# 2019q1 Homework7 (skiplist)
contributed by < `LiunuXXX` , `jeffcarl67`>
## 預期目標
1. 思考 Linux 核心內部的資料結構,特別是 cache-oblivious data structures 的考量
2. 實作 Skip list,設計對應的效能分析框架
3. 開發適用於使用者層級和核心層級的程式碼
## 開發環境
<`jeffcarl67`>
```
$ lscpu
架構: x86_64
CPU 作業模式: 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
Address sizes: 39 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
CPU(s): 4
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3
每核心執行緒數: 2
每通訊端核心數: 2
Socket(s): 1
NUMA 節點: 1
供應商識別號: GenuineIntel
CPU 家族: 6
型號: 60
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4210M CPU @ 2.60GHz
製程: 3
CPU MHz: 859.812
CPU max MHz: 3200.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 5190.32
虛擬: VT-x
L1d 快取: 32K
L1i 快取: 32K
L2 快取: 256K
L3 快取: 3072K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3
```
```
$ uname -r
4.19.45-1-MANJARO
```
```
$ gcc --version
gcc (GCC) 8.3.0
```
## 作業要求
* 完成 [第 11 週測驗題 (中)](https://hackmd.io/s/BkFJPHriE) 和所有延伸題目
* 在 Linux 核心原始程式碼使用 skip list 的案例,介紹其原理,設計 Linux 核心模組的實驗
* 需要涵蓋 kernel API 同步機制的運用
* 執行時期的分析 (提示: 可善用 eBPF)
## 作業區
==完成 [第 11 週測驗題 (中)](https://hackmd.io/s/BkFJPHriE) 和所有延伸題目==
### 測驗 `1`
給定一個 circular linked list 實作如下: (檔案 `list.h`)
```cpp
#ifndef INTERNAL_LIST_H
#define INTERNAL_LIST_H
/* circular doubly-linked list */
typedef struct __list_t {
struct __list_t *prev, *next;
} list_t;
/*
* Initialize a list to empty. Because these are circular lists, an "empty"
* list is an entry where both links point to itself. This makes insertion
* and removal simpler because they do not need any branches.
*/
static inline void list_init(list_t *list) {
list->prev = list;
list->next = list;
}
/*
* Append the provided entry to the end of the list. This assumes the entry
* is not in a list already because it overwrites the linked list pointers.
*/
static inline void list_push(list_t *list, list_t *entry) {
list_t *prev = list->prev;
entry->prev = prev;
entry->next = list;
prev->next = entry;
list->prev = entry;
}
/*
* Remove the provided entry from whichever list it is currently in. This
* assumes that the entry is in a list. You do not need to provide the list
* because the lists are circular, so the list's pointers will automatically
* be updated if the first or last entries are removed.
*/
static inline void list_remove(list_t *entry) {
list_t *prev = entry->prev;
list_t *next = entry->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
/*
* Remove and return the first entry in the list or NULL if the list is empty.
*/
static inline list_t *list_pop(list_t *list) {
list_t *foo = list->prev;
if (foo == list)
return NULL;
LL1
}
#endif
```
請參照上方程式註解,補完對應程式碼。
LL1 = ?
---
首先我們看看`list_pop`的要求
```clike
/*
* Remove and return the first entry in the list or NULL if the list is empty.
*/
```
可知我們需要用到 `list_remove` 將 list 的 first entry 移除後並且回傳,若 list 為空就回傳 NULL
接著看 `list_remove` 的實作
```clike
/*
* Remove the provided entry from whichever list it is currently in. This
* assumes that the entry is in a list. You do not need to provide the list
* because the lists are circular, so the list's pointers will automatically
* be updated if the first or last entries are removed.
*/
static inline void list_remove(list_t *entry) {
list_t *prev = entry->prev;
list_t *next = entry->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
```
* prev 記錄 entry 的前一個 node
```clike
list_t *prev = entry->prev;
```

---
* next 記錄 entry 的後一個 node
```clike
list_t *next = entry->next;
```

---
* prev 的 next 指標指向 next
```clike
prev->next = next;
```

---
```clike
next->prev = prev;
````
* next 的 prev 指標指向 prev

* 最終狀態如下圖

---
以上完成了 `list_remove` 的一次操作,可以注意到此方法僅改變前後指標, entry 並未被移除,其 prev 及 next 指標並未變動。
接下來回到 `list_pop` 中的第一行
```clike
list_t *foo = list->prev;
```
* foo 記錄 list 的前一 node ,此 node 即為 list 的 first entry

---
因此我們用 `list_remove` 將 foo 移除,再將其回傳即可,如下圖

故答案選擇 `(e)` list_remove(foo); return foo;
---
## 延伸問題:
### 1. 研讀 2019q3 Week11 的 cache-oblivious data structures 參考資料,記錄所見所聞:
---
[Maximize Cache Performance with this One Weird Trick: An Introduction to Cache-Oblivious Data Structures](https://rcoh.me/posts/cache-oblivious-datastructures/)
文章中提到,Postgres 利用固定大小的 blocks ,又稱為 "pages" 實作 B-Tree,其目的是為了與 OS 中的 page sizes 做對應,而 OS 又對應到硬體。
然而,上述做法實作於不同硬體時,必須針對其挑選一最適合的 page size 以達到較好的效能。
因此本篇的主題便是想設計不被 underlying cache size 影響的資料結構及演算法,如此我們不需自己調整 cache size,程式碼便會最佳化的利用 cache layers,擁有此性質的資料結構及演算法,我們稱之為 "cache-size oblivious"。
首先,我們來看一張 BST 的效能比較圖
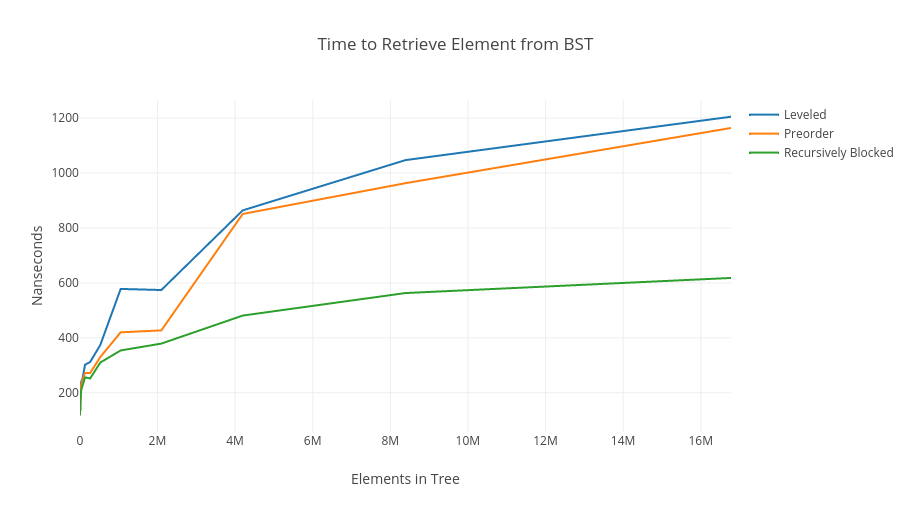
上圖中我們可以看到三種不同策略的 BST 走訪:
1. blue line : level by level 的走訪,又稱為 "bread first traversal".
2. orange line : (preorder) "depth first traversal".
3. green line : 利用 "recusive blocking" 法實作上述的 cache obivious 概念.
由上圖我們發現,在 elements in tree 達到 1600 萬的時候,"recursive blocking" 法的效率為另外兩種方法的近兩倍之外。
接下來我們探討如何實作 green line 的方法,以及其如何效能遠高於其他兩種方法的原因。
#### A new scheme for analyzing algorithms
一般分析演算法效能的 Big-$O$ notation,是假設讀取成本與記憶體中的 byte 成正比,然而真實世界的運作方式是以 block 為單位,即便你只想讀少量 bytes 的資料,還是得付出其所在整個 block 的成本,反之,若你想從同一個 block 讀取更多的 bytes,幾乎不用負擔任何額外成本。
因此 cache 利用率較好的演算法應該有以下特質:
When we read a block of data, we make use of every byte in that block.
然而使用一般演算法分析無法看出 "cache-oblivious" 的效益,因此我們介紹一種較接近真實世界運作 (work in blocks) 的演算法分析模型。
探討這種不受 cache size 影響又能最佳化運作的演算法時,我們假設 memory 有兩個區塊,small fast layer 及 big slow layer,其擁有以下特性:
1. memory 只可以從 slow layer 移動到 fast layer,且單位為固定大小的 block, $B$
2. slow layer 的大小為無限大,而 fast layer 的大小為 $M$
3. 我們分析演算法時以 $M$ 為 cache 的單位,$B$ 為 block 的單位
4. 分析時一單位的工作量為從 slow memory 載入 a block 至 fast memory,其他皆視為極快速的工作,不納入考量
回到前面那張 BST 效能比較圖

我們可以發現,在 Elements in Tree($N$)很小時,效能幾乎沒有差異,那是因為所有樹都在同一 block 內,讀取成本相差無幾,此外,blue and orange lines 中平坦的部分發生在特定的 internal cache sizes,而當$N$越大,cache-oblivious 的優勢就越大。
接著我們看看上圖三種方法的運作方式:
#### Blue line : By Level (Breadth)

* 其在 memory 內的觀點是以上圖的橘框為單位,elements 內的數字即為其在 array 內的位置
* 這種方法有個明顯的缺點,當 level 夠大時,每個 level 就代表一個 block,不但前面低階層的 block 利用率極低,如第一個 block 只存了 1 個 element ,且從樹根走訪至樹葉時,每經過一 level 就相當於讀取不同的 block,導致讀取成本高達 $\log_2N$
#### Orange line : Preorder (Depth First)

* 這種方法在讀取至下一個 block 之前,會持續往下走訪,在上圖的橘框內作樹根至樹葉走訪時,都在同一個 block 內讀取,為最佳情況。
* 最靠右下的 block 只存放一個 element,若是做最右邊的走訪,讀取成本也是 $\log_2N$
* 此方法僅比 BFS 好一點
#### Green line : Recursive Block Approach

* 利用 divide and conquer strategy 實現 cache-oblivious data structures and algorithms
* 從樹高 $(logN)$ 一半處 split ,則上半部有 $2^{\log_2(N)/2}=\sqrt{N}$ 個 nodes,而其 child nodes 也有大約 $\sqrt{N}$ 個 nodes,如此遞迴 split,如上圖
* 每個綠框為一個 block,橘框為 superblock
* blocks 間以及 superblocks 間皆是連續的
* 再讀取下一個 block 前,隨著讀取的 block size 變大,能走訪的 level 也越大
例如 :
讀取一 block of size $B$,可以走訪 $\log_2B$ 的 levels
樹有 $\log_2N$ 個 levels,則讀出的 blocks 數為
$\frac{\log_2N}{\log_2B}=\log_BN=F(N)$
### 2. 依據之前給定的 Linux 核心 linked list 實作,開發 cache-oblivious 的版本,並證實其效益
---
一般在設計 cache-oblivious 的 data structures and algorithms 時有三個常用策略:
1. van Emde Boas (vEB)
2. Weighted 平衡樹
3. Packed Memory Structure
而前面所利用的 Recursive Block Approach 便是採用 vEM 策略,如下圖

而設計 cache-oblivious linked list 常用的策略為 Packed Memory Structure
在 [Cache-Oblivious Algorithms and Data Structures](http://erikdemaine.org/papers/BRICS2002/paper.pdf) 中提到:
The packed-memory structure maintains N elements consecutive
in memory with gaps of size $O(1)$, subject to insertions and deletions in $O(\log2N)$
amortized time and $O((\log_2N)/B)$ amortized
接著我們介紹在 [Data Structures Libraries](http://www.lsi.upc.edu/~lfrias/thesis/thesis-lfrias.pdf?fbclid=IwAR0r3a8tTkC2QDVxR6cyEWN41JhZiQwdnQht8IJBJz3cGjVhfrr2aEYGqT8) 中與 packed-memory structure 相關的三種資料結構,其概念是在 linked list 配置 array 儲存資料,並將整個結構稱為 bucket

( a ) Contiguous: 在 linked list 內配置的 array 作連續性配置
* 優點:在同一個 bucket 內的 array 存取資料時,因為容易在同一個 memory block 內,存取速度會相較於原本的 linked list 快
* 缺點:和 array 一樣,插入或刪除資料時必須付出移動資料的成本
( b ) With gaps: bucket 內部 array 的元素間允許存在空隙
* 減少因插入刪除而移動資料的成本,較 Contiguous 好一些
* 每一個 element 必須耗費額外空間記錄此空間是否存資料
( c ) Linked: 內部元素間由 link 連接
* 須耗費額外空間儲存 link
* 插入或刪除時不須負擔額外移動資料的成本
* scalability 較佳
---
[github](https://github.com/jeffcarl67/unrolled_linked_list)
以下是 contiguous 的 unrolled list 實作:
* Data Structure of unrolled lsit
```clike=
struct listitem
{
struct list_head list;
int i[CAPACITY];
int stored;
int cap;
};
```
* Initialization
```clike=
void init_listitem(struct listitem *item) {
if (!item)
return;
item->cap = CAPACITY;
item->stored = 0;
}
```
每個 listitem 沿用了 list.h 的 list_head 之外,另有一陣列儲存資料,stored 記錄佔用格數,cap 為每個 bucket
element 格數,以下是幾個基本操作
(a) insertion
```clike
int insert_unrolled(struct list_head *list, int item) {
struct listitem *tmp = NULL;
struct listitem *last = NULL;
if (!list)
return 0;
last = list_entry(list->prev, struct listitem, list);
if (list_empty(list) || last->stored >= (last->cap / 2 + 1)) {
tmp = (struct listitem *)malloc(sizeof(struct listitem));
if (!tmp) {
printf("malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
init_listitem(tmp);
list_add_tail(&tmp->list, list);
last = list_entry(list->prev, struct listitem, list);
}
last->i[last->stored] = item;
last->stored++;
return 0;
}
```
(b) deletion
```clike=
int delete_unrolled(struct list_head *list, int index) {
struct listitem *entry = NULL;
int i = 0;
list_for_each_entry(entry, list, list) {
if (i <= index && i + entry->stored > index) {
memcpy(entry->i + index - i, entry->i + index - i + 1,
sizeof(int) * (i + entry->stored - index) - 1);
entry->stored--;
}
i += entry->stored;
}
return 0;
}
```
備註: [演算法筆記](http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/Data.html?fbclid=IwAR3dF04fF4gthJ_RuaC1jYpPr-TaO9ChuptqolrmBHUUiiQau6g3xn7yWnM)的資料結構中,假設 $N$ 筆資料,分成 $A$ 個 Bucket,每個 bucket 約 $B=N/A$ 個元素,而在刪除資料時,若是相鄰兩塊小於等於 $B$ 就要合成一塊。
本實作演算法尚未加上上述合併的功能。
### 效能分析
---
### 開發環境
<`LiunuXXX`>
```
$ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 4
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 2
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 58
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-3230M CPU @ 2.60GHz
Stepping: 9
CPU MHz: 2934.994
CPU max MHz: 3200.0000
CPU min MHz: 1200.0000
BogoMIPS: 5188.25
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 3072K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3
```
```
$ uname -r
4.15.0-51-generic
```
```
$ gcc --version
gcc (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.11) 5.4.0 20160609
```
```
$ gnuplot
gcc (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.11) 5.4.0 20160609
```
### Traversal
* Traversal Test of list
```clike=
void test_traverse(struct list_head *list, int num) {
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
struct timeval result = {0, 0};
struct listitem *entry, *next, *item;
int i;
int ret;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
item = (struct listitem *)malloc(sizeof(struct listitem));
item->i = i;
list_add_tail(&item->list, list);
}
system("echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches");
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
list_for_each_entry(entry, list, list) {}
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
timersub(&end, &start, &result);
printf("%d %lu %lu\n", num, result.tv_sec, result.tv_usec);
list_for_each_entry_safe(entry, next, list, list) {
list_del(&entry->list);
free(entry);
}
```
* Traversal Test of unrolled list (aware)
```clike
void test_traverse(struct list_head *list, int num) {
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
struct timeval result = {0, 0};
struct listitem *entry, *next;
int i;
int ret;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
ret = insert_unrolled(list, i);
}
system("echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches");
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
list_for_each_entry(entry, list, list) {
i = 0;
while (i < entry->stored) {
i++;
}
}
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
timersub(&end, &start, &result);
printf("%d %lu %lu\n", num, result.tv_sec, result.tv_usec);
list_for_each_entry_safe(entry, next, list, list) {
list_del(&entry->list);
free(entry);
}
```
利用 timeval 分析走訪 list 及 unrolled list (aware) 的時間,結果如下圖

推測此處差異主要是在時 unrolled list 內的 array 使其在讀取時較有優勢,而原本的 list 在存取時較常跳到不同的 block 而產生 cache miss 。
### Insertion
* Insertion test of list
```clike
void test_insert(struct list_head *list, int num) {
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
struct timeval result = {0, 0};
struct listitem *entry, *next, *item;
int i;
int ret;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
system("echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches");
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
item = (struct listitem *)malloc(sizeof(struct listitem));
item->i = i;
list_add_tail(&item->list, list);
}
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
timersub(&end, &start, &result);
printf("%d %lu %lu\n", num, result.tv_sec, result.tv_usec);
list_for_each_entry_safe(entry, next, list, list) {
list_del(&entry->list);
free(entry);
}
}
```
* Insertion test of unrolled list (aware)
```clike
void test_insert(struct list_head *list, int num) {
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
struct timeval result = {0, 0};
struct listitem *entry, *next;
int i;
int ret;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
system("echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches");
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
ret = insert_unrolled(list, i);
}
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
timersub(&end, &start, &result);
printf("%d %lu %lu\n", num, result.tv_sec, result.tv_usec);
list_for_each_entry_safe(entry, next, list, list) {
list_del(&entry->list);
free(entry);
}
}
```
Insertion 效能比較如下圖

類似 traversal,效能差異來自於 unrolled list 內的 array 於循序寫入時的效益。
### 3. 實作 Skip list,並且比照之前的 unit test 提供對應的測試、效能分析,還有改善機制
---
==在 Linux 核心原始程式碼使用 skip list 的案例,介紹其原理,設計 Linux 核心模組的實驗==
* 需要涵蓋 kernel API 同步機制的運用
* 執行時期的分析 (提示: 可善用 eBPF)
# References
1. [Maximize Cache Performance with this One Weird Trick: An Introduction to Cache-Oblivious Data Structures](https://rcoh.me/posts/cache-oblivious-datastructures/#fnref:assum)
2. [關於算法,那些你不知道的事](https://www.itread01.com/articles/1475818714.html?fbclid=IwAR39mapd0cR55YSU4rgLAPqOjR0L6gBE9JxbTzdIq2H8sOF44kbiFs3xL9s)
3. [Cache-Oblivious Algorithms and Data Structures](http://erikdemaine.org/papers/BRICS2002/paper.pdf)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

