# How to implement a GNN
```python
import torch
from torch_scatter import scatter
```
### We will use this graph:
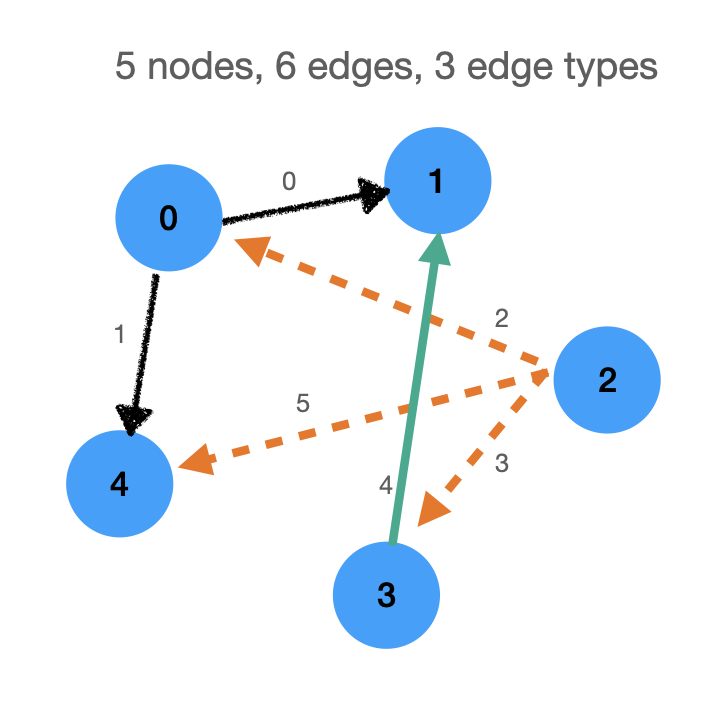
```python
num_nodes = 5
num_edges = 6
num_edge_types = 3
```
```python
edge_index = torch.LongTensor([
[0,1], [0,4], [2,0], [2,3], [3,1], [2,4]
]).t()
edge_index
```
tensor([[0, 0, 2, 2, 3, 2],
[1, 4, 0, 3, 1, 4]])
```python
embed_dim = 10
x = torch.randn(num_nodes, embed_dim)
x.size()
```
torch.Size([5, 10])
## Define the `MessagePassing` class
```python
import inspect
import torch.nn as nn
class MessagePassing(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MessagePassing, self).__init__()
# get the list of arguments as a list of `string`
self.message_args = inspect.getfullargspec(self.message)[0][1:]
self.update_args = inspect.getfullargspec(self.update)[0][2:]
def propagate(self, aggr, edge_index, **kwargs):
'''
edge_index.size(): [2, number_of_edges]
'''
assert aggr in ['sum', 'mean', 'max']
kwargs['edge_index'] = edge_index
dim_size = None
message_args = []
for arg in self.message_args:
if arg.endswith('_i') or arg.endswith('_j'): # will almost always be `x_i` or `x_j`
x = kwargs[arg[:-2]] # get `x`, has shape [number_of_nodes, embed_dim]
dim_size = x.size(0)
j = 0 if arg.endswith('_i') else 1
x_j = x[edge_index[j]]
message_args.append(x_j)
else:
message_args.append(kwargs[arg])
update_args = [kwargs[arg] for arg in self.update_args]
out = self.message(*message_args)
out = scatter(out, edge_index[0], dim=0, dim_size=dim_size, reduce=aggr)
return self.update(out, *update_args)
def message(self):
raise NotImplementedError
def update(self):
raise NotImplementedError
```
### Create a `nn.Module` that inherits `MessagePassing`
```python
class MyGNN(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, embed_dim=embed_dim):
super(MyGNN, self).__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.message_output = None
self.update_output = None
def message(self, x_j, a_random_argument):
'''
`x_j` has shape (num_edges, embed_dim)
`a_random_argument` can be any argument. In this case it is a tensor of shape `(embed_dim,)`
'''
print(f'\tInside message method. `x_j.size()` is {x_j.size()}')
output = x_j * a_random_argument.view(1,-1)
self.message_output = output
return output
def update(self, out):
print(f'\tInside update method. `out.size()` is {out.size()}')
output = out
self.update_output = output
return output
def forward(self, x, edge_index):
return self.propagate('mean', edge_index, x=x, a_random_argument=torch.ones(self.embed_dim)*2)
```
```python
model = MyGNN()
```
```python
model_output = model(x, edge_index)
model_output.size()
```
Inside message method. `x_j.size()` is torch.Size([6, 10])
Inside update method. `out.size()` is torch.Size([5, 10])
torch.Size([5, 10])
```python
model.message_output
```
tensor([[-3.9773, -1.1126, -0.0140, 3.8670, 1.2074, -1.7092, 0.3560, 3.2655,
-2.3335, -4.1227],
[-1.3679, -3.1507, -1.1292, 1.1108, -2.8639, 1.0764, -1.2942, -2.1353,
-1.2333, -0.1250],
[ 0.2759, -3.5196, -0.0355, -0.4968, 0.6988, 0.3293, -1.4655, 1.2332,
-0.5728, -0.9543],
[ 0.1292, 0.8452, -1.5253, 4.7322, -0.6898, -0.2914, -0.8749, 0.1460,
0.2724, 1.6101],
[-3.9773, -1.1126, -0.0140, 3.8670, 1.2074, -1.7092, 0.3560, 3.2655,
-2.3335, -4.1227],
[-1.3679, -3.1507, -1.1292, 1.1108, -2.8639, 1.0764, -1.2942, -2.1353,
-1.2333, -0.1250]])
```python
model.update_output
```
tensor([[-2.6726, -2.1317, -0.5716, 2.4889, -0.8283, -0.3164, -0.4691, 0.5651,
-1.7834, -2.1239],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.3209, -1.9417, -0.8967, 1.7820, -0.9516, 0.3714, -1.2115, -0.2520,
-0.5112, 0.1769],
[-3.9773, -1.1126, -0.0140, 3.8670, 1.2074, -1.7092, 0.3560, 3.2655,
-2.3335, -4.1227],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000]])
## Now let's run these results manually
### Before calling `message`, `propagate` moves messages from nodes to edges.
This can be done in two ways:
1. For each edge, move the message (node embedding) of the source node: happens if `x_i` is an argument of `message` method
1. For each edge, move the message (node embedding) of the target node: happens if `x_j` is an argument of `message` method
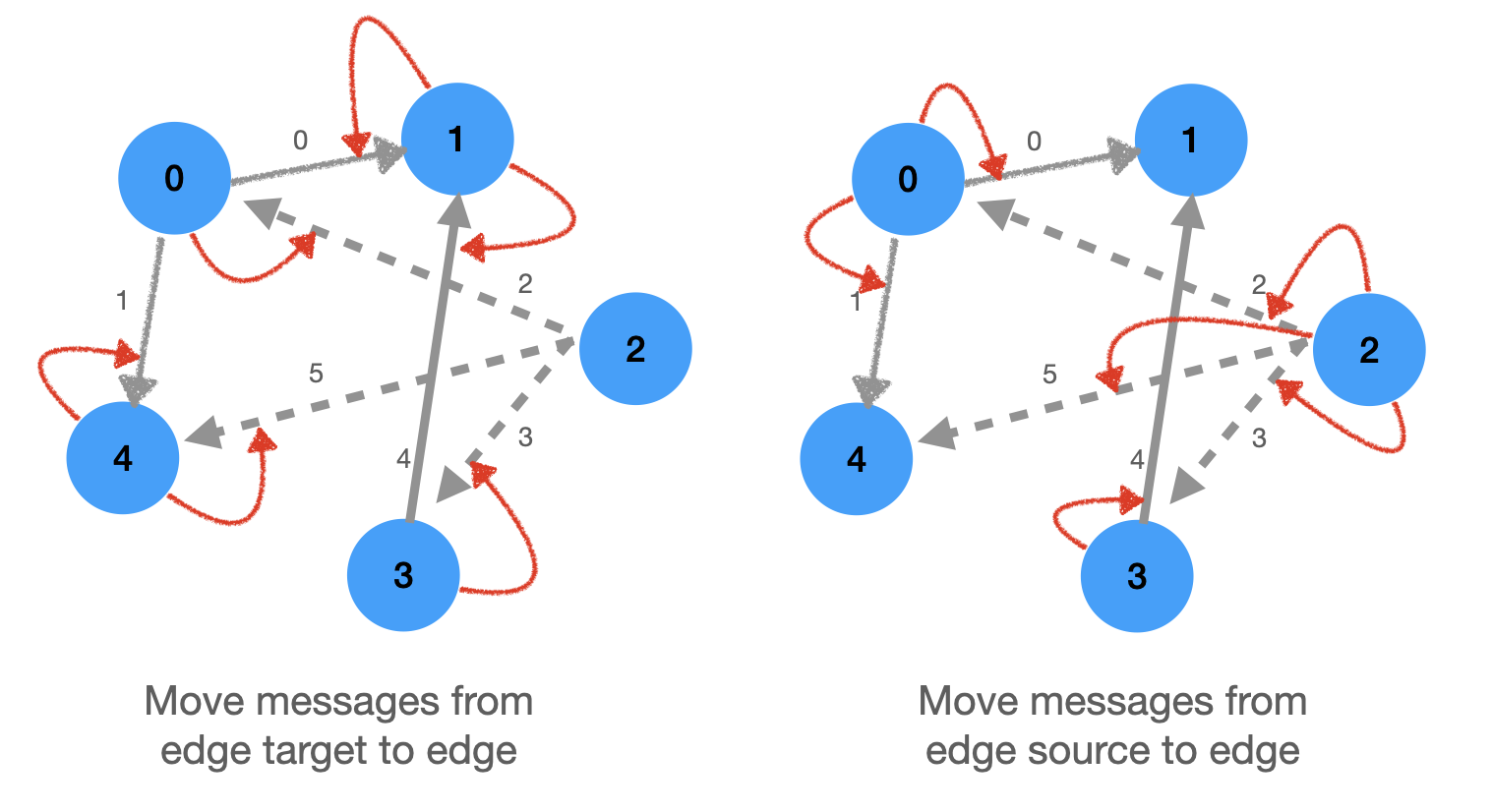
```python
edge_index
```
tensor([[0, 0, 2, 2, 3, 2],
[1, 4, 0, 3, 1, 4]])
```python
torch.equal(x[edge_index[1]] * 2, model.message_output)
```
True
### Now let's modify the argument of `message` to `x_i`
```python
class MySecondGNN(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, embed_dim=embed_dim):
super(MySecondGNN, self).__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.message_output = None
self.update_output = None
def message(self, x_i, a_random_argument):
'''
`x_j` has shape (num_edges, embed_dim)
`a_random_argument` can be any argument. In this case it is a tensor of shape `(embed_dim,)`
'''
print(f'\tInside message method. `x_j.size()` is {x_i.size()}')
output = x_i * a_random_argument.view(1,-1)
self.message_output = output
return output
def update(self, out):
print(f'\tInside update method. `out.size()` is {out.size()}')
output = out
self.update_output = output
return output
def forward(self, x, edge_index):
return self.propagate('mean', edge_index, x=x, a_random_argument=torch.ones(self.embed_dim)*2)
```
```python
model = MySecondGNN()
model_output = model(x, edge_index)
model_output.size()
```
Inside message method. `x_j.size()` is torch.Size([6, 10])
Inside update method. `out.size()` is torch.Size([5, 10])
torch.Size([5, 10])
```python
torch.equal(x[edge_index[0]] * 2, model.message_output)
```
True
### Now let's take a look at what happens before update is called: the messages are put back from edges to nodes
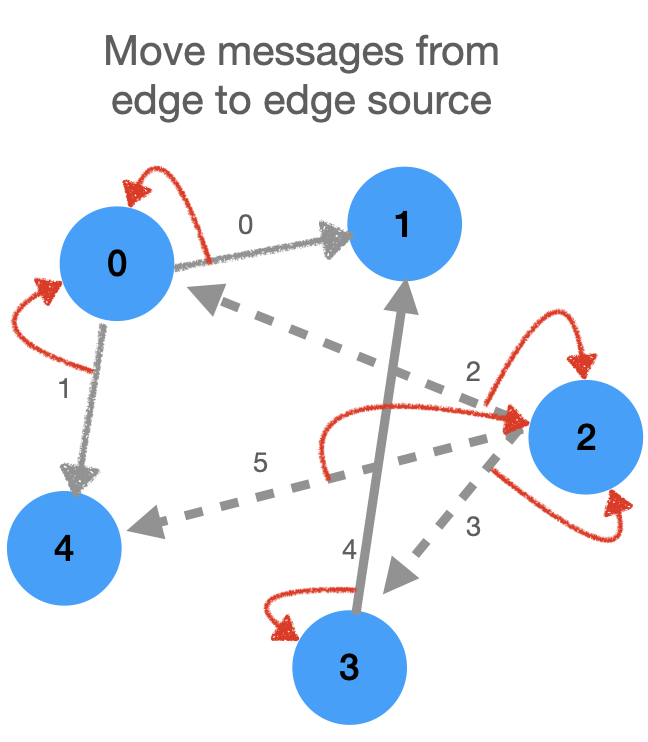
Note that this is not one to one - a node can have many edges. As a result it can receive messages from many edges. Thus we need a way to _aggregate_ these messages. This is exactly what the `aggr` function does in `scatter`.
```python
edge_index
```
tensor([[0, 0, 2, 2, 3, 2],
[1, 4, 0, 3, 1, 4]])
### Messages received by node `0`:
```python
message_output = x[edge_index[0]] * 2
torch.equal(message_output[[0,1]].mean(dim=0), model.update_output[0])
```
True
### Messages received by node `2`:
```python
torch.equal(message_output[[2,3,5]].mean(dim=0), model.update_output[2])
```
True
### We can pass messages to all the nodes using `scatter`
```python
scatter(message_output, edge_index[0], dim=0, dim_size=num_nodes, reduce='mean')
```
tensor([[ 0.2759, -3.5196, -0.0355, -0.4968, 0.6988, 0.3293, -1.4655, 1.2332,
-0.5728, -0.9543],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.5084, 2.1698, 2.5749, -1.7214, -2.0338, 0.1578, -0.6327, -0.6667,
2.7229, 2.0444],
[ 0.1292, 0.8452, -1.5253, 4.7322, -0.6898, -0.2914, -0.8749, 0.1460,
0.2724, 1.6101],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000]])
```python
torch.equal(scatter(message_output, edge_index[0], dim=0, dim_size=num_nodes, reduce='mean'), model.update_output)
```
True
###### tags: `pytorch`, `gnn`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet