## Getting Started with Smart Contracts on Polygon PoS
### 1. Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Explained
Polygon creates blockchain protocols & technologies that enable developers to build scalable user-friendly dApps on Ethereum, with low transaction fees but without ever sacrificing security. Like Ethereum, Polygon's live blockchain in production uses the [Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism](https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/consensus-mechanisms/pos/) (PoS for short). In this guide, we'll learn how to build and deploy our first Solidity smart contracts to Polygon PoS.
##### Key Features of Polygon
- **Speed** The Polygon Network uses a high-throughput blockchain with consensus provided by a group of Block Producers selected by stakeholders at each checkpoint. A Proof of Stake layer is used to validate blocks and periodically post proofs of Block Producers to the Ethereum mainnet. This enables rapid block confirmation rates of about 2 seconds while preserving a high amount of decentralization, resulting in excellent throughput for the network.
- **Scalability** Polygon Network achieves a hypothetical transaction speed of fewer than 2 seconds on a single sidechain. Using multiple sidechains helps the network to handle millions of transactions per second. This mechanism (already demonstrated in the first Matic sidechain) allows the Polygon network to scale easily.
- **Security** Polygon's smart contracts rely on Ethereum’s security. To safeguard the network, it employs three critical security models. It uses Ethereum's staking management contracts and a group of incentivized validators running Heimdall and Bor nodes. Developers can also implement both models (Hybrid) into their dApp.
- **EVM-Compatability** Polygon is designed to provide the ultimate Layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum. You don't have to worry about the underlying architecture while moving or deploying your dApps to the Polygon Network as long as it is EVM-compatible. Deploying your dApp to the Polygon Mainnet allows you to leverage Polygon as a faster transaction layer for your dApp.
#### Building on Polygon
If you are an Ethereum developer, you are already a Polygon developer. Simply switch to the Polygon RPC and get started. All the tools you are familiar with on the Ethereum blockchain are supported on Polygon by default, such as Truffle, Remix, and Web3js.
You can deploy decentralized applications to either Polygon Mumbai Testnet or the Mainnet. The Polygon Mumbai Testnet connects with the Ethereum Goërli Testnet, which acts as its ParentChain. You can find all the network-related details in the network documentation.
#### Interacting with the Polygon Network: two approaches
##### Wallets
Polygon PoS runs on Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). To interact with the Polygon Network, you need to have an [Ethereum-based wallet](https://ethereum.org/en/wallets/) like Metamask or Arkane Wallet. Ethereum wallets are applications that let you interact with your Ethereum account. Think of it like an internet banking app – without the bank. Your wallet lets you read your balance, send transactions and connect to applications.
##### Smart Contracts
Polygon supports many services you can use to test, compile, debug, and deploy [smart contracts](https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/smart-contracts/), the programs that decentralized Ethereum applications run on, onto the Polygon Network. Where wallets allow users to interact with the Ethereum blockhain manually, smart contracts let us automate the interactons between the blockchain and aDapp. Examples of interactions include deployment using Alchemy, Chainstack, QuickNode, Remix, Truffle, Hardhat, and Replit.
### Question 1. What consensus mechanism does Polygon's public chain use?
- A Proof of Work
- B Proof of Stake
- C Proof of Storage
- D Proof of History
### Question 2. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about smart contracts?
- A The allow Dapps to launch transactions on the Ethereum blockchain
- B They speed up transactions on Ethereum
- C They collections of code and state that run on Ethereum
- D They can only be used to request the creation of new blocks on the Ethereum blockchain
# Smart Contract Example: Minting an NFT
🎫 One of the simplest use cases for Ethereum smart contracts is using them to trigger minting [Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs)](https://ethereum.org/en/nft/). This guide will take you through minting your own NFT as a worked example to learn basics of Polygon PoS.
🌟 Your final deliverable will be an app that lets users purchase and transfer NFTs. Deploy your contracts to a testnet, and then build and upload your app to a public web server. This solution uses a template React app full of important Polygon components and hooks. This will let you deploy an NFT to a public network to share with friends! 🚀 Like in the image below:

## 1. Before we start: 📦 Set up your dev environment and look 📚
This worked example assumes you have the following dependencies installed in your system before you start:
1. Install [VS Code IDE](https://code.visualstudio.com/)
2. Install the [👷♀️ HardHat](https://hardhat.org/getting-started/) extension for VS code will let you compile and deploy smart contracts.
3. Install and set up [Git](https://git-scm.com/downloads)
4. Install [Node JS](https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v16.x/) (🧨 Currently use Node v16 as v17 & v18 are unstable 🧨)
5. Install [Yarn](https://classic.yarnpkg.com/en/docs/install/#mac-stable) (⚠️ Don't install the linux package `yarn` make sure you install yarn with `npm i -g yarn` or even `sudo npm i -g yarn`!)
6. Set up your [Metamask](https://metamask.io/) wallet (You will need a wallet installed for all the following activities in this guide. If you don't currently have one installed, follow ETH Global's [getting started with Metamask guide](https://ethglobal.com/guides/getting-started-with-metamask-cjf72) to set one up first.)
## 2. Preview the minting Dapp for your contract
You can see the starter code for your Dapp following the steps below on your command line:
```sh
git clone https://github.com/llsourcell/scaffold-eth-challenges.git challenge-0-simple-nft
```
```sh
cd challenge-0-simple-nft
git checkout challenge-0-simple-nft
yarn install
yarn chain
```
> in a second terminal window, start your 📱 frontend:
```sh
cd challenge-0-simple-nft
yarn start
```
> in a third terminal window, 🛰 deploy your contract:
```sh
cd challenge-0-simple-nft
yarn deploy
```
> You can `yarn deploy --reset` to deploy a new contract any time.
> 📱 Open http://localhost:3000 on your browser to see the app

---
## 3. Setting up your wallet to work with 📦 the Polygon testnet
**Testnets** are test blockchain networks that act and perform similarly to the main networks (mainnets) they are associated with. Since they operate on separate ledgers from the mainnet, the coins on a testnet have no connection to transactions and value on the mainnet. This allows developers to deploy, test, and execute their projects on a functioning blockchain freely.
The cost of failure or mistakes on a mainnet is very high and at times irreversible so developers need an environment where they can comfortably work without these risks.
The Polygon testnet is called Mumbai. Like other testnets, Mumbai allows developers to deploy and test their applications on the Polygon network without having to spend real money. We can use what's called a 'faucet' to receive your first test tokens.
**Faucets** are smart contracts that allow developers to receive test tokens instantly.
Let's Install and connect your metamask wallet to the Mumbai testnet, and use a faucet to collect your first test tokens.
**Setting up your wallet to work with the Polygon Mumbai Tesnet**
1. After your first install, your Metamask wallet is by default connected to the Ethereum network. In order to connect your wallet to the Mumbai Testnet, lets change its configuration by clicking the account icon on the top right of the app.
2. Select *“Settings”* from the drop down menu on the top right corner of your Metamask wallet.

3. Select *“Networks”* from the menu to the left.

3. In the Networks UI, complete the form to connect your wallet to the Mumbai Testnet using the following parameters.
**Network Name:** Polygon Testnet
**New RPC URL:** https://matic-mumbai.chainstacklabs.com
**ChainID:** 80001
**Symbol:** matic
**Block Explorer URL:** https://mumbai-explorer.matic.today/

Once you save the form,notice the addition of Polygon testnet to the network list dropdown next to the account icon. You can now select the Polygon testnet to perform your transactions on the Polygon network.
**Using the Matic faucet to get test tokens in your wallet**
1. Access the following website: https://faucet.matic.network/ and make sure the following parameter are set:

2. Add your address. Note that this address is the same for your ETH wallet.

3. Confirm the transaction.

4. Once the transaction is confirmed, you will be able to check the settled transaction the Polygonscan block explorer app, Matic’s version of [Etherscan](https://etherscan.io/) when clicking on the following link: https://explorer-mumbai.maticvigil.com/
5. As you can see, here is a quick summary of the amount transferred to you in Polygonscan.

## 4.: ⛽️ Setting up a Burner Wallet to test NFT contracts 👛
A **Burner Wallet** is a quick web wallet used to move small amounts of crypto quickly. It is basically an Ethereum address that is associated to your browser window and you can use to peform blockchain transactions with a simple interface. It is ephemeral, meaning that when you close that window, the wallet (and the funds left in it) is gone. Sending funds is as easy as a QR code scan. Burner wallets are great for local development but you'll move to more permanent wallets when you interact with public networks.
In this guide we will use burner wallets to examine how our contract assigns ownership of an NFT to a specific wallet address, and how ownership can be transferred from one wallet to another through a transaction.
⛽️ To test this we'll use 🔥**burner wallets**🔥 on localhost and start by getting some gas on our burner wallet.
1. Explore how **burner wallets** work. Reload your starter app and open a new *incognito* window.
2. Navigate the incognito window to http://localhost:3000. You'll notice it has a new wallet address in the top right different from the wallet address in your starter app window.
3. Use the [faucet](https://faucet.matic.network/) to put some gas funds in the incognito wallet.

4. Copy the incognito browsers' wallet address and send funds from the localhost burner wallet to it. Once you see the funds in the initial wallet, you are ready to go.

5. Close your incognito window.
>👨🏻🚒 Careful! When you close an incognito window, the burner wallet, account address and any funds remaining in it are gone forever.
## 5. 🖨 Minting some NFTs and modding your Dapp.
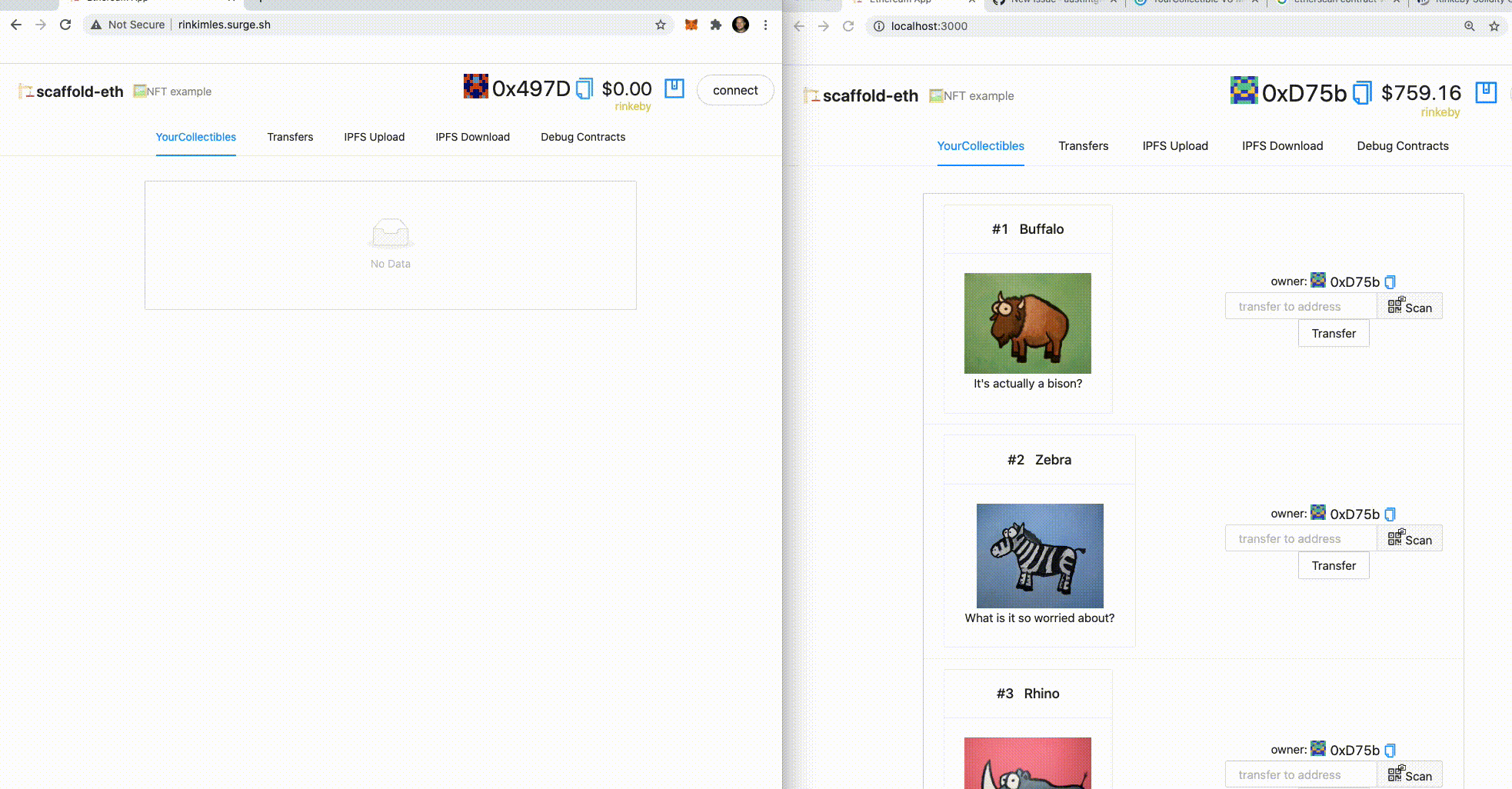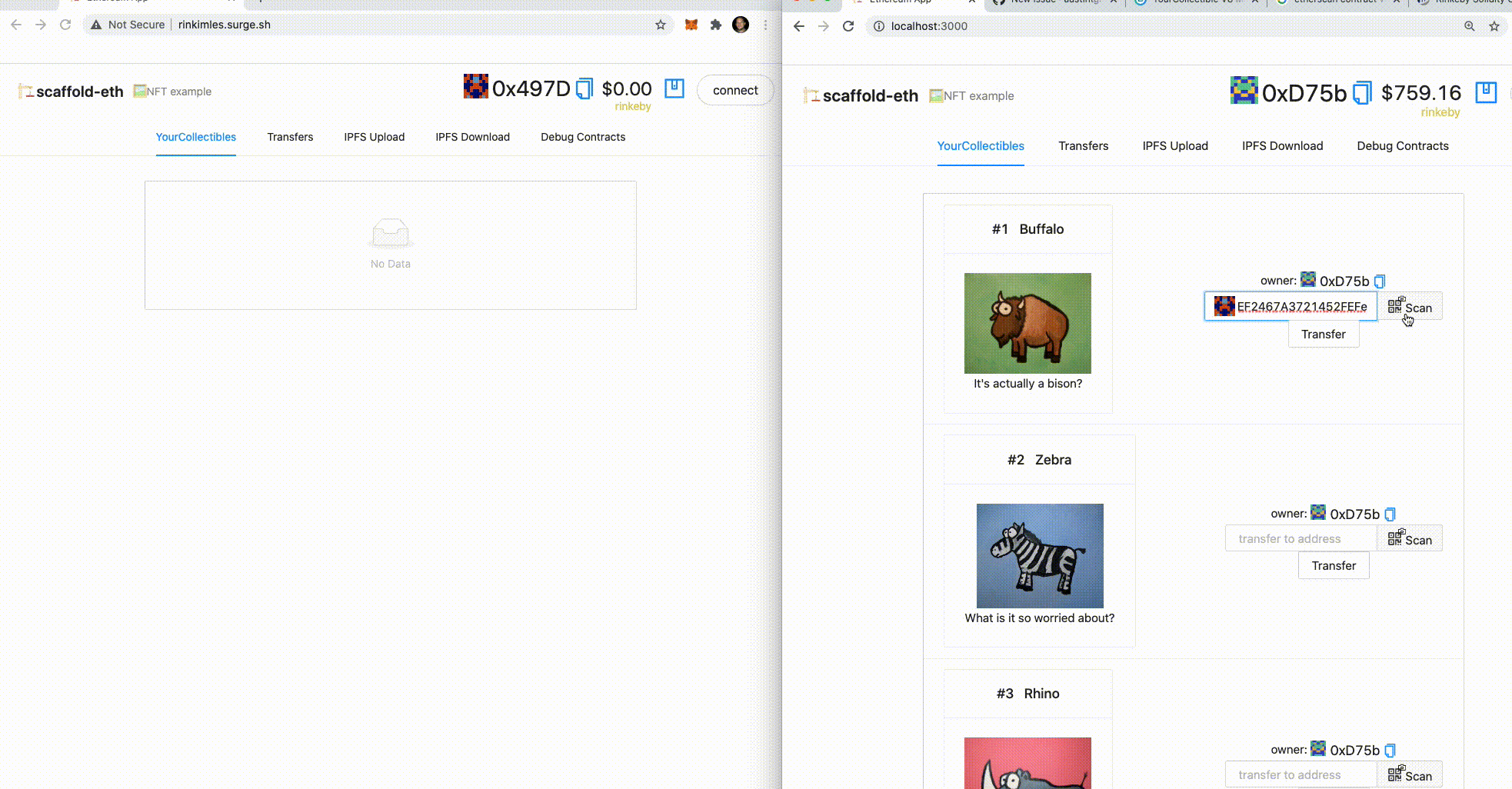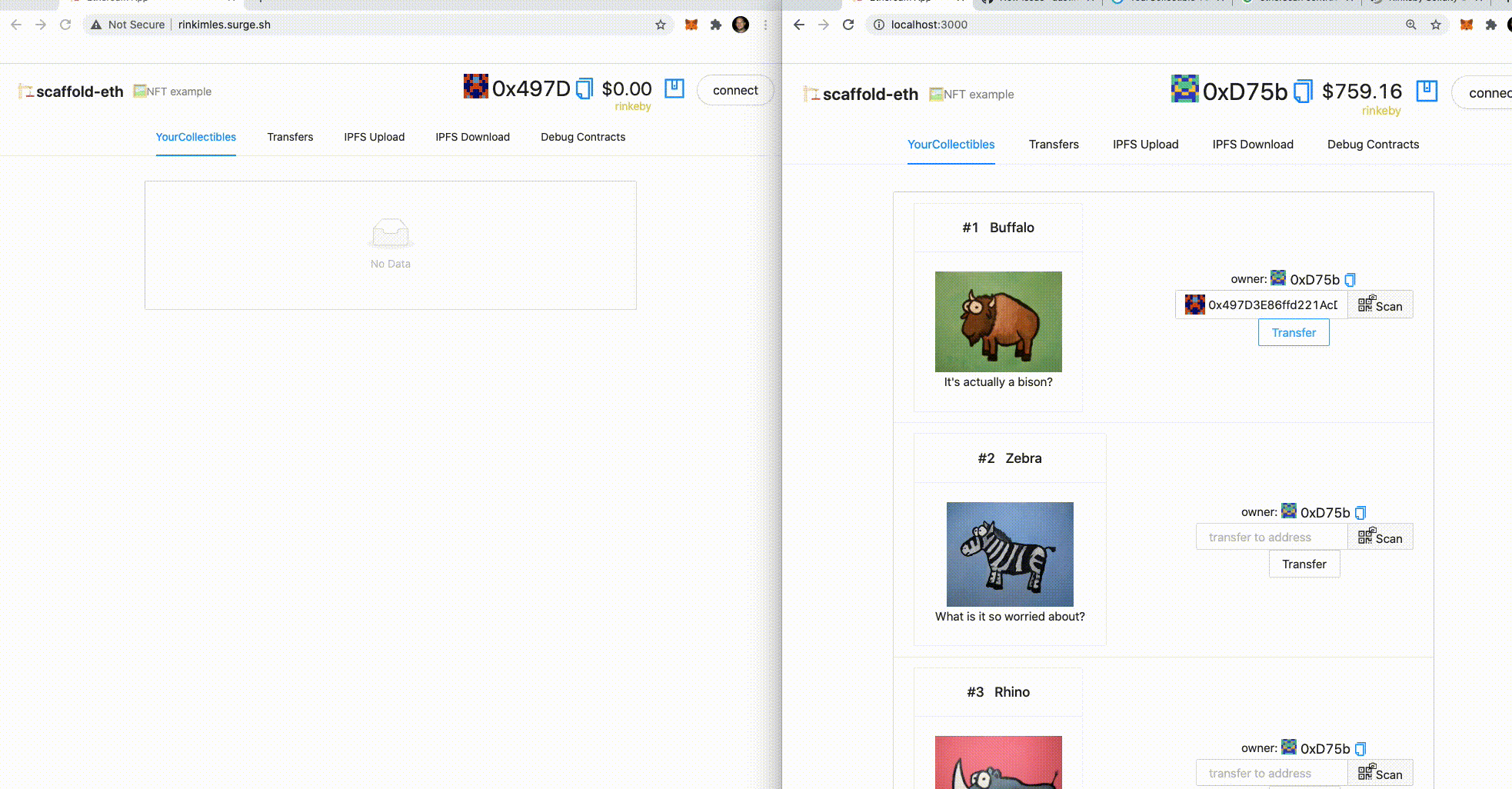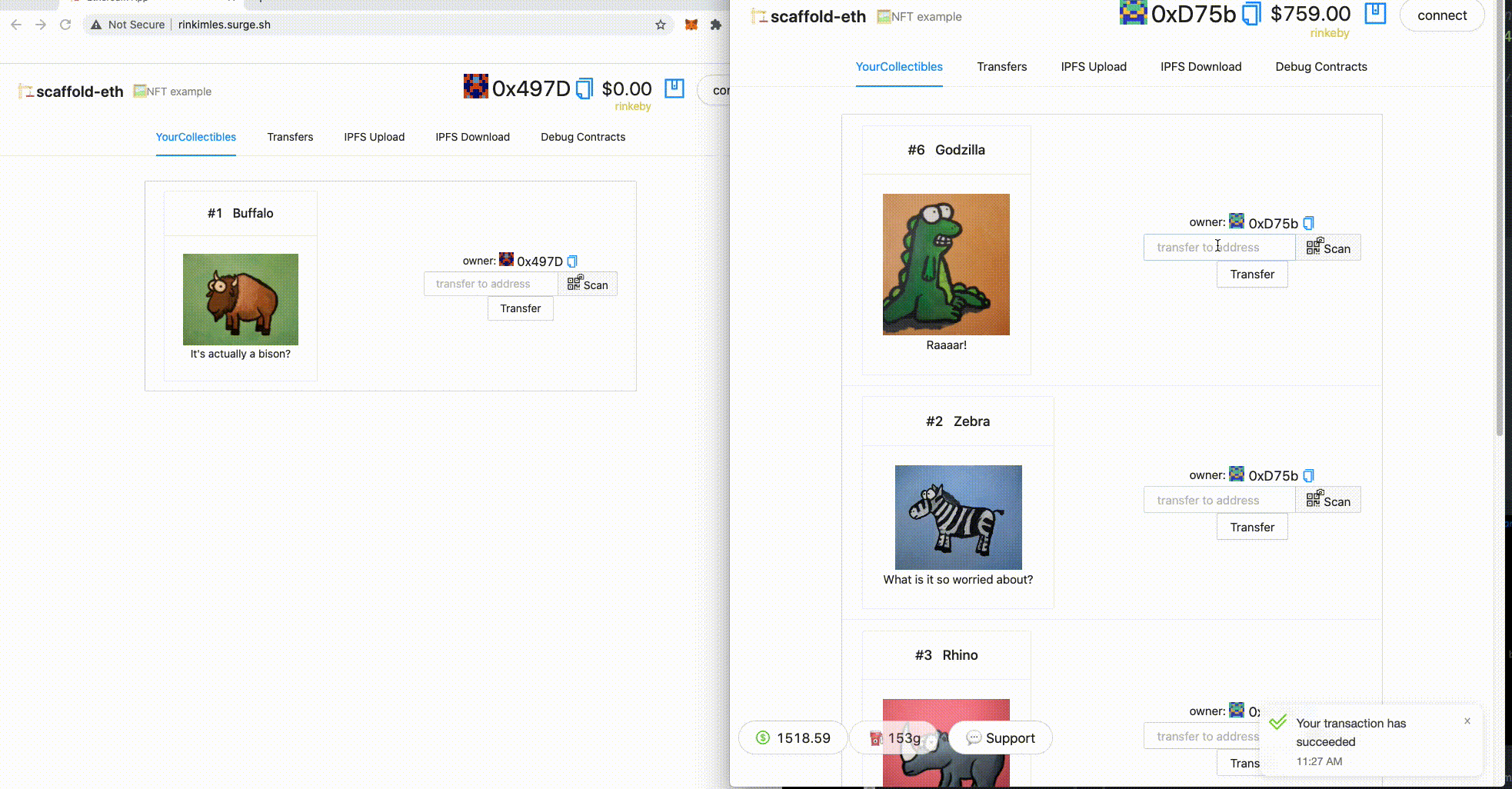
1. On your starter code window app let's ✏️ mint some NFTs! Click the `MINT NFT` button in the YourCollectables tab.

👀 You should see your collectibles start to show up:

2. Open an **incognito** window and navigate to http://localhost:3000 to open a burner version of the minter app.
3. 🎟 Transfer an NFT to the burner (incognito) address using the UI:

4. Try to mint an NFT from the incognito window.
>Notice that you can't mint an NFT with no funds in this address! Try grabbing some funds from the faucet to pay the gas!
5. When the transfer is complete. 🕵🏻♂️ Inspect the `Debug Contracts` tab. What address is the `owner` of `YourCollectible`? Notice that it is now the destination address.
## 6. Checking your Dapp's main files
Now that you have seen a smart contract in action, let's look at some of the key files that make it work:
1. 🔏 You can also see your smart contract `YourCollectible.sol` in `packages/hardhat/contracts` folder of the app source. This is the file that contains all the solidity code that the smart contract runs to kick off Ethereum transactions.
YourCollectible.sol
```sh
pragma solidity >=0.6.0 <0.7.0;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
contract YourCollectible is ERC721, Ownable {
using Counters for Counters.Counter;
Counters.Counter private _tokenIds;
constructor() public ERC721("YourCollectible", "YCB") {
_setBaseURI("https://ipfs.io/ipfs/");
}
function mintItem(address to, string memory tokenURI)
public
onlyOwner
returns (uint256)
{
_tokenIds.increment();
uint256 id = _tokenIds.current();
_mint(to, id);
_setTokenURI(id, tokenURI);
return id;
}
}
Footer
```
3. 💼 Take a quick look at your deploy script `00_deploy_your_contract.js` in `packages/hardhat/deploy`. This deploys the contract for use in the public testnet.
```sh
import {HardhatRuntimeEnvironment} from 'hardhat/types';
import {DeployFunction} from 'hardhat-deploy/types';
import {parseEther} from 'ethers/lib/utils';
const func: DeployFunction = async function (hre: HardhatRuntimeEnvironment) {
const {deployments, getNamedAccounts} = hre;
const {deploy} = deployments;
const {deployer, simpleERC20Beneficiary} = await getNamedAccounts();
await deploy('SimpleERC20', {
from: deployer,
args: [simpleERC20Beneficiary, parseEther('1000000000')],
log: true,
autoMine: true, // speed up deployment on local network (ganache, hardhat), no effect on live networks
});
};
export default func;
func.tags = ['SimpleERC20'];
```
4. 📝 If you want to make frontend edits, open `App.jsx` in `packages/react-app/src`.
---
## 7. Deploy the smart contract to testnet 🛰
🛰 Ready to deploy to a public testnet?!?
1. Change the `defaultNetwork` in `packages/hardhat/hardhat.config.js` to `mumbai`
2. 🔐 Generate a **deployer address** with `yarn generate'. This is the wallet address your app will use to interact with the polygon testnet.
4. ⛽️ Use a faucet like [https://faucet.polygon.technology/](https://faucet.polygon.technology/) to fund your **deployer address**.
🚀 Deploy your NFT smart contract:
```sh
yarn deploy
```
> 💬 Hint: You can set the `defaultNetwork` in `hardhat.config.js` to `mumbai` OR you can `yarn deploy --network mumbai`.
---
## 8. 🚢 Update your Dapp front end to use the deployed contract and test your Dapp on testnet 🚁
1. ✏️ Edit your frontend `App.jsx` in `packages/react-app/src` to change the `targetNetwork` to `NETWORKS.mumbai`:
You should see the correct network in the frontend (http://localhost:3000). It should say mumbai instead of goerli:

> 🦊 At this moment, you will need to connect the dapp to a browser wallet where you have some ether available to mint tokens. Keep in mind that the address you generated in the previous step to deploy the contract will likely be different from the one you have configured in your wallet.
🎫 Ready to mint a batch of NFTs for reals? Use the `MINT NFT` button.

📦 Build your frontend:
```sh
yarn build
```
💽 Upload your app to surge:
```sh
yarn surge
```
(You could also `yarn s3` or maybe even `yarn ipfs`?)
> 😬 Windows users beware! You may have to change the surge code in `packages/react-app/package.json` to just `"surge": "surge ./build",`
⚙ If you get a permissions error `yarn surge` again until you get a unique URL, or customize it in the command line.
⚠️ Run the automated testing function to make sure your app passes
```sh
yarn test
```

## 9: 📜 Contract Verification
Update the `api-key` in `packages/hardhat/package.json` file. You can get your key [here](https://etherscan.io/myapikey).

Now you are ready to run the `yarn verify --network your_network` command to verify your contracts on etherscan 🛰
---
## 10 💪 Share with friends!
👩❤️👨 Share your public url with a friend and ask them for their address to send them a collectible :)
---
### Question 3: How many times can an NFT be replicated?
- A Once
- B Never
- C Infinitely
- D Twice
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

