# DSA : Subarrays
---
title: Introduction to arrays
description:
duration: 900
card_type: cue_card
---
### Introduction
#### Definition
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
**Note:**
* Single element is also a subarray.
* Whole array is also a subarray.
* Subarray is considered from left to right.
Consider the following array of integers:
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | -1 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 12 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
* `2, 3, -1, 6` is a subarray of length 4.
* `9` is a subarray of single element.
* `4, 1, 2, 3, -1, 6, 9, 8, 12` is a subarray consisting of all the array elements.
* `4, 12` is **not** a subarray because loop does not count as subarray.
* `1, 2, 6` is **not** a subarray beacuse the array elements must be contiguous.
* `3, 2, 1, 4` is **not** a subarray because order of the elements in a subarray should be same as in the array i.e. left to right.
#### Length of subarray
Given an array, the formula to find the length of subarray with start index as `start` and end index as `end` is given by -
```cpp
Length of subarray = end - start + 1
```
---
title: Quiz 1
description:
duration: 45
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
How many subarrays of the following array start from index 1
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
# Choices
- [ ] 6
- [ ] 7
- [x] 21
- [ ] 36
---
title: Quiz Explanation
description:
duration: 600
card_type: cue_card
---
**Explanation:** To count the number of subarrays that start from index 1, we need to consider all the possible contiguous part of array that start at index 1. Here are all the possible subarrays that start from index 1:
[2] (starting from index 1)
[2, 10]
[2, 10, 3]
[2, 10, 3, 12]
[2, 10, 3, 12, -2]
[2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
Therefore, there are a total of 6 subarrays that start from index 1.
---
title: Quiz 2
description:
duration: 45
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
How many subarrays of the following array start from index 3
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
# Choices
- [ ] 3
- [x] 4
- [ ] 5
- [ ] 6
---
title: Quiz Explanation
description:
duration: 600
card_type: cue_card
---
**Explanation:** Here are all the possible subarrays that start from index 3:
[3] (starting from index 3)
[3, 12]
[3, 12, -2]
[3, 12, -2, 15]
Therefore, there are a total of 4 subarrays that start from index 3.
---
title: Quiz 3
description:
duration: 45
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
Number of subarrays in the given array? [4, 2, 10, 3]
# Choices
- [ ] 7
- [ ] 8
- [ ] 9
- [x] 10
---
title: Quiz 4
description:
duration: 45
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
Given ar[N] elements, how many subarrays are starting from index 0
# Choices
- [ ] N-1
- [ ] N-2
- [x] N
- [ ] 1
---
title: Introduction to arrays continued
description: Formula to count no. of subarrays
duration: 600
card_type: cue_card
---
#### Formula to count no. of subarrays
Let's say we have an array of size N.
No. of subarrays starting from index 0 = N
No. of subarrays starting from index 1 = N-1
No. of subarrays starting from index 2 = N-2
No. of subarrays starting from index 3 = N-3
...........
...........
...........
No. of subarrays starting from index N-1 = 1
So, Using the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series, total number of subarrays = N + (N-1) + (N-2) + (N-3) + . . . . . . + 3 + 2 + 1 = N(N+1)/2.
``` cpp
Total_no_subarrs = n(n + 1) / 2
```
---
title: Print the subarray
description: Print the subarray of the array that starts from the start index and ends at the end index
duration: 900
card_type: cue_card
---
### Coding Question 1
#### Problem Statement
Given an array of integers and two indices, a start index and an end index, we need to print the subarray of the array that starts from the start index and ends at the end index (both inclusive).
#### Solution
To solve this problem, we can simply iterate over the elements of the array from the start index to the end index (both inclusive) and print each element.
#### Pseudocode
```java
public static void printSubarray(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n)
* SC - O(1)
---
title: Print all possible subarrays
description: Print all possible subarrays of the array
duration: 900
card_type: cue_card
---
### Coding Question 2
#### Problem Statement:
Given an array of integers, we need to print all possible subarrays of the array.
#### Example
```cpp
Input: [1, 2, 3]
Output:
[1]
[1, 2]
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 3]
[2]
[2, 3]
[3]
```
#### Solution
We can generate all possible subarrays of the array as follows -
* Begin a nested for loop with variable i initialized to 0 and running up to n-1. The variable i will be used to represent the starting index of a subarray.
* Inside the first for loop, begin another nested for loop with variable j initialized to i and running up to n-1. The variable j will be used to represent the ending index of a subarray.
* Inside the second for loop, begin a third for loop with variable k initialized to i and running up to j. This loop will be used to iterate through the subarray and print its elements.
#### Pseudocode
```java
public static void printSubarrays(int[] arr, int n) {
// Generate all possible subarrays
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
// Print the current subarray
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
System.out.print(arr[k] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n^3)
* SC - O(1)
---
title: Sum of all possible subarrays
description: Find the sum of all possible subarrays of the array
duration: 2700
card_type: cue_card
---
### Coding Question 3
#### Problem Statement
Given an array of integers, we need to find the sum of all possible subarrays of the array.
#### Example
```cpp
Input: [1, 2, 3]
Output:
[1] = 1
[1, 2] = 3
[1, 2, 3] = 6
[2] = 2
[2, 3] = 5
[3] = 3
```
#### Solution
To solve this problem, we can use two nested loops to generate all possible subarrays of the array. At each iteration, we calculate the sum of the subarray using another loop, and print its value when corresponding subarray sum has been calculated.
#### Pseudocode
```java
public static void printSubarraySum(int[] arr, int n) {
// Generate all possible subarrays and calculate their sum
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
int subarray_sum = 0;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
subarray_sum += arr[k];
}
System.out.println(subarray_sum);
}
}
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n^3)
* SC - O(1)
#### Optimized Solution
We can optimize the solution using the prefix sum technique.
* First calculate the prefix sum array of the input array.
* Then use two nested loops to iterate over all possible subarrays of the array. At each iteration, calculate the sum of the subarray using the prefix sum array.
* If the starting index of the subarray is 0, directly use the prefix sum of the ending index as the sum of the subarray.
* Otherwise, subtract the prefix sum of the starting index-1 from the prefix sum of the ending index to get the sum of the subarray.
#### Pseudocode
```cpp
public static void printSubarraySum(int[] arr, int n) {
// Calculate the prefix sum of the array
int[] prefix = new int[n];
prefix[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + arr[i];
}
// Print the sum of all possible subarrays using the prefix sum
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
System.out.println(prefix[j]);
} else {
System.out.println(prefix[j] - prefix[i-1]);
}
}
}
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n^2)
* SC - O(n)
#### More optimized Solution
Before going to the main carry forward approach, lets try to solve below question -
**Question -** Given an array arr[N], print the sum of all subarrays starting at 3rd index.
**Example -** arr[10] = [3, 8, 4, 7, 9, 4, 3, 2, 10, 6]
**Solution -**
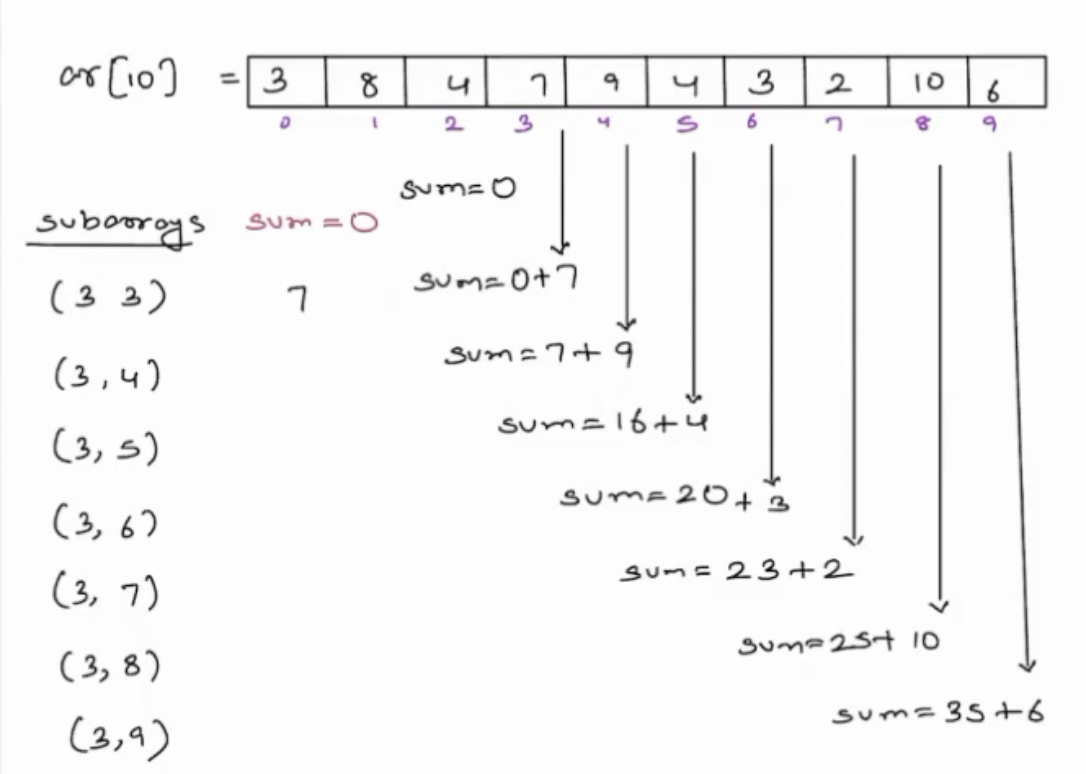
With the help of above example, we can now build up the logic to find the sum starting from all start indexes.
**Main logic -**
The idea to find the sum of all possible subarrays of the array is to initialise the sum with 0 for every start index. Now, carry forward the sum from start index to end index.
#### Pseudocode
```cpp
public static void printSubarraySum(int[] arr, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int subarray_sum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
subarray_sum += arr[j];
System.out.println(subarray_sum);
}
sum += subarray_sum;
}
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n^2)
* SC - O(1)
---
title: Total sum of all possible subarrays
description: Find the total sum of all possible subarrays of the array
duration: 1200
card_type: cue_card
---
### Coding Question 4
#### Problem Statement
Given an array of integers, find the total sum of all possible subarrays.
#### Solution
For each such pair of indices, calculate the sum of the corresponding subarray and add it to the total sum of all subarrays. This can be done by maintaining a variable say `subarray_sum` that stores the sum of the current subarray using carry forward technique and adding it to the total sum say `total_sum` for each iteration of the inner loop.
#### Pseudocode
```cpp
public static void printSubarraySum(int[] arr, int n) {
int total_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int subarray_sum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
subarray_sum += arr[j];
total_sum += subarray_sum;
}
}
System.out.println(total_sum);
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n^2)
* SC - O(1)
#### Optimized Solution (Contribution Technique)
We can optimize the above solution further by observing a pattern in the subarray sums.
Let's take the example array ``[1, 2, 3]`` again. The subarrays and their sums are:
```
[1] -> 1
[1, 2] -> 3
[1, 2, 3] -> 6
[2] -> 2
[2, 3] -> 5
[3] -> 3
```
* the first element 1 appears in 3 subarrays: [1], [1, 2], and [1, 2, 3].
* the second element 2 appears in 4 subarrays: [2], [1, 2], [2, 3], and [1, 2, 3].
* the third element 3 appears in 3 subarrays: [3], [2, 3], and [1, 2, 3].
---
title: Quiz 5
description:
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
In how many subarrays, the element at index 1 will be present?
A: [3, -2, 4, -1, 2, 6 ]
# Choices
- [ ] 6
- [ ] 3
- [x] 10
- [ ] 8
---
title: Quiz 6
duration: 90
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
In an array of size N, how many subarrays will contain the element at index i?
# Choices
- [ ] i*(N-1)
- [ ] (i+1)*(N-i+1)
- [x] (i+1)*(N-i)
- [ ] (i-1)*(N-i)
<!-- Notice that each element in the array appears in exactly `(i+1) * (n-i)` subarrays, where i is the index of the element starting (0-based indexing) and n is the length of the array. -->
---
title: Quiz explanation
description:
duration: 600
card_type: cue_card
---
**Explanation:**
If we take an array 'arr',
There are i+1 elements from arr[0] to arr[i].
There are n-i elements from arr[i] to arr[n-1].
Thus, the total number of subarrays containing arr[i] is i+1 multiplied by n-i.
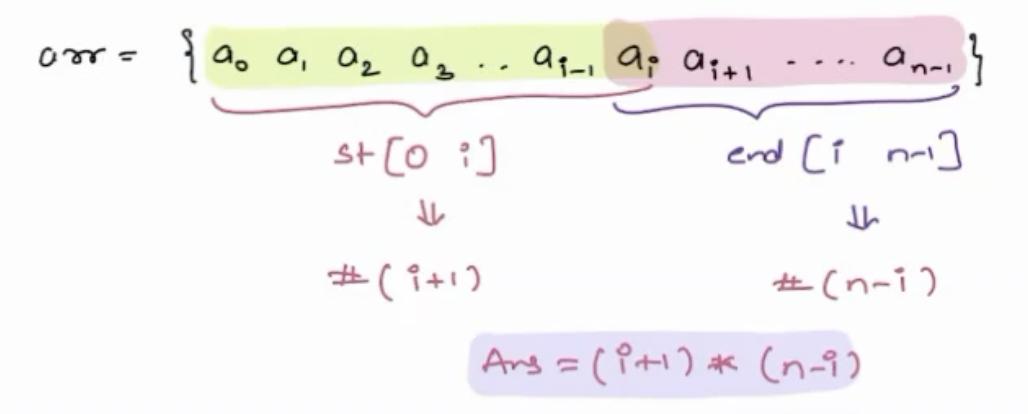
This gives us the expression `(i+1) * (n-i)` where i is the index of the element starting (0-based indexing) and n is the length of the array.
---
title: Total sum of all possible subarrays continued
description:
duration: 1200
card_type: cue_card
---
We can use above pattern to compute the total sum of all subarrays in O(n) time complexity. The steps are as follows:
* Initialize a variable total_sum to zero.
* Iterate over all elements of the input array arr. For each element arr[i], compute `arr[i] * (i+1) * (n-i)` and add it to total_sum.
* Return total_sum as the output of the function.
#### Pseudocode
```cpp
public static int findTotalSubarraySum(ArrayList<Integer> arr) {
int n = arr.size();
int total_sum = 0;
// Iterate over all elements of the array and compute the sum of all subarrays containing that element
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total_sum += arr[i] * (i+1) * (n-i);
}
return total_sum;
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
* TC - O(n)
* SC - O(1)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

