:dart: W6 - Collocation
===
<!-- ## Table of Content
[Toc] -->
## 名字:俞辰
### Named-Entity Recognition (NER)
Name Entity是具有重要成分以及意義的某段文字,可以協助我們了解某段文本。人的閱讀能力比電腦厲害非常多,人腦可以把閱讀到的資訊,自動地去做關聯跟給出意義,但對於電腦來說,拿到一篇文章就只是拿到了很多字串而已。以新聞為例,我們會注意的不外乎就是:跟誰有關,發生甚麼事,時間,地點(人事時地)。
以新聞中取來的一句話為例:
少女cosplay攜帶槍械造成民眾驚恐結果只是虛驚一場。
若特地將順序打亂: 少女、造成、驚恐、槍械、只是、cosplay、結果、民眾、攜帶、虛驚、一、場。
就連人來看都只能大略的猜猜看這句話原文是甚麼,但是不同的組合方式,可能出現的意義也會截然不同。但如果我們儲存分析的單位不是以詞而是entity的話(如少女cosplay、攜帶槍械、虛驚一場、民眾驚恐),就更具有語意成分。
假如我們先定義好,對於這個新聞有那些name entity可以幫助我們了解的話,那我們產生出來的結構就會更具有意義。
起因: 少女cosplay、攜帶槍械
結果: 虛驚一場、民眾驚恐
我們通常在訂定Name Entity的時候,通常會從有兩個點依序下去思考:
這個domain有哪些可能的task。
那每個task可能會需要知道的Name Entity。
基本上基於這兩個點,我們才不會定義出不相關的或是未來可能還有該辨識的但是當初沒有定義到的。
[Reference](https://medium.com/royes-researchcraft/%E8%87%AA%E7%84%B6%E8%AA%9E%E8%A8%80%E8%99%95%E7%90%86-3-%E5%91%BD%E5%90%8D%E5%AF%A6%E9%AB%94%E6%A8%99%E8%A8%BB-name-entity-recognition-%E7%90%86%E8%AB%96%E8%A8%AD%E8%A8%88%E7%AF%87-923348c31a7b)
### Precision@k、Recall@k、F1@k
Precision@k衡量一個搜尋引擎在回傳Top-K個結果時的精確率。對於現代的搜尋引擎來說是個有利的衡量標準,以Google為例,一個頁面預設取得Top-10的查詢結果,那麼我們的Precision@k就可以設定在P@10,並且計算在這十個文件中有多少文件符合了使用者的資訊需求(稱作相關)。
Recall@K召回率是指前topK結果中檢索出的相關結果數和庫中所有的相關結果數的比率,衡量的是檢索系統的查全率。一般來說,Precision就是檢索出來的條目有多少是準確的,Recall就是所有準確的條目有多少被檢索出來了。
F1@k則是兩者的調和平均數,算是一個比較概略的指標來看這個模型的表現
[Reference 1](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10217441)
[Reference 2](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43797817/article/details/103976568)
[Reference 3](https://medium.com/nlp-tsupei/precision-recall-f1-score%E7%B0%A1%E5%96%AE%E4%BB%8B%E7%B4%B9-f87baa82a47)
### Mann-Whitney U test (曼惠特尼U檢定)
曼惠特尼U檢定是用於比較兩組獨立樣本間中位數是否有差異的檢定,是當獨立樣本t檢定違反基本假設時所使用的檢定方式(例如:常態分配、變異數同質性假設等等)。
Mann-Whitney U test的統計過程及公式可以參考以下步驟,我們拿一筆資料當作範例進行說明。這筆範例資料中,實驗組與控制組各有三筆分數,我們進行以下五個步驟。

(一)、將兩組人的分數一起進行排序,兩組樣本數分別為n1及n2
在這六筆資料中,分數原始數據排序依序為2、2、3、4、5、5,n1及n2皆為3。
(二)、將所有分數從最低(設為rank 1)排至最大(設為rank N),若有重複的原始分數則取其Rank的平均,接著進行兩組別的Rank加總
由於第一步驟最前面兩筆及最後兩筆數字一樣,因此我們在排序上取平均,最終的Rank值為1.5、1.5、3、4、5.5、5.5,我們可以將其排序整理成以下表格。

根據上述表格,我們可以算出R1為12.5,R2為8.5,接著進行第三步。
(三)、計算出U1及U2值
U1 & U2之公式如下圖。

根據公式我們可以得知

(四)、取U=Min(U1 ,U2)
從6.5及2.5的最小值,故U為2.5。
(五)、進算出Z值並進行檢定
Z值公式如下圖,由下圖公式計算可知,Z值為-0.872未達顯著,表示兩組之間差異不大。

[Reference](https://www.yongxi-stat.com/mann-whitney-u-test/)
---
## 名字:予茜
### Collocation(搭配詞)
最早提出這個概念的人是J.R. Firth(1957)
意思是: certain lexical items tend to **co-occur more frequently** in natural language use.
有很多方法可以計算搭配值
Rule-based: MWEs
Statistical-based: AMs, MI值, LL值,t-test…
Hybrid-based: combined rule-based and statistical-based
### Pooling
如果一個bigram被i或i個以上的AM萃取出來,表示其為真實搭配(不太懂),最好是11,當i小於10,有些方法可能效能下降,而其他方法處於顛峰;當i大於11,條件過於嚴格,導致召回率低,F1分數低,導致所有方法的性能都很差。
好處:可以避免字典中,一些搭配頻率較低的詞
### K值: 代表最有可能為真的搭配
這裡不太確定指的是KNN還是K-means,所以都放進來~
**分群**:將相同性值的資料歸納為同一群,希望以群體內差異小、群體間差異大為目標
**分類**:依據事先給定的條件,譬如說年齡大於30歲,性別為男性等等標準來判定類別
**KNN**(K鄰近)模式運作模式
觀念是根據資料彼此之間的距離進行分類,距離哪一種類 別最近,就分到哪一類,所以 KNN 常被用於分類問題。
計算方式:
一、首先我們要計算要各個樣本與預測目標的距離,常用的距離計算方式為**歐式距離**
二、決定k值:距離計算完後我們要決定用**距離最接近預測目標的k個樣本**去決定目標類別
三、投票決定類別:k個樣本中每個樣本進行投票,簡單說就是k個樣本中最多的類別去決定預測目標的類別
**K-means** (用於分群比較好,是聚類分析的一種)
一、決定k值(分成k群)
二、隨機給定k個群心(中心點)
三、計算每個樣本與每個中心之距離,並將樣本歸類分配給距離最近的群心
四、通過分配給每個先前群心的所有樣本的平均值來創建新的中心
五、重複步驟3與步驟4,直到中心不再有太大的變動
[reference1](https://medium.com/@SCU.Datascientist/python學習筆記-聚類分析k-means-clustering-63fd65027c98)
[reference2](https://medium.com/@SCU.Datascientist/python學習筆記-knn-k-nearest-neighbor-531a95336f71)
### 混淆矩陣(confusion matrix)
要預測搭配詞的模型,可以用混淆矩陣(confusion matrix)解釋,有四個要素: **TP(True Positive), TN(True Negative), FP(False Positive), FN(False Negative)** 用於分辨模型的性能,True/False 預測正確與否,Positive/Negative 預測方向。

以檢測病患是否得癌症為例:
TP:預測該病患患有癌症,且實際也患有癌症 (預測正確)
FP:預測該病患有癌症,但實際無癌症 (預測失敗)>>理論是錯的,但實驗結果卻對
FN:預測該病患無癌症,但實際有癌症 (預測失敗)>>理論是對的,但實驗結果卻錯
TN:預測該病患無癌症,且實際上也無癌症 (預測正確)>>準確率和召回率不考慮,因為是答對的Null Hypothesis,是無聊的答案
通常會希望模型的TP或TN多多出現,而FP或FN盡量不要出現,機器學習想要知道的是**TP**
但如果光看數值看不出來,需要用一些指標,分類模型的好壞,如以下四種。
### 1.Accuracy(準確率):
(TP+TN)/(TP+FP+FN+TN) 預測正確的比例,但在正向例子很少的狀況下,不適用。
### 2.Recall score(召回率):
TP/(TP+FN) 在實際情形為正向的狀況下,預測「能召回多少」實際正向的答案。計算目標的誤判率(miss)。
### 3.Precision(精確率):
TP/(TP+FP) 看的是在預測正向的情形下,實際的「精準度」是多少(有多少正樣本)。計算警告誤報(False alarm)出現的機率。
### 4.F1 score:
2 * Precision * Recall / (Precision + Recall) 前面兩者的調和平均數
### Mann-Whitney U test:
比較兩組獨立樣本間**中位數**是否有差異,是當獨立樣本t檢定違反基本假設時所使用的檢定方式(例如:常態分配、變異數同質性假設等等)。
由於Mann-Whitney U test是**無母數**的統計方式,其適用於以下三種情形:
1、非常態資料
2、小樣本資料(N<30)
3、依變數可以為次序型資料
[reference1](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10302523?sc=rss.iron)
[reference2](https://ycc.idv.tw/confusion-matrix.html)
---
## 名字:植棻
### Pooling 池化
最常見的使用地方是在深度學習 (Deep learning) 的卷積神經網路 (CNN) 中的池化層 (pooling layer),而池化層主要作用有兩個:降維、特徵萃取
**卷積神經網路 Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)**
主要是讓電腦可以讀取特徵,經過轉換,進行深度學習
- **卷積層 Convolution layer**
一般在影像上,經過卷積運算後,再進行非線性轉換,之後得到的圖片會稱為特徵圖(feature map)
- **池化層 Pooling layer**
用來壓縮圖片並保留重要資訊,會有一個滑動視窗,視窗矩陣要多大可自行定義。
以下圖為例,原本的feature map是一個5X5的矩陣,經過降維並保留特徵至3X3的矩陣。而滑動視窗是一個2X2的矩陣。


Pooling中提取特徵有分幾種不同形式,以下舉兩種常見形式:
- Max pooling 最大池化 ⇒ 視窗中取最大值保留
- Average pooling 平均池化 ⇒ 視窗中所有值取平均
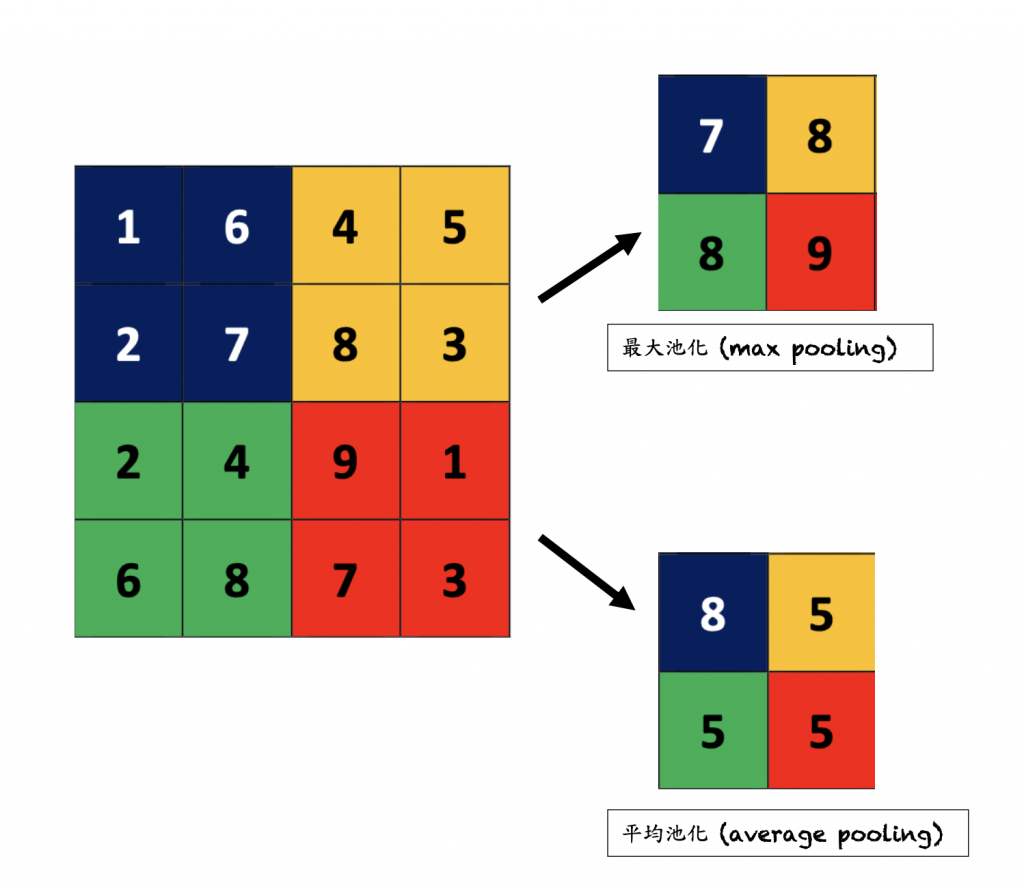
> 在這篇paper中的pooling好像應該是跟CNN沒有關聯,用在這裡就是當一個collocation只要通過一定門檻的標準時,就可被認證,有點像pooling的概念,去filter掉一些不必要資訊的只保留必要的(?)
[Reference_1](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/upload/images/20231009/20161909zoDh06TFPZ.png)
[Reference_2](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10337086?sc=rss.iron)
[Reference_3](https://bc165870081.medium.com/ai科普-池化以及維度縮減-25fa0ab2d6c2)
### Mutual information 互信息/相互資訊 (MI)
互信息是一個隨機變量 (X) 包含另一個隨機變量 (Y) 信息量的度量。互信息也是在給定另一個隨機變量知識的條件下,原隨機變量不確定度的縮減量。
下圖視覺化了互信息的關係,兩個完整的大圓分別是H(X)和H(Y),其中兩個圓交疊的部分是I(X;Y),兩個圓不重疊的部分則是H(X|Y)和H(Y|X)。

假設有一個隨機變數(X) ,其信息量為H(X),而確定另一個隨機變數 (Y) 的情況下條件信息量為H(X|Y)。當我們知道隨機變數(Y) 的值,我們的不確定性從H(X)降低成了H(X|Y),也就是說我們得到了**H(X)-H(X|Y)**的資訊量,此獲得的資訊量稱為X和Y的互信息,寫作I(X;Y)。
互信息公式如下:

而H(X)和H(Y)可能會有以下幾種分布:
1. 有重疊
2. 完全不重疊⇒X,Y 完全獨立,I(X;Y)永遠大於等於0
3. 完全重疊

隨機變數也有可能大於兩個,如下圖所示:

[Reference_1](https://chih-sheng-huang821.medium.com/笨蛋-問題在data-2-從訊息理論來看資料的影響-9aa2e2b420c6)
[Reference_2](https://medium.com/@acamvproducingstudio/從熵-entropy-到條件熵-conditional-entropy-和互信息-mutual-information-b5ac7ff93405)
[Reference_3](http://takenoteyourself.blogspot.com/2018/03/machine-learning-3.html)
---
## 名字:瓈萱
### Jaccard Index 雅卡爾指數
可以用來衡量兩個樣本之間的“相似度”,主要是計算“交集”在“連集”裡佔的比例。舉例來說,要衡量兩個句子是否相似 可以先把句子看作兩個集合,如果即合理重疊部分越大 代表他們相似度越高。
算式:
分子為交集部分(在A 和B 都觀察到的值),分母是聯集部分(所有在A 和B 觀察到的值),算出來的值會介於0~1之間 1 會代表兩者之間完全一樣。
例子:
A: 政大雄鷹棒棒
B: 政大雄鷹四連霸
交集:政、大、雄、鷹
聯集:棒、棒、四、連、霸
Jaccard index: 交集/聯集 ⮕4/9 Jaccard index:0.44

* Jaccard distance
用來算兩個樣本之間的距離,距離越遠相似度越小,距離越近相似度越大
所以結果如果算出來是0代表兩個樣本100%相似
公式:
[reference](https://myapollo.com.tw/blog/jaccard-index-explaination/)
### Mutual Information (MI) 互見訊息
在資訊理論中用來計算兩個變數之間的依賴程度,A與B共享訊息的量,ex. A: 今天下雨 B:今天陰天,A提供了一些訊息給B,換句話說可以用來計算兩個事件的“相關性”,用這個方法來計算配詞的結果也可以因此了解兩個詞之間的關聯程度。 如果A跟B互相獨立,則算出來的值會是0(MI算出來的值會是正的)
計算方式: 
(以算字詞搭配強度的觀點)x,y 分別代表不同的字,分子代表x和y 一起出現的機率;分母則代表x和y各自出現的機率。
計算出來的值如果越高,代表兩個詞之間的關聯性越高,可能是常見的人名、地名等。對出現頻率低的字詞影響較大。
* MI³(MI 的變體)
計算方式:

* Difference between MI and MI3 :
基本上是一樣的計算方式,不過會在觀察值上做加權(乘上3),為了去減上面MI 對低頻詞的影響。
### Named entity recognition (NER) 命名實體識別:
人在聽到名詞時可以自動歸類所聽到的字詞是人物、地點、位置等 這可以幫助我們迅速的理解上下文,(像是一講到政治大學 我們會自動有這些訊息 地點:台北 機構:大學 等..., )但是電腦沒辦法像人一樣,而NER 就是希望能跟人一樣,看到一個詞就能將其歸類。
NER 的方法可以處理結構化或非結構化的資料,可以檢測文檔的一個詞或是一系列的詞,也可以將字詞分類到事先定義的類別(地點、人名、產品名...等)
他的目標是希望能對文本中的實體進行標註,並對其進行分類,而藉由這個方式也可以讓機器更好理解文本,提高處理效率和精確度。
實體分類的例子如下圖:

圖例中辨別了三個實體:人-Luke Rawlence、地點-Milton Keynes,組織-Aiimi,University of Lincoln

而透過NER取得了這些重要的訊息可以讓我們推測情感、情緒、意圖...等,進一步取得一些相應的回覆,就如同人類在溝通一樣,因次NER的技術很常使用在聊天機器人、搜尋引擎和情感分析上應用。
但是機器分類還是會遇到字詞有歧異的狀況,因此需要透過數據來大量訓練、分類。
創建NER 的方法:
* 規則法:基於預先設定的規則來提取,可基於語義、語法等進行設計
優點:可以明確定義其規則和模式。
* 機器學習:使用標記好的數據對模型進行訓練(例如決策樹、SVM),也能較了解模型決策到過成。
* 深度學習:通常能適應不同數據和任務,有較強的泛化能力。
[reference](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10321744)
[reference](https://zh-tw.shaip.com/blog/named-entity-recognition-and-its-types/)
---
## 名字:孟桁
Mutual Information (MI)
MI is a notion linked with entropy, and can be explained as the amount of information one can obtain of one variable by observing the other variable. It also serves as a measurement of how 2 variables are dependent of each other. As a collocation measurement this translates to the extent of co-occurrence of words compared to their individual occurrence.
The score ranges from 0 to infinity (theoretically). A zero score indicates independency between variables, and while there is no upper bound, values do not typically go higher than 2.0 as it is a logarithmic value.
MI is not a heavily preferred method in collocation because it is strongly affected by frequency.
[reference1](https://www.kaggle.com/code/ryanholbrook/mutual-information)
[reference2](https://www.sketchengine.eu/my_keywords/mi-score/)
Minimum Sensitivity (MS)
MS is the minimum number of 2 values: (a) the number of collocations divided by the base and (b) number of collocations divided by the collocate. The higher the co-occurrences and the less individual occurrences of either word gives a high MS.
[reference3](https://www.sketchengine.eu/my_keywords/minimum-sensitivity/)
---
## 名字:靖涵
### Mutual Information (MI)
- 量化兩個變量之間的關係,可以衡量一個隨機變量(random variable) 對另一個隨機變量提供多少訊息。
源自於資訊理論,單位為bit。可以理解為已知一個隨機變量之後,對另一個隨機變量的不確定性為多少。
MI 數值越大代表不確定性越小,相反MI數值越小代表不確定性越大。另外若MI為0,代表MI之間互相獨立,即無法從已知的隨機變量推測出另一個未知的隨機變量結果。
Mutual Information 和 entropy 也有相關,即 MI 可以告訴我們當「知道一個變量」之後他「減少另一個隨機變量的不確定性的量」,也就是「減少另一個隨機變量的entropy 的量」。
- MI 公式如下:
$$I(X;Y) = ∑_{x\in X} ∑_{y \in Y} P(x,y) log \frac{P(x,y)}{P(x)P(y)}$$
可以看見公式中包含 joint probability 和 marginal probability:
- **Joint probability(聯合機率)**:即計算兩個或多個隨機變量對某特定取值的機率,可以知道隨機變量之間的關係。(例如: A事件為從52張的撲克牌抽出一張6,B 事件為從撲克牌抽出一張紅色,則 P(A ∩ B) = 4/52\*2/4 = 2/52,因為52張中只有4張6,4種花色中只有2種是紅色),即 P(A ∩ B)。
- **Marginal probability(邊際機率)**: 即僅計算一個事件本身發生的機率(例如:從一副52張的撲克牌中抽出一張 6,則 P(A) = 4/52 ,因為52張中只有4張6。),即 P(A)。
- (額外補充) **Conditional probability (條件機率)**:則為在一件事情發生的前提之下,另一件事情的發生的機率。舉例:P(A | B) 即為在 B事件發生的前提之下,A發生的機率。公式如下:分母 P(B) 為B事件發生的前提之下,分子 P(A∩B) 事件A發生的機率。
$$ P(A|B) = \frac{P(A \cap B)}{P(B)}$$
- 舉例而言:在機器學習的分類任務中有多組 features,即可以計算 feature 和 label之間的 MI。
以下圖為例,可以比較 features: 喜歡爆米花 和 label: 喜歡電影 之間的關係,並且把上方表格的資訊先轉換為下方有joint probability 和marginal probability 的表格。

如下圖,再把 probability 放入MI 公式計算,結果即可知道 feature(這裡為 喜歡/不喜歡爆米花) 和 label(這裡為 喜歡電影) 之間量化後的關係。並且公式中會加總所有可能:即 喜歡爆米花也喜歡電影/ 喜歡爆米花不喜歡電影/ 不喜歡爆米花喜歡電影/ 不喜歡爆米花也不喜歡電影。
- Note: log 底數可為任意數,但機器學習中通常使用 natural log (也就是 常數e,約等於2.71828,以便後續的數學計算。)

- 從計算結果出來的數值即可以知道從已知的隨機變量中,對另一個隨機變量的不確定性為多少。也可以比較 feature 喜歡/不喜歡爆米花 和 feature 身高 對於預測 label 喜歡/不喜歡電影各自的 MI值。
- Note: 像身高這樣的 numerical value 可以先轉換成**直方圖(histogram)** 再依照轉換出來 bin 可以變成離散的類別 (discrete category)。
- 計算的結果中也可以發現,絕對的正相關(喜歡爆米花的人都喜歡電影)跟負相關(喜歡爆米花的人都不喜歡電影)算出來的 MI 數值都會很大,因為不管計算的是關聯度而非正向或負向。相反的,如果所有人都喜歡爆米花,但其中有些人喜歡電影有些人不喜歡,則算出來的MI極可能為0,因為從前者無法預測出後者的結果。
[Reference_MI_1](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eJIp_mgVLwE)
[Reference_MI_2](http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Mutual_information)
[Reference_probability](https://datasciocean.tech/machine-learning-basic-concept/basic-probability-joint-marginal-conditional/)
### Mann-Whitney U test (曼惠特尼U檢定)
- 檢測兩個獨立母體(independent groups)是否有差異。Null hypothesis為:排序總和在兩個獨立母體沒有差異。
- t-test vs. Mann-Whitney U test:
- t-test 也可以檢測兩個獨立母體是否有差異,但 t-test 要求 data 需為常態分佈。而 U test 可視為 `non-parametric counterpart to the t-test for independent samples` ,是一種非參數統計方法,即沒有預設 data 的分佈。
- t-test 和 Mann-Whitney U test 的另一個不同是,前者通常計算「mean 是否有不同」,但後者是計算「rank sum 是否有不同」,指把兩個母體合併做排序,再計算各自得到的總數為何(如下圖)。

- Mann-Whitney U test 的計算:
假設有兩組獨立樣本,分別為樣本大小為 n1 和 n2 ,首先會將兩組值合併並進行排序,然後計算每個樣本中排名的總和,n1 和 n2 的排名總和為 R1 和 R2,即可計算 Mann-Whitney U統計量 \(U值\)。
- 公式如下:
$$U_1 = n_1 \times n_2 + \frac{n_1(n_1 + 1)}{2} - R_1 $$ $$ U_2 = n_1 \times n_2 + \frac{n_2(n_2 + 1)}{2} - R_2$$
並且通常會在 U1 和 U2 中選擇較小的U值作為最終的 Mann-Whitney U統計量。
$$ U = \min(U_1, U_2)$$
[Reference_Utest_1](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Twk6lBhBl88)
[Reference_Utest_2](https://www.yongxi-stat.com/mann-whitney-u-test/)
---
## 名字:喻璞
### collocation
#### 定義
- 搭配詞中的詞之間的關係比偶然發生的組合更頻繁地被一起使用。
- 此外,搭配詞的組成在語詞、語義或語用上受到更多OR更少限制。
#### 種類
* Firth (1957/1968: 179): 一個詞與「它所搭配的伙伴」的組合
* frequency-oriented (Siepmann, 2005)
* distributional (Evert, 2005: 15)
* semantically-based (Siepmann, 2005) - 搭配詞之間語義上是獨立的
* intentional (Evert, 2005: 16) - 由 Hausmann (1985, 2004) 提倡,強調搭配詞成分之間的語義關係(後者被前者吸引)
> 搭配詞的組成在形式和意義上在目前學說中尚未達成共識。
#### 抽取搭配詞的方法 (collocation extraction)
##### language-specific (e.g. Pivovarova et al., 2017; Seretan, 2011)
識別句法或語義之間的關係,此方法會受到 linguistic parser 影響。
##### language-independent approaches (e.g. Seretan & Wehrli, 2006)
衡量詞語對之間的關聯強度
### linguistic parser 語法分析器
#### 定義
在 NLP 領域中的 Paser 可以將分析出來的 token 建立出一個 Parse tree,以利後續工作的語意分析。
#### 種類
##### Top-down parsing
先由 root 開始,遞歸地向下處理到樹的 leaves
##### Bottom-up parsing
從字符串本身(leaves)開始向上建構,反向地透過產生式處理到起始符號。一般來說,bottom-up parsing 的演算法比強大,但結構也比較複雜(code比較難寫)。
[ref1](https://jaceju.net/simple-compiler/3-1.html) [ref2](https://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs143/cs143.1128/handouts/100%20Bottom-Up%20Parsing.pdf)
### 資訊檢索 information retrieval (IR) (Zobel, 1998)
#### 定義
資訊檢索可以定義為一種軟體程序,用於處理文件儲存庫中的資訊的組織、儲存、檢索和評估,從一個龐大且結構化的資料中去滿足使用者檢索資訊的需求。簡而言之,資訊檢索目的就是根據使用者提問(Query)找出符合的相關文章(Document)並回傳結果。
#### IR分為三個規模
1. Web Search (網路搜索)----->分散
2. Personal information (個人資訊)----->輕量
4. Enterprise (企業機構)----->集中
#### IR 模型
資訊檢索模型選擇使用者需要的或使用者以查詢的形式請求的文檔並對其進行排序。
流程分為:
1. Acquisition: 透過由爬蟲收集並儲存在資料庫中
2. Representation: 建立摘要和書目描述(如,作者、標題、來源、資料和元資料等)
3. File Organization: 文件組織方法,分為Sequential(contains documents by document) 與 Inverted(contains term by term)
4. Query: 使用者查詢。一個query不會唯一地識別集合中的單個對象。相反,可能會有好幾個搜尋結果匹配,其中可能具有不同程度的相關性。
> 補充:information retrieval 與 data retrieval 不同,data retrieval 具有明確定義的結構和語義,而容許小錯誤及語意上的歧異。
[ref1](https://andy6804tw.gitbooks.io/information-retrieval/content/boolean-retrieval/he-wei-zi-liao-jian-7d223f.html) [ref2](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10233314) [ref3](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-information-retrieval/)
### Multiword Expressions (MWEs)
#### 定義
多字表達式 (MWE) 是由至少 2 個單字組成的表達式,並且本質上可以在語法和/或語義上具有idiosyncratic(特殊性)。
#### 分類
1. Fixed expressions: 固定表達式是完全詞彙化的,既不能在形態語法上發生變化,也不能在內部進行修改。
2. Semi-fixed expressions: 在半固定表達中,詞序和構成是嚴格不變的,而詞形變化、反身形式和限定詞選擇的變化是可能的。Non-decomposable idioms, compound nominals, Proper names 都是這一類。
> 以 non-decomposable idioms舉例:
kick the bucket 可以有詞形變化(He kicks the bucket),但無法接受被動句式(*as the bucket was kicked)因為語意改變。
3. Syntactically-Flexible Expressions
這一類比上述兩點具更廣泛的句法可變性,如:decomposable idioms, verb-particle constructions 以及 light verbs。
4. Institutionalized Phrases
制度化短語是約定俗成的短語,如:traffic light。這類詞語的語義是與句法組合的。對於短語“traffic light”,“traffic ”和“light”都保留了單義,但透過構式組合產生了compositional reading。
#### 在 NLP 中的問題
##### overgeneration problem 過度生成問題
如,遇到不同語言變體中的正確的表達式 - telephone booth (American) or telephone box (British, Australian),可能泛化接受不完美的組合 - telephone cabinet, telephone closet。
##### idiomaticity problem 慣用性問題
如,kick the bucket這種詞彙的語義與 kick / the / bucket 三個構成成份的語義毫無關聯。
[ref](https://aclweb.org/aclwiki/Multiword_Expressions)
### 相互資訊/互信息 mutual information (MI)
#### 定義
互信息在某種程度上類似於correlation(相關性),因為它**衡量兩個量之間的關係**。但MI的優點在於它可以檢測任何類型的關係,而相關性只能檢測線性關係。
除此之外,MI適用於初期階段的feature development,因為他使用起來簡單且容易解讀、計算效率高、在理論上有良好的基礎、抗過度擬合且能夠檢測任何類型的關係。
#### 公式:
$I(X;Y)=\sum_{x\epsilon \chi }^{} \sum_{y\epsilon \nu }^{}p(x,y)log\frac{p(x,y)}{p(x)p(y)}$
X與Y為兩個隨機變量,他們的聯合機率密度函數為p(x,y),其邊際機率密度函數分別為p(x)與p(y),MI I(X;Y) 的聯合分佈 p(x,y) 和 p(x)p(y) 之間的相對熵為上述公式。
#### 舉例

[ref1](https://www.kaggle.com/code/ryanholbrook/mutual-information) [ref2](https://blog.csdn.net/tangxianyu/article/details/105759989)
---
<!-- ## tags, 拜託不要刪除以下 -->
###### tags: `QL2024`
<!-- ---
## 名字:
### 以下如果要用到標題請打三個以上的井字號 -->
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

