## [662\. Maximum Width of Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/)
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the **maximum width** of the given tree_.
The **maximum width** of a tree is the maximum **width** among all levels.
The **width** of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is **guaranteed** that the answer will in the range of a **32-bit** signed integer.
**Example 1:**
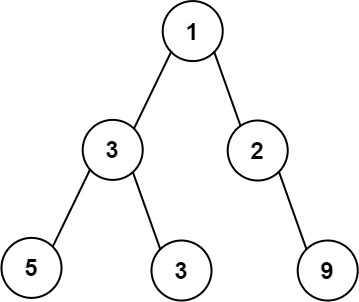
**Input:** root = \[1,3,2,5,3,null,9\]
**Output:** 4
**Explanation:** The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
**Example 2:**
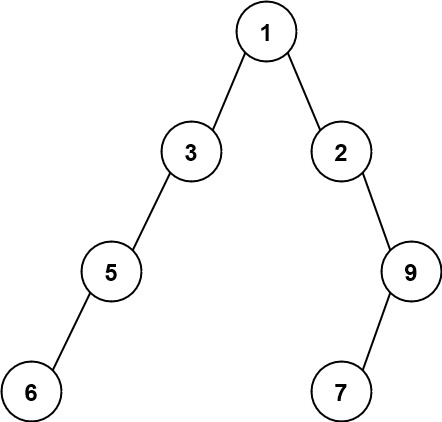
**Input:** root = \[1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7\]
**Output:** 7
**Explanation:** The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
**Example 3:**
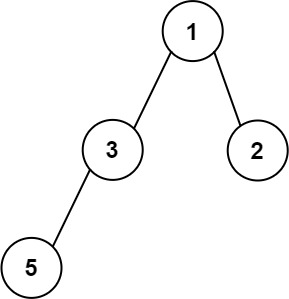
**Input:** root = \[1,3,2,5\]
**Output:** 2
**Explanation:** The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
**Constraints:**
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[1, 3000]`.
- `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
```cpp=
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
#define ll long long
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
// 使用 pair 的結構 {目前的節點, 節點的 index}
queue<pair<TreeNode*, ll>> q;
q.push({root, 0});
ll maxWidth = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
ll qSize = q.size();
// 最左邊 node 的 index
ll left = q.front().second;
// 最右邊 node 的 index
ll right = q.back().second;
// 寬度公式:右邊節點的 index - 左邊節點的 index + 1
maxWidth = max(maxWidth, right - left + 1);
// 走訪每一層
for(int i = 0; i < qSize; i++) {
auto node = q.front(); q.pop();
// levelIndex = 目前節點的 index - 最左邊節點的 index
ll levelIndex = node.second - left;
if(node.first->left) {
// 將左邊節點推到 queue
q.push({node.first->left, 2 * levelIndex});
}
if(node.first->right) {
// 將右邊節點推到 queue
q.push({node.first->right, 2 * levelIndex + 1});
}
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
};
```
:::success
- 時間複雜度:$O(N)$
- 空間複雜度:$O(N)$
:::