---
robots: index, follow
tags: NCTU, CS, 共筆
description: 交大資工課程學習筆記
lang: zh-tw
dir: ltr
breaks: true
disqus: calee
GA: UA-100433652-1
---
# 資料庫系統概論----曾新穆
**ER-Mod****el**
Relational Data Model ( Ted Codd )
Before = Network Data Model (Cobol ans DDL, DML)
Very contentious: Database Wars (Charlie Bachman vs. Mike Stonebraker) -> Postgres->IIIustra->Informix->IBM
1st prototypes:
Ingres -> CA
Postgres -> IIIustra -> Informix -> IBM
System R -> Oracle, DB2
Why Relations?
Math:
sets: R = {1,2,3} S = {3,4}
A relation on R, S is any subset U R x S (e.g: {(1,4), (3,4)} )
DB:
Branch = {A, B, ....}
Accounts = { a, b, ...}
=> A U B = A x B ( e.g: {(A,a) (A,b) (A,...) (B,a) (B,b) (B, ...) } )
- Key
Keys and Relations
Key can map to Relations
Candidate key
=> Primary key <--> Composite key
=> Super key
(Key can also check integrity constraints)
Key Reference: [Wiki](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%85%B3%E7%B3%BB%E9%94%AE)
**Enhanced ER Modle (EER) (ch13)**
- Overview
- 1980s
- add semantic concepts (Superclass and Subclass)
- Superclass and Subclass
- Superclass
entity type include one or more distinct subgroupings of its occurences
- Subclass
distinct subgrouping of occurrences of an entity type
- Relationships
- attribute inheritance (屬性繼承)
- Specialization (差異最大化)
The process of maximizing the differences between members of an entity by identifying their distinguishing characteristics
- Generalization (最小化)
The process of maximizing the differences between entities by identifying their common characteristics
- Participation constraint
- mandatory
- optional
- Disjoint constraint
- and (subclass 可兼職)
- or (subclass 不可兼職)

(img source: [http://goo.gl/TyMvRM](http://goo.gl/TyMvRM))

(img source: [http://goo.gl/xfxD9K](http://goo.gl/xfxD9K))
- Aggregation
- has-a
- is-part-of
- whole
- part
**The Relational Model (ch4)**
- Overview
- Terminology
- tables use to replace data
- connection between mathematical relations and relations in the relational model
- properties
- candidate, primary, alternate, foreign keys
- meaning of entity integrity and referential integrity
- Terminology
- Relation: a table
- Attribute: column of relation
- Domain: set of allowable attributes
- Tuple: row of relation
- Degree: number of attribute
- Cardinality: number of tuple
- Relation database

- Key
- Super key
- Candidate key
- Primary key
- Foreign key
- Alternate key (candidate key that is not primary key)
(URL : [http://www.mysql.tw/2015/04/super-keycandidate-keyprimary.html](http://www.mysql.tw/2015/04/super-keycandidate-keyprimary.html) )
- Mathematical Definition
- subset of cartesian product (D1 x D2 = {(d11,d21)...}) (R = {x,y | x ∈ D1, y ∈ D2})
- Relations
- Relation schema: relation defined by set of attribute and domain name pairs
ex. {(a,b,c,d,e)}
- Relational database schema: set of relation schema
R = {R1,R2,R3...}
- Relation name must distinct
- each cell of relation is single value
- each attribute has distinct name
- value of attribute are from same domain
- each tuple is distinct
- order of attributes not important
- order of tuple not important
- Integrity constraints
- NULL: attribute value is currently unknown or not applicable for tuple
- Deals with incomplete or exceptional data
- Represents the absence of a value and is not the same as zero or spaces(value)
- Entity Integrity (primary key cannot be NULL)
- Referential Integrity
- foreign key exists in a relation
- General Constraints
- additional rules specified by user
- View
- Base relation
- View
- virtual relation
- been defined as query on base relations
- dynamic
- Purpose
- powerful, flexible, security (hiding parts of info from certain users)
- customized way by different users
- simplify
- Update
**Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus (ch5)**
1. Introduction
- formal languages associated
- Relational algebra: high-level procedural language
- Relational calculus: non-procedural language
- equivalent to one another
- relationally complete: A language produces a relation that can be derived using relational calculus
2. Relational Algebra
- work on relation to define another relation without changing the original relations
- operands and results are relations
- nesting
- 5 Basic operations
- Selection, Projection, Cartesian product, Union, Set Difference
- Other operations
- Join, Intersection, ~~Division~~

- Selection
- σ(R)
- tuple(rows) of R satisfy specified condition
- Projection
- π(R)
- vertical subset of R that extracting the values of specified attributes and eliminating duplicates -> 可能會有多人有同一特徵
- Union
- R∪S
- R and S must union-compatible
- Set difference
- R-S
- R and S union-compatible
- Intersection
- R∩S
- union-compatible
- R∩S = R - (R-S)
- Cartesian product
- R × S
- Join
- derivative of cartesian product
- forms of join
- Theta join
- contains tuples satsfying the predicate F from the Cartesian product of R and S
- degree is the sum of R and S
- the predicate F is of the form R.ai theta S.bi where theta may be one of the operator of (> = <)

- Equijoin (theta join with operator only is =)
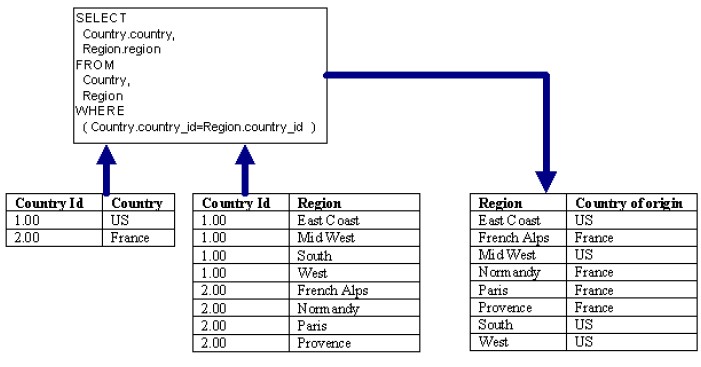
- Natural join
- Equijoin of two relations R and S and elimate redundont attriable
- Outer join
- display row in the result that do not have matchine values in the join column
- (Left) outer join is join in which tuples from R that do not have ...
- * (顯示沒有被join的cotition procuct)
- Semijoin
- defines a relation that contains the tuples of R that participate in the join of R with S
- useful if we only want to see the full attributes of staff for the result
- Division (/)
- defines a relation over the attributes C that consists of set of tuples from R that match combination of every tulpel in S
- expression of basic operation
- 選出元素必須含有全部被除數 (有點像整除的概念)
- Aggregate Operations
- the number of elements in set
- τcount
- ex: how many properties cost more than 350 rant per month
- Grouping Operation
- GAτAL(R)
1. Relational Calculus
- tuple based
- Interested in finding tuples
- Specify range of a tuple variable S as the Staff relation as: Staff(S)
- ex: Find details of all staff earning 10000: {S | Staff(S) ^ S.salary = 10000}
- 較像要找到的東西 (algebra 較像尋找方法)
**SQL (ch6)**
- Objectives of SQL
- create database and relation structures
- insertion modification deletion
- queries
- command
- reserved words, user-defined words
- case insensitive
- BNF notation
- Upper-case for reserved words
-
- Literals
- non-number ' '
- number
- SELECT
- SELECT [DISTINCT | ALL]
{* | \[columnExpression[AS newName]\][,...] }
FROM TableName\[alias\][,...]
[WHERE condition]
\[GROUP BY columnList\][HAVING condition]
[ORDER BY columnList]
- order of the clauses can't change
- [ ] for optional
- { } for must
- ; end
- *: all column
- DISTINCT : list without reduncicy
- AS : rename when viewing(won't change database)
- WHERE BETWEEN...AND, NOT, >=<, LIKE, %name%(squence of char), _(just one char)
- comment IS NULL
- % for 1 or upper number of non-define char
- _ just 1 char
- ORDER by
- COUNT(*), MIN, MAX -> to numeric and non-meric
- SUM, AVG -> numeric
- 除了COUNT,其它的實作都會先把NULL去除
- Aggregate function can be used only in SELECT list and in HAVING cause
- COUNT(DISTINCT selecting_row)
- HAVING 搭配 GROUP 用
- ex: HAVING COUNT(staff) > 1
- Subquery (去別的table查詢)
- SELECT
- can't use ORDER BY
- must used only single column name or expression except for EXIT
- SOME/ANY/ALL
- Multi-Table quary
- can used alias
- JOIN
- NATUAL JOIN
- ON
- USING
- EXISTS
- Union/Intersect/Difference/Except
- operator \[ALL\] [CORRESPONDING [ BY {column1 [,...] } ] ]
- INSERT INTO {...(...)}
- VALUES(...)
- UPDATE
- SET
- DELETE FROME
**Objectives (CH7)**
- Required Data
- position VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL
- Domain Constraints
- CHECK
sex CHAR NOT NULL
CHECK(sex IN('M','F')
- CREATE DOMAIN:
CREATE DOMEAIN DomainName[AS] dataType
[DEFAULT defaultOption]
[CHECK (searchCondition)]
[CHECK (searchCondition)]
CREATE DOMAIN DOMAIN SexType AS CHAR
CHECK(VALUE IN('M','F'));
sex SexType NOT NULL
- PRIMARY KEY( )
- FOREIGH KEY( ) REFERENCES branchs -> ALTER TABLE
- UNIQUE
- Update and Delete
- CASCADE
- SET NULL
- SET DEFAULT
- NO ACTION
- ALTER TABLE
- CREATE ASSERTION
CREATE ASSERTION j bn
- catalogs
- schema (no include data: table,view,doman)
- CREATE ACHEMA [Name | AUTHORIZATION Creatorld]
- DROP SCHEMA Name [RESTRICT | CASCADE]
CREATE DOMAIN OwnerNiumber AS VARCHAR(5)
CHECK(VALUE IN(SELECT ownerNo FROM PrivateOwner));
CREATE DOMAIN StaffNumber AS VARCHAR(5)
ALTER TABLE Staff
ALTER position DROP DEFAULT;
ALTER TABLE
- View
- Virtual relation
- defined as query
CREATE VIEW ViewName [ (newColumnName[])]
AS subselect
[WITH [CASCADED | LOCAL] CHECK OPTION]
- WITH CHECK OPTION
- UPDATE ... SET ...
- DELETE FROM ...(TABLE/VIEWING) ....
- WITH CHECK OPTION
- Transaction
**Normalization(CH14)**

- produce a set of suitable relations
- suitable set
- minimal number of attribute
- close logical relationship
- minimal redundancy
- purpose
- maintain
- assess
- Lossless-join and dependency
- Functional Dependency
- full functional dependency
- partial dependency
- one-to-one relationship between left and right hand side
- hold for all time
- determinat has minimal number of attributes
- Transitive dependency
- a -> b and b -> c then c is functional delpency on a
- Determinants
- attribuate 越少越好
- Inference rule
- idendify a set of minima functional dependencies
- X+ is the extend of X
- A, B, C are subsets of the attributes of the relation R -> Armstrong's axioms:
- Reflexivity
- If B is subset of A, then A -> B
- Augmentation
- A-> B, then A,C -> B,C
- Trans
- Self-determination
- A -> A
- Deco
- mposition
- A -> B,C, then A -> B and A -> C
- Union
- Composition
- Minimal set
- Every dependency in X has a single attribute on its right-hand side
- cannot replace any dependency A->B to C->B where C is a proper subset of A
- cannot remove dependency from X and still have a set of dependencies that is equivalent to X
- BCNF
- A relation is in BCNF if
- defference between 3NF and BCNF is that for a functional dependency of
- suppose X -> A violates BCNF, thenone of the following holds
- X is a subset of some key K
- X is not a subset of ...
- Third Normal Dorm
- BCNF + A is part of some key for R
- similar to that of BCNF, with the only difference being the third condition
- a key for a relation is a minimal set of attributes that uniquely determines all other ...
- X -> A cause a violation of 3NF:
- X is a proper subset of some key K --- partial dependency
- X is not a proper subset of any key --- transitive dependency
- Decomposition
- R1 U R2 U R3 U ... U Rn = R => Decomposition
- Theorem:
- R: a relation schema
- F: set of functional dependencies on R
- The decomposition of R into relations with attribute sets R1, R2 is a lossless-join decomposition iff
- (R1 ^ R2) -> R1 in F
- or
- (R1 ^ R2) -> R2 in F
- Dependency Preservation
- s
**Objectives(CH15)**
- two main techniques for query optimization
- heuristic rules that order operations in a query
- comparing different stategies based on relative costs, and selecting one that minimizes resource usage
- disk assess tends to be dominant cost in query processing for centralized DBMS
- Query Processing
- activities involved in retrieving data from that database
- aim:
- transform query written in high-level language, into correct and efficient execution strategy expressed in low-level language
- execute strategy to retrieve required data
- reduce total execution time and response time
**Query Processing(CH23)**
- analysis
- query tree
- normalization
- conjunctive normal form (Product Of Sum)
- disjunctive normal form (Sum Of Product)
- Semantic analysis
- relation connection graph
- node for relation and result
- edge for join and source of projection operations
- normalized attribute connection graph
- node for reference to attribute, or constant 0
- directed edge between nodes represent to a join, and between node and constant 0 represents a selection operation
- weight
- if cycle, the sum must be positive
- simplification (反正把表格變小就對了)
- query restructuring
- heuristical processing strategies
- selection operations as early as possible
- c
**Transaction**
ACID
-
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

