---
title: 演算法
type: slide
tags: 資芽簡報
---
# 演算法介紹
2023 資訊之芽北區 Py 班
---
**Outline**
- 時間複雜度
- 演算法是什麼
- Python 資料型態之演算法
- 奇葩的演算法
----
台大資工系有兩門魔王等級的演算法必修
- 資料結構與演算法
- 演算法設計與分析
為了學演算法
每個台大資工的學生都至少花了一整年
每週三小時上課 N 小時寫作業
這樣還只能算是「稍微懂一點演算法」而已
----

----
這堂課很難,非常難
~~雖然可能問題是我講課很爛啦~~
我沒有一定要講完全部內容,隨時歡迎打斷我
後面一整排助教全部都被上述兩門課虐過了
也可以問他們
----
何謂演算法?
- 演算法(Algorithm):一個詳細的、逐步的執行過程
- 每個步驟都被詳細且嚴謹地定義
- 保證會終止(不會跑進無窮迴圈之類的)
- 與程式語言無關,演算法是數學概念,可以用任何一個程式語言寫出來
- 不精確地說,可以把**演算法**理解成一支程式或者完成某件事情的步驟
----
- 問題(Problem):一個嚴謹定義輸入與輸出的陳述
- 舉例來說,如果我們要算一個 list 的總和
- 輸入:一個只有整數的 list
- 輸出:該 list 所有數字的總和
- 如果一個演算法保證在任何問題輸入下都可以得出問題輸出,則可以說這個演算法「解決」(solve)該問題
----
一個算 list 總和的程式
```python=
for v in list1:
summation += v
print(summation)
```
這個程式實作了什麼演算法?
這個演算法在所有可能輸入下都是對的嗎?
---
## 時間複雜度是什麼
我們除了會演算法的正確性以外,我們也常關心這個演算法有多「好」
通常會用兩個指標來衡量一個演算法有多「好」
* 使用的**時間**
* 使用的**空間**
今天的課程主要會先著重在「時間」部份
「空間」的部分有空再說
----
但是直接測量一個演算法的執行時間通常不是很實際的作法
----
再看一次這個算 list 總和的程式
```python=
for v in list1:
summation += v
print(summation)
```
這個程式會跑多久?
----
|code|次數|時間|
|-|-|-|
|next(i)|n-1|$t_1$
|summation += v | n|$t_2$
|print(summation)|1|$t_3$
n 是 list 的長度
總共耗時就是每一個code的時間加總
$(n-1)t_1+n(t_2)+t_3$
----
會影響一支程式執行時間的因素可能有:
- 機器(計算能力)
- 環境(溫度、濕度、被宇宙射線打到)
- 輸入( `[1, 1, 1]` 還是 `[10000, 10000, 10000]`?)
- 其他...
----
即使如此,我們還是希望能夠衡量一個演算法的執行效率
因此需要一個方法,能夠衡量演算法的執行效率,且不被以上因素影響
----
但... 等等
為什麼我們需要在乎時間與空間的使用量?
----
- 電腦很快,但不是無限地快
- 記憶體很便宜,但不是免費
---
## 漸近符號
<img src="https://miro.medium.com/max/1200/1*j8fUQjaUlmrQEN_udU0_TQ.jpeg" alt="drawing" width="600"/>
----
先舉個例子,假設你要讀兩科期末考,你會
1. 從書包中翻出國文、數學課本課本(10sec * 2)
2. 找到鉛筆盒(20sec)
3. 突然覺得桌面好髒沒辦法讀書,整理桌面(1hr)
4. 房間好亂,乾脆一起整理一下(2hr)
5. 讀書(30min * 2)
6. 肚子餓了,吃晚餐(1 hr)
你總共用了 5hr 40sec,其中 1hr 真的在讀書
----
但如果你有十科呢?
1. 從書包中翻出國文、數學課本課本(10sec * 10)
2. 找到鉛筆盒(20sec)
3. 突然覺得桌面好髒沒辦法讀書,整理桌面(1hr)
4. 房間好亂,乾脆一起整理一下(2hr)
5. 讀書(30min * 10)
6. 肚子餓了,吃晚餐(1 hr)
你總共用了 10hr 2min,其中 5hr 真的在讀書
----
如果你有一百科要考呢?$N$ 科要考呢?
你會用 $(4 + N/2)hr \quad (10N + 20)sec$
無論你花多久時間整理房間,只要讀的科目夠多,最後都主要是由 $N$ 決定你要花多少時間!
----
接著我們來看數學吧
----
漸近符號在分析演算法效率上非常有用
以下是漸近符號家族
* $O(g(n))$
* $\Omega(g(n))$
* $\Theta(g(n))$
* $o(g(n))$
* $\omega(g(n))$
----
### $O(g(n))$ - Big-Oh Notation
中文唸作大O符號
今天只會講這個,其他有興趣可以下課討論
----
舉個例子,假設一個演算法的執行時間(或者所需步驟數)可以用
$$
T(n) = 2n^2 + n + 10
$$
表示,其中 $n$ 為輸入的大小
----
$$
T(n) = 2n^2 + n + 10
$$
當$n$夠大的時候,除了$2n^2$以外的其他項的影響可以忽略
* $n = 10, T(n) = 200 + 10 + 10 = 220$
* $n = 100, T(n) = 20000 + 100 + 10 = 20110 \approx 2 \cdot 100^2$
* $n = 1000, T(n) = 2000000 + 1000 + 10 = 2001010 \approx 2 \cdot 1000^2$
----
這時我們會寫作 $T(n) = O(n^2)$
沒那麼精確地說,使用 big O notation 時,我們會把影響比較小的項以及係數省略
----
更多例子
* $T(n) = n + 10 \implies T(n) = O(n)$
* linear time 線性時間
* $T(n) = 100n^2 + 5 + \frac{1}{n} \implies T(n) = O(n^2)$
* quadratic time 平方時間
* $T(n) = 8763 \implies T(n) = O(1)$
* constant time 常數時間
* $T(n) = 2^n \implies T(n) = O(2^n)$
* exponential time 指數時間
---
### 補充
大O符號有精確的數學定義,其中兩個等價定義如下,長到塞不下
$$
f(n) = O(g(n)) \iff \limsup_{n \to \infty} |\frac{f(n)}{g(n)}| < \infty
$$
$$
f(n) = O(g(n)) \iff \exists c > 0, n_0 > 0\\
\text{such that} \ \forall n > n_0, |f(n)| \leq |cg(n)|
$$
----

----
用人話來說就是對所有夠大的 $n$,$f(n)$ 的大小會被 $g(n)$ 的某個常數倍壓住
---
### 舉個例子

----
假設你把備審資料放在某個置物櫃裡面,但你忘記它在哪個置物櫃中,因此你需要一一檢查每個置物櫃。假設有 $n$ 個置物櫃,請問最壞的狀況下,你需要花多少時間才能找到備審資料?
* 假設你檢查一個置物櫃需要一秒鐘
----
方法:依序檢查
```python=
for i in range(n):
if data_is_in(lockers[i]):
return i
```
----
最壞的狀況:東西在最後一個你檢查的置物櫃
因此最壞需要花$n$秒
我們會說這個方法需要花費$O(n)$時間
----
* Q1: 如果今天是你阿嬤幫你翻櫃子,每翻一個櫃子需要花費 10 秒鐘,而且她會在開始翻櫃子以前花 5 分鐘確認你吃飽了沒。在這個情況下最壞需要花 $10n+300$ 秒,用 big O notation 表示的話,這個方法會花費 $O(?)$ 時間?
----
* Q2: 翻櫃子世界紀錄保持人來幫你檢查櫃子,他每翻一個櫃子只需要 0.1 秒,用 big O notation 表示的話,這個方法會花費 $O(?)$ 時間?
----
A: 都是$O(n)$時間(線性時間)
----
有個超人可以馬上知道你的備審資料在哪個櫃子裡。
他每次使用這個超能力時需要 10 秒鐘充能。用 big O notation 表示的話,這個方法會花費 $O(?)$ 時間?
----
A: $O(1)$ 常數時間,因為跟輸入大小 $n$ 無關
---
### 生活化的例子2
假設現在這 $n$ 個櫃子上鎖了,每個櫃子都有一把對應的鑰匙,這 $n$ 把鑰匙全都混在一個袋子裡,你不知道哪把鑰匙對應到的櫃子是哪一個。
你每次只能用一把鑰匙去試一個櫃子,假設這個過程需要一秒鐘。打開櫃子的過程時間可以忽略不計。
----
* 每個櫃子最爛會試到 $n$ 把鑰匙,所以每開一個櫃子需要 $n$ 秒
* 總共有 $n$ 個櫃子,這樣加起來總共需要 $n^2$ 秒
* 用 big O notation 來表示,我們會需要 $O(n^2)$ 時間
---
## 時間複雜度 - Python
以下給出幾個 Python 指令相對應的時間複雜度
----
Python 常見的一些指令的複雜度
- 加減乘除 $O(1)$
- 存取list裡面的一個元素 $O(1)$
- traverse一個list $O(n)$
- append/pop list的最後面 $O(1)$
- insert/delete list最前面的元素 $O(n)$
- sort一個list $O(n\log n)$
- 存取dict某個key對應的value $O(1)$(?)
----
回到最一開始的例子
```python=
for i in l:
sum += i
print(sum)
```
這個程式是 $O(n)$
因為需要traverse所有元素
----
```python=
sum = 0
for i in range(n):
sum += i
if sum > 1000:
break
```
這個程式是$O(?)$
<span>$O(1)$<!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1" --></span>
----
```python=
for i in range(len(l)):
m = min(l)
l[i] += m
```
這個程式是$O(?)$
<span>$O(n^2)$<!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1" --></span>
---
### Python 的 list, set, dict
[source](https://www.ics.uci.edu/~pattis/ICS-33/lectures/complexitypython.txt)
----
### List
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | ------------ | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Index | `l[i]` | O(1) | |
| Store | `l[i] = 0` | O(1) | |
| Length | `len(l)` | O(1) | |
| Append | `l.append(5)`| O(1) | |
| Pop | `l.pop()` | O(1) | |
| Clear | `l.clear()` | O(1) | `l = []` |
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Slice | `l[a:b]` | O(b-a) | `l[1:5]`:O(l), `l[:]`:O(len(l)-0)=O(N) |
| Extend | `l.extend(...)`| O(len(...)) | 取決於延長多少 |
| Construction | `list(...)` | O(len(...)) | 取決於 iterable 的長度 |
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Insert | `l[a:b]` = ... | O(N) | |
| Delete | `del l[i]` | O(N) | 取決於 `i`,最慘是 O(N) |
| Containment | `x in l`, `x not in l`| O(N) | linear search |
| Copy | `l.copy()` | O(N) | `l[:]`|
| Remove | `l.remove(...)`| O(N) | |
| Pop | `l.pop(i)` | O(N) | `l.pop(0)`: O(N) |
| Extreme value | `min(l)` / `max(l)`| O(N) | linearly search |
| Reverse | `l.reverse()` | O(N) | |
| Iteration | `for v in l` | O(N) | |
----
### Set
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Length | `len(s)` | O(1) | |
| Add | `s.add(5)` | O(1) | |
| Containment | `x in s`, `x not in s`| O(1) | list: O(N) |
| Remove | `s.remove(..)` | O(1) | list: O(N) |
| Discard | `s.discard(..)`| O(1) | |
| Clear | `s.clear()` | O(1) | `s = set()` |
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Construction | set(...) | O(len(...)) | 依賴於 iterable 的長度 |
| check ==, != | s != t | O(len(s)) | |
| <=/< | s <= t | O(len(s)) | issubset |
| >=/> | s >= t | O(len(t)) | issuperset s <= t == t >= s |
| Union | s | t | O(len(s)+len(t)) | |
| Intersection | s & t | O(len(s)+len(t)) | |
| Difference | s - t | O(len(s)+len(t)) | |
| Symmetric Diff| s ^ t | O(len(s)+len(t)) | |
| Iteration | for v in s: | O(N) | |
| Copy | s.copy() | O(N) | |
----
整體而言,set 比 list 多了許多 O(1) 的操作
不用記得順序使得 set 更有效率
然後 set 是用 hash table 實作的
----
### Dict
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| Index | `d[k]` | O(1) | |
| Store | `d[k] = v` | O(1) | |
| Length | `len(d)` | O(1) | |
| Delete | `del d[k]` | O(1) | |
| get/setdefault| `d.get(k)` | O(1) | |
| Pop | `d.pop(k)` | O(1) | |
| Clear | `d.clear()` | O(1) |`s = {}` |
----
| Operation | Example | Complexity Class | Notes |
| ------------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ----------------------------- |
| View | `d.keys()` | O(1) | |
| View | `d.values()` | O(1) | |
| Construction | `dict(...)` | O(len(...)) | |
| Iteration | `for k in d:` | O(N) | |
----
Dict 有更多的 O(1) 操作
問題:所以 dict 一定比 list 快,對嗎?
---
## 時間複雜度列表
[常見時間複雜度列表](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%97%B6%E9%97%B4%E5%A4%8D%E6%9D%82%E5%BA%A6#%E5%B8%B8%E8%A7%81%E6%97%B6%E9%97%B4%E5%A4%8D%E6%9D%82%E5%BA%A6%E5%88%97%E8%A1%A8)
---
## 常見的演算法
接下來會介紹一些有趣的演算法
---
### 二分搜尋法
給定一個排序好的數列,決定給定目標是否存在以及其位置
Eg. `[1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]`,5有沒有在這裡面?
玩過「終極密碼」嗎?
----
1. 一開始先從中間切一刀
1. 看中間那個數是否是我們要的
1. 如果是,那就做完了
1. 如果中間那個數比我們要的小,就往右邊再切一刀並回到2.
1. 如果中間那個數比我們要的大,就往左邊再切一刀並回到2.
1. 切到最後還是沒找到,那我們要的數字不在這個數列裡面
----
```python=
def binary_search(arr, left, right, hkey):
while left <= right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if arr[mid] == hkey:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < hkey:
left = mid + 1
elif arr[mid] > hkey:
right = mid - 1
return -1
```
----
#### 時間複雜度分析
* 我們可以去計算總共要切幾刀
* 每次切一刀下去會淘汰掉這個數列一半的元素。
* 也就是說,假設一開始數列大小為$n$,切完一刀後只會剩下$n/2$這麼多需要檢查。
* 只剩下一個元素時直接檢查就好。
* 因此大約需要切$\log n$這麼多刀
總結來說,時間複雜度為$O(\log n)$
---
### 泡沫排序
一個簡單暴力的排序方法
----
```python=
def bubble_sorted(l):
n = len(l)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n - i - 1):
if l[j] > l[j + 1]:
l[j], l[j + 1] = l[j + 1], l[j]
```
----
簡單算一下可以發現中間的 nested for-loop 總共會跑
$$
1 + 2 + ... + (n-1) = n(n-1)/2
$$
這麼多次,因此時間複雜度為 $O(n^2)$
---
### 沒那麼簡單演算法介紹-合併排序
Mergesort
----
使用分治法(divide and conquer)
1. 把list分兩半
2. 每一半分別排序(還是用merge sort)
3. 兩半合併
----

----
```python=
def merge(left, right):
output = []
l, r = 0, 0
len_l, len_r = len(left), len(right)
while l<len_l and r<len_r:
if left[l] <= right[r]:
output.append(left[l])
l+=1
else:
output.append(right[r])
r+=1
if l<len_l:
output.extend(left[l:])
if r<len_r:
output.extend(right[r:])
return output
```
----
```python=
def merge_sort(arr):
l = len(arr)
if l <= 1: return arr
left, right = arr[:l//2], arr[l//2:]
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
return merge(left, right)
```
----
時間複雜度
`merge`的部分是O(n)
總共合併$O(\log n)$次
可以算出$T(n)=O(n\log n)$
---
### 簡單演算法介紹-計數排序
Counting Sort
----
剛剛前面提到的 sort 都是比較排序(comparison based)
比較排序的時間下界是$n\log n$
如果要更快的話,要用空間換時間
----
### Counting Sort
- 只能 sort 一群知道上下限的整數
- 適合最大最小值差距不大的數據
----
1. 開一個新的陣列,用來記每個元素出現幾次
2. traverse 原本的陣列,就可以把元素 sort 到該出現的位置
----

----
```python=
def counting_sort(arr):
a_min = min(arr)
a_max = max(arr)
count = [0 for _ in range(a_max-a_min+1)]
for i in arr:
count[i-a_min] += 1
for i in range(len(count)):
if i == 0: continue
count[i] += count[i-1]
output = [0 for _ in range(len(arr))]
for i in arr:
output[count[i-a_min]-1] = i
count[i-a_min] -= 1
return output
```
----
時間複雜度
可以看出counting sort只有做traverse,沒有遞迴。
traverse `arr`要花$O(n)$時間
traverse `count`要花$O(k)$時間 ($k=$最大最小值的差)
總共的時間複雜度是$O(n+k)$
----
空間複雜度
因為需要多開一個`count`的陣列,加上原本要排序陣列的,總共需要的空間是$O(n+k)$
---
所以 Python 用的 sort 是哪個?
----
不是上述三種 sorting
而是一種名為 [Timsort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timsort) 的演算法
但 Timsort 非常複雜,所以就不多講了
---
### 龜兔賽跑演算法
用於判斷一個鍊結串列(linked-list)是否有環

----
* Floyd Cycle Detection Algorithm
* Floyd's Tortoise and Hare Algorithm
----
#### What is a linked-list?
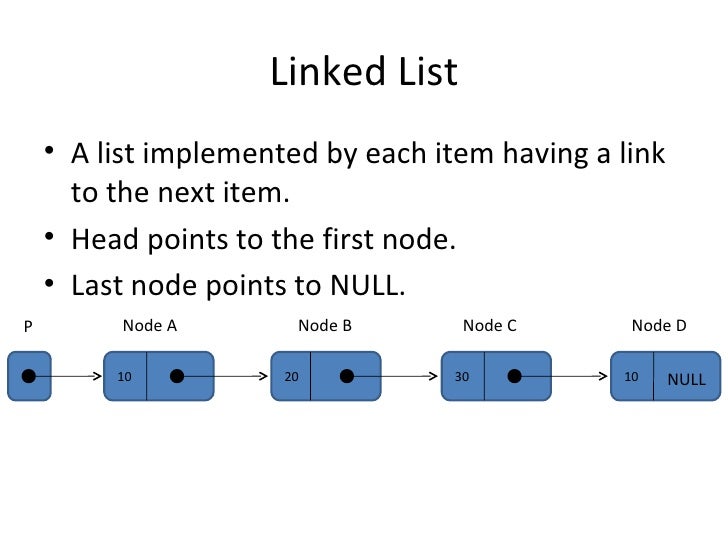
----
這就叫做一個有環的 linked-list
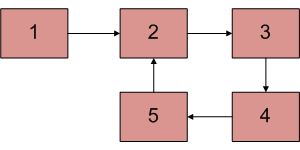
----
演算法:
1. 烏龜和兔子一開始都在起點
2. 烏龜走一步,兔子走兩步,然後做以下檢查:
* 如果兔子抵達終點,則此鍊結串列無環
* 如果兔子和烏龜相遇,則此鍊結串列有環
* 如果都不是,再做一次2.
----
#### 正確性分析
鍊結串列無環的情況顯然正確(因為兔子一定走得到終點)
以下假設鍊結串列有環
----
- 假設鍊結串列長度為 $N$ ,環的大小是 $C>0$
- 每做一次步驟2. 烏龜和兔子的距離會增加1
- 當烏龜和兔子都進到環裡以後,最多再走 $C$ 次步驟2.,他們的距離總會變成 $C$ 的某個整數倍,這時烏龜和兔子就會相遇
----
#### 時間複雜度分析
鍊結串列無環的情況比較簡單,兔子走到終點大略需要做 $N/2$ 次步驟2.,因此是 $O(N)$
鍊結串列有環的狀況下,烏龜進到環裡面以後最多只能再走一圈,因此時間複雜度為 $O(N)$
---
## 稍微更理論一點點的演算法
----
接著我們來看個有趣的問題
高中有學過線性規劃對吧?
----

([source](https://math.ymhs.tyc.edu.tw/chenjt99/ScrClass/1051/%E9%AB%98%E4%BA%8C/%E7%BF%92%E4%BD%9C%E7%94%B2/%E7%BF%92%E4%BD%9C%E7%94%B22-2%20%E7%B7%9A%E6%80%A7%E8%A6%8F%E5%8A%83.pdf))
----
在 1974 年,Leonid Khachiyan 證明了線性規劃可以在多項式時間內解出來
目前最常見的解線性規劃的演算法叫做 Interior-point method
(還有一個也很常見的東西叫做 Simplex algorithm,但它是 exponential time 的)
----
有時我們可能只在乎格子點
(也就是解是整數的狀況)
出乎意料的,當解只能是整數時,這個問題會變得非常難
----

([source](https://math.ymhs.tyc.edu.tw/chenjt99/ScrClass/1051/%E9%AB%98%E4%BA%8C/%E7%BF%92%E4%BD%9C%E7%94%B2/%E7%BF%92%E4%BD%9C%E7%94%B22-2%20%E7%B7%9A%E6%80%A7%E8%A6%8F%E5%8A%83.pdf))
----
什麼是「非常難」?
簡單來說,我們目前不知道是否存在任何可以在多項式時間解開的此問題的方法
(這個定義非常不嚴謹,甚至有些誤導,詳細可以看[維基百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NP-hardness))
----
但這樣太慢了,所以怎麼辦?
- 亂猜、擲筊、賽到賺到:randomized algorithm
- 拿個粗估的值,用精準度換時間:approximation algorithm
----
事實上,許多重要的問題都可以用整數線性規劃表示
(進貨量要多少、工廠要設在哪裡、工作要怎麼排程、背包問題)
----
換言之,如果能有效地解開整數線性規劃問題,就能有效地解開上述這些問題
反之則不成立,解開背包問題不代表解開整數線性規劃問題
為什麼?
---
最後,我們來看這題入芽考的魔王題
```
小明覺得入芽考太難了,讓他很委屈,於是他決定來做一些簡單一點的事情。他打開世界地圖,突然在想:有沒有可能靠開任意汽車往返世界中的任意兩點?小明輕易地證明了:不存在一種方法可以使人開任意汽車往返任意兩地點。給定小明的證明是正確的,下列何者描述是正確的?
(A) 小一寫了一個程式,會不斷地在地圖上選出 A, B 兩點,並模擬從 A 點開任意汽車到 B 點,他的程式遲早會遇到無法開任意汽車往返 A、B 兩點的狀況。
(B) 小二發現,所有任意汽車能夠往返的兩點,走路也都能往返,所以如果存在兩點是任意汽車無法往返的,則一定也存在兩點是走路無法往返的。
(C) 小三開的不是隨便的汽車,而是超厲害的「『1 韋伯之磁通量均勻而垂直地通過 1 平方公尺面積之磁通密度』電動車」,所以不能僅憑小明的證明就說超厲害電動車無法往返世界上的任意兩點。(註:電動車是一種汽車)
(D) 小四看不懂小明的證明過程,他只要勤勞點,不要跟出題者一樣連主角名字都懶得想,把所有可能都窮舉一遍,如果都沒找到反例,就可以證明小明的理論是對的。
Hint:請只依照題目給的條件作答,不要考慮現實世界長怎樣,不要思考車子有什麼特性、有沒有跨海大橋、走路會不會走到腳斷掉之類的,這樣只會被誤導而已。
```
----
這題答案是 C
為什麼?
---
# Q & A
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

