
---
# Building Multi-Agent Systems with Agentic RAG
By Abhishek Mishra, Tune AI
---
## What are Multi-Agent Systems?

---
*image by Gelareh Taghizadeh*
---
## What are Multi-Agent Systems?
* A system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents.
* **Characteristics:**
- Autonomous
- Distributed
- Interactive
- Specialized
---

*(image by Stewart Chien)*
*Think of a group of robots exploring a new planet.*
---
## Why use multiple agents?

---
- Complex Problems: Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable subtasks.
- Efficiency: Parallel processing and specialized skills can lead to faster and better results.
- Robustness: The system can still function even if some agents fail.
- Scalability: Easier to add more agents to handle increasing workload.
- Emergent Behavior: Agents working together can create novel solutions that no single agent could come up with on its own.
---
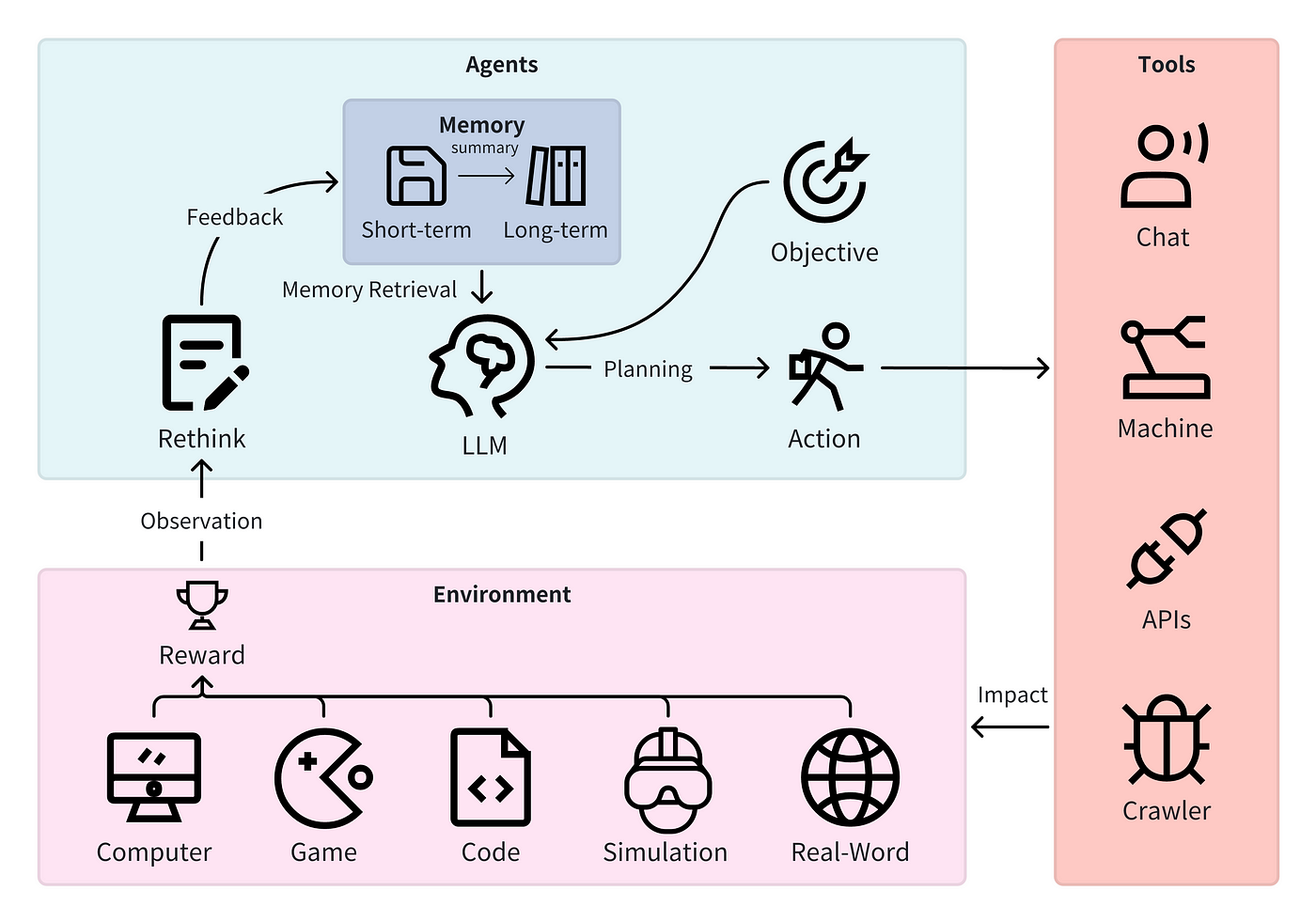
## Memory in Multi-Agent Systems 🧠
The ability of an agent to store and recall information about past interactions, experiences, and knowledge.
**Why is it Important?**
- Contextual Awareness
- Learning and Adaptation
- Personalization
- Consistency
---
**Types of Agent Memory:**
- **Short-Term Memory:** information about recent events (e.g., current conversation turn).
- **Long-Term Memory:** stores more persistent information (e.g., learned facts, user preferences, world knowledge).
---
## Introducing Agentic RAG
- **RAG:** Enhancing language models with external knowledge.
- **Agentic RAG:** Equipping each agent in a multi-agent system with RAG capabilities (giving access to retrieval tools)
---
## How it works
Query: Agent formulates a query based on its current task and context.
Retrieve: Agent searches a relevant knowledge base for information.
Augment: Agent integrates retrieved information into its input.
Generate: Agent's language model generates a response informed by the retrieved knowledge.
---
## Advantages of Agentic RAG
- Improved Accuracy
- Reduced Hallucinations
- Specialized Knowledge
- Dynamic Updates
- Coherent Collaboration
---
## Demo: NovelAI - A Multi-Agent Novel Writing System
* Collaborative fantasy novel creator.
* **Agents:**
* **Worldbuilder:** creates and maintains the fantasy world.
* **Plotter:** develops the overall plot.
* **Character Agent:** creates and develops characters.
* **Chapter Writer:** writes individual chapters.
* **Agentic RAG:** Each agent has access to a specialized knowledge base.
---
> show the sequence diagram reference
---
## Technology Stack
- LangChain
- Hugging Face Sentence Transformers
- FAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search)
- Tune AI API (gpt-4o)*
- Streamlit/CLI
---
## Code Walkthrough - Agent Class
```python
class Agent:
def __init__(self, name: str, knowledge_base_directory: str, task: str):
self.name = name
self.db = create_embeddings(knowledge_base_directory)
self.task = task
self.llm = create_chat_openai_instance(tuneai_api_key=os.environ["TUNE_API_KEY"])
def query_knowledge_base(self, query: str, top_k: int = 5):
# ... (RAG retrieval using FAISS) ...
def generate_response(self, user_input: str, context: str) -> str:
# create a knowledge base query
rag_query = f"Relevant information for task '{self.task}': {context}\nUser input: {user_input}"
# Retrieve relevant information
relevant_docs = self.query_knowledge_base(rag_query)
# combine for augmented input
augmented_input = f"Task: {self.task}\nContext from other agents: {context}\n"
if relevant_docs:
augmented_input += "Relevant knowledge:\n"
for doc in relevant_docs:
augmented_input += f"- {doc['content']}\n"
augmented_input += f"\nUser input: {user_input}\n"
# generate response using LLM
# ... (Prompt templating and LLM call) ...
```
---
## Code Walkthrough - Knowledge Base Creation
```python
from langchain.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
from langchain_huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
def create_embeddings(directory: str, glob: str = "**/*.txt") -> FAISS:
# load documents from the directory
loader = DirectoryLoader(directory, glob=glob)
documents = loader.load()
# split documents into chunks
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# create embeddings using Sentence Transformers
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="all-mpnet-base-v2")
db = FAISS.from_documents(texts, embeddings)
return db
```
---
## Code Walkthrough - Agent Initialization and Interaction
```python
# Initialize agents
worldbuilder = WorldbuilderAgent()
plotter = PlotterAgent()
character_agent = CharacterAgent()
chapter_writer = ChapterWriterAgent()
# ... (User input and agent interaction logic) ...
# Example: Worldbuilding
world_context = worldbuilder.generate_response(user_input, "")
# Example: Plotting
plot_context = plotter.generate_response(user_input, world_context)
# ... (And so on for other agents) ...
```
---
## How does the memory work in NovelAI?
* Basic short-term memory through context passing between agents.
---
## Enhanced Memory Possibilities:**
---
- **Conversation Buffer:** Store recent interactions in a limited-size buffer (short-term).
- **Vector Database (FAISS):** Use the existing FAISS index to store and retrieve important events, summaries, or learned facts (long-term).
- **External Database** (e.g., SQLite, PostgreSQL): Store more structured information about the story, characters, and user interactions (long-term).
- **Better RAG**: an agent could query its memory for past interactions related to a specific character before querying its knowledge base.
---
]
---
## Code Repo
*github.com/abhishekmishragithub/novelai*
---

---
## Thank YOU!!
**🌐 ☎️ @stalwartcoder**
Checkout: tunehq.ai/developers / studio.tune.app / finetune.new
DM me for some cools stcikers!
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

