# _MongoDB_ encryption
All this is valid for _MongoDB_ version >= 4.2
## Transport layer
Full support for _TLS_ for free, only _FIPS_ mode is enterprise only
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/security-transport-encryption/>
## Encryption at rest
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/security-encryption-at-rest/>
### Server side: enterprise only
Only supported with the _WiredTiger_ storage engine:
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/security-encryption-at-rest/>
has full support for queries,
_AES256-GCM_ only for linux, _AES256-CBC_ supported for linux and windows
### Field level client side encryption
Field level encryption: <https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/>
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/reference/encryption-schemas/#mongodb-autoencryptkeyword-autoencryptkeyword.encrypt.algorithm>
_Encrypt-then-MAC_ deterministic or random initialization vector is used, _MongoDB_ only supports _AEAD\_AES\_256\_CBC\_HMAC\_SHA\_512_
#### Explicit (manual) encryption: free
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/manual-encryption/>
The client is required to encrypt and decrypt data on its own, this is basically transparent for the server, the server can enforce encryption of certain fields using the validation schema.
This could be done trough the _mongosh_ provided methods:
- _getClientEncryption()_
- _ClientEncryption.encrypt()_
- _ClientEncryption.decrypt()_
#### Automatic encryption: enterprise only
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/automatic-encryption/>
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/queryable-encryption/>
Applications must create a database connection object with the automatic encryption configuration settings. Applications do not have to modify code associated with constructing the read/write operation but only some operations are supported and can be done transparently: <https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/reference/supported-operations/>
##### How it works
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/automatic-encryption/#how-encrypted-writes-and-reads-work>
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/keys-key-vaults/>
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/manage-keys/>
<div style="page-break-after: always; visibility: hidden">
\pagebreak
</div>
<div style="page-break-after: always; visibility: hidden">
\pagebreak
</div>
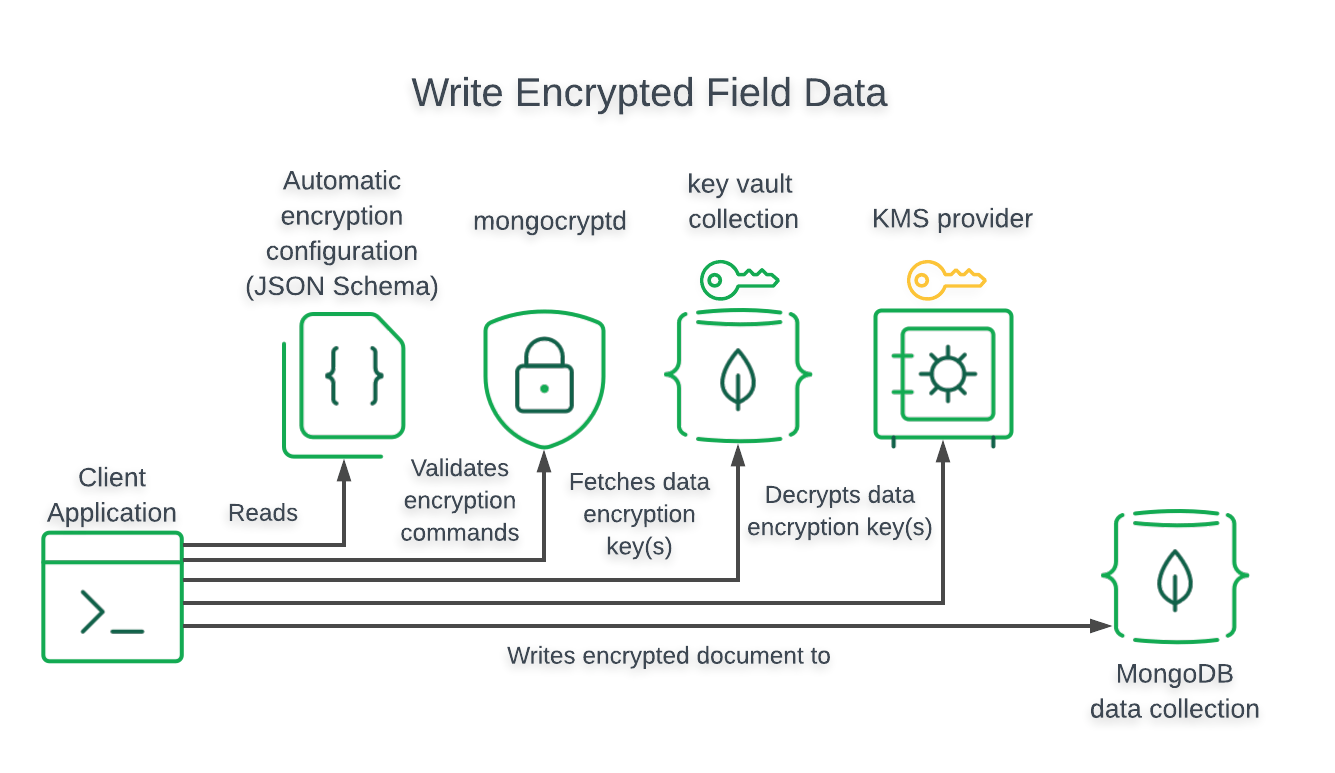
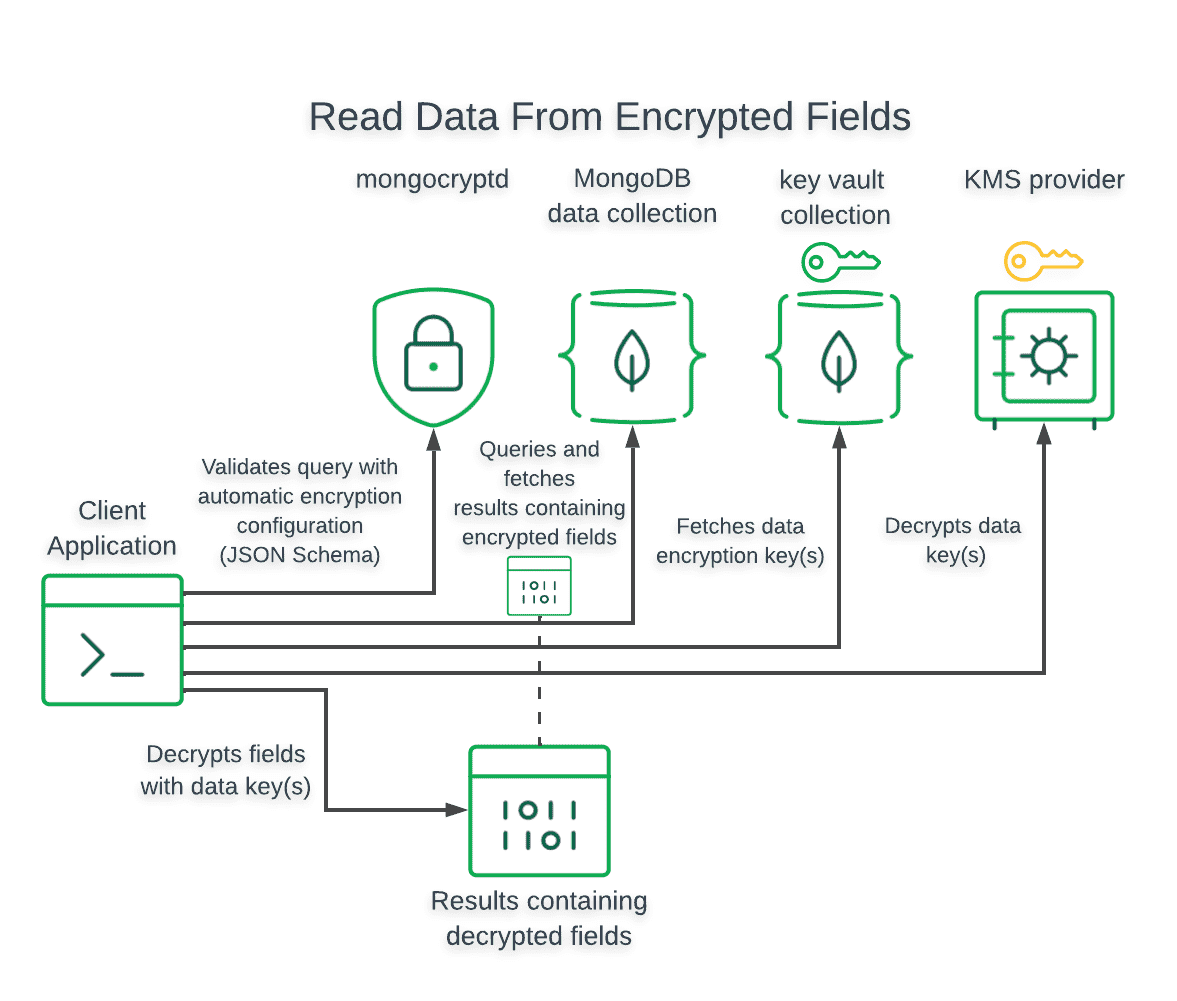
In the automatic decryption process the encrypted data is stored in a BinData blob that contains metadata about the Data Encryption Key and Encryption Algorithm.
The data encryption key will be automatically stored by _MongoDB_ in a Key Management Service (KMS) encrypted with a Customer Master Key (CMK).
Deleting the CMK renders all data encryption keys encrypted with that CMK as permanently unreadable, which in turn renders all values encrypted with those data encryption keys as permanently unreadable.
The BinData blob metadata includes the data encryption key _id and encryption algorithm used to encrypt the binary data.
The automatic decryption process works as follows:
1. Check the BinData blob metadata for the data encryption key and encryption algorithm used to encrypt the value.
2. Check the key vault configured in the current database connection for the specified data encryption key. If the key vault does not contain the specified key, automatic decryption fails and the driver returns the BinData blob.
3. Check the data encryption key metadata for the Customer Master Key (CMK) used to encrypt the key material.
- For the supported KMS platforms:
- Amazon Web Services KMS,
- Azure Key Vault,
- Google Cloud Platform KMS,
send the data encryption key to the KMS provider for decryption. If the CMK does not exist or if the connection configuration does not grant access to the CMK, decryption fails and the driver returns the BinData blob.
- For the
- Locally Managed Key,
retrieve the local key and decrypt the data encryption key. If the local key specified in the database configuration was not used to encrypt the data encryption key, decryption fails and the driver returns the BinData blob.
4. Decrypt the BinData value using the decrypted data encryption key and appropriate algorithm.
Applications with access to the _MongoDB_ server that do not also have access to the required master key and data encryption keys cannot decrypt the BinData values.
Automatic client-side field level encryption is available with _MongoDB_ Enterprise only.
Since the _MongoDB_ server cannot decrypt nor introspect the contents of the encrypted field, it cannot validate the encryption options.
This means the server can't prevent clients pushing randomized encryption data instead of deterministic meaning that queries expecting deterministically encrypted data for that field will return inconsistent results, as the server cannot match any of randomly encrypted fields.
#### Field encryption types
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/encryption-algorithms/>
##### Deterministic
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/encryption-algorithms/#std-label-csfle-deterministic-encryption>
Ensures a given input value always encrypts to the same output value each time the algorithm is executed, provides greater support for read operations, nut encrypted data with low cardinality is susceptible to frequency analysis recovery.
For sensitive fields that are not used in read operations, applications may use Randomized Encryption for improved protection from frequency analysis recovery.
For sensitive fields that are used in read operations, applications must use Deterministic Encryption for improved read support on encrypted fields.
##### Randomized
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/fundamentals/encryption-algorithms/#std-label-csfle-random-encryption>
Ensures that a given input value always encrypts to a different output value each time the algorithm is executed, provides the strongest guarantees of data confidentiality, but it also prevents support for any read operations which must operate on the encrypted field to evaluate the query.
Randomized encryption also supports encrypting entire objects or arrays, while this protects all fields nested under those fields, it also prevents querying against those nested fields.
<div style="page-break-after: always; visibility: hidden">
\pagebreak
</div>
## Recap
<https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/csfle/features/#comparison-of-features>

 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

