---
robots: index, follow
tags: NCTU, CS, 共筆, 計網概, 陳志成
description: 交大資工課程學習筆記
lang: zh-tw
dir: ltr
breaks: true
disqus: hackmd
GA: UA-100433652-1
---
計算機網路概論--陳志成
===
> [TOC]
# Syllabus
- 除加簽者外,上課不點名
- 考試時間不調整,分數不調分
- 四次考試各佔 25%
- [其他共筆Test3](https://hackmd.io/s/BJXghQ2me)
# Course
## **01 Introduction**
**Web Classification (geographical scope)**
###### LAN, MAN, WAN
- Local Area Networks (LANs)
- Share and exchange data among systems / expensive resources
- Small scope
- usually owned by the same organization that owns the attached devices --> purchase and maintenancefaster (1~100Mbs)
- High-Speed LANs
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs)
- Middle ground
- 少用此區分
- Wide Area Networks (WANs)
- large geographical area
- public right-of-ways (大家都可以用) (ex. 電話線)
- *interconnected internal (switching) nodes*
- Relatively modest capacity
- slower (56k)
- xDSL (ADSL, HDSL, SDSL, VDSL)...
- High-Speed WANs
- Tiered LANs (階層式)
- Private WAN
- Internet (Public WAN)
- Cost saving
- Offloading management to public network provider
- public -> Less secure
- Private WAN
**Security**
- Security methods
- Authentication (認證)
- Password: Static, Dynamic
- Token
- Biometric tech.
- Authorization (授權)
- Integrity: protect from unauthorized change (不被竄改)
- parity check (檢查碼check bit)
- Confidentiality (保密)
- Availability (可用性)
- Non-repudiation (不可拒絕的) -> 凡走過必留痕跡
- Firewall
- Packet-filtering firewalls (過濾式):擋住特定連線 <- 最多用的
- proxy (代理式) -> (效能最差)
- Application-level proxy servers
- Circuit Level gateway
- Stateful inspection firewalls (檢查式) -> 追蹤連接狀態(效能較差)
- Hybrid (混合式)
- IP Security (IPsec)(網際網路安全協定)
- protecting IP datagrams and upper layer protocols
- IETF
- IPv4, IPv6
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) (綜合private & public network)
- 利用已加密的[通道協議](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%80%9A%E9%81%93%E5%8D%94%E8%AD%B0)(Tunneling Protocol)來達到保密、傳送端認證、訊息準確性等私人訊息安全效果
**Switch Network**
### Circuit Switching, Packet Switching
- Switch node (router)
- Switch network

- 打電話前幾秒無聲時間:尋找連線路徑中......
- 打手機的空白時間比家用電話長,因為手機會移動
- Circuit Switching
- Dedicated communication path between two stations
- circuit establishment -> Information transfer -> Circuit disconnect
- feature:
- Low channel utilization
- Delay prior to data transfer for session establishment
- data transmitted at a fixed data rate with no delay other than a propagation delay
- cons:
- bursty traffic ([非連續的資料傳遞](http://sls.weco.net/blog/tzef/10-jan-2009/12441))
- devices must transmit and receive at the same data rate (with no delay)
- Packet Switching
- packet -> transmit randomly -> arrived
- 每個packet包含:
- Header: 信封
- Payload: 內容
- 每個packet各自找路徑(router幫它找)
- router裡面有routing table來決定要送往哪個方向
- 使用「最短路徑演算法」
- **「store and forward」**
- 不需要reserve一條獨立的路徑
- Packet行為 [[1]](http://sls.weco.net/node/10669) [[2]](http://cs.uccs.edu/~cs522/F99rout.PDF)
- Datagram
- 每個packet獨自處理
- 相同目的地的packet不一定走相同路徑
- packet不會照順序到達
- Advantages
- no call-setup
- quicker for few packets
- avoid congestion (避免壅塞)
- reliable (find an alternate route if a node fails)
- Virtual Circuit (VC)
- 路徑會先建好
- 所有packet 走同一條路
- VC ID: 記錄下一個node要到哪,每過一個node都會更改(減少封包標頭VC欄位長度)
- 路徑上的所有router都會參與VC的建立,而且每台router都完全知道通過它的VC
- Advantages
- assure packet arrived in order
- error control: assure packet arrived currently
- flow control: receiver 可要求暫停傳送
- more rapidly
- packet可能傳到不見
- router當機
- router記憶體不夠
- 線路斷掉
- 線路雜訊
- 處理方法:
- 重傳(non-real-time資料)TCP
- 算了(real-time資料)UDP
- pros
- efficiency for bursty traffic
- carry out data-rate conversion (不用一定要相同的data rate)
- priorities can be used
- Packet Size
- 大小可以不固定
- size切越小,傳越快(但切太多會變慢)
**Delays**
[(要會算)](https://blog.gtwang.org/web-development/network-lantency-and-bandwidth/)
- propagation delay (傳送時)
- transmission time (出介面)
- processing delay (考慮位址)
- queuing delay (in queue)
- latency vs jitter (其實我還是不懂,可是考出來了GG)
- latency : delay 就是延遲
- jitter : delay 不同造成的延遲 (variance in delay)
**Layered Architecture**
- exchange data between two systems
- task => subtasks (模組化)
- relay on next lower level to perform more primitive functions and conceal the details (抽象化)
- change in one layer does not require changes in other layers
- protocol 協定(同級layer的溝通規則)
- OSI七層 (老式)
- TCP/IP五層
- 下到上 L1 ~ L5 (phy 到 app)
**OSI (7)**
- ISO制定的標準
- protocol:
- L1, L2: IEEE set (e.g. L2: MAC frame)
- L3: IETF -> IP
- L4: IETF -> TCP/UDP
### **1.physical layer**
- 實際傳資料 (bit / signal)
### **2.data link layer**
- package -> Frame [ header(目標地), message, trailer(偵錯碼)x]
- 做錯誤偵測error detection(real end-to-end的偵測, client端要求)
- 做錯誤重傳error correction(non-realtime[TCP]才要)
- MAC (Medium Access Control) Sub-Layer
- Share media rather than "point to point"
- Multi-access communication
### **3.network layer**
- generate packet header => higher layer for packet info.
- 做**flow control**和做**routing**
- routing: 找路徑
- flow/congestion control: 路徑選擇 (e.g. 控制流量)
- 走別條路
- buffer management
- all nodes must work together
- 產生和處理control message (ICMP) -> (目標地)
### **4.transport layer**
- virtual end-to-end link (出發點到目標點假設值直接end-to-end)
- virtual end的錯誤重傳,確認,以免link斷掉/node掛掉
- reassemble packets into messages (reorder)
- messages ----> packets --(reorder)--> messages
### **5.session layer**(包在application layer裡就變五層)
- 不真實存在 -> 後來發現不需要 (應用層做就好了)
- Directory service: 聯絡人要有table才連絡得到
- Load balance
- Access rights
### 6.presentation layer(包在application layer裡就變五層)
- 不真實存在 -> 後來發現不需要 (應用層做就好了)
- encryption 加密
- compression
- code conversion (ASCII <--> EBCDIC)
### 7.application layer
**TCP/IP (5)**
- experimental packet-switched => ARPANET
- DARPA
- IETF
- protocol:
- L1, L2: IEEE set (e.g. L2: MAC frame)
- L3: IETF -> IP, TCP/UDP
- L4: IETF -> port
### **1.Physical layer**
### **2.Network Access Layer**
- Addressing
- L2: MAC Address: **EA:10:08:EF****:......**
- L3: IP Address: **140.113.93.101**
- L4: Port number: **80**
- Services (e.g. priority)
- Many different standard
- NAP (Network Access Protocol)
### **3.Internet Layer**
- IP (Internet protocol) provides routing)
- router: connect two networks
### **4.Transport Layer**
- transfer of data between end points
- end-to-end error recovery and flow control
- TCP / UDP
### **5.Application**
**Internetworking**
- 將不同網路連在一起
- Internet
- Intranet
- Bridge
- Router
**Standardization**
- ISO, ITU, IEEE, IETF, ETSI, ANSI, etc...
## 02.phy
- analog -> digital
- analog
- quality, fidelity(保真)
- Tech
- ASK (amplitude 振幅): 0, 1
- FSK (frequency 頻率): less susceptible to error 較不易錯誤
- [PSK](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9B%B8%E4%BD%8D%E5%81%8F%E7%A7%BB%E8%AA%BF%E8%AE%8A) (phase 相位): more noise resistant 最不易出錯
- digital
- encoding
- receiver must know begins and ends
- receiver must recognize the value of each bit
- the higher the data rate, the more difficult for receiver's task is
- multiplexing (多工)
- [參考](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~b6506031/ExpReport/intro_1.html)
- carry multiple signal on a single medium
- Tech:
- FDM(Frequency-division mul...): 不同頻率代表不同傳輸者
- TDM(Time-division mul...): 時間排程
- [CDM](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/CDMA)(Code-division mul...): 分碼多重進接
- [Spread Spectrum](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%89%A9%E9%A2%91)(SS) 展頻
- Spread information signal over a wider bandwidth to avoid jamming and interception (傳輸頻寬變大,免疫雜訊干擾)
- Type:
- [DSSS](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E6%89%A9%E9%A2%91): 在傳送端,直接用高碼率的展頻碼序列去擴充功能訊號的頻譜,在接收端,用相同的展頻碼序列將訊號解擴
- [FHSS](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%B7%B3%E9%A2%91%E6%89%A9%E9%A2%91): 載波快速在不同頻率中切換,並在接收與發射端使用一種偽隨機的過程 (每次傳的頻率不同,只要對方知道你的hopping patten,就可以接到你的signal,而其他的傳輸者的hopping patten跟你不同就ok) (pseudorandom code)
- Transmission Media
- Guided media: 實體媒介傳輸
- twisted pair 雙向線: 兩銅線捲起來
- coaxial cable 同軸電纜
- optical fiber 光纖
- Unguided media: ex. 電磁波
- IR (Infrared) 紅外線
- unregulated (無規範的)
- diffusely reflected (漫射)
- 不穿透的
- security
- Interference 干擾
- 低成本
- 會被陽光干擾 noise
- directed beam: 一對一 (used for cross-building)
- omnidirectional: 全向的
- diffused
- Microwave radio
- long distance
- 穿牆
- regulation 有規範的
- ISM
## **03.Ethernet**
- IEEE 802 (LAN)
- 802.2: LLC
- 802.3: CSMA/CD
- 802.4: Token Bus
- 802.5: Token Ring
- 802.6: MAN
- 802.7: Broadband
- 802.10: Security
- 802.11: Wireless
- 802.14: Cable Modem
- Ingredients of LAN
- LAN/MAN Topology(拓樸)
- Bus

- Tree
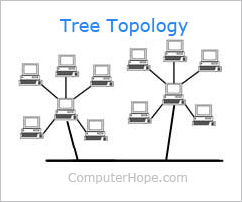
- Bus & Tree
- 所有 station 都看得到
- 必須校正傳輸 (MAC)
- no need to remove frames from the medium (absorbed by terminator)
- 多節點multipoint
- MAC protocol: regulate which station on medium may transmit at any point in time
- Centralized 集中
- Distributed 分散式
- Signal balancing (訊號要多強)
- Divide the medium to smaller segments
- Repeater
- phy layer 將訊號加強,重複
- 雙向
- in ring, repeater 作用是連接device, 並且是無向的
- 10 base 5 (10 Mbps, baseband, 500m cable) (?)
- 2.5m between two taps
- maximum of 100 taps in allowed
- Ring
- 點跟點之間用repeater連接
- 無方向性
- 目標將frame複製到自己的buffer
- frame繞一圈回到發送點後回收
- 有token才能傳 (802.3,802.4,802.5)


- Star
- 中心物件 hub
- hub功用跟repeater一樣
- Star physically, bus logically (邏輯上其實就是bus只是有分層)
- Hierarchical configuration (階層式)
- header hub (HHUB) 最高的hub
- intermediate hub (IHUB) 中間的hub

- Two-Level star Topology
- 有兩層的star -> HHUB IHUB 連接

- Hub(第一層)
- multiport (跟repeater最大的不同)
- like Shared media bus
- Hub
- only one station can transmit at a time 一次只能有一個傳
- Hub內可以把有問題的msg處理掉
- 10Mbps
- LAN Switch (第二層 -> 可以看到目的地)
- 用switch(到第二層找路徑,看mac位址), 不會全部都傳, 不會碰撞, 較有效率
- 同時間其他沒用到的路徑還是可以傳(因為第一點的緣故)
- 連上去的device不用做任何事情, throughput(傳輸量)就可以增加
- 易擴大
- type of Switch
- Store-and-forward
- 進來都儲存然後才傳送
- 會做錯誤偵測以及修復
- 優:錯誤率低
- 缺:慢
- cut-through
- switch一知道位址就直接傳送
- 優:快
- 缺:錯誤率高
- adaptive switch
- 一開始先用cut-through,發現有錯再改成store-and-forward
- Protocol Reference Model
- Two sublayers in OSI layer 2
- LLC(logical link control):
- 802.2
- provide one or more service access points (SAPs) (不只一個接點,模組化)
- MAC(medium access control):
- 傳送方將data包裝成有address以及erroe-detection fields的frame
- 接收方將frame分解(?)然後處理address以及錯誤偵測
- govern(控制) access to the LAN transmission medium

- LLC
- similar to other link layer
- transmission of a link level PDU (protocol data unit) between two stations, without an intermediate node
- different
- support multiaccess
- 不做error-detection -> 留給mac做
- 由mac解決連接問題
- Two-Level of Addressing
- MAC address
- 表示硬體的位置
- 點到點(每次到node就會改到下一個)
- LLC adderss
- 表示LLC使用者(?
- LLC address是紀錄使用者而非station(?)
- 終端到終端(一個傳出只有一種)

- MAC
- polling
- 類似開會,主席問誰要發言,如果有多人,只選其中一個
- round robin
- 輪流
- reservation
- 預約制
- contention
- 想傳就傳
- 當傳輸量少的時候,碰撞的幾率小,如bursty network,這個方法的 效率就很好。
- 最常用
- Generic MAC Frame Format

- 錯誤偵測及修復
- MAC
- 偵測錯誤並砍掉有錯誤的frames
- LLC
- 有錯誤的時候重傳
- LAN Protocols in Contex

- Bridge(第二層)
- no modification(類似郵差,只轉送不修改)
- 與router不同點
- 看mac address (local) ; router看ip(全世界)
- bridge在第二層 ; router在第三層
- 與switch不同點
- 都在第二層
- bridge是store-and-forward ; switch是兩種都有
- switch速度較快但是貴
- 用來連接兩個以上的LANs
- Router(第三層)
https://hackpad-attachments.imgix.net/nctucs08course.hackpad.com_1u8lA1PnbR9_p.672309_1479027139867_2016-11-13%2016-52-00%20的螢幕擷圖.png?fit=max&w=882
- Networking Devices總結
- gateway(4up)
- 連接兩個不同的網路系統
- 例如 電話 <-> circuit <-> gateway <-> packet <-> 電腦
- router(3)
- bridge (2)
- lan switch(2)
- multiport bridge
- bridge一次只能處理單一frame,而switch可以同時處理多個frames
- bridge用store-and-forward,而switch兩種都用
- repeater(1)
- hub(1)
- multiport repeater
- Ethernet LANs (乙太網路)
- 802.3
- commercial and light industrial environment
- define:
- physical layer
- mac layer: csma / cd
- Pure ALOHA
- 想傳就傳,失敗就再傳一次
- 如何知道失敗? 等傳過去又傳回來所需最長時間後,若沒收到回覆(ack)即為失敗
- 任兩個訊息只要稍微交錯到就失敗了
- Slotted ALOHA
- 將時間切為許多小段(time slot),只有該時段開始時可以傳
- CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)
- 傳之前先聽(listen),若有人在用就等
- 還是可能會失敗:
- propagation delay: 已經有人傳了但在聽的時候有時差沒聽見
- 兩個人以上同時在等
- 一樣要等ack
- non-persistent CSMA
- 發現有人在傳就等一下再聽一次
- 缺:可能會浪費時間,因為不知道何時可以傳
- 優:碰撞率低,因為每個人選擇的時間不一樣
- 1-persistent CSMA
- 一直聽直到可以傳
- 優:不浪費時間
- 缺:兩個人以上在等的時候,會碰撞
- p-persistent CSMA
- 一直聽直到可以傳(idle)
- 可以傳的時候有p的機率會傳,沒傳的話就繼續等
- 每個人傳的機率都不一樣故可降低碰撞率
- 一直再聽所以不會浪費時間
- 決定不傳的話,delay 1 time slot 再決定要不要傳 (中間就沒有listen了)
- performance
- n stations,np期望值
- np>1必定失敗
- 繼續等的話要跟後面來的人競爭
- throughput(吞吐量) -> 0
- p越小傳的機率越低,等的時間也越久
- CSMA delay 原理上來說,delay 會很長(不適合在廣域網路)
- CSMA/CD
- 傳的時候同時聽
- 如果傳送失敗(collision),就發出阻斷訊息(jamming signal)通知所有人停止傳送停止傳送
- 最差情況要等多久才偵測到碰撞
- twice the end-to-end propagation delay
- persistence in CSMA/CD
- 802.3 use 1-persistence
- Binary exponential backoff (2^n後回來試)
- 2秒試 4秒試 8秒試 .....
- 最多試16次後放棄
- 後傳的人成功機率高,因為兩次之間等待時間短
- Carrier Sense & Collision Detection
- A collision should produce substantially higher voltage swings
- 因為訊號會衰減,且太長的話要過很久才會知道,所以802.3限制線路最長500m
- hub偵測到collision,傳送CP (collision presence)
- collision domain (區域內會collision的這個區域)
- Auto Negotiation
- A station can be automatically configured to run at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
## **04. WLAN**
- Wireless LAN
- 802.11 (b/a/g/n [加速]/i [安全] /e [Queue] /f [協同工作] )
- BSS: basic service set 訊號可達範圍
- STA: station
- AP: access point (bridge)
- IBSS: **independent** BSS ([ad hoc的](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%84%A1%E7%B7%9A%E9%9A%A8%E6%84%8F%E7%B6%B2%E8%B7%AF) / peer-to-peer)
- ESS: extended service set (可以是多個BSS的集合)
- AP
- multiple BSS connected together form an ESS
- mobile stations to access fixed resource
- node 間不能互傳,一定要先經過 AP
- ad hoc
- Direct communication 直接傳
- One BSS
- **不需要既有的網路架構**,相互都可以傳,只要有一個BSS給他們傳出去就好了

- Infrastructure
- AP (access point -> bridge)和 stations 構成,所有的資料都要通過AP
- 離AP越近,傳送越快
- distribution system
- 多個BSS串成ESS
- allow mobile stations to access fixed resource

- Protocol Entities
- interact with MAC and PHY
- PMB bit -> signal
- Modulation(調變) and encoding
- PLCP
- SAP 讓下層了解上層
- carrier sense 看 channel 是否 busy
- MAC
- 同步
- 省電
- Roaming: Station 移動時可以自動換到下一個 AP
- MIB 網路管理
- MAC entity
- 基本機制
- 切封包
- 加密
https://hackpad-attachments.imgix.net/nctucs08course.hackpad.com_1u8lA1PnbR9_p.672309_1481637485456_2016-12-13%2021-57-42%20的螢幕擷圖.png?fit=max&w=882
- 802.11 Services
- Association 連線
- Reassociation 移動到下個AP的重連線
- Disassociation 斷線
- Authentication 802.11認證
- Privacy
- station to station (not end-2-end)
- station to station指加密ap跟station之間
- end to end整段加密
- only payload are encrypted
- WEP 已被破解的 MAC entity
- Station
- No transition
- BSS transition 跨 BSS
- ESS transition 跨 ESS
- Protocol Architecture
- PHY
- FHSS / DSSS / IR
- MAC
- 一個MAC可以support多個phy layer
- DCF (distributed coordination function)
- protocol : polling
- contention algorithm
- PCF(point coordination function)
- optional (沒有用)
- Inter Frame Space(IFS)
- SIFS(short inter frame space)
- transmitor 和 receiver 同一時間只有一個在工作
- 要傳的時候transmitor要打開,打開需要時間
- 硬體運作需要的時間
- 最少需要等這個時間(跟physical layer有關)
- PIFS(PCF IFS)
- polling需要用的時候需要的時間
- SIFS + slot time(去的時間)
- DIFS(DCF IFS)
- SIFS + 2* slot time(去+回的時間)

- DCF
- collision detection (CD) 不容易做 (但也是作的到)
- 因為要**邊聽邊傳**
- 用CSMA/CA (collision avoidance) 代替
- 聽到IDLE不傳,直到DIFS過後沒人傳才傳
- 還是可能撞 -> 兩個人同時
- 2種傳法
- 如果一聽就是IDLE,等DIFS後就直接傳
- 如果一聽是busy, 等到IDLE時要等cWindow,避免是很多人都在等IDLE
- 傳完的 cWindow 是為了不要讓傳過的人再搶到channel, 讓別人也有機會傳
- 聽到medium是busy時,聽到DIFS後也不傳,繼續等contention window (random 0~7) ,如果等的時候有人傳了就停下來等medium IDLE,等完後把沒等完的contention window等完如果是IDLE才傳
- 因為ramdom 0~7 撞到的機率低
- 傳完的人必須再等一個contention window
- PHY layer 有 CCA (clear channel assessment) 會作carrier sense

- CSMA/CA + ACK
- UniCast : 一對一傳輸
- desitination收到的時候要等SIFS的時間才ack
- 確定資料是對的
- receive轉成transmit正好需要SIFS的時間

- 傳回去的ack一定不會跟別人collsion,因為SIFS比較短
- hidden terminal
- C因為在A的訊號範圍外,所以A不知道C的存在(反之亦然)
- CSMA/CA會有問題

- AC都要傳給B但是AC互相不知道對方存在(聽不到是否在傳),故可能會碰撞
- virtual sensing
- 為了解決hidden terminal的問題
- RTS: request-to-send
- CTS: clear-to-send
- 要傳的人發出RTS給目標,目標收到後會發出CTS告訴所有人它在某段時間已經被預訂了
- NAV(Net Allocation Vector) 表示某段時間 Contain a duration field that defines theperiod of time the medium is to be reserved
- RTS thershold : data沒有長到一個程度,不要用virtual sensing,因為搞不好直接傳就好了
- PCF
- contention free
- Protocol : centralized polling master
- 主席,負責問誰要傳還有決定誰可以傳
- Superframe
- PCF和DCF交互使用
- PCF和DCF在不同時間要傳,如果時間內傳不完,就把下一段的DCF時間移過來用,PCF時間則不變,使下次的DCF時間減少
- Scanning
- Initial setup
- Infrastructure 找network
- ad hoc找IBSS
- Roaming
- 找新AP
- Passive Scanning
- AP自己大喊我在這裏 (Beacon)
- Active Scanning
- 使用者問說那裡有AP,然後AP回說我在這 (Probe)
- 會回覆可以加入一個network所需要的資訊
- beacon 服務設定識別碼
- roaming approach
- SNR(signal noise ratial) = S/N
- SNR<40%時找 (太早找會找不到)
- 另一個AP的SNR>50%時連上
- PCF vs DCF
- 當channel is busy,一個人用PCF,一個人用DCF,當一idle的時候,誰會先搶到?
- PCF。因為PIFS 等的時間比較短。(短於DIFS)
- 乒乓效應(Ping - Pong effect):一高過現有訊號就換的話,訊號可能又會降下來,所以又換回來,換來換去稱為乒乓效應
- power management
- 能睡就睡,隔一段時間後醒來看有沒有人要送(ap會說),睡的時候AP幫收
- 802.11b
- 傳輸率最高爲11Mbps
- 離AP太遠可能會降到1Mbps
- 802.11a
- 2.4GHz的干擾太嚴重
- 用5.8GHz
- 802.11n
- improving 802.11a && 802.11g
- 54Mbps~600Mbps
- 增加了 multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)
- 多根天線
- 802.11e
- 改善MAC quality of service (QoS)
- 利用SIFS和contention來提高一個人的成功率
- SIFS短 / contention window 短 成功率高
- enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA)
- 改善DCF
- 增加AIFS (4 level >= DIFS)
- 有限次數可以傳成功後不用等contention window
- Wi-Fi(Wireless Fidelity)Certification
- Wi-Fi,不是一種網絡,是一種certification
- 是802.11網絡的認證
## **05. Supplementary: Security**
- encryption
- Enciphering (encryption) 加密
- plaintext (cleartext) -> ciphertext
- Deciphering (decryption) 解密
- ciphertext -> plaintext (cleartext)
- two categories
- Secret-key algorithm
- 用同一把密鑰來作加解密
- DES(Data Encryption Standard)
- AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Ex.鎖頭
- Public-key algorithm
- 用不同的鑰匙來作加解密
- RSA
- Ex.喇叭鎖
- Secret-key algorithm
- Transposition Ciphering
- 交換順序
- Substitution Ciphering
- 代換
- DES (Data Encryption Standard)
- 原始資料切斷,每段64bits,先排列以後,每段再進行subtitution and transposition
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- NIST制定
- AES-128/192/256 (數字表示key的長度)
- Public-Key Algorithm
- Public Key任何人都可以拿到
- Secret (private) key 只有擁有者有
- plaintext -> **public key** -> ciphertext -> **secret key** -> plaintext
- RSA
- 兩個很大的質數相乘得到public key
- Message Authentication
- assure data integrity and to authenticate the data origin
- 解出來是對的˙的話,代表資料正確且確實是secret key的擁有者傳的
- Message Authentication Code (MAC)
- one-way hash function
- hash: 將任意長度的訊息變成一段固定長度的訊息
https://hackpad-attachments.imgix.net/nctucs08course.hackpad.com_1u8lA1PnbR9_p.672309_1481527664691_2016-12-12%2015-27-13%20的螢幕擷圖.png?fit=max&w=882
- hash function
- Unkeyed hash
- **no secret key** between the communicating parties
- MD5
- produce an 128-bit fingerprint or message digest
- 接收者從收到的訊息產生digest再拿去跟收到的比對
- SHA-1
- 160-bit message digest
- Keyed hash
- HMAC
## **06. ARQ**
- 為甚麼要ARQ
- 資料傳送會有錯誤
- Error detection
- Parity Check (算整個bitstream contains odd/even 1)
- CRC
- Error Correction
- 直接更正錯誤的frame
- Retransmission
- 錯誤的frame直接重傳
- ARQ
- 分類
- Stop and Wait ARQ (Go back 1)
- Go Back N ARQ
- Selective and Repeat ARQ
- 實作
- Node A (Trasmitter) 傳送資料,Node B (receiver)接收資料,並回傳ack如果正確,回傳nak (negative ack)如果packet出錯
- 缺點: delay is arbitrary and some packets are never to be arrived
- 解法 : LLC Header 包含Serial number (SN)
- 還是有問題,可以比較兩者packet是否相等,但還是identical就掛了
- 解法 : 回傳的Packet 也要編號 (RN)
- 重傳(Go Back N )是全部都傳,只傳錯的叫Selective and Repeat (不好做)
- SN/RN in LLC frame
- 對於transmitter,要填SN、packet
- 對於receiver,要填RN,但沒有packet
- RN只要填在等的SN就不用區分ack/nak
- 假設A傳1失敗,B傳1(nak)
- A傳1成功,B傳2(ack)
- Piggy Backing
- 用在兩個node互傳做其他事情的時候順便回會填SN(別人的)、會填RN(別人的)、也會給Packet
- 舉例 : 我去買酒的時候順便去幫弟弟買菸
- SN/RN 變大怎麼辦?
- 同時modulo(模)一個數就好
- Stop and wait ARQ : Modulo 2
- Go Back N ARQ : Modulo N
- Go Back N ARQ
- Why Go Back N?
- 因為Rn回來需要時間,可以連續送n筆資料不需要等ack,Node B 的運作方式跟stop and wait 一樣
- N : how many successive packets can be sent in the absense of a request for a new packet
- Allow to send packet i+n-1 before i has been acked
- ARQ解題小技巧(你不用懂ARQ是甚麼就會算)

- Node A SN 就是一路0、1、2填下去
- 更新window: 看著A吃到的箭頭,往回對,她左邊的RN 如果是X, window 要填[X,X+N]
- 更新RN: 看著B吃到的箭頭,往回對,如果對到號碼一樣,收下來,RN+1,下一個要填的RN就是frame傳送前一刻的RN
- 如果對到號碼不一樣,代表回傳nak,RN不會變
- 代表我要的packet沒有來
- 這時候會觸發time out(超過window的upper bound)
- 回傳出錯怎麼辦
- Window 不會動
- 有可能會導致重傳

- 這裡為甚麼2直接接4?
- 因為收到4的ack,代表3成功收到,不用重傳
- 不想要的重傳
- 即使沒有error也會重傳
- 發生在short frame in one side,long frame in another
- 
- RN太長了,累計了太多SN,node A遲遲收不到ack因此timeout
- Link Layer (L2) v.s. Transport Layer (L4)
- 相同
- Frame、packet 可能會出錯
- delay可能會不一樣
- 相不同
- two nodes with a link in between in L2
- two sites with a link in between in L4
- All frames using the link are sequentially numbered at L2
- sequence numbering involves only the packets of a given session at L4
- Frames must stay in order in a link
- Packets may arrived out of order
- end - to - end link in L2
- virtual end - to - end link in L4
## **07. LLC**
- 待更新xD
- why LLC
- ARQ怎麼放到protocol裡面
- 802.2 LLC 是一種標準
- Primitives and Parameters
- Primitive : 最基本的服務(像function name)
- Parameters : 額外增加的東西(像 Parameter)
- 在802.2要重傳要用ARQ,不用就不用
- LLC服務種類
- Connection-mode service
- 兩個要互傳要先把連線建起來
- 一對一 (unicast)
- 有error recovery / flow control
- Unacknowledged connectionless service
- connectionless : 想傳的人想傳就傳,不管要收的人要不要收
- unacknowledged : 不會回ack
- 沒有error control / flow control
- Acknowledged connectionless service
- 會回ack的 connection less service
- Support individual, multicast, and broadcast addressing
- multicast 可以針對, broadcast 是所有人都收
- Reset
- 可能因為out of synchronization
- 可能不想斷掉重新連
- LLC Class
- 說自己可以支援哪些type
- 如Class IV 可以支援 Type 1~3
- SAP
- LLC的地址
- LLC PDU
- 
- control 可能有 8 bit / 16 bit ,有三種格式
- Information
- Supervisory
- Unnumbered
- 有 PiggyBacking : information
- 前面的一兩個bit是要判斷哪種種類的
- Source Address
- I/G : Individual/Group 這個bit不是I就是G
- I bit is used for unicast, G bit is used for multicast
- C/R : Command/Response 這個bit不是C就是R
- Control
- 當C/R是C的時候,P/F(Poll/Final)要用P來解釋
- 相反,當C/R是R的時候,P/F要用F來解釋
- Poll 設成1的時候,代表一定要回
- 回的時候有很多PDU,回的最後(Final)一個PDU,F設成1代表傳完了
- Supervisory
- error control / flow control
- 因為兩個 S bit,有四種組合(實際用了三種)
- RR : ack收到了
- RNR : ack收到了,但還沒有ready(做flow control)
- REJ : 沒收到ack,傳回nak
- Unnumbered
- various control message
- 有五個bit可以控制,Unnumber 最短 PDU lingth = 24
- information 可能會塞東西,例如Go back N 的 N 等等
- information
- carry user data
- Type I operation
- Unnumbered PDU
- 有一種Unnumberd PDU 叫做UI PDU
- is used to transfer user data
- 另外一種叫做 XID PDU (exchange PDU)
- Exchange “type of operation” supported, and “window size”
- 交換資料用
- Type II、Type III也會用
- 還有一種叫做 Test PDU
- 測試有沒連線成功用
- Loop-Back Test : 不傳出去,只在自己的Protocol Stack跑
- Type II operation
- connection-mode
- 三種PDU (Information,Supervisory,Ummumbered) 都用到了 (Piggy Back)
- 三個Phase(相位)
- connection establishment
- 用到了Unnumbered PDU
- data transfer
- 用到了Information + Supervisory PDU
- connection termination
- 用到了Unnumbered PDU
- Type III operation
- 必須要回ack
- 收到之後用AC回
## **08.IP** ##
- ip功能
- addressing
- route packets
- fragmentation
- 把資料切得很小塊
- 分開送
- IP Address
- 代表ID和位置
- a specific ip address can only be used in a specific subnet
- 優點 : routing table 變小
- 缺點 : 一移動就會斷線
- IP routing只要看netid就知道要送到哪個地區,接著再由那個地區來送,因此不需要擁有所有hosts的表
- Format of IPv4 Address

- Subnet
- subnet mask 決定subnet要切在那裡

- Supernetting (classless addressing)
- 很多個ip prefixes指定給同一個組織
- Ex. NCTU(140.112.0.0 , 3) -> 140.112 ~ 140.114 都是交大的
- CIDR Address and Mask
- ip prefixes的表示法
- xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z -> z表示從最前面開始有幾個bit是固定的

- ex : 10/8 代表從10.0.0.0開始一樣附屬於mask長度8的地方
- lowest : 10.0.0.0
- higest : 10.255.255.255
- IPV4 header
- at least 20 bytes (option)
- ver : 判斷是IPV4 還是 IPV6
- IHL : specify header 有多長
- service type (給某些人方便)
- total length : specify payload 有多長
- time to live : 可以經過幾個 router/hub 再多的話就丟掉那個packet
- 因為太多可能 packet is considered 壞掉.
- Header Checksum
- 檢查錯誤
- Padding
- header 有規定要幾個 byte,把它補起來
- 欺敵,竊聽者不知道你 packet 真正的長度
- 跟 fragmentation 有關的欄位
- identifier : 相同的一組 data 寫一樣
- fragmentation offset : 第一塊填0,第二塊填1等等
- flag : 用來 identify 最後一塊,最後一塊設為1
- 收的人有辦法根據這三個欄位,把 fragmentationed 的資料組回來
- Protocol
- Protocol id is used to identify layer-4 protocol such as TCP or UDP
- routing table
- 告訴router要怎麼傳或是下一站在哪
- 有一個問題: 資料通過router時,router不能改dest. IP address,要怎麼辦?
- 解法: 透過MAC層,比如說Source 傳給router B,MAC 的 source 依然是 source,但dest. 是 router,有點像寄信時郵差分類的帆布袋,再送給郵政總局
- 總局 (router) 送給另一個總局 (router),只動 mac address (暫時的地址),而不改變IP Header (你家&別人家的地址)
- 每次傳的 MAC address 都不一樣
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- 解決不知道 MAC 地址的問題
- source 大喊 (broadcast) 說誰有地址 (send ARP request) ?
- 發現有的就回答 (give ARP reply)
- ARP cache : 問一次就把他記起來
- 缺點 : routing 變了就不能送
- solution : 如果要送的人要跑走主動講
- solution : 自己- Proxy ARP
- Gratuitous ARP
- 自己走自己回
- Proxy ARP
- 幫別人代回
- Broadcast
- 對象: 同一個 subnet
- Directed Broadcast
- 假設要 broadcast 到 140.113.62.125
- 要知道 subnet id,broadcast到 140.113.62.255
- 255代表 broadcast,平常不能用
- Broadcast a packet on a remote network to a specific network
- Limited Broadcast
- Address with thirty-two 1s
- 255.255.255.255
- May be used as part of a startup procedure
- Special IP Address
- 要求IP address 用,有時候需要問某個 server 自己的 ip 多少,但又沒有 ip 導致聯不上的矛盾情況
- source 全部填 0 ,dest 全部填 1
- Loopback : 127 開頭, never be a vaild ip,用來 run 一遍整個protocol stack
- Address Authority
- ICANN : 現在管理世界ip位址的機構,也是階層式的架構放給各國
- 可以要求 domain name 等等(ex:nctu.edu.tw)
- DNS server : 把 domain name 跟 ip address 合起來
- BOOTP
- 1990年代沒有硬碟,但要連上 internet ,開機的時候取得 ip address
- 是 DHCP 的前身
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- 目的 : 在 configure 你的 host
- 動態幫你分配一個 IP address
- 因為 IP address 有限,但可以連的人很多
- Address issue
- static
- 永遠給你
- dynamic
- 需要再給你,不需要就收回
- 第5層 (Application level) 的 protocol
- 用來 configure 第3層的ip位址
- Movable network : 換到別的地方還是能連
- Client-Server architecture
- client : 使用者
- server : 給 ip 服務的人(例如計中)
- A mechanism rather than a policy
- server 把 subnet mask, default gateway 還有 ip address 傳給client
- Automatic allocation
- DHCP 常用
- Manual allocation
- 遠端給真人手動給一個 ip address
- Terminology
- Lease : 給一個 ip 位址可以用多久
- DHCP Message

- initialization
- DHCPDISCOVER... protocol 規定的寫法
- DHCPDISCOVER : 對網路 broadcast
- DHCPOFFER : server 給 client位址
- DHCPREQUEST: 如果有多個的話,選一個回 request (我要定這個位址了!)
- DHCPACK : 確定收到地址
- Graceful shutdown
- ip位址不要的時候,主動傳 DHCPRELEASE 來跟 server 說
- 重連的時候: 不用那麼麻煩
- 只要送 request 跟 ack就好
- Subsequent ignored
- 
- Reacquisition and Expiration in DHCP
- 續約的方式
- 兩個timer T1,T2
- T1 expired : 要找自己的 server (renewing state) 比較短
- T2 expired : 去找別的 server (rebinding state) 比較長
- Nat (Network address translation)
- 因為IPv4最多只能有$2^{32}$個
- 把 address 轉換
- 通常是 private ip address 透過 NAT router 轉成 public address 連出去
- 也可以是 public 轉 public 等等
- 可以 IPv4 轉 IPv6 or 相反
- 一個 public ip address 可以對應多個 private address
- IP分享器 : 就是一個例子
- 優點: security 經過轉換的地址就不知道在哪裡
- 有分 srcNAT, dstNAT
- NAPT (PAT)
- 只有一個 public address
- 有很多 private address
- 利用 port number
- **理論上** ICMP 等沒有 port 的協定無法支援
- NAPT operation
- 這兩張圖,是給兩個 private address 192.168.1.4 / 192.168.1.8 用的
- 三個階段
- 
- 
- before translating
- source port : 對外 IP address 對應的 port
- source IP : 對外的 IP address
- destiation port : NAT server 的 port
- destiation IP : NAT server 的IP
- Look up mapping table in NAT
- 去對照Private port 以及其所對應的IP address
- Inbound packet after translating
- source port : 對外 IP address 對應的 port
- source IP : 對外的 IP address
- destiation port : private IP 對應的 port
- destiation IP : private IP
- 透過NAT server當中繼站,轉錄跟轉譯IP
## **09.TCP** ##
- (2018 Fall 沒教完)
- 第四層叫Transport layer
- UDP
- 不重傳
- header 只有 source port 跟 destiation port
- port number : 第四層的地址
- SAP 也是 port number
- TCP Header
- source/dest port : 就是地址
- Sequence number : SN ,用 Go Back N 或 Selective-repeat ARQ
- Window Size : 意義 : 連續傳 N 個不用等packet回來
- 
- TCP Error Control/Flow Control
- Error Control : 就是出錯了就重傳
- [Flow Control](https://notfalse.net/24/tcp-flow-control) 兩種方法 :
- [Congestion](https://notfalse.net/28/tcp-congestion-control) : 用RTP來看
- RTP一大,就不傳,大到一個地步就動他的Window size
- timeout : 不讓太多的flow通過
- TCP Port
- Numbers less than 1024 are well-known port
- 常用的port
- 21 : FTP
- 22 : SSH
- 80 : HTTP
- 443 : HTTPS
## **Appendix : Homework & Past Paper** ##
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

