# Developing with GigaDevice's RISC-V 32 Bits MCU Development Board
###### tags: `RISC-V`, `MCU`, `riscv64-elf-gcc`
## Development Environment
* My host is an Arch Linux (x86_64) system. The target chip is a RISC-V 32 bits MCU. Therefore, install the `riscv64-elf-` toolchain packages:
* **riscv64-elf-binutils**
* **riscv64-elf-gcc**
* **riscv64-elf-newlib**
* **riscv64-elf-gdb**
Here lists the supported architectures:
```shell=
$ riscv64-elf-gcc --print-multi-lib
.;
rv32i/ilp32;@march=rv32i@mabi=ilp32
rv32im/ilp32;@march=rv32im@mabi=ilp32
rv32iac/ilp32;@march=rv32iac@mabi=ilp32
rv32imac/ilp32;@march=rv32imac@mabi=ilp32
rv32imafc/ilp32f;@march=rv32imafc@mabi=ilp32f
rv64imac/lp64;@march=rv64imac@mabi=lp64
rv64imafdc/lp64d;@march=rv64imafdc@mabi=lp64d
```
* I prefer the Makefile tool. So, **make** is installed, too.
* Also, need **[OpenOCD](https://sourceforge.net/p/openocd/code/ci/master/tree/)** to flash and debug. I use the `master` branch now.
## Developing with [Sipeed Longan Nano](https://longan.sipeed.com/en/)
* [Nuclei SDK](https://doc.nucleisys.com/nuclei_sdk/design/board/gd32vf103c_longan_nano.html) 
* Schematic 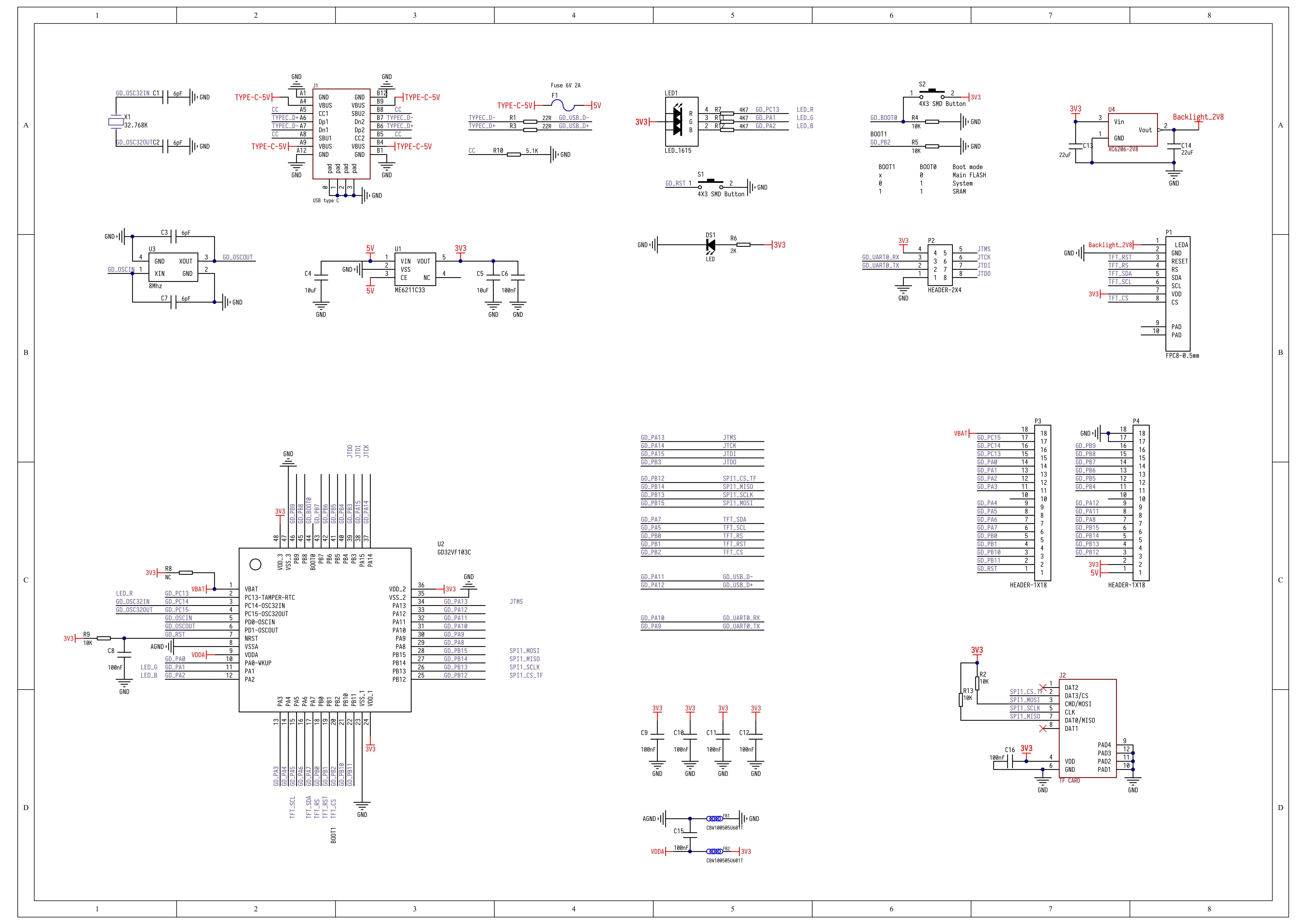
* The MCU is GigaDevice's [GD32VF103CBT6](https://www.gigadevice.com/product/mcu/risc-v/gd32vf103cbt6), or [GD32VF103C8T6](https://www.gigadevice.com/product/mcu/risc-v/gd32vf103c8t6). It is according to the chip version on the board.
* RISC-V Microcontroller has [GD32VF103_Firmware_Library](https://github.com/riscv-mcu/GD32VF103_Firmware_Library). However, it suggests [Nuclei SDK](https://github.com/Nuclei-Software/nuclei-sdk)!?
## Developing with Nuclei SDK
```shell=
git clone https://github.com/Nuclei-Software/nuclei-sdk
cd nuclei-sdk
```
### Prepare
I have some modification to use the bare-metal toolchain `riscv64-elf-`:
1. [Use common RISC-V 64 bare-metal toolchain](https://github.com/starnight/nuclei-sdk/commit/fe42e9c60481e5925d738b0d65928b365f4ac79b)
2. [Set ISA spec version as 2.2 to support extension zicsr](https://github.com/starnight/nuclei-sdk/commit/aab62b5b21d906784b390bb73c3f12bd52ed5e20)
3. [Use mainline OpenOCD's gd32vf103.cfg as the config](https://github.com/starnight/nuclei-sdk/commit/92b09dd0cb92d016a33f560bc9caad50aad6e531). Besides, I use FTDI FT232HQ board as the the JTAG interface. So, use [um232h.cfg](https://sourceforge.net/p/openocd/code/ci/master/tree/tcl/interface/ftdi/um232h.cfg) as the config.
### Have an LED application
I add the [LED application](https://github.com/starnight/nuclei-sdk/commit/85e36061fe7e4260286f902561119fb84da9d58f).
1. Get into the led app: `cd application/baremetal/led`
2. Disable the optimization for GDB with [`-O0`](https://github.com/starnight/nuclei-sdk/blob/85e36061fe7e4260286f902561119fb84da9d58f/application/baremetal/led/Makefile#L9).
3. Build: `make SOC=gd32vf103 BOARD=gd32vf103c_longan_nano all`
4. Flash: `make SOC=gd32vf103 BOARD=gd32vf103c_longan_nano upload`
5. It will light RGB LEDs in order periodically.
### Debugging
Debug with GDB via OpenOCD and [FT232H](https://hackmd.io/@starnight/OpenOCD-JTAG-interface#FTDI-FT232H) as JTAG interface.
1. Connect the `TCK`, `TDO`, `TDI`, `TMS` and `GND` pins between FT232H and the Sipeed Longan Nano board.
2. Start the gdb server with FT232H as JTAG interface and GD32VF103 as the target configs:
```sh=
$ openocd -f interface/ftdi/um232h.cfg -f target/gd32vf103.cfg
Open On-Chip Debugger 0.12.0-rc2+dev-00007-gdc1e6d4d4 (2022-11-13-14:48)
Licensed under GNU GPL v2
For bug reports, read
http://openocd.org/doc/doxygen/bugs.html
Info : Listening on port 6666 for tcl connections
Info : Listening on port 4444 for telnet connections
Warn : An adapter speed is not selected in the init scripts. OpenOCD will try to run the adapter at the low speed (100 kHz)
Warn : To remove this warnings and achieve reasonable communication speed with the target, set "adapter speed" or "jtag_rclk" in the init scripts.
Info : clock speed 100 kHz
Info : JTAG tap: gd32vf103.cpu tap/device found: 0x1000563d (mfg: 0x31e (Andes Technology Corporation), part: 0x0005, ver: 0x1)
Info : JTAG tap: auto0.tap tap/device found: 0x790007a3 (mfg: 0x3d1 (GigaDevice Semiconductor (Beijing) Inc), part: 0x9000, ver: 0x7)
Warn : AUTO auto0.tap - use "jtag newtap auto0 tap -irlen 5 -expected-id 0x790007a3"
Info : datacount=4 progbufsize=2
Info : Examined RISC-V core; found 1 harts
Info : hart 0: XLEN=32, misa=0x40901105
Info : starting gdb server for gd32vf103.cpu on 3333
Info : Listening on port 3333 for gdb connections
```
It shows that the gdb server is listening on port **3333**.
3. Have the gdb client connecting to the gdb server to debug the `led.elf` flashed on the MCU chip GD32VF103C8T6:
```shell=
$ riscv64-elf-gdb led.elf
GNU gdb (GDB) 13.1
...
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from led.elf...
(gdb) target extended-remote localhost:3333
Remote debugging using localhost:3333
0x080016a6 in __LW (addr=0xd1000004)
at ../../../NMSIS/Core/Include/core_feature_base.h:1474
1474 __ASM volatile ("lw %0, 0(%1)" : "=r" (result) : "r" (addr));
(gdb) break main.c:66
Breakpoint 1 at 0x8001d94: file main.c, line 66.
Note: automatically using hardware breakpoints for read-only addresses.
(gdb) break main.c:70
Breakpoint 2 at 0x8001db4: file main.c, line 71.
(gdb) break main.c:77
Breakpoint 3 at 0x8001de2: file main.c, line 77.
(gdb) continue
Continuing.
Breakpoint 2, main () at main.c:71
71 gpio_bit_reset(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_1);
(gdb) list
66 gpio_bit_reset(GPIOC, GPIO_PIN_13);
67 gpio_bit_set(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_2);
68 delay_1ms(1000);
69
70 /* turn on LED_G, turn off LED_R */
71 gpio_bit_reset(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_1);
72 gpio_bit_set(GPIOC, GPIO_PIN_13);
73 delay_1ms(1000);
74
75 /* turn on LED_B, turn off LED_G */
(gdb)
```
## Reference
* [RISC-V Compile Targets, GCC](https://five-embeddev.com/toolchain/2019/06/26/gcc-targets)
* [intexc_gd32vf103.S uses unsupported extension zicsr on architecture rv32imac](https://github.com/Nuclei-Software/nuclei-sdk/issues/51)