# D03: assessment
contributed by <`vulxj0j8j8`>
Latex list symbols:
https://oeis.org/wiki/List_of_LaTeX_mathematical_symbols
https://www.sharelatex.com/learn/Integrals,_sums_and_limits
## 測驗 `一`

請完成下方程式碼,依循 IEEE 754 單精度規範,輸出 $2^x$ 的浮點數表達法,而且考慮兩種狀況:
* 當 $x$ 過小的時候,回傳 $0.0$
* 當 $x$ 過大的時候,回傳 $+\infty$
注意:這裡假設 `u2f` 函式返回的浮點數值與其無號數輸入有著相同的位數,也就是至少 32-bit
```Clike
#include <math.h>
static inline float u2f(unsigned int x) { return *(float *) &x; }
float exp2_fp(int x) {
unsigned int exp /* exponent */, frac /* fraction */;
/* too small */
if (x < 2 - pow(2, Y0) - 23) {
exp = 0;
frac = 0;
/* denormalize */
} else if (x < Y1 - pow(2, Y2)) {
exp = 0;
frac = 1 << (unsigned) (x - (2 - pow(2, Y3) - Y4));
/* normalized */
} else if (x < pow(2, Y5)) {
exp = pow(2, Y6) - 1 + x;
frac = 0;
/* too large */
} else {
exp = Y7;
frac = 0;
}
/* pack exp and frac into 32 bits */
return u2f((unsigned) exp << 23 | frac);
}
```
根據[IEEE 754](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_754-1985#Examples)
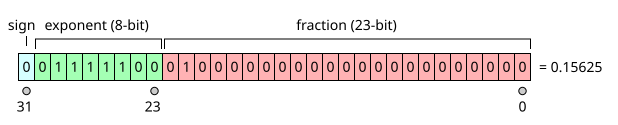
demormalized number:
exponent的bits 全為0
nomalized number:
exponent 部份非0, 此時fraction部份若1011000xxxx...., 但實際上為.1011000xxxx...., 因為在denomalized的狀況下, 實際上是一個整數部份為一的二進位小數
```Clike
/* too small */
if (x < 2 - pow(2, Y0) - 23) {
exp = 0;
frac = 0;
```
因為他是太小的狀況, 意思是說數字小於float可表達的範圍, 因為是求 $2^x$ 所以僅考慮此數為正之狀況
此時數字為 denomalized 那denomalized 可表達的最小數字為 fraction 部份僅最後一位 == 的狀況, 因此此數為 $2^{-23} \times 2^{-126} = 2^{-149}$
$2^{-23}$ 為exponent部份
$2^{-126}$ 為fraction部份
所以要讓 x < 2 - pow(2, Y0) - 23 = -149
得 -149 + 23 - 2 = -128 = $-2^{7}$ = - pow(2, Y0)
因此 Y0 = 7
```Clike
/* denormalize */
else if (x < Y1 - pow(2, Y2)) {
exp = 0;
frac = 1 << (unsigned) (x - (2 - pow(2, Y3) - Y4));
```
最小的nomalized 數為 $2^{-126}$, 小於此數便為denomalized
故 Y1 - pow(2, Y2) = -126
離126 最近的 pow(2, Y2) = 128, 得Y2 = 7, Y1 = 2
denomalized 數前面的bias 為 $2^{-126}$, 加上fraction 部份最末位為 $2^{-23}$
故x 在做位移的時候需要把這個量補回來 因此(2 - pow(2, Y3) - Y4) = -126 -23 = -149
發現跟/* too small */ 狀況一模一樣
得 Y3 = 7, Y4 = 23
```Clike
/* normalized */
} else if (x < pow(2, Y5)) {
exp = pow(2, Y6) - 1 + x;
frac = 0;
```
最大的normalized 數為 $(2−2^{-23}) \times 2^{127} = 2^{128} - 2^{104} < 2^{128}$
故x < 128 = pow(2, Y5), 得Y5 == 7
根據IEEE 754 浮點數的 actual exponent = exponent $- (2^{k-1} - 1)$
其中k 為expnoent 的位數
因此現在exp 要把剪掉的$(2^{k-1} - 1) = (2^{7} - 1) = 127$加回來
因此Y6 == 7
```Clike
/* too large */
} else {
exp = Y7;
frac = 0;
}
```
此部份為表示INF, 根據IEEE 754, INF為exponent 為exponent 部份全為1, fraction部份全為0
因此得選一個共有 8 位 1 的數, 因此 Y7 == 0xFF
:::info
延伸題: 給定一個單精度的浮點數值,輸出較大且最接近的 $2^x$ 值,需要充分考慮到邊界
:::
根據這個題目寫完的程式 [link](https://github.com/vulxj0j8j8/outputClosePowerOf2)
只考慮數字為正的狀況下,那麼僅需考慮exp的部份,並且把frac部份全部歸零,就可以找到最接近且較大的2^{x}值
因為最大的float 能代表的數字為0 | 1111 1110 | 111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 |
float 最大能代表$2^x$的 x 為127
且此數的位元表達為0 | 1111 1110 | 000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 |
所以若數字大於$2^{127}$ 的話就得輸出 "over the bound"
## 第三周測驗題 第1題
```Clike
#include <stdint.h>
/* A union allowing us to convert between a double and two 32-bit integers.
* Little-endian representation
*/
typedef union {
double value;
struct {
uint32_t lsw;
uint32_t msw;
} parts;
} ieee_double_shape_type;
/* Set a double from two 32 bit ints. */
#define INSERT_WORDS(d, ix0, ix1) \
do { \
ieee_double_shape_type iw_u = { \
.parts.msw = ix0, \
.parts.lsw = ix1, \
}; \
(d) = iw_u.value; \
} while (0)
//line 25 is designated initializer
//the following is the intro. of designated initialer
//https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Designated-Inits.html
/* Get two 32 bit ints from a double. */
#define EXTRACT_WORDS(ix0, ix1, d) \
do { \
ieee_double_shape_type ew_u; \
ew_u.value = (d); \
(ix0) = ew_u.parts.msw; \
(ix1) = ew_u.parts.lsw; \
} while (0)
static const double one = 1.0, tiny = 1.0e-300;
double ieee754_sqrt(double x)
{
double z;
int32_t sign = 0x80000000;
uint32_t r, t1, s1, ix1, q1;
int32_t ix0, s0, q, m, t, i;
EXTRACT_WORDS(ix0, ix1, x);
/* take care of INF and NaN */
if ((ix0 & KK1) == KK2) {
/* sqrt(NaN) = NaN, sqrt(+INF) = +INF, sqrt(-INF) = sNaN */
return x * x + x;
}
/* take care of zero */
if (ix0 <= 0) {
if (((ix0 & (~sign)) | ix1) == 0)
return x; /* sqrt(+-0) = +-0 */
if (ix0 < 0)
return (x - x) / (x - x); /* sqrt(-ve) = sNaN */
}
/* normalize x */
m = (ix0 >> 20);
if (m == 0) { /* subnormal x */
while (ix0 == 0) {
m -= 21;
ix0 |= (ix1 >> 11);
ix1 <<= 21;
}
for (i = 0; (ix0 & 0x00100000) == 0; i++)
ix0 <<= 1;
m -= i - 1;
ix0 |= (ix1 >> (32 - i));
ix1 <<= i;
}
m -= KK3; /* unbias exponent */
ix0 = (ix0 & 0x000fffff) | 0x00100000;
if (m & 1) { /* odd m, double x to make it even */
ix0 += ix0 + ((ix1 & sign) >> 31);
ix1 += ix1;
}
m >>= 1; /* m = [m/2] */
/* generate sqrt(x) bit by bit */
ix0 += ix0 + ((ix1 & sign) >> 31);
ix1 += ix1;
q = q1 = s0 = s1 = 0; /* [q,q1] = sqrt(x) */
r = 0x00200000; /* r = moving bit from right to left */
while (r != 0) {
t = s0 + r;
if (t <= ix0) {
s0 = t + r;
ix0 -= t;
q += r;
}
ix0 += ix0 + ((ix1 & sign) >> 31);
ix1 += ix1;
r >>= 1;
}
r = sign;
while (r != 0) {
t1 = s1 + r;
t = s0;
if ((t < ix0) || ((t == ix0) && (t1 <= ix1))) {
s1 = t1 + r;
if (((t1 & sign) == sign) && (s1 & sign) == 0)
s0 += 1;
ix0 -= t;
if (ix1 < t1)
ix0 -= 1;
ix1 -= t1;
q1 += r;
}
ix0 += ix0 + ((ix1 & sign) >> 31);
ix1 += ix1;
r >>= 1;
}
/* use floating add to find out rounding direction */
if ((ix0 | ix1) != 0) {
z = one - tiny; /* trigger inexact flag */
if (z >= one) {
z = one + tiny;
if (q1 == (uint32_t) 0xffffffff) {
q1 = 0;
q += 1;
} else if (z > one) {
if (q1 == (uint32_t) KK4)
q += 1;
q1 += 2;
} else
q1 += (q1 & 1);
}
}
ix0 = (q >> 1) + 0x3fe00000;
ix1 = q1 >> 1;
if ((q & 1) == 1)
ix1 |= sign;
ix0 += (m << KK5);
INSERT_WORDS(z, ix0, ix1);
return z;
}
```
### 思考及想法
首先先從老師給的[wiki page](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methods_of_computing_square_roots#Binary_numeral_system_(base_2))下手
我們得讓 $err(x, y) = y - x^2$ 儘量為零
將上式改為
$err(x+p, y) = y - (x+p)^2$
$=$ $y - (x^2+ 2 \cdot x \cdot p + p^2)$ $=$ $err(x, y) - p \cdot (2 \cdot x +p)$
儘量讓 $0 =$ $err(x, y) - p \cdot (2 \cdot x +p)$ 成立
假設 $x$ $>>$ $p$
$x^2$ 是 y的估計值
:::danger
用 LaTex 語法改寫數學式
:notes: jserv
:::
以下程式碼是以二進位進行計算
其中下面的 bit 參數是$e \cdot e$的部份, 因為現在是一個位數一個位數分別抓出來做運算, 所以$e \cdot e$是 $2^m$ ===>e 是這一個位數的估計值
因此得到bit 參數為$(2^m)^2$ $=$ $4^m$
res參數是 $2 \cdot r \cdot e$ ===>r 是目前精準到的數字
```clike
short isqrt(short num) {
short res = 0;
short bit = 1 << 14; // The second-to-top bit is set: 1 << 30 for 32 bits
// short type is 2 bytes which is 16 bits
// THe second-to-top bit is the highest bit of short becuase the first bit of short is for the sign
// "bit" starts at the highest power of four <= the argument.
while (bit > num)
bit >>= 2; //var bit is 4^m so it moves two bits(which is mutiply 4) each time
while (bit != 0) {
if (num >= res + bit) {
num -= res + bit;
res = (res >> 1) + bit;
}
else
res >>= 1;
bit >>= 2;
}
return res;
}
```
macro 裏面要用 do{} while(0)的原因是要避免不小心產生的語法錯誤
:::info
這術語叫做 dangling-else,去找更詳盡的資料並舉例
:notes: jserv
:::
<s>
詳細可見現下連結
http://kezeodsnx.pixnet.net/blog/post/28380463-do-...-while%280%29-for-多語句的macro </s>
union 特性:
union裏面的變數是共用同一個記憶體
資料是以最後一筆寫入變數為主,所以只能取出最後一筆寫入的資料, 寫入新的資料後, 前面的資料會被洗掉
分配的記憶體是以最大的資料結構做為分配的依據。
0x80000000 => binary: 10000000000000000000000000000000
:::info
然後時間都快結束了還是做不出來........
:::
### 測驗 `2`
考慮到下方函式 `shift_right_arith` 和 `shift_right_logical` 分別表示算術右移和邏輯右移,請嘗試補完程式碼。可由 `sizeof(int) * 8` 得知整數型態 `int` 的位元數 `w`,而位移量 `k` 的有效範圍在 0 到 `w - 1`。
```Clike
#include <stdio.h>
int shift_right_arith(int x, int k) {
int xsrl = (unsigned) x >> k;
int w = sizeof(int) << P1;
int mask = (int) -1 << (P2);
if (x < 0)
return xsrl P3 mask;
return xsrl;
}
unsigned shift_right_logical(unsigned x, int k) {
unsigned xsra = (int) x >> k;
int w = sizeof(int) << P4;
int mask = (int) -1 << (P5);
return xsra P6 P7;
}
```
根據定義知道
算術右移: 再最高位補sign位置相同的數字(若負補1, 若正補0)
邏輯右移: 最高位補0, 最低位丟掉
```Clike
int shift_right_arith(int x, int k) {
int xsrl = (unsigned) x >> k;
int w = sizeof(int) << P1;
int mask = (int) -1 << (P2);
if (x < 0)
return xsrl P3 mask;
return xsrl;
}
```
不確定 (unsigned) x >> y 左邊補位的行為, 但是確定右邊位被捨棄
此為題目提示的`sizeof(int) * 8` 向左位移等同式子乘上 $2^k$
P1 == k, 因此 P1 == 3
```Clike
int w = sizeof(int) << P1;
```
若int 為 4 bytes則(int) -1 其補數為11111111111111111111111111111111
共3個1
```Clike
int mask = (int) -1 << (P2);
```
根據這邊可以現 mask的目的是要讓x 為負的時候, 右移補上的位全部變成1
故得知mask只需要蓋到右移新補上的位就好, 並且要透過 | 讓不管xsrl再該位是 0 或 1 都變成 1
得知mask 需位移w - k位
```Clike
if (x < 0)
return xsrl P3 mask;
```
邏輯位移的部份
```Clike
unsigned shift_right_logical(unsigned x, int k) {
unsigned xsra = (int) x >> k;
int w = sizeof(int) << P4;
int mask = (int) -1 << (P5);
return xsra P6 P7;
}
```
此為題目提示的`sizeof(int) * 8` 向左位移等同式子乘上 $2^k$
P4 == k, 因此 P4 == 3
```Clike
int w = sizeof(int) << P4;
```
```Clike
int mask = (int) -1 << (P5);
return xsra P6 P7;
```
因為邏輯右移所有補的新位皆為 0, 因此 mask的作用是要讓所以新補的位都為0
故可得知 P5 = w - k, P6 = &, P7 = ~mask
### 延伸題目: 在 x86_64 和 Aarch32/Aarch64 找到對應的指令,並說明其作用和限制
參考ARM的[document](http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.dui0489h/CIHDDCIF.html)
Rm http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.dui0489c/CIHEBCBI.html
Operand2 http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.dui0489f/CIHFDDHB.html
算術右移為ASR
邏輯右移為LSR
其中並無算術左移指令, 僅有邏輯左移, 應是因為邏輯左移及計算左移其行為一樣, 故無需多一個指令
### 測驗 `三`
考慮到某些實數的二進位表示形式如同 $0.yyyyy...$ 這樣的無限循環小數,其中 $y$ 是個 $k$ 位的二進位序列,例如 $\frac{1}{3}$ 的二進位表示為 $0.01010101...$ (y = `01`),而 $\frac{1}{5}$ 的二進位表示為 $0.001100110011...$ (y = `0011`),考慮到以下 y 值,求出對應的十進位分數值。
* y = `010011` => $\frac{19}{X1}$
* y = `101` => $\frac{5}{X2}$
* y = `0110` => $\frac{2}{X3}$
### 解題
因為是循環小數所以其實可以以 $\sum_{n = 1}^{\infty} g(x)$ 表達, 其中 $g(x)$ 為以$x^{-a}$ 所組成的多項式
例如$\frac{1}{3}$ 的二進位表示為 $0.01010101...$ 他的$\Sigma$ 可表達為$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-2k}$
並可以無窮等比及數和公式求解$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-2k} = \frac{2^{-2k}(2^{-2\times\infty} -1)} {2^{-2} - 1} = \frac{1} {3}$
* y = `010011` 可表達為$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} (2^{-(6k-4)} + 2^{-(6k-1)} + 2^{-6k}) = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k} \times 2^{4} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k} \times 2^{1} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k}$
套入等比級數和公式可得 $\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k} \times 2^{4} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k} \times 2^{1} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-6k} = (2^{4} + 2^{1} + 1) \frac{-2^{-6}} {2^{-6} - 1} = 0.3016$
$19 \div 0.3016 = 63$
* y = `101` $\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-(3k-2)} + 2^{-3k} = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-3k} \times 2^{2} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-3k} = (2^{2} + 1) \frac{-2^{3}} {2^{-3} - 1} = 0.7143$
$5 \div 0.7143 = 7$
* y = `0110` $\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-(4k-2)} + 2^{-(4k-1)} = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-4k} \times 2^{2} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} 2^{-4k} \times 2^{1} = (2^{2} + 2) \frac{-2^{4}} {2^{-4} - 1} = 0.4$
$2 \div 0.4 = 5$
## 因為自動飲料機而延畢的那一年
身為一個機械係學生他所經歷的事情我也有遇到,近期也正進行開發電動車的專案,一群學生什麼都不懂要從無拼出一台電動車,焊接什麼的都沒學過也是非常辛苦。不過好的事我有金錢支持還有一群隊友可以幫忙。當初會選擇雙主修也是對自己有期許希望能一個人幹出一台機器的能力
## 目前三周心得
不管怎麼讀進度都獨不完,考試每次都幾乎在完全看不懂的狀態作答,不管怎樣分數都很糟糕作業也總是看不懂要求,跟從何下手。
太多東西都是之前從來沒有學過的Linux, gcc, gdb, makefile, etc
修這堂課是對自己大學生活的一個期許
雖然曾經萌生退選的想法但恍神回來時間已經過了。
對於目前自己的狀態真的很心死,但也不知道怎麼辦。接下來其他科的做也會出來。只能走一步算一步了
## Week 3 Note
program counter == instruction pointer
CPU內部有 micro-architecture
ILP: 指令級平行處理
是指微處理器再同個時間能處理多少道指令
指令的操作順序

Fetch 擷取指令
真正耗時的點是在記憶體存取
如果都在暫存器裏面運作就會快很多
Execution Unit:
* ALU (Arithmetic-Logic Unit): 算術邏輯單元
布林帶數操作, goto
* MMU (Memory Management):
將虛擬記憶體轉換為實體記憶體
從virtual memory轉換為 physical memory的時候, 讓共享的資料的資料對到相同的physical memory
Access control
I-cache: instruction cache
D-cache: data cache
RAM: Random Access Memory
隨機存取的, 所以存在RAM裡面的任何位置讀取速度都差不多
Cache: 循序的
每次存取的量是一個cache line
pipelinf hazard:
* structural Hazard: 因為得等速度較慢的周邊, 會導致顯著延遲, 但是不會導致錯誤。硬體資源不足時所造成的為害,因為要平行處理某些動作,如讀寫記憶體,但是該資源已經正在使用,所以造成衝突。
* Data Hazrad: 發生在資料之間彼此有相關的地方,因為資料的讀取和寫入的先後順序而造成資料的讀取錯誤。發生的時間RAW, WAR, WAW。當將資料寫入之後又要再去讀取該資料時會發生資料錯誤,因為第一個指令可能還沒有將資料寫進去。讀資料之後馬上把資料再寫進去也會造成問題,因為資料可能還沒有讀到新的資料就已經被寫進去,所以讀到的資料是新的資料而不是舊的資料。當兩個值要寫入時,原本要先寫進去的值變成後來才寫進去,造成資料錯誤
* Control Hazard: 發生在處理器被要求作branch時,要等到條件是否滿足才知道要取得的下一個指令在哪裡,而在pipeline的處理過程中可以先預測要取得的下一個指令,如果判斷錯誤造成的暫存器資料的改變,需要還原回來。
superscalar 讓電腦可以把一個指令分成很多指令分別處理, 但是若指令之間有相依性, 則就沒辦法分開處理, 一定得上一道指令處理完, 才能處理下一道
可以用VLIW的方式解決相依的問題, 把相依的指令一次全部塞到 instruction word裏面
或者發現裏面有不用的指令, 直接移除就刪去沒用的指令
cmolve d, b
out-of-order(OOO): 對於指令順序重新排列, 效率可能比較高
in-order: 省電, 但效率可能比較低
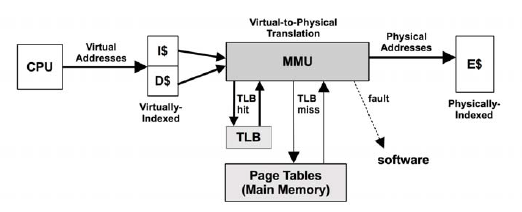
MMU: 收到 I-cache, d-cache指令, 將虛擬記憶體轉成實體記憶體
TLB: 加速MMU, 也是種cache
數狀結構: 電腦難以從前面的行為推測接下來的行為
loop unrolling搭配 prefetch可以有最佳化效果
prefetch: [link](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r89004/hive/cache/page_2.html)
預先將資料放進cache裏面, 不用等到需要的時候再去找RAM拿資料
## 參考資料
http://www.azillionmonkeys.com/qed/sqroot.html
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

