# DBMS and SQL
[Master Resource](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/30-days-of-sql-from-basic-to-advanced-level/)
Password for SQL DB: Sysdba_1
An application consists of:
* UI: User Interface
* BL: Bussiness Logic
* DB: Database
* **DBMS**
* Mechanism which allows you to store & access data.
* Set of programs that defines datatypes & constraints and constructs storage and manipulates the stored data.
### Database Models
* Hierarchical Model - 1950's-60's
* Tree Structure
* non-directional
* Does not support many to many relationship
* Revamp structure for adding or removing levels
* Network Model - 1960's
* directed graph instead of the tree structure
* In this model a child can have more than one parent
* complexity of pointers
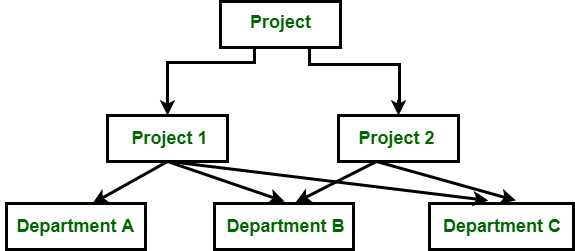
* Relational Model - 1970's
* Data is stored in the form of tables (2 dimensional matrix)
* Father of RDBMS - Edgar F. Codd Ji
* 1st RDBMS - Oracle
* Sybase, SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB
### RDBMS works on Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Operations
Set Oriented
* Union
* Intersect
* Minus
* Product
Relational Oriented
* Projection
* Restriction (Selection)
* Join
### Basic Syntax for queries
* not case sensitive
* string and dates are in '...'
```sql=
-- for creating the table
create table DEPT( GRADE int,
LOSAL int,
HISAL int );;
-- for fetching all columns from the table
Select * from DEPT;
-- for fetching specific columns fromt the table
Select col1, col2, col3 from DEPT;
-- getting the summary or details for the table
describe DEPT;
-- COMPARISION
!= not equal
<> not equal
-- conditioning
Select * from Table where DEPTNO>10;
select * from SomeTable where Name='Clerk';
select * from SomeTable where DEPTN0 BETWEEN 10 AND 20;
-- logical operators
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE condition1 AND condition2 and ...conditionN;
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE condition1 OR condition2 OR ... conditionN;
-- between operator
Select * from Table_name WHERE some_feature BETWEEN 10 AND 20;
-- IN operator
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE some_feature IN (100,1000,2000);
-- pattern matching: LIKE and NOT LIKE
# name starting with J
SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME
WHERE ENAME LIKE 'J%';
# names not containing 's'
# this
-- ‘a%’ Match strings which start with ‘a’
-- ‘%a’ Match strings with end with ‘a’
-- ‘a%t’ Match strings which contain the start with ‘a’ and end with ‘t’.
-- ‘%wow%’ Match strings which contain the substring ‘wow’ in them at any position.
-- ‘_wow%’ Match strings which contain the substring ‘wow’ in them at the second position.
-- ‘_a%’ Match strings which contain ‘a’ at the second position.
-- ‘a__%’ Match strings which start with ‘a’ and contain at least 2 more characters.
--'%\_%' \is escape character; this pattern matches underscore somewhere in between the string
-- selecting the null values
select * from table where some_feature IS NULL;
```
## Codd's 12 Rules
[TutorialsPoint](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/dbms/dbms_codds_rules.htm)
## Database Users
## Database Architecture
* External Level (individual user views)
* Conceptual Level (community user view)
* Internal Level (storage view)
* Database
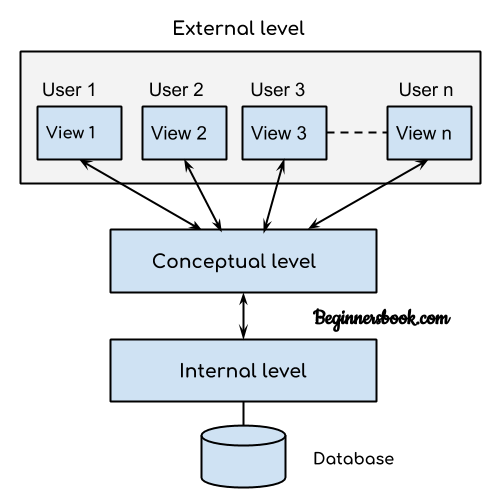
Root User is in the internal level.
3 level architecture is required for 2 purposes:
1. Abstraction
<p>Objects in an OOP language provide an abstraction that hides the internal implementation details. Similar to the coffee machine in your kitchen, you just need to know which methods of the object are available to call and which input parameters are needed to trigger a specific operation. But you don’t need to understand how this method is implemented and which kinds of actions it has to perform to create the expected result.</p>
3. Data Independence
* ablity of higher level of abstraction not to be affected by changes in lower level of abstraction
* they are of two types:
* logical - between external and conceptual layers
* physical - between conceptual and internal layers
## Methods for creating tables
* from existing tables
* copy structure and data
* copy structure only
```sql=
-- copy structure and data
create table new_table as select * from old_table;
-- copy structure only
create table new_table as select * from old_table where any_false_condition;
```
* creating our own table
```sql=
create table TABLENAME
(
col datatype(size),
col2 datatype(size)
)
```
### Data Definition Language (DDL)
* create - new objects(tables,...)
* alter
* changing constraints of existing columns
* drop
* deleting columns or tables
* truncate
### DML (Data Manipulation Language)
* insert - new rows
* update - modifying old rows
* delete
### INSERT
* Default order
```sql=
insert into table_name values(value1,value2);
```
* Changed order
```sql=
insert into table_name(col2,col1) values(value2,value1);
```
* Nulls
```sql=
insert into table_name(col1,col2) values(value1,Null);
```
* Multiple rows
```sql=
insert into table_name values(value1,value2),(value1,value2)
```
* SET option
```sql=
set @name='chandu';
set @dob='2003-07-11';
insert into birth_tab values (@name, @dob);
```
* copying rows
```sql=
insert into birth_tab select ename, hiredate from emp;
```

#### Update
```sql=
update birth_tab set dob='2005-08-21' where name='chandu';
```
#### Delete
```sql=
delete from birth_tab where name in (list of names);
```
#### Alter
```sql=
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name DATA_TYPE;
--convention is to name the constraint that's where pk_student comes in
alter table student add constraint pk_student primary key(id);
```
## Constraints
* contraints enforce rules at the table level
* constraints prevent the deletion of a table if there are dependencies
* the following constraint types are valid:
* not null
* cannot be empty
* it's compulsory man!
* unique
* cannot be repeated
* allows nulls
* primary key
* combines not null and unique
* Foreign key
* null allowed
* duplicates allowed
* values depend upon parent table
* values are refered from a reference table
```sql=
create table for_tab(c1 int, c3 char(1), foreign key(c1) references pri_tab(c1));
insert into for_tab values (1,'a');
insert into for_tab values (1,'b');
insert into for_tab values (3,'c'); -- error beacause 3 is not there in the referenced table
```
* Check
* checks for the constraint when the data is entered.
```sql=
create table vote(age numeric(3) check(age>=18), name varchar(20));
insert into vote values(19,'test2');
```
---
1<sup>st</sup> September, '22
## Database Application Design
Steps for designing the database:
1. collect the data
2. prepare ER diagrams
3. convert ER diagrams into tables
4. normalize the tables
**ER - Entity Relationship Diagram**

### ER conversion to tables
* Entity will become table name.
* Attributes will become columns.
#### Attributes
* simple
* multivalued
* represented by double ellipsak), in this case
* derived
* derived from other attributes
* example age from dob.
* composite
* combination of different columns

### Misc Functions
* timestampdiff(year,date1,date2)
* concat(col1,col2,'some other string')
```
Usually the number of rectangles is equal the number of tables, or maybe lesser.
```

Bank ER Diagram table Conversion (2 methods)
1st Method
* Account
Savings
Current
2nd Method
* Savings
Current

1-M and M-N relationship may require more tables.
### Normalization
* process of decomposing and arranging the attributes in a schema, which results in a set of tables with very simple structures.
* The purpose of normalisation
#### Why Normalisation?
To avoid data anomalies.
**Note: Candidates Keys are keys which can become primary keys
Composite Keys: combination of Candidate Keys**
### Normal Forms
[Resource hai lala](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/normal-forms-in-dbms/)
**1st Normal Form**
* rows converted to columns
* Removes MULTIVALUED/REPEATING columns
* Ensures ATOMIC VALUES
**2nd Normal Form**
* removes partial dependency
**3rd Normal Form**
* removes transitive dependency
### Dependicies
* Partial Dependency
* Functional Dependency
* Fully Functional Dependency
### Data integrity
It's of three types:
* entity integrity
* referential integrity
* done using foreign key
* domain integrity (check constraint)
### Some misc commands
* order by
```sql=
select col1,col2 from table_name
order by col1,col2 ASC|DESC;
```
* having
* having is used because where clause is not usable with aggregate functions
```sql=
SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country
FROM Customers
GROUP BY Country
HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5
ORDER BY COUNT(CustomerID) DESC;
```
* group by
* distinct
* to get the unique values
```sql=
select distinct COLUMN_NAME from TABLE_NAME;
```
## Column Aliasing
* to change display headlines
* SQL aliases are used to give a table, or a column in a table, a temporary name.
* Aliases are often used to make column names more readable.
* An alias only exists for the duration of that query.
* An alias is created with the AS keyword.
```sql=
select dname as DEPNAME
from dept where deptno=30;
```
```sql=
select col1,col2,col3 as ALIAS
from emp
order by ALIAS;
```
### Set
* used for setting variables which can be used later
```sql=
set @name='dhruv';
--now the variable can be used
select * from emp
where ename=@name;
```
### limit
* to select top 5 entries
```sql=
select distinct sal from emp order by sal desc limit 5;
--To skip the top 2 salaries
select distinct sal from emp order by sal desc limit 2,3;
```
### Concat
```sql=
--combining the two columns
select concat(ename," ",job) from emp;
```
## Types of SQL functions
* Single row functions - single line input & single line output
* character functions
**Concat()**
```sql=
--combining the two columns, in this case they both are strings
select concat(ename," ",job) from emp;
```
**lower() and upper()**
```sql=
select upper("hello world") as upper,
lower('HELLO WORLD') as lower ;
```
**substr()**
```sql=
-- take from the 7th character onwards
select substr('hello world',7);
-- take from the 8th character of length 1
select substr('hello world',8,1);
--just the last character
select substr("something",-1)
```
**instr()**
```sql=
-- gives position of specified character(1st occurence in case of multiple occurence)
select instr('hello word', 'l');
```
**left() and right()**
```sql=
select left(ename,3) "left", right(ename,3) "right" from emp;
```
**lpad() and rpad()**
```sql=
select lpad(dname,15,'%') "lpad", rpad(dname,15,'@') "rpad" from dept;
```
**String Functions**
* trim - for trimming spaces either in the begining or in the end.
```sql=
select trim(" string with spaces ");
select rtrim("dfads ");
select ltrim(" trime me please from the left");
select trim('data' from 'database') "trimchar"; -> o/p - base
```
* replace
```sql=
select replace('mary had a little lamb','lamb','bomb');
```
* mod
```sql=
select * from table
where mod(some_numeric_col,3)=2 --for 10%3
```
* sign
```sql=
--takes in the two numbers and returns 1,0,-1 respectively for greater, equal and less.
sign(first number - second number);
```
* abs, power, sqrt
* ceil, floor, round, truncate
```sql=
select ceil(10.23), truncate(10.12312312,2)
--truncates everything after the
--first 2 decimal points
```
#### Date functions
```sql=
select current_date --gives the current date
select curdate() --also gives the current date
select now() -- entire timestamp with date
select sysdate() -- entire timestamp with date
select year(curdate()); --just the year man!
select month(curdate()); --just the month man!
select quarter(curdate()); --just the quarter man!
select date(now()); -- only date
select time(sysdate()); -- only time
select dayname(curdate()); -- only day
select date_format(curdate(),'%a')"3 letter day", date_format(curdate(), '%W') "fully spelt day name";
select date_format(curdate(),'%b')"3 letter month", date_format(curdate(), '%M')"fully spelt month name";
select date_format(curdate,'%j'); -- no of days since 1st Jan
select date_format(curdate,'%y'); -- 2 digit year
select date_format(curdate,'%Y'); -- 4 digit year
select date_format(curdate(),'%w'); -- wth day of the week
select date_format(curdate(),'%d'); -- dth day of the month
select date_format(curdate(),'%D'); -- dth day of the month with superscript
--modifying dates
--we can add/substract year,month,days
select date_add(curdate,interval "1" year);
select date_sub(curdate,interval "1" year);
select curdate()+interval '1' year;
select curdate()+interval '1' day;
select curdate()+interval '1' month;
select last_day(curdate()); -- last date of the month
select ename,timestampdiff(year,date_first,curdate())
as service_year from emp; --gives the difference between two dates
select ename,datediff(date_first,curdate())
as service_year from emp; --gives the difference between two dates in days
```
##### Assignment
Q. find the numbers of 'a's in "mary had a little lamb and it was best damn goat in the whole world. ".
```sql=
--enter code here
set @word='mary had a little lamb'
SELECT LENGTH(@word) - LENGTH(REPLACE(@word, 'a', '')) AS A_Count
-- would and should return A_count as 4
```
### Control Functions
**CASE-WHEN-THEN-ELSE**
```sql=
--method 1
SELECT ENAME,JOB,SAL,
(CASE WHEN JOB="CLERK" THEN 1.5*SAL
WHEN JOB="SALESMAN" THEN 1.75*SAL
WHEN JOB="ANALYST" THEN 2*SAL
ELSE
SAL
END) "BONUS"
FROM EMP ORDER BY 2;
--method 2
SELECT ENAME,JOB,SAL,
(CASE JOB WHEN "CLERK" THEN 1.5*SAL
WHEN "SALESMAN" THEN 1.75*SAL
WHEN "ANALYST" THEN 2*SAL
ELSE
SAL
END) "BONUS"
FROM EMP ORDER BY 2;
--example
set @bd='2022-08-01';
set @hb='happy birthday';
set @ahb='avdanced bithday wishes';
set @bhb='belated bithday wishes';
select datediff(@bd, curdate()),
(case when datediff(@bd, curdate())=0 then @hb
when datediff(@bd, curdate())<0 then @bhb
when datediff(@bd, curdate())>0 then @ahb
end)
"bday wish";
select job,
(CASE WHEN JOB="CLERK" THEN concat("max sal = ",MAX(SAL))
WHEN JOB="SALESMAN" THEN AVG(SAL)
WHEN JOB="ANALYST" THEN MIN(SAL)
ELSE
COUNT(EMPNO)
END)
from emp group by job;
```
**IF(A,B,C)**
iF a IS TRUE RETURN b ELSE C
```SQL=
select IF(CONDITION,Value1,Value2);
```
**IFNULL(A,B)**
if A is null returns B else A.
```sql=
SELECT ENAME, ifnull(SAL+COMM,Sal) FROM EMP;
```
**NULLIF(A,B)**
if A=B returns Null else A
```sql=
select nullif(4,4);
```
**converting String to date**
```sql=
select str_to_date("10-may-2015","%d-%b-%Y");
```
## multiple row functions - multiple line input & single line output
Aggregate / group funtions
command to use before group by -
set @@sql_mode="only_full_group_by";
```sql=
--count
select count(*) from emp; -- includes nulls
select count(comm) from emp; -- does not include nulls
select min(sal), min(hiredate), min(ename);
select max(sal), max(hiredate), max(ename);
select avg(sal);
select sum(sal);
```
**group by and Having Clause**
* aliases are not taken by group by clause
* other than aggregate functions, columns that are there in select list must also be there in group by clause.
```sql=
select sum(sal), job from emp group by job;
```
### Inline view (subquery)
```sql=
select count(*) cnt from emp group by job;
-- this will have some output say b
select min(b.cnt) from (select count(*) cnt from emp group by job)b;
-- selecting min from the output b of the subquery
```
### Set Operators
* mysql does not support minus and intersect operators.
* to select data from similar select statements
* no of columns should be same in all statements
* column headings always come from 1st statement
```sql=
select job from emp where deptno=10
union
select job from emp where deptno=20;
-- for unequal number of columns
select ename,null "dname" from emp
union
select null,dname from dept order by ename;
```
### JOINs
Types of joins:
* inner
* uses = operator for joining condition
* both tables should have one common column
```sql=
select e.ename, d.dname
from emp e
inner join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
```
* additional conditions can be applied using and, where clause.
* outer
* inner join + missing data
```sql=
select e.ename, d.dname
from emp e
right outer join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
```
* non equi join
* no common columns required.
```sql=
select e.ename, s.grade
from emp e join salgrade s
on e.sal
between s.losal and s.hisal;
```
* cross
* it is not used in practice.
* self
* a join in a single table.
* natural
* joined on common columns
* common columns should have same datatype
* using
* when multiple columns are there we can specify which column be used for joining
* suitable for common columns in both the tables with different datatypes
```sql=
select ename, dname from emp join dept using (deptno);
```
**Oracle Prop Syntax does not support natural, using and full outer joins.**
#### Rules of SQL-99 Syntax
* column names should have the format
E.ENAME or EMP.ENAME
D.DNAME or DEPT.DNAME
(E and D are called table aliases)
* type of join must be specified (inner, natural, cross, outer)
* join condition uses on clause
## Subquery / Inner Query
A subquery is a select statement inside a select statement.
```sql=
select ename
from emp
where sal=(select max(sal) from emp);
--some examples
select e.ename "emp" ,m.ename "manager"
from emp e join emp m
on e.mgr=m.empno
and m.ename="king";
--same thing with subquery
select ename from emp where mgr=(select ename from emp where ename="king")
-- selecting grade of given name
-- with join
select e.ename, s.grade from
emp e join salgrade s on e.sal
between s.losal and s.hisal and e.ename='allen';
--with subquery
select grade from salgrade where (select sal from emp where ename='allen') between losal and hisal;
```
Subquery gets executed first and gives result.
Result will be used by the outer query and gets executed.
Subqueries are of 5 types:
* Single Row
* returns 1 row
* Operators used =,<,>,<=,>=,<>
* Multiple Row
* returns more than 1 row
* Operators used in, any, all, not in
```sql=
select ename, hiredate from emp where dayname(hiredate) in (select dayname(hiredate) from emp where ename in ('ford', 'clark'));
```
* Multiple Column
* returning more than 1 column
```sql=
--find out the emps who are taking max sal in each dept
select ename, sal,deptno from emp where (sal,deptno) in (select max(sal),deptno from emp group by deptno);
```
* Nested
```sql=
--find out the max sal for the dept in which turner is working
select ename,sal, deptno from emp
where sal=(select max(sal) from emp
where deptno=(select deptno from emp
where ename='turner'));
-- find out the job having max no of employees.
select count(empno), job from emp
group by job having count(empno)
in (select max(b.cnt)
from (select count(empno) cnt, job from emp group by job)b);
```
**Aggregate of aggregate is not allowed in mysql**
* Correlated
* inner query supports outer query and vice versa.
```sql=
--find emp earning sal higher than avg sal of their respective dept
select ename, sal, deptno
from emp E
where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp
where deptno=E.deptno);
```
## Creating a table (Revised)
```sql=
create table odd_even(id numeric(2), description varchar(4));
insert into odd_even(id) values((1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9),(10));
update odd_even set description="even" where id in (1,3,5,7,9);
-- or
update odd_even set description=if(id%2=0,"even","odd");
```
### Practice Problems
```sql=
--create table with constraints
create table student1(student_id int(4) primary key, student_name varchar(20), result char(1) check(result in ('p','f')) );
-- inserting from pre-existing table
insert into student1(student_id,student_name) select empno,ename from emp;
--updating result column with some condition
update student1 set result=if(student_name like '%s%','p','f');
--displaying no of students passed or failed
select count(student_id),result from student1 group by result;
```
## other useful queries
```sql=
--to see all the constraints of a table
show create table student1;
--other method is to use information_schema
select * from information_schema.table_constraints where table_name='t1';
--to show the tables in the database
show tables;
-- to use a specific database
use database_name;
--using default values while creating
create table default_tab(slno int primary key,
time1 timestamp default current_timestamp);
insert into default_tab values(1888,default);
--auto increament --only on primary key
create table company(comp_id int primary key auto_increment, comp_name varchar(20));
insert into company(comp_name) values ('happiest minds'), ('wipro'), ('accenture'), ('tcs');
--truncate removes the data keeps the structure
truncate table table_name;
-- delete is like truncate but can be used with a where clause
delete from sal2 where some_condition;
```
### Altering Tables
```sql=
-- -----------------altering tables--------------------
--adding columns
alter table table_name add new_column_name datatype; -- column added at the end
alter table table_name add c6 timestamp first; -- added at the first place
alter table table_name add c7 year after c2; -- added after c2
--adding constraints
alter table t1 add constraint pk_t1 primary key(c1);
alter table t1 add constraint chk_t1 check(c3 in ('a','b')); -- use show create t1; to see the constraint
alter table t1 add constraint uni_t1 unique(c4);
alter table t1 add constraint fk_t1 foregin key(c2) references t2(c2) -- reference another table t2 where c2 is the primary key
alter table t1 modify c5 smallint not null; --column level
--renaming the columns
alter table t1 rename column c5 to c_5;
-- renaming the tables
alter table t1 rename t_1;
--dropping columns
alter table t1 drop column c_5;
--dropping constraints
alter table t_1 drop constraint chk_t1;
```
* constraints are defined at 2 levels:
* table level
* column
### Transaction Control
* Commit
* Saving changes
* DDL commands are auto commited and cannot be rollbacked.
* Rollback
* Undoing modifications
By default, auto-commit is enabled in mysql
**ACID: atomicity, consistency, isolation, durablity.**

## Views
* certain data visible to certain people.
```sql=
create view v1 as select * from emp where deptno =10;
create view v3 as select * from emp where deptno=30 with check option; --not able to alter ig
```
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

