FILE STRUCTURE
===
# Introduction
When a new FILE structure is allocated and its pointer returned from fopen(). , glibc has actually allocated an internal structure called struct `_IO_FILE_plus`, which contains struct `_IO_FILE` and a pointer to struct `_IO_jump_t`, which in turn contains a list of pointers for all the functions attached to the FILE. Overwrites a ‘FILE’ pointer (stdin, stdout, stderr or any other file handler opened by `fopen()`) to point to own forged structure for gain control over execution flow.
File structure contains `vtable`, which is a pointer to a table which contains functions which are called when the original ‘FILE’ pointer is used to perform different operations (such as fread, fwrite, ...).
## File stream
- Stream buffering: fprint, open, stdout, stdin, stderr,…
## File structure
- a file stream descriptor
- Created by fopen
[_IO_FILE](https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/libio/bits/types/struct_FILE.h.html#49) or [other link](https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.35/source/libio/bits/types/struct_FILE.h#L49)
- flags:
```c
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
```
- record the attribute of the file stream: 'r', 'r+', 'w', 'w+', 'a', 'a+'.
- Stream buffer:
```c
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
char *_IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char *_IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char *_IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char *_IO_write_base;/* Start of put area. */
char *_IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char *_IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char *_IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char *_IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
```
- read buffer
- write buffer
- reserve buffer
- _fileno
```c
int _fileno;
```
- File descriptor
- return by sys_open
- [`_IO_FILE_plus`](https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.35/source/libio/libioP.h#L324) struct is the extended version of `_IO_FILE` struct, which is `_IO_FILE` + `vtable` (virtual table = array of pointers to the helper fucntions during executing the IO operation):
```c
// in FILE.h
typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE;
// This contains a pointer to the function jump table used.
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
FILE file;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};
```
How the `vtable` will be filled during creating a new extended `File` struct. Depending on the method u use. Ex: [fopen()](https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.24/source/libio/iofopen.c#L60), the `vtable` initialized with the existed `vtable` called `_IO_file_jumps` (other `vtavle` like `_IO_str_jumps`).
```c
_IO_FILE *
__fopen_internal (const char *filename, const char *mode, int is32)
{
...
_IO_JUMPS (&new_f->fp) = &_IO_file_jumps;
...
}
```
[_IO_jump_t](https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/libio/libioP.h.html#_IO_jump_t)/ [glibc2.35](https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.35/source/libio/libioP.h#L293):
- stdin/stdout/stderr, fopen also use it.
- Extra Virtual function table.
- The export symbol of this type in the libc file is [_IO_file_jumps](https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/libio/fileops.c.html#_IO_file_jumps).
- Every FILE associate with a `_chain` (linked list). The head of linked list is called `_IO_list_all`
```c
struct _IO_FILE
{ ...
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
...
}
```
# Exploitation of File
Some good targets in FILE structure:
## vtable (Virtual function Table)
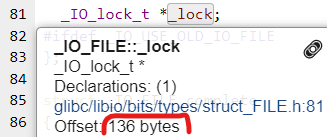
`_lock` (usually need to construct it for exploitation)
- prevent race condition in multithread
```c
struct _IO_FILE
{ ...
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
}
```
We can find out the offset of `_lock` = 0x88
## stdin/stdout/stderr
This is also a FILE structure in glibc. We can overwrite the global variable in glibc to control the flow execution. (in glibc symbol table)
## FSOP (File stream oriented programing)
Control the linked list of File stream:
- _chain
- _IO_list_all
Powerful function:
[_IO_flush_all_lockp](https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/libio/genops.c.html#_IO_flush_all_lockp)
```c=
for (fp = (FILE *) _IO_list_all; fp != NULL; fp = fp->_chain)
{
run_fp = fp;
...
if (( (fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0
&& (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base) )
) && _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
result = EOF;
}
```
It will process all FILE in FILE linked list. We can construct the linked list to do oriented programing. Then line 9 will trigger virtual function.
## Vtable verification in File
The vtable must be in libc `_IO_vtable` section. Otherwise, it will check if the vtable permits virtual function call.
```c
IO_validate_vtable (const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable)
{
/* Fast path: The vtable pointer is within the __libc_IO_vtables
section. */
uintptr_t section_length = __stop___libc_IO_vtables - __start___libc_IO_vtables;
uintptr_t ptr = (uintptr_t) vtable;
uintptr_t offset = ptr - (uintptr_t) __start___libc_IO_vtables;
if (__glibc_unlikely (offset >= section_length))
/* The vtable pointer is not in the expected section. Use the
slow path, which will terminate the process if necessary. */
_IO_vtable_check ();
return vtable;
}
```
### Check the foreign vtables
[_IO_vtable_check](https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/libio/vtables.c.html#_IO_vtable_check)
For compatibility:
```c
/* Honor the compatibility flag. */
void (*flag) (void) = atomic_load_relaxed (&IO_accept_foreign_vtables);
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (flag); // Demangle w/ pointer guard
#endif
if (flag == &_IO_vtable_check)
return;
```
- Can't overwirte _IO_accept_foreign_vtable, because of the ponter guard.
For shared lib:
```c
Dl_info di;
struct link_map *l;
if (!rtld_active ()
|| (_dl_addr (_IO_vtable_check, &di, &l, NULL) != 0
&& l->l_ns != LM_ID_BASE))
return;
```
# References
https://outflux.net/blog/archives/2011/12/22/abusing-the-file-structure/
https://www.slideshare.net/AngelBoy1/play-with-file-structure-yet-another-binary-exploit-technique
- [file-struct-attack-p1](https://chovid99.github.io/posts/file-structure-attack-part-1/)
###### tags: `research` `pwn`