
3. Cryptography
Why encode data?
1. efficiency (*ex. Hoffman Code*)
2. error detection / correction (*ex. binary [5,3]-code -> codewords*)
3. secrecy / authentitation (*ex. DES*)

- Cryptology (保密學)
- Cryptography
- Cryptanalysis
- Cryptography (密碼學)
- study and allpicaty of secure
- Cryptanalysis (破密學)
two types of Cryptosystems
- symmetric-key (ency-key = dency-key)
- block cipher (塊狀加密)
key 針對 分塊的 text 分別加密
e.g. AES, DES
- stream cipher (串流加密)
key 以某方法(ex. 除質數,找小數)產生無窮字串,利用字串直接對整串 text 加密
e.g. RC4
- asymmetric-key (public key != private key)

- ciphertext (密文)
$c = m^e \mod n$
- plaintext (明文)
$m = c^d \mod n$
$d = e^{-1} mod \phi(n)$
$\phi(n) = (p-1)(q-1)$
**A public-key cryptosystem is usually based on a hard math problem!**
3 hard math problems
1. Factorigation $n = p * q$
2. Discrete log $g^x$
3. Closest vector of a **lattice** (最接近格子點)
給 n 個 vector 代表座標軸及其單位座標,給 P(a,b),求最接近的格子點 ex.
$$
base=
\begin{bmatrix}
3 & 0\\
0 & 2
\end{bmatrix}
$$
and
$$P = (100,210)$$
Find closest point $Q$ (lattice)
## Ch1 Classical Cryptography
### Introduction: Simple Cryptosystems

:::info
A cryptosystem is a five-tuple (P,C,K,E,D) satisfies
:::
- P: finite set of possible *plaintexts (明文)*
- C finite set of possible *ciphertexts (密文)*
- K: *keyspace*, finite **set** of possible keys
- for each K, ther is an *encryption (加密)* rule $e_k$ and corresponding *decryption (解密)* rule $d_k$
:::info
a and b are integers, m is a positive integer
congruece: $a \equiv b \mod m$ if m divides $b - a$
:::
:::info
$Z_m = set of \{0, 1, ..., m-1\}$
:::
- with 2 operations + and *
- $10 + 20 = 4 \ in \ Z_{26} (10+20\mod26=4)$
- $10*20 = 18 \ in \ Z_{26} (10*20\mod26=18)$
---
#### Shift Cipher (平移)
- $P = C = K = Z_{26}$
- $K,x,y \in Z_{26}$
- $e_k(x) = (x + K) \mod 26$
- $d_k(y) = (y - K) \mod 26$
Suppose $K=11$
- Plaintext: student
- Ciphertext: DEFOPZE
#### Subsititution (取代)
$e_{\pi}(x) function$

#### Affine Cipher
模函式
affine function
$f(x) = (ax + b) \mod m$
($\gcd(a,m) = 1$)
- $\phi(m)$: 小於 m 中與 m 互質的個數
- $\phi(m) = p^e - p^{e-1}$
- $\phi(mn) = \phi(m)\phi(n)$
- e.g. $e_K(x) = (7x+3)\mod26$
#### Vigenere Cipher
eg. $key = (2,8,15,7)$
加一個固定的質(序列),加完後重頭加

#### [Hill Cipher](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B8%8C%E5%B0%94%E5%AF%86%E7%A0%81)
key=可逆矩陣
$e_k(x)=xk$
$c_k(y)=yk^{-1}$
#### Permutation Cipher
字串中的相對位置改變

第一個跑到第三個
第二個跑到第五個
...

---
### Cryptanalysis (密碼破密)
Kerckhoffs' principle
你一定要告訴我你怎們加密,你一定要告歲我 key
### Attech module
- [ciphertext only attack](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%94%AF%E5%AF%86%E6%96%87%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB) (最難的,僅知已加密文字(即密文)的情況下進行攻擊)
- [known plaintext attack](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B7%B2%E7%9F%A5%E6%98%8E%E6%96%87%E6%94%BB%E5%87%BB) (攻擊者掌握了 "某段" 明文 x 和對應密文 y)
- chosen plaintext attack (指定的明文要他加密,我再回推 => 可以指定任意明文)
- chosen ciphertext attack (給密文,請他給相對的明文)
### 解密:
1. 暴力找
$$
y = ax + b \\
x = a^{-1}y - b
$$
2. 用經驗找常見的字母或字串先 try (做字典)
3. find m
- Index of coincidence of x (Friedman)
- 先檢查 m=? (用 x 算出來大概接近 0.06)
- 每 m 個抓出來,可算出 swift 了多少格
- 找出 block shift 了多少
- Kasaski
- 找出類似字串的距離,m 可能等於其距離的公因數
- 找 swift
4. Hill Cipher
- $\phi(n)$ 1~n 間跟 n 互質的個數
- $\phi(p) = p-1$
- $\phi(p^2) = p^2 - p$
- $\phi(p^k) = p^k - p^{k=1}$
- $\phi(pq) = (p-1)(q-1)$ $(\gcd(m,n) = 1)$
- $\phi(26) = \phi(2) * \phi(13) = 12$
- $3^{-1} = 9 (mod 26)$
- $m \geq 2$ is an integer
- $P = C = (Z_{26})^m$
- k = {m*m invertible matrices over Z_26}
- for a key K
- $e_k(x) = xK$
- $d_k(y) = yK^{-1}$
- Hill Cipher is difficult to break with a ciphertext-only attack
- known plaintext attack
- 需有曾經看過的加密 (知道明文a與加密後的密文b)
- 用反舉證的概念
- $a = b * k$
$$
\begin{bmatrix}
\end{bmatrix}
$$
### DES
Keysize: 56
blocksize: 64
**Feistel cipher:**
1. 分一半(32 + 32)
2. 每一次 round 用原來的 key (56 bit) 產生 subkey (4 8bit)
3. IP($IP(x) = L_0R_0$): initial permutation
4. 位置調動
- $L_{new} = R_{old}$
- $R_{new} = L_{old} \oplus f(R_{old}\& key)$
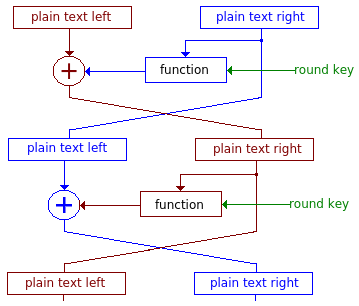
5. function (bent functions)
$$f: \{0,1\}^{32} * \{1,0\}\&{48} → \{0,1\}^{32}$$

2-DES
Meet in the middle attack 可解 DES
## Asymmetric key (public key)
DES (Secret key)
RSA (public/private key)
- function
- authentication
- confidentiatiality
- Used
- Asymmetric
- Certificate
- PKI (public key infrastructure)
- Secret
- Authentication 確實是某人送出的
- Key exchange
- Digital signature
- encryption/decryption
- Encryption
- with public
- with private key
- term
- plaintext: 明文
- encryption algo: 加密 algo
- cyphertext
- decryption algo
- msg -> your private en -> his public en -> his private de -> your public de -> msg
### RSA
Select p, q (big prime, p != q)
n = p * q
$\phi(n)=(p-1)(q-1)$
select e s.t. $gcd(\phi(n),e)=1, 1<e<\phi(n)$
$d==e^{-1}(mod\phi(n))$
Public: {e,n}
Private: {d,n}
- encryption
- Plaintext M
- Ciphertext: $C = M^e \mod n$
- decryption
- Ciphertext: C
- Plaintext: $M = C^d \mod n$
### 群環體
Group
- +, \*
- +, \* 單位元素
- +, \* 反元素
- 封閉性
- 交換律, 結合律...
四元數 (Quarternion)
- a + bi + cj + dk
- $-1 = i^2 = j^2 = k^2$
- 沒有交換性 (i \* j = -j \* i)
- 八元數 (Octonion) // ...數學家真的太無聊了吧 XD
1. (G, \*) is a group
- $Z_p^* = Z_p - 0 = \{1,2,3,...,p-1\}$
- \* is closed
- \* is associative
- $\exists$ identity $e \in G$
- $\exists a^{-1} \in G$ for any $a \in G$, s.t. $a*a^{-1} = a^{-1}*a = e$
- if G is commutative, G is called a commutative group(abelian group)
2. (G, +, \*) is a ring
- (G, +) is [abelian group](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%98%BF%E8%B4%9D%E5%B0%94%E7%BE%A4)
- \* is closed
- \* is associative
- 分配律: (a+b)\*c = (a\*c) + (b\*c)
3. (G, +, \*) is a field
- (G, +, \*) is a ring
- (G\\\{0\}, \*) is a abelian group, where 0 is 加法單位元素
- finite / infinite
Why $Z_p$ is a field
- because $\forall{a} \in Z_p, \exists{a^{-1}}$
- how to find $a^{-a}$ => 輾轉相除法
### Finite Field
- Example
- Z5
- $2/4 = 2/4^{-1}=2\times 4 = 3$
- $(x+1)/(x^2+x+1) = (x+1)\times (x^2+x+1)^{-1}$
- e.g. $Z_{2^2}, x^2+1=(x+1)^2$
- $Z_4$ is not a field (4 is not prime) (乘法沒封閉性)
- $F_8$ is a field (but ring)
### Fermat's and Euler's Theorems
[Carmichael function](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%8D%A1%E9%82%81%E5%85%8B%E7%88%BE%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B8)
[Fermat Theorems](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%B4%B9%E9%A9%AC%E5%B0%8F%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86)
$$a^{p-1}\equiv1\pmod p$$
pf:
[Euler Theorems](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%AC%A7%E6%8B%89%E5%AE%9A%E7%90%86_(%E6%95%B0%E8%AE%BA))
$$a^{\phi(n)}\equiv1\pmod n (\phi(n): 與n互質的數)$$
e.g. $747^100802 \bmod1000 =?$
```
ϕ(1000)=ϕ(2^3 5^3)=ϕ(2^3)ϕ(5^3)=4*100=400
```
How to get ϕ
1. if p is prime: $\phi(p^n)=p^n-p^{n-1}$
2. if gcd(m,n) = 1: $\phi(mn)=\phi(m)\phi(n)$
### CRT 中國餘數定理
$x\equiv a_1\pmod{m_1}$
$x\equiv a_2\pmod{m_2}$
...
$x\equiv a_n\pmod{m_n}$
if $m_i$ 兩兩互質 =>
$\exists!x\bmod M=m_1m_2...m_n$
$$x=(\sum a_iM_i(M_i^{-1}\bmod m_i)) \pmod M$$
$$M_i=\frac{M}{m_i}$$
pf:
若 m 沒有互質, 將 m 質因數分解即可
### RSA proof
M -> (e_A, n_A)
C = M^e \mod n
M = C^d \mod n
Why works
By Eulers
If gdc(a,n) = 1, htena=1 Imod n)
................ 漏掉好多多多多多..............
## SHA-X
### BirthDay paradox
n 個人中,有人同一天生日的機率是多少?
都在不同天生日:$1\times(1-\frac{1}{365})\times(1-\frac{2}{365})\times...$
有衝突的:$1-[1\times(1-\frac{1}{365})\times(1-\frac{2}{365})\times...]=1-e^{\frac{-r^2}{2N}}$
- 生日攻擊法
- 要幾次 hashes 可以得到 collision
### SHA-1
- Preimage(one-way property)
- 給 h(x) 找一個 x 都很難(x 會有無限多個)
- Second preimage(weak collision resistant)
- **給定 x**,找到 y != x, s.t. h(x) == h(y) 很難
- Collision(strong collision resistant)
- 隨便要找出 x, y 使得 h(x) == h(y)
- 難度

### 訊息傳遞驗證
1. 明文 M 及 Hash(M) 一起加密傳送
2. M 及 加密後的 Hash(M) 一起傳送
3. M 及 Hash(共有secart) 後再一起 Hash 後傳送
4. M 及 Hash(secart) 一起 Hash 後,再加密傳送
- 加密通常都對 hash 完的值做,以減少複雜度
### 數位簽章
1.
### Compression function

- IV: 一開始給的,例如 前 n 個質數的 sqrt
- $CV_i = f(Y_{i-1},CV_{i-1})$
- 只要 f() 可以打亂即可,例如:一開始 f() 是用 DES
- 執行:
1. 原值 + padding + length => 1024bit 的倍數
- padding: 100000....0
- length: 原值的長度
2. 進 function
3. 得到 hash(msg)
## Primality test
- $Z_n^*$:所有跟 n 互質的數的集合
- $\phi(n) = N(n) = \Pi(質因數次方-1)$
- 費馬小定理
- 尤拉定理
- order: (?)
1. ord(n): $n^o = 1 \mod k$ 中最小的 o
- generator
- 中國餘數定理
- Square-and-Multipl
### Quadratic Residue
a 是 quadratic residue modulo n,代表 $a\in Z_n^*$ 而且 a 的開根號也是 $Z_n^*$
- $Z_n=Q_n U \overline{Q_n}$
- p > 2 is prime and $α$ is a generator of $Z_p^*$
- $\alpha$ 的偶數次方會是 $Q_p$,$\alpha$的奇數次方會是 $\overline{Q_p}$
- $N(Q_p) = N(\bar{Q_p})=\frac1 2$
- 如果 $a\in Q_p$,則 $x^2=a$ 會有兩個解(一正一負)
- **$a^\frac{p-1}{2}=-1\mod p$**
- 定義 Legendre symbol:$\begin{pmatrix}\frac{a}{p}\end{pmatrix}$
- Euler's criterion:
- $(\frac{a}{p})=a^{\frac{p-1}{2}}\mod p$
- e.g. $(\frac{3}{23})=\frac{23-1}{2}=1011_2$
- Jacobi symbol$(\frac{a}{n})$:
- n > 2 is an odd integer, $p_i$ is prime and $n=p_1^{e_1}p_2^{e_2}...p_n^{e_n}$
...
### Prime numbers
- 如何產生質數
1. 隨機產生奇數,prime test
2. 質數離散性:$\Pi(x)~\frac{x}{\ln(x)}$ ($\Pi$:質數個數)
- Solovay-Strassen primality test
1. 原始方法:測 $[2,\sqrt n]$ 有沒有 n 的因數
### Miller-Rabin
- Fact
- P: odd prime
- p-1 = 2^sr, where r is odd
- For all $a\in N$ & $gcd(a,p)=1$
- then $a^r=1\mod n$
- or $a^{2^j r}=-1\mod n$
## SHA3

- 2006, NIST
- 作法
1. 將 msg 用 10\* 的 padding 方式
- padding
- simple: $10*0$
- multirate: $10*1$
...
## MAC
Message authentication code
有 key 的 hash
- M || H(M) => M' || H(M') => 一般的 hash 無法認證
- 專詞
- Disclosure: 資料洩漏
- Traffic analysis: 分析資料送出頻率
- Masquerade: 資料認證 (防止第三者串改package)
- Content modification: 內容竄改
- Sequence modification: 順序竄改
- Timing modification: Delay
- Source repudiation: 寄件者拒絕承認(數位簽章)
- Destination repudiation: 接收方確認收到
- 認證作法
- Hash function
- Message encryption
- Message authentication code(MAC)
- MAC
- Confidentiality: 機密信
- Authentication: 確認信


- 對稱式:加密 + 認證
- 公鑰:加密
- 私鑰:認證
- 公私鑰:加密 + 認證

- HMAC
- Base on Hash
- ...
- CMAC
- 用 block cypher
## 數位簽章
- 用私鑰對 hash(msg) 簽章 => S
- 用公鑰確認 public_key(S) 產生的值是否與 hash(msg) 相同
- 可是要如何確認某人的 pub_key 確實是他的? => 第三方公證人
- Attack:
- (public)Key-only attack
- 攻擊者只有 pub_key 卻可以產生 msg & Sign(msg)
- known message attack
- chosen message attack
- C 把 msg 拿去請 A 簽章
- Adaptive chosen message attack
- Forgeries(M 和 簽章後的 M)
- Existential forgery
- Selective forgery
## Secret Sharing Schemes
n 個人或以上才能開鎖
- Secret Splitting
- 將秘密分為 k 份,每人持一份
- 用 mod 分
- Threshold Schemes
- 兩點決定一條線
- 把秘密放在線上 (ex. 某個係數上)
- e.g. 兩人各持有一點 (x,y),key 就是 斜率
- Vandermonde matrix
- alternative approach
- 利用 拉格朗日插值法 快速找到 threshold schemes
- 階乘
- 權限不同
- e.g. 一個 A == 兩個 B
- 多給幾把 key to 比較有權的人
- or say 小於一定程度的 key count 就不能有權限
- VSS (Verifiable Secret Sharing)
- 參加者可以驗證
- PVSS (publicly verifiable secret sharing)
- 外面的人可以驗證
- i.g. e-Vote, e-Cash
## Blind Signature
第三者做簽章 (不是 sender)
- i.g. 網路投票,不是選民簽章,而是選委會簽章
- 簽章的人不知道她在幫誰簽章


1. blinding: $H(m)\times r^e$ (r 是 random value, e 是選委會的 public key)
2. Singing: 選委會用自己的 private key 簽章 $(H(m)\times r^e)^d = H(m)^d\times r$
3. Unblinding: 選民把傳回來的值再除以 r => $H(m)^d$ 也就是有簽章的 $H(m)$
4. 最後投票,機器可以認出簽章
:::info
r 的用意是為了讓選委會不知道你投給誰
:::
## BitCoin
# HW
# Exam
作業跟考試有 8成 一樣,再加一兩題額外的題目
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

