---
tags: LINUX KERNEL, LKI
---
# [Linux 核心設計](https://beta.hackfoldr.org/linux/): 不僅是個執行單元的 Process
Copyright (**慣C**) 2018 [宅色夫](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/User/jserv)
==[直播錄影](https://youtu.be/kcEcN43J3CQ)==
## 誰殺了 Process?
我不知道[誰摔死了李新](https://www.facebook.com/%E8%AA%B0%E6%91%94%E6%AD%BB%E4%BA%86%E6%9D%8E%E6%96%B0-250766819115136/),但我知道誰殺了 Process!
Linux 核心對於 UNIX Process (繁體中文翻譯為「行程」,簡體翻譯為「進程」) 的實作相當複雜,不僅蘊含歷史意義 (幾乎每個欄位都值得講古),更是反映出資訊科技產業的變遷,核心程式碼的 task_struct 結構體更是一絕,廣泛涵蓋 process 狀態、處理器、檔案系統、signal 處理、底層追蹤機制等等資訊,更甚者,還很曖昧地保存著 thread (繁體中文翻譯為「執行緒」,簡體中文翻譯為「線程」) 的必要欄位,好似這兩者天生就脫不了干係。
本講座期望帶著聽眾得知 Linux 核心設計的特有思維,像是如何透過 [LWP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-weight_process) 和 [NPTL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Native_POSIX_Thread_Library) 實作執行緒,又如何透過行程建立記憶體管理的一種抽象層,再者回顧行程間的 context switch 及排程機制,搭配 signal 處理 (千萬不要小看 kill,裡頭可是大有玄機!)。聽眾應可不至於迷失在茫茫程式碼大海中。
## 背景知識
交大資工曹孝櫟教授的〈[作業系統設計與實作](https://ocw.nycu.edu.tw/course_detail.php?bgid=9&gid=0&nid=664)〉線上課程:
* [Process Management – Part I](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bw3aRZCfsL4)
* [Process Management – Part II](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M69ENFe0Agc)
## Linux 設計的 trade-off 和 evolution
依據國家教育研究院學術詞彙,trade-off 有斟酌,妥協、取捨;折衷、抵換、權衡得失、綜合分析,和比較評定等意思,回顧超過 25 年 Linux 核心在 Process 設計和實作的變化,就是個生動的歷程。
儘管 [Linux 不屬於 microkernel (微核心) 設計](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tanenbaum%E2%80%93Torvalds_debate),但後者許多概念逐步融合到 Linux 核心中。
* [Microkernels: The veterans of OS design](http://www.slideshare.net/JakubJermar/microkernels-the-veterans-of-os-design)
* 1985 年至今 30 年間,microkernel 的演化和對產業的衝擊
* [Microkernel Evolution](http://www.slideshare.net/jserv/microkernel-evolution) (2013)
microkernel 不是新的概念,這個名詞至少在 1970 年代初期就有。一般認為,microkernel 源自 [Brinch Hansen](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brinch_Hansen) 在 1969 年提出的 [RC 4000 multiprogramming system](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RC_4000_multiprogramming_system),而更早之前就在電腦系統應用此概念了。
**Mach microkernel**
Mach (發音 [mʌk] ) 是美國 Carnegie-Mellon 大學 (CMU) 的 microkernel 作業系統,發展於 1980 年代,著眼點是,隨著功能越來越多,UNIX 也日漸龐大複雜而難以掌握,Mach 的設計概念就是「去蕪存菁」,僅留下真正關鍵的部份,其餘的功能都用使用者層級 (user-level) 的程式 (特徵 server) 來實作,藉此減低核心的複雜度。
:::info
Linux 的確也將典型核心服務搬去使用者層級實作,例如 [FUSE](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man4/fuse.4.html) (file system) 和 X Window System 的 video device driver,而隨著虛擬化技術的多元發展,探討一個作業系統是否為純粹的 microkernel,可能不是這麼明確了。
:::
Mach 設計目標:
* 與 UNIX 相容
* 物件導向設計
* 跨平台:在單處理器、多處理器上都能執行
* 適合分散式運算環境
值得一提的是,儘管 Mach 已式微,但 Mach 的眾多技術突破陸續被 BSD 和 Linux 核心所吸收。Mach 2.5 是許多商業 UNIX,像是 DEC OSF/1, NeXTSTEP (後來移轉到 Apple Computer) 的基礎,Mach 3.0 才是真正純粹的完全 microkernel 化的實作,而 Mach 4.0 則由 Utah (猶他) 大學維護。
Mach 的主要開發者 [Richard Rashid](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Richard_Rashid) 自 1991 年就在 Microsoft 服務,領導 [Microsoft Research](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft_Research) 若干技術突破,另一位主要 Mach 開發者 [Avie Tevanian](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Avie_Tevanian) 曾在 [NeXT](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NeXT) 擔任軟體主管,並在 Apple 收購 NeXT 後,成為 Apple Inc. 的技術長。
Mach 被視為以下這些元件所組成:
* ports (埠)
* messages (訊息)
* tasks (工作)
* threads (執行緒)
* virtual memory (虛擬記憶體)
如同一個設計成熟的物件導向系統,這些物件的介面已經定義明確,因此物件內的改變不會影響到使用這些物件的行程 (process)。
可將 Mach 中的 task 看待為 UNIX 環境中的 process。 對執行中的行程而言,它是一個可執行的環境,如同虛擬記憶體或是處理器的執行週期。不過,相對於傳統 UNIX 的 process,Mach 的 task 並不表示包含一個正在執行的 thread,對 Mach 而言,thread 也是一個獨立的物件 (!)
:::info
對比 Android,後者底層是 Linux 核心,但是設計卻高度有 microkernel 的影子,像是:
* Framework: task, thread, activity, service (微核心用語)
* Android: [binder IPC/RPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenBinder)
:::
因此,一個有用的 task 必須包含至少一個 thread。Mach 的 thread 與其它常見作業系統的 thread 相仿,在同一個 task 中的 thread 相互分享記憶體與其它資源。Mach 在設計時,就希望成為一個 multi-threaded,而可有效執行於多處理器 (SMP) 上。
**回頭看 Linux**
相較之下,Linux 發展之初,只是一個以 single thread 為導向的作業系統,multi-threaded 與 SMP 也在發展 10 年後才納入,早期甚至得用彆腳的 LinuxThread 套件來實現 multi-threading,而 Mach 與 Hurd 在設計初期,就已經考慮這些需求。在 [NPTL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Native_POSIX_Thread_Library) 出現之前,Linux 的 multi-threaded 實作非常奇怪,仍然把 process 當作最基本的 abstraction,也就是說 scheduling, context switch 等基本操作對象仍是 process,而thread / LWP 只是和別人分享定址空間和資源的 process。因此:
* 用 [clone()](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/clone.2.html) 產生的 thread 本質上仍是 process,可以說 Linux 核心中定義的 "thread" 只做到了資源共享,而不構成執行工作的最基本單位
* 嚴格來說,Linux 只實作一半的 thread,但這並不是壞事,因為許多的應用程式不見得用到 thread,而且簡化 thread 實作的結果,使得 process 管理變得更有效率,副作用是產生出來的 "thread" 比其它作業系統的實作,顯得更 heavy-weight,可以說,過去 Linux 犧牲 thread 的效率,以換取 process 的效率
* 以 abstraction 的角度來看,Linux 過去並非在本質上支援 thread,但以 programming model 來看,Linux 的確是有 thread 可用,儘管效率較差
早期 Linux 的 process 和 thread 的效能和其他作業系統的客觀數據比較,可參照論文 "[An Overview of the Singularity Project](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2005/10/tr-2005-135.pdf)" (Microsoft Research, 2005 年) 的第 31 頁

延伸閱讀: [UNIX 作業系統 fork/exec 系統呼叫的前世今生](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/unix-fork-exec)
## 「Process 和 Thread 有什麼差異?」

大部份的學生很快就可以「背誦」作業系統課程給予的「心法」,回答一長串,可是,其中多少人「看過」Process 和 Thread 呢?多少人知道這兩者怎麼實作出來?又,為何當初電腦科學家和工程師會提出這兩個概念呢?
書本說 thread 建立比 process 快,但你知道快多少?是不是每次都會快?然後這兩者的 context switch 成本為何?又,在 SMP 中,是否會得到一致的行為呢?
我們希望透過一系列的實驗,藉由統計來「看到」process 與 thread。物理學家如何「看到」微觀的世界呢?當然不是透過顯微鏡,因為整個尺度已經太小了。統計物理學 (statistical physics) 指的是根據物質微觀夠以及微觀粒子相互作用的認知,藉由統計的方法,對大量粒子組成的物理特性和巨觀規律,做出微觀解釋的理論物理分支。今天我們要「看到」context switch, interrupt latency, jitter, ... 無一不透過統計學!
取自 Donald E. Porter 教授的 [CSE 506: Operating Systems](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/) 教材
- [ ] [Process Address Spaces and Binary Formats](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/s16/slides/address-spaces.pdf)






VM Area structure tracks regions that are mapped
* Efficiently represent a sparse address space
* On both a list and an RB-tree
- Fast linear traversal
- Efficient lookup in a large address space
* Cache last lookup to exploit temporal locality
==Page 17-26==
- [ ] [Scheduling (1)](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/s16/slides/scheduling.pdf)


==Page 13-16==
==Page 20-47==
- [ ] [Scheduling (2)](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/s16/slides/scheduling2.pdf)

- [ ] [Signals and Inter-Process Communication](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/s16/slides/ipc.pdf)



- [ ] [Native POSIX Threading Library (NPTL)](http://www.cs.unc.edu/~porter/courses/cse506/s16/slides/nptl.pdf)

參照 [linux/include/linux/sched.h](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/linux/sched.h),將近 2000 行的標頭檔 (!),而且超過 300 位開發者變更過此檔案。
```clike
struct task_struct {
...
struct mm_struct *mm;
struct mm_struct *active_mm;
/* Per-thread vma caching: */
struct vmacache vmacache
...
/* PID/PID hash table linkage. */
struct pid *thread_pid;
struct hlist_node pid_links[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct list_head thread_group;
struct list_head thread_node;
...
/* CPU-specific state of this task: */
struct thread_struct thread;
```



## 執行緒和同步議題
[ [Thread & Synchronization](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/2015q1w9/thread-sync.pdf) ]
* Shared Code and Reentrancy
* [reentrancy](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reentrancy_(computing)) 會造成問題的案例: strtok()
* 解決辦法: strtok_r()
* newlib 實作:
* [strtok](https://github.com/eblot/newlib/blob/master/newlib/libc/string/strtok.c)
* [strtok_r](https://github.com/eblot/newlib/blob/master/newlib/libc/string/strtok_r.c)
* 避免全域變數
* 有個工作區,去保存變數
```C
char *
_DEFUN (strtok_r, (s, delim, lasts),
register char *s _AND
register const char *delim _AND
char **lasts)
{
return __strtok_r (s, delim, lasts, 1);
}
```
* Mutex in Linux: Various implementations for performance/function tradeoffs
* Speed or correctness (deadlock detection)
* lock the same mutex multiple times
* priority-based and priority inversion
* forget to unlock or terminate unexpectedly
* [Priority Inversion on Mars](http://www.slideshare.net/jserv/priority-inversion-30367388)
* FUTEX (fast mutex)
* Lightweight and scalable
* In the noncontended case can be acquired/released from userspace without having to enter the kernel.
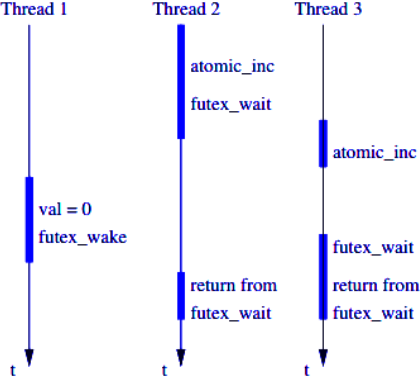
* invoke `sys_futex` only when there is a need to use futex queue
* need atomic operations in user space
* race condition: atomic update of unlock and system call are not atomic
* Kernel preemption
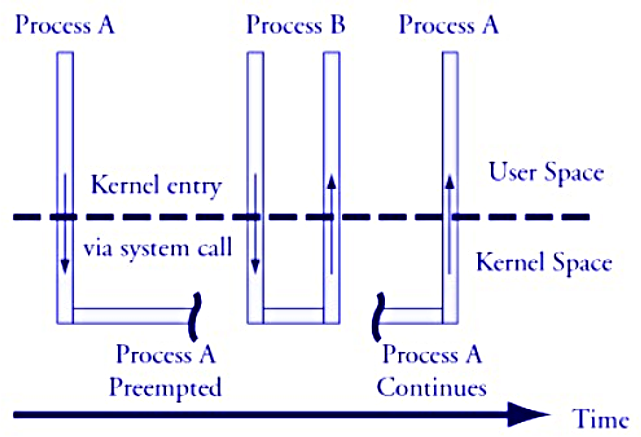
* a process running in kernel mode can be replaced by another process while in the middle of a kernel function
* process B may be woken up by a timer and with higher priority
* 考量點: 降低 dispatch latency
* Linux kernel thread
```C
static struct task_struct *tsk;
static int thread_function(void *data) {
int time_count = 0;
do {
printk(KERN_INFO "thread_function: %d times", ++time_count);
msleep(1000);
} while(!kthread_should_stop() && time_count<=30);
return time_count;
}
static int hello_init(void) {
tsk = kthread_run(thread_function, NULL, "mythread%d", 1);
if (IS_ERR(tsk)) { ... }
}
```
* Work Queue
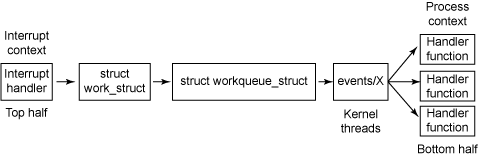
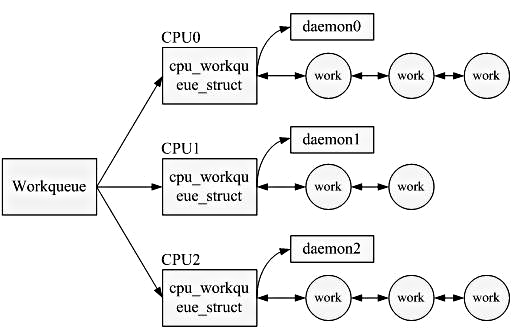
* tasklets execute quickly, for a short period of time, and in atomic mode
* workqueue functions may have higher latency but need not be atomic
* Run in the context of a special kernel process (worker thread)
* more flexibility and workqueue functions can sleep.
* they are allowed to block (unlike deferred routines)
* No access to user space
## Process 管理
[ [Process Management](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/ProcessManagement.pdf) ]
* Scheduling
* Find the **_next suitable_** process/task to run
* Context switch
* Store the context of the current process, restore the context of the next process
* Process context + interrupt context
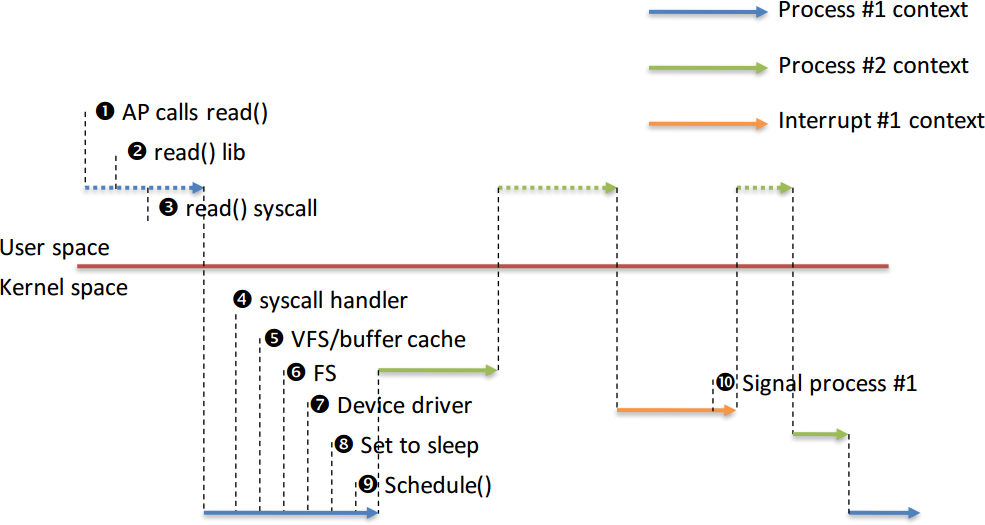
* Linux kernel is possible to preempt a task at any point, so long as the kernel does not hold a lock
* Kernel can be interrupted ≠ kernel is preemptive
* Non‐preemptive kernel, interrupt returns to interrupted process
* Preemptive kernel, interrupt returns to any schedulable process
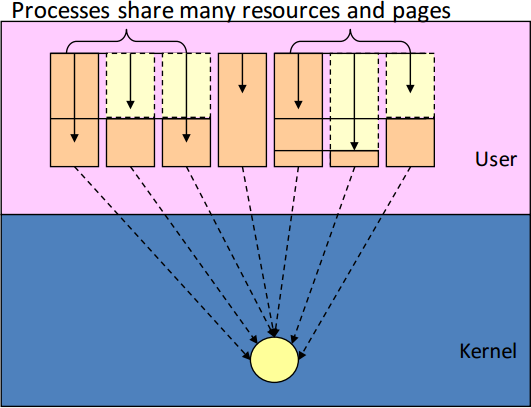
* [ Page 48 - 51 ] Process vs. Thread
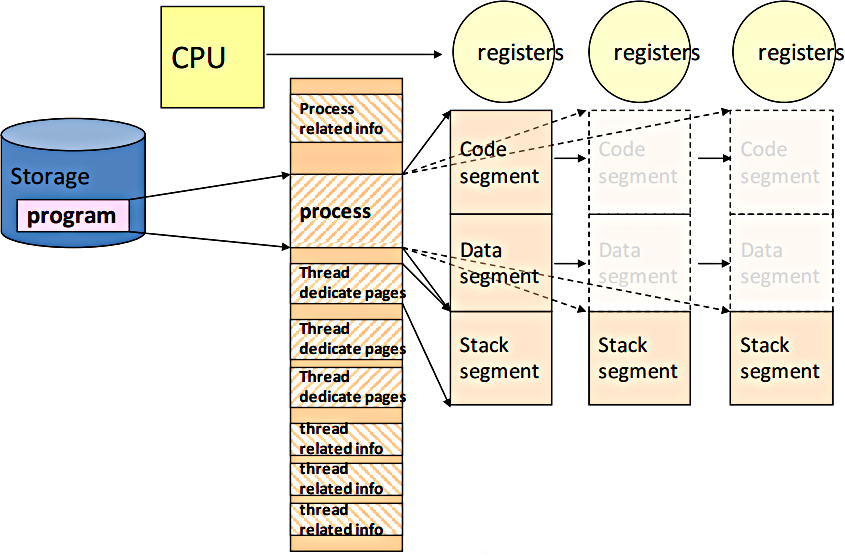
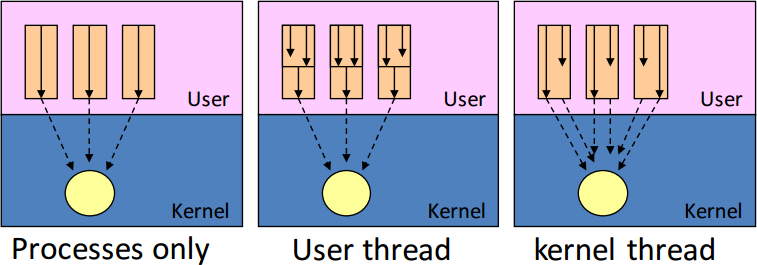
(和作業系統和計算機組織結構的設計有極大的落差)
* Scheduling simulation
* [LinSched: Simulating the Linux Scheduler in user space](http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/l-linux-scheduler-simulator/)
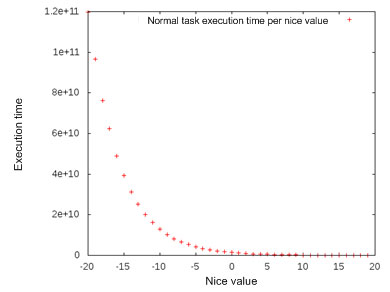
* [Cheddar project : real-time scheduling analyzer](http://beru.univ-brest.fr/cheddar/)
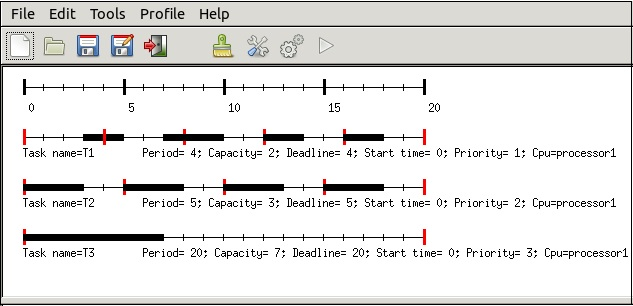
對照 [ARM-Linux 技術報告](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/arm-linux)
* [Concurrency in The Linux Kernel](https://hackmd.io/@VIRqdo35SvekIiH4p76B7g/Hy9JyrBw)
- [ ] 取自東京大學 Shinpei Kato 教授的 Advanced Operating Systems 課程投影片 [Process Management: Abstracting Computing Resources](https://web.archive.org/web/20221028025241/https://www.pf.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/AdvancedOperatingSystems4.pdf)


## Process 組成
[Elements of a process](https://www.bottomupcs.com/elements_of_a_process.xhtml)
[Program startup process in userspace](https://0xax.gitbooks.io/linux-insides/Misc/linux-misc-4.html)
## 待整理
* [Evolution of the x86 context switch in Linux](http://www.maizure.org/projects/evolution_x86_context_switch_linux/index.html)
* [Decoded: The 'top' utility (procps)](http://www.maizure.org/projects/decoded-top-procps/index.html)