# ST-CS120: Computer Network
[](https://hackmd.io/WKGXaV_ZSsSa5E43PDg9lQ)
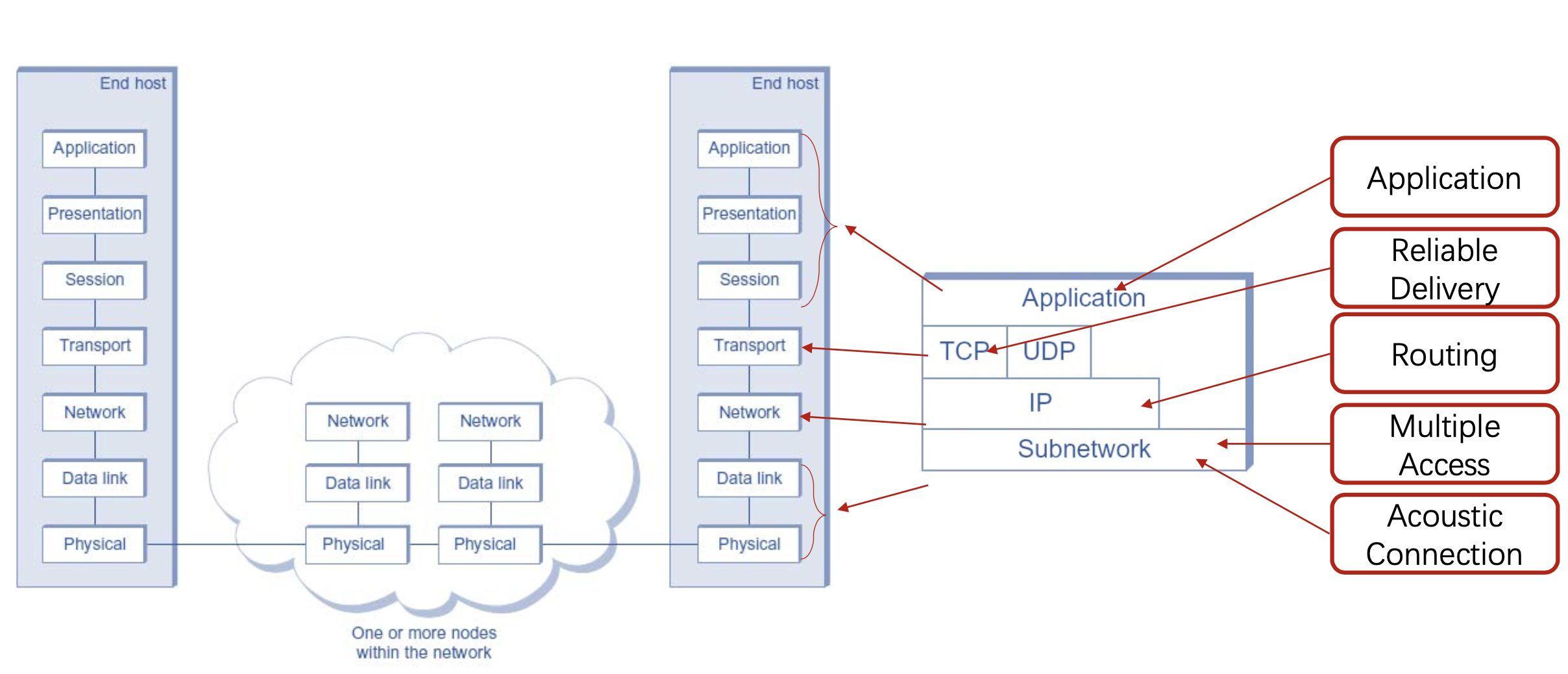
## OSI Model
- https://www.forcepoint.com/zh-hans/cyber-edu/osi-model
- 
## Performance
- Metrics (性能与指标)
- Bandwidth (Throughput)
- Unit: bps, kbps, Mbps, Gbps, where `b` stands for `bits`
- Latency
- RTT: Round-Trip Time: calc the time of send and recieve. Local because of the avoidance of time shift between devices.
- 计算往返的时间,也就是本地从发出到收到的时间差。对应的,单程 (One-way Latency) = T2 - T1 or T3 -T2
- Latency = Transmit Delay + Propagation Delay + Queueing Delay
- Transmit Delay = TransferSize/Bandwidth
- Propagation Delay = Distance/SpeedofSignal
- 
- Effective Bandwidth (throyghput) = TransferSize/Latency
- tools: iperf, ping (https://networktools.he.net/)(https://ping.sx)
## L1: Physical Layer
网线一类的东西
- 介质
- 需要调制与解调(以通过物理介质传输)
### Upper bound of throughout
#### Shannon-Hartley Theorem
The theoretical throughput upper bound:
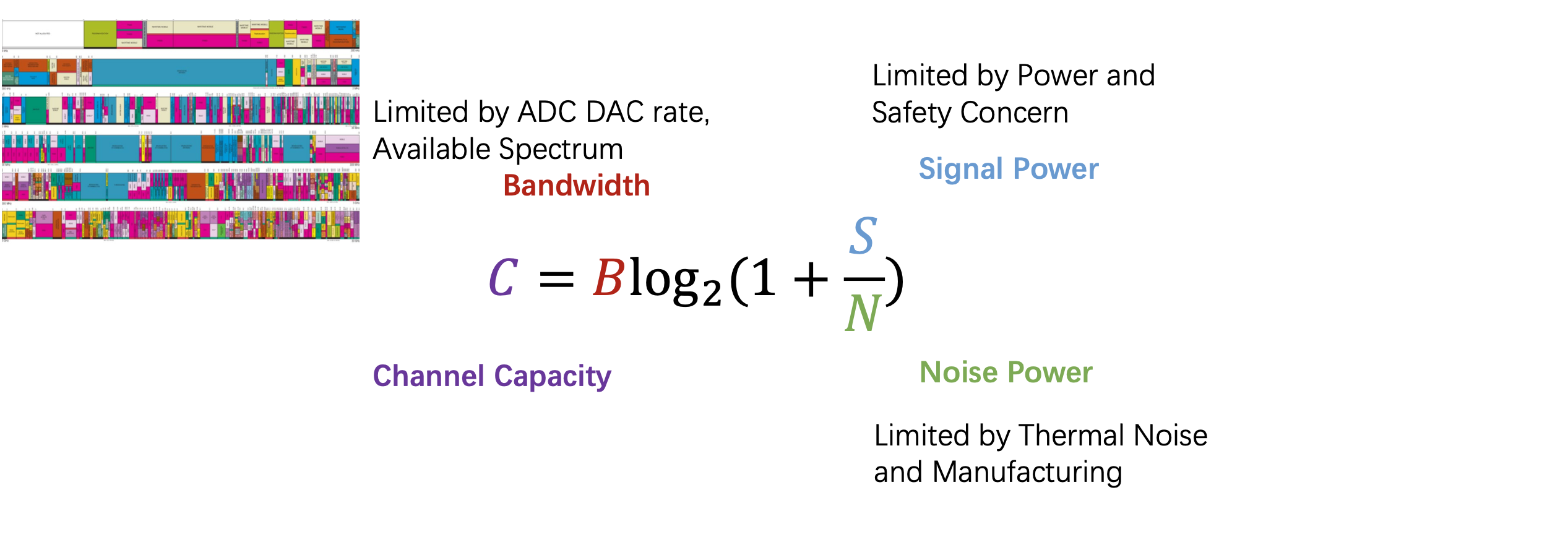
### Transmission Method
#### Baseband Transmission (Line Coding)
- 无载波
- 串行
#### Passband Modulation
- 载波
- 并行
- $A \cdot \sin (2 \pi f t+\phi)$
- Amplitude
- Frequency
- Phase
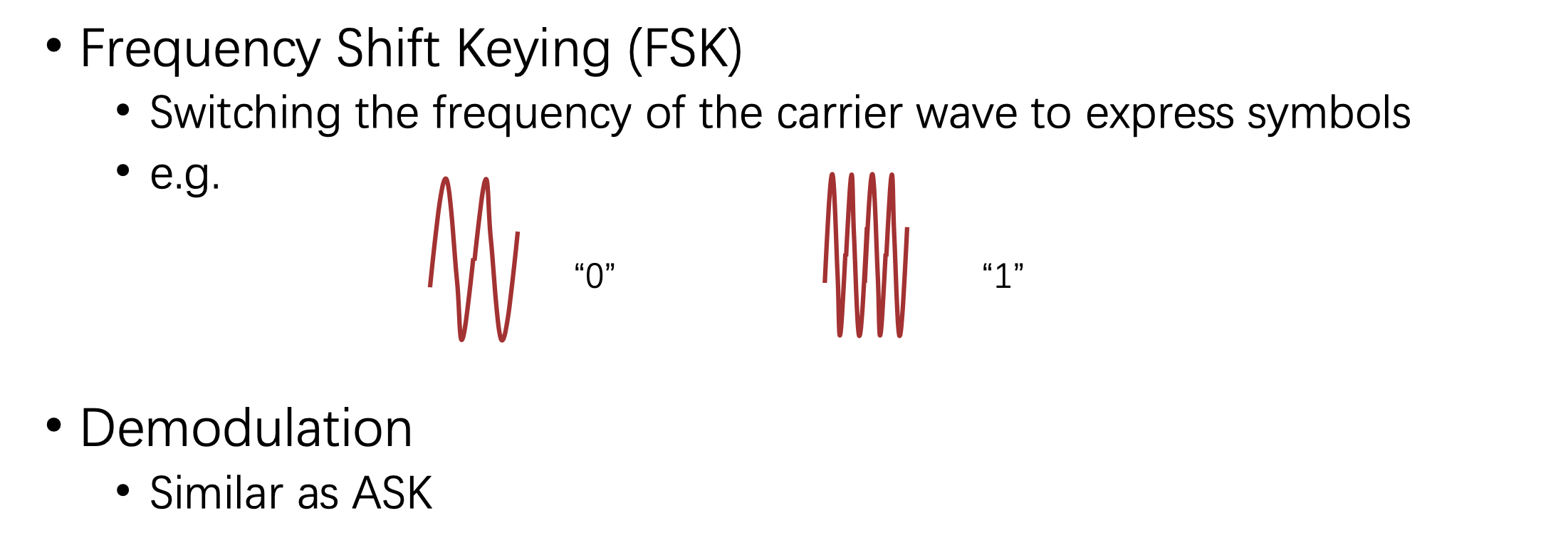
#### Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
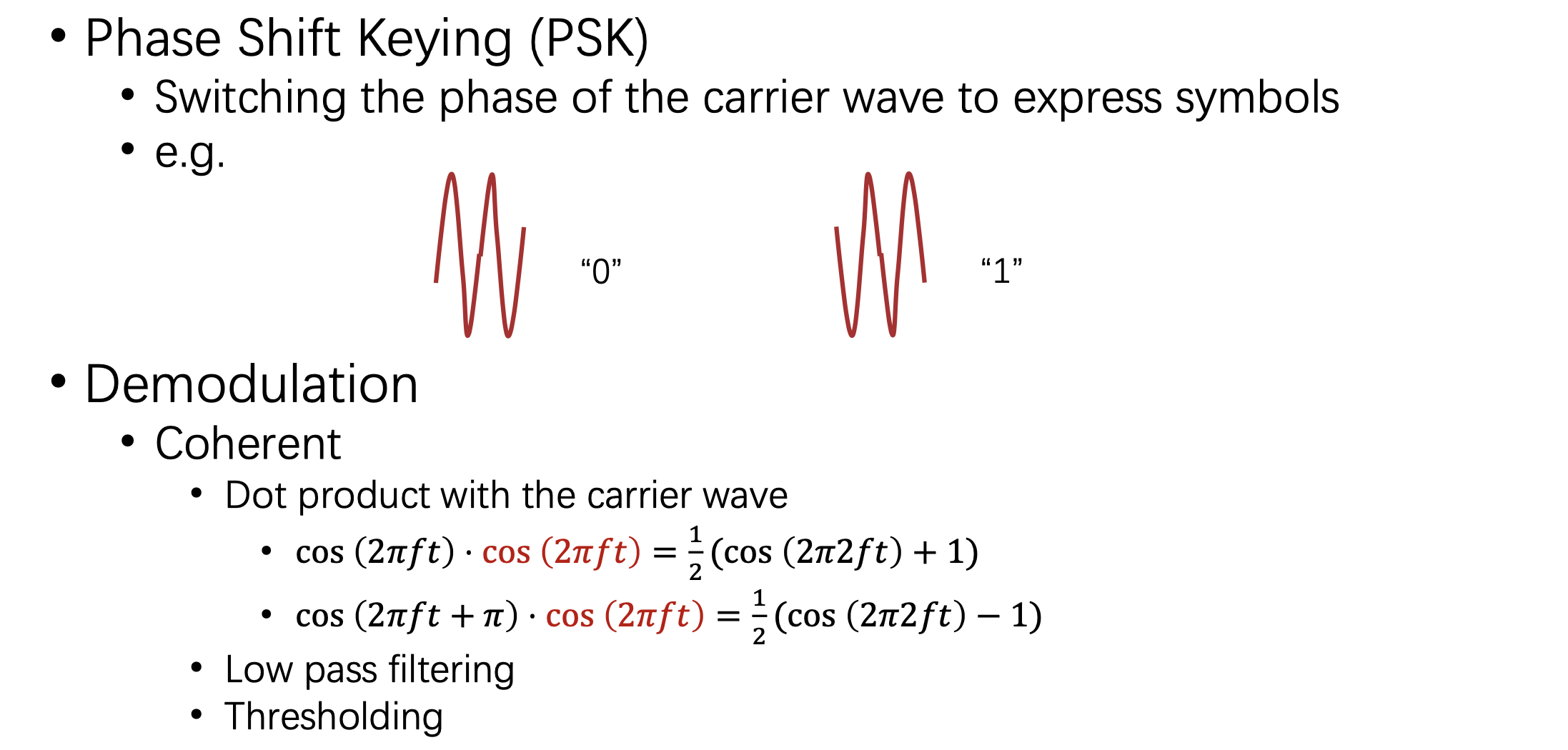
#### Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
#### Frequencty shift passing
- 高频部分解码归零
- 低频部分保留
#### Amplitude shift passing
- $A\cos(2\pi ft)\cos(2\pi ft)= \frac12A(cos(2 \pi ft)+1)$
- 乘以载波解码
- 信号不稳定时效果较差
#### Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
- ASK + PSK
- 传输更多的信息 (4 symbols)
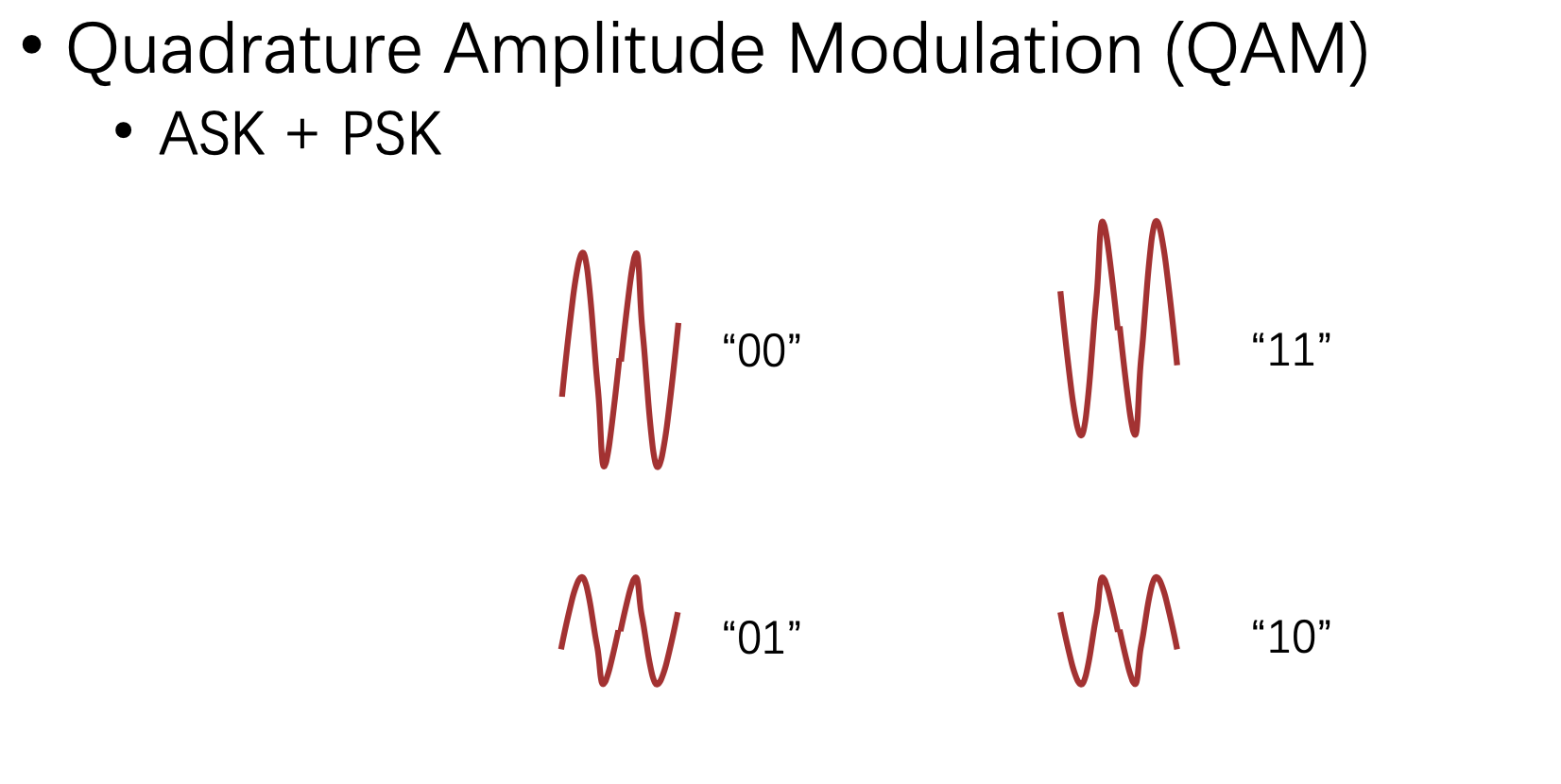
总结: Baseband * coherence wave = Passband
### 纠错与恢复
> analog goes wrong
- Bit error rate (BER) = error bits/transmitted bits
- High rate <-> Low reliability
#### 2D Parity Check
是不是有偶数个 0
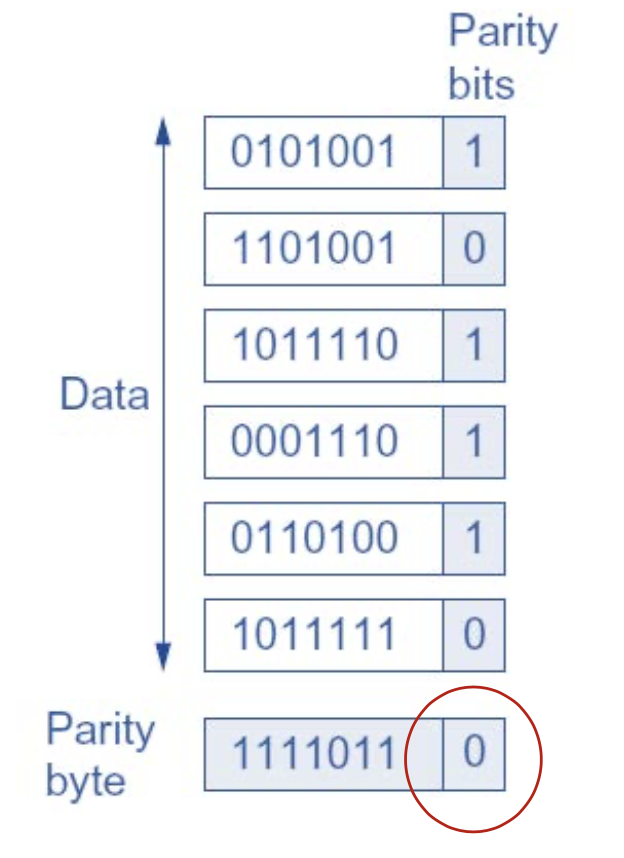
- overhead $\frac 18$
- 1,2,3 bit wrong OK to recover
- 4 bit may ERROR
#### Check sum
- TCP/IP header
- sum all, check sum
- 作为补码加起来
- 快但低能
#### CRC Performance
多项式
https://users.ece.cmu.edu/~koopman/crc/
#### 汉明码
#### 多路复用
- 分时复用
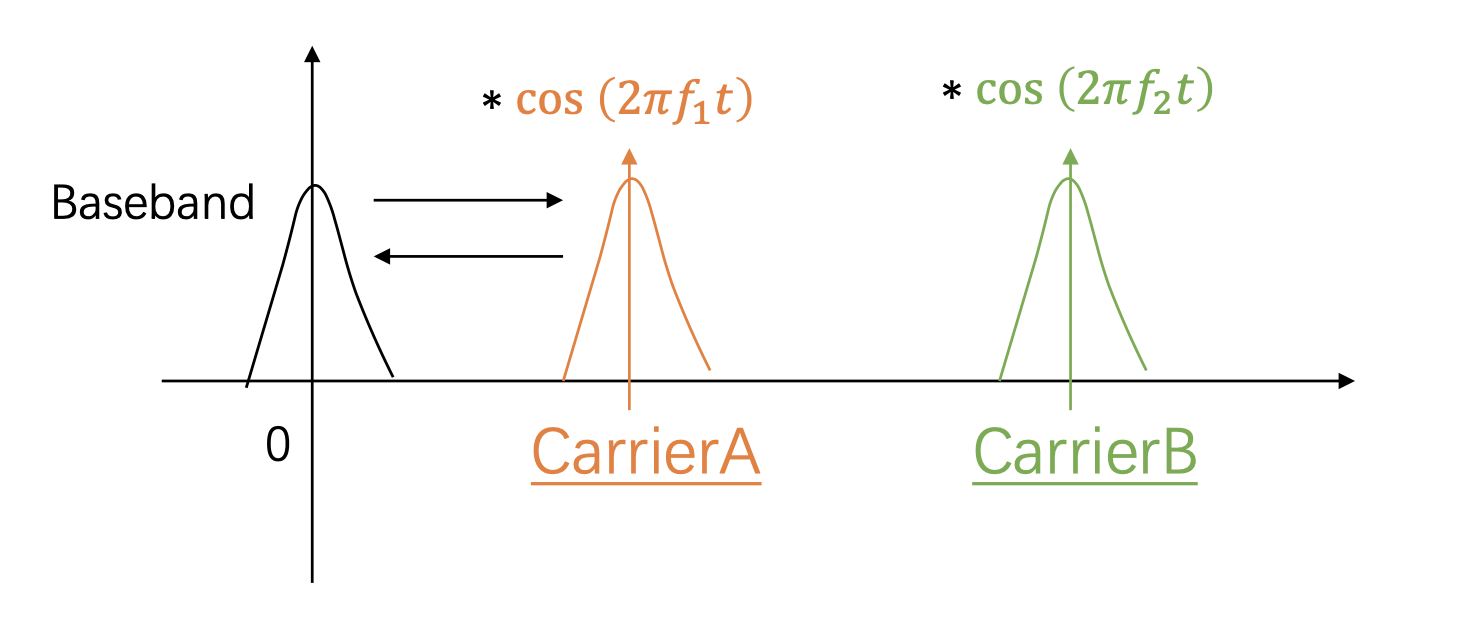
- 分频复用 Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM)
- 
- 分码复用
- 传输介质无法承载我们的传输
#### Rate Selection
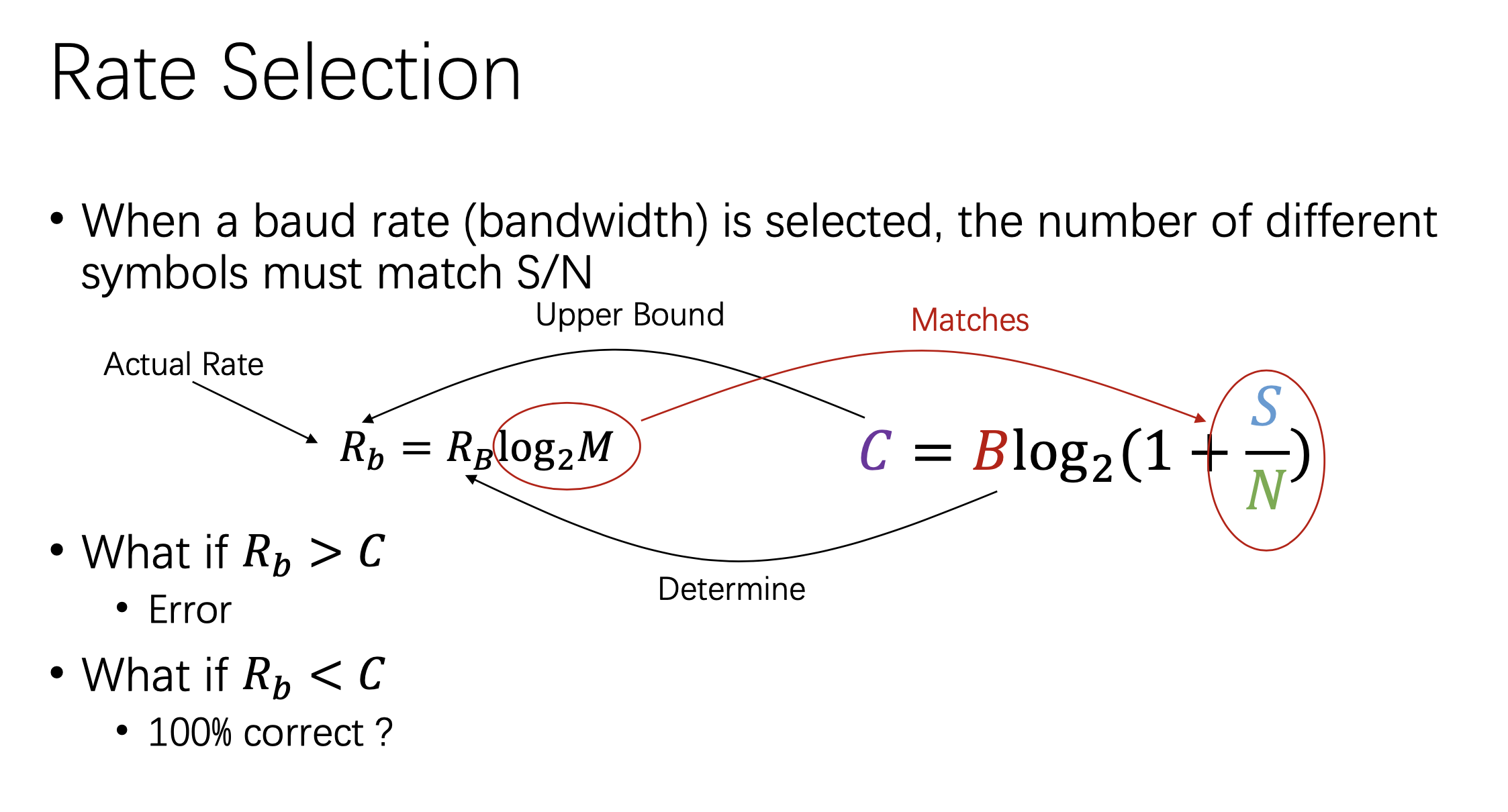
### ACK
🐱:喵 \
😺:喵 \
🐱:喵喵 \
😺:喵喵
#### Stop and Wait
http://www2.rad.com/networks/2004/sliding_window
规定时间内收不到就等,效率不高(利用 buffer 解决)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bandwidth-delay_product
https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks/wiki/Optimizing-Shadowsocks
#### NACK (Negative ACK)
接收方定时把所有未收到的包序号通过反馈报文通知到发送方进行重传。
#### Sliding Window
- 不对等的传输
- Send buffer size: Delay $\cdot$ Bandwidth
- Receive buffer size: Flow control
- 拥塞控制: 控制 buffer 大小
### 并行
#### Random Access
*Transmit and Pray*
#### Slotted ALOHA
- For each slot, the probability of successful transmission is $\operatorname{Np}(1-\mathrm{p})^{\wedge}(\mathrm{N}-1)$
- $\mathrm{p}$ is the probability of transmission. It is determined by the number of nodes $N$ in the network, when $N$ is large, $p$ should be small.
- The optimal p can be calculated by derivation
- $f(p)=N p(1-p)^{\wedge}(N-1)$
- $f^{\prime}(p)=N(1-p)^{\wedge}(N-1)-N p(N-1)(1-p)^{\wedge}(N-2)$
- Thus the optimal $\mathrm{p}$ is $1 / \mathrm{N}$
- So when $p=1 / N$, the probability of successful transmission is $(1-1 / N)^{\wedge}(N-1)$, when $N$ is large, it is close to $1 / e$. Thus the utilization of the channel is about $30 \%$
- Efficiency: 1/e
## L2: 链路层,介质访问子层
### Main function
- 连接协议 (e.g. Hola)
### Ethernet
```bash
ip addr show
```
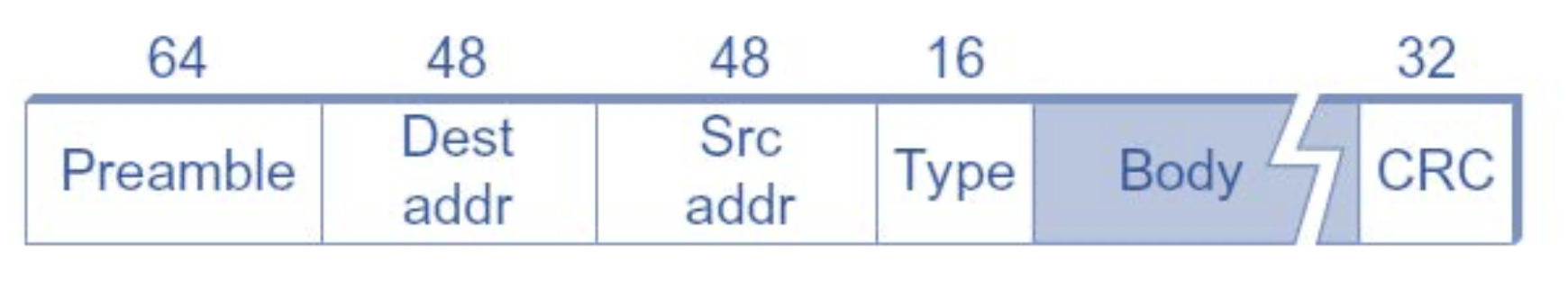
### WIFI and Cecullar
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27847237/article/details/104098817
- 半双工
- 不对称
#### RTS/CTS
通过监听其它 client 之间的通讯来推测 server 与它的连接情况
- RTS/CTS does not solve hidden terminal and exposed terminal
completely
- Designing Wireless MAC is non-trivial
- overhead too large
#### IEEE 802.11 MAC

WIFI 包经过再打包走 Ethernet
- 3-Addr: A -> AP -> C
- 4-Addr: A -> B -> C -> D (mesh)
See https://github.com/SpacehuhnTech/esp8266_deauther for a security issue for WIFI
### Switch
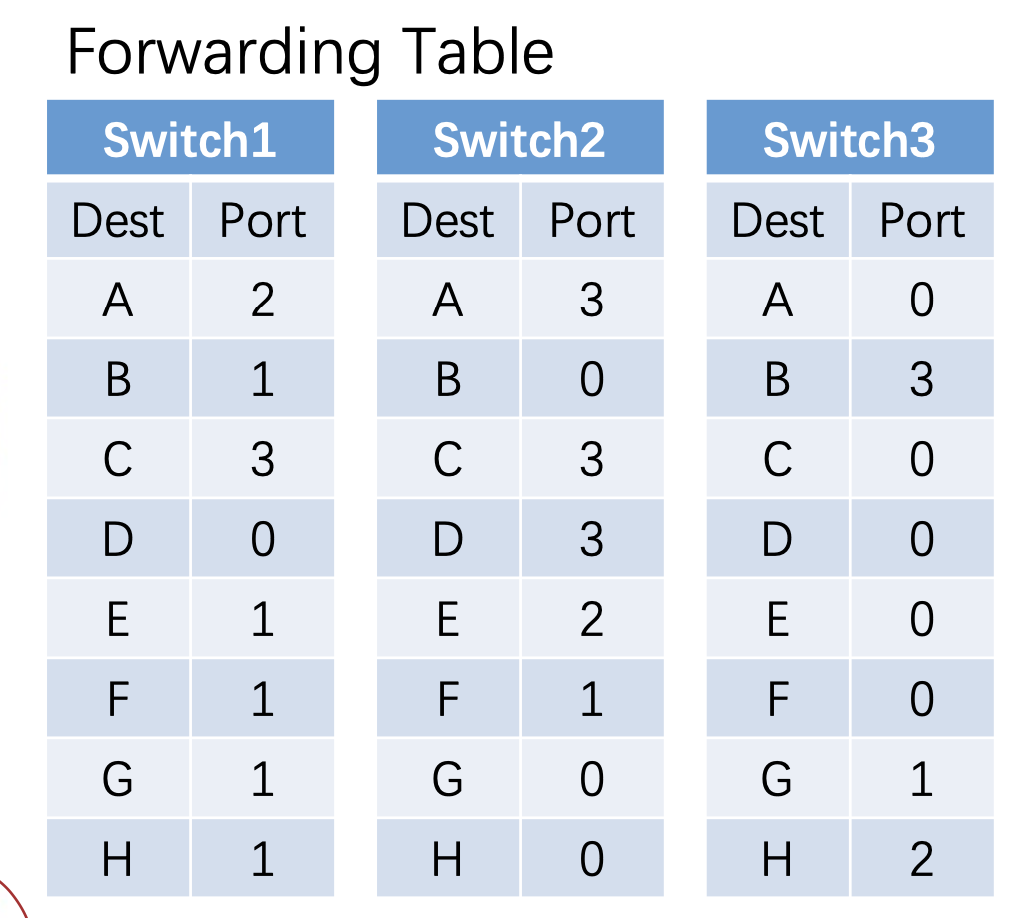
#### learning Bridge
- Switching method
- Datagram / Connectionless
- 转发表:记录下来这条链路上的所有主机和对应走哪个端口
- No Guarantee for
- Success delivery
- Performance
- Delay, Throughput
- Packet Order
- 打电话给 ISP
- 
- Vitual Circuit/Connection
- Procedure
- 预留资源 (入口与 index)
- 当链路上的所有 switch 都有足够的资源,destination 会发回一个 ack, 然后链路就建立起来了
- Source Routing
- 带路由信息
- Learning Switch
- 知道 A 从哪来 (port 1)
- 广播 (X 收到包)
- 其它节点也知道 A 在哪了
- 同一个冲突域内 drop
- Cycle:
- 成因: 错误的网络管理、冗余
- 结果: Storm
- 占用网络资源
- 重复包
- Distributed Spanning Tree Algorithm
- Each switch is a vertex
- Each connection is an edge
- 最小生成树
- 计算 hof, speed, rtt 将形成环路的节点断掉
## L3: 网络层
### Internet Protocal
多协议之间的网络通信
- Addressing Scalability
- Network Heterogeneity
#### IP Addressing

#### IP Forward
- Each router maintains a forwarding table
- if IP.network == Connected network
- forward to the host (How? ARP: IP->MAC)
- if IP.network != Connected network
- forward to some router
#### IP jisuanqi
ipjisuanqi.com
#### IP Packet
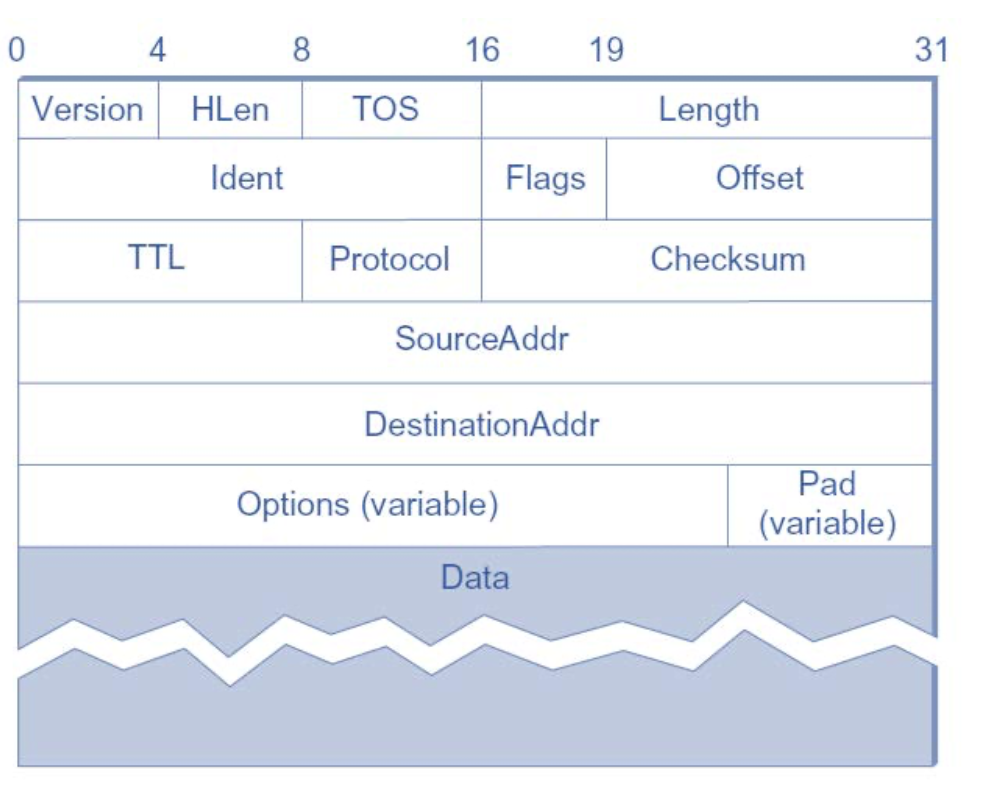
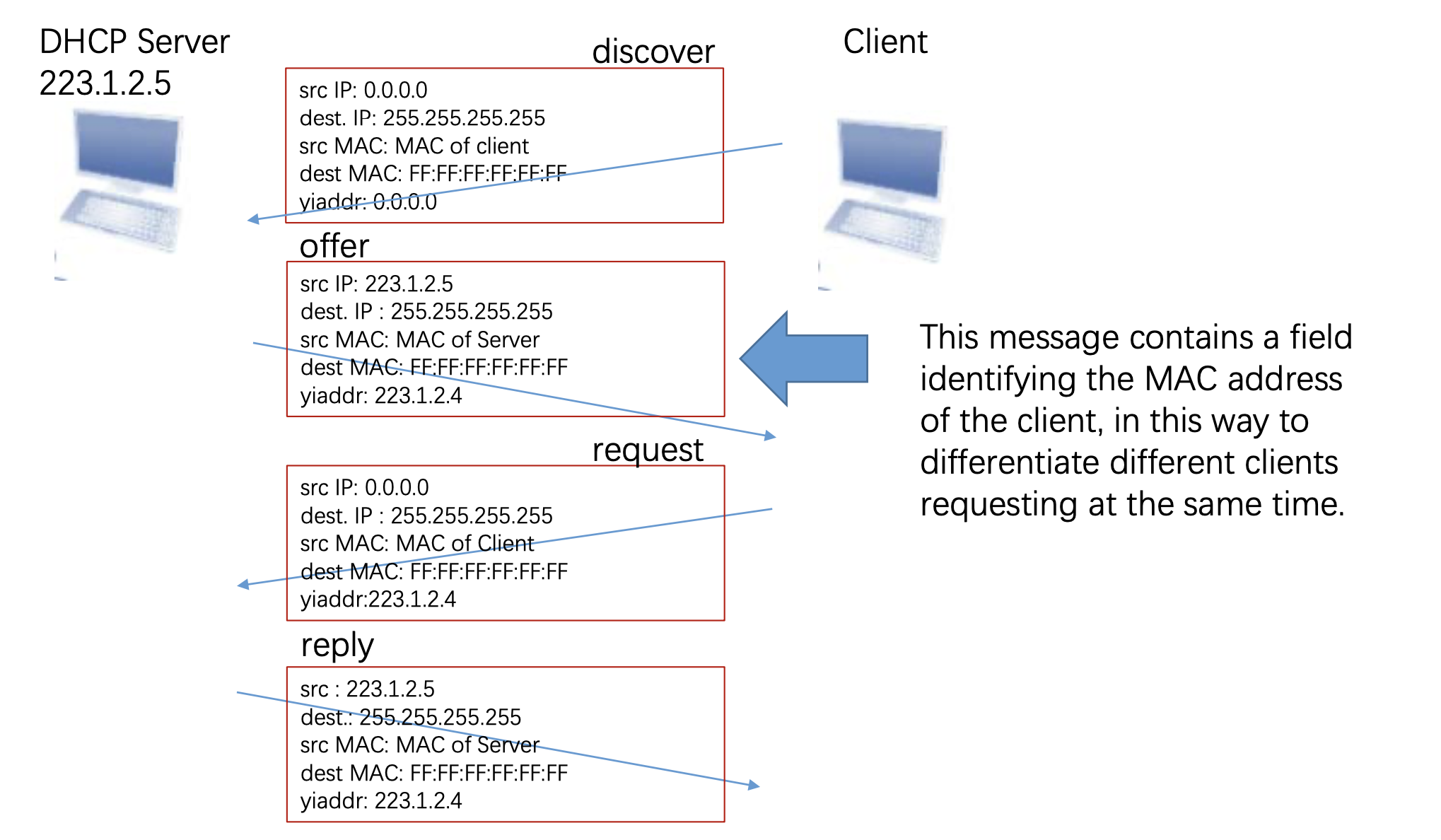
#### Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
分配 IP 地址并记录
#### Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- ARP table: each IP node (host, router) on LAN has table IP/MAC address mappings for some LAN nodes
- < IP address; MAC address; TTL>
- 200.155.11.3; 58-23-D7-FA-20-B0 200.155.11.5;
- 1A-2F-BB-76-09-AD 200.155.11.2;
- 0C-C4-11-6F-E3-98
#### Fragmentation and Reassembly
包会分割成 MTU 的大小传输,之后再重组 (There is Offset-bits in IP packet)
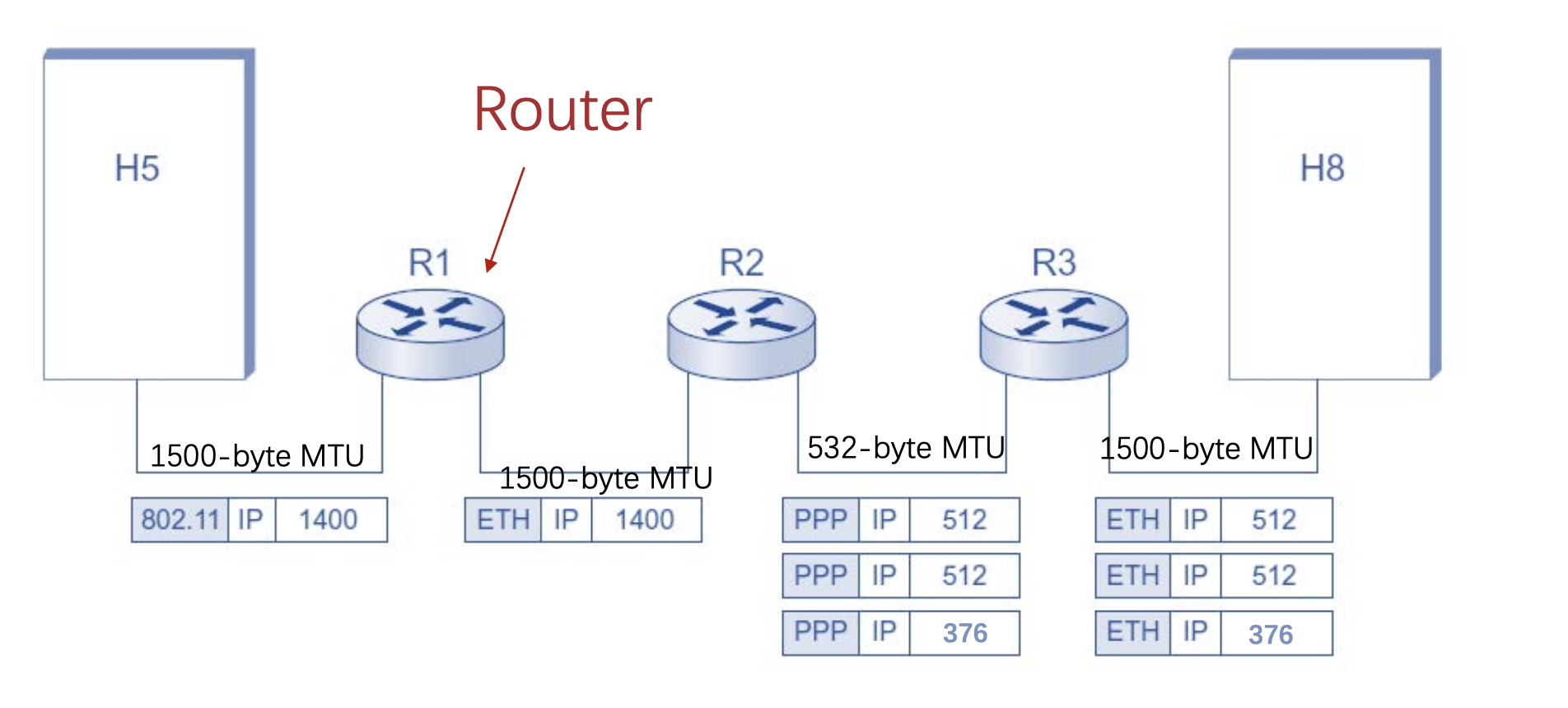
### Routing
The basic problem of routing is to find the lowest-cost path between any two nodes

#### RIP
- Bellman-Ford Equation
- $d_{A \to C} = min \{A \to B + B \to C \}$ foreach $B$ in $A \to C$ 松弛操作
- 每个节点不断的估计和其它节点的最短距离,并不断收敛
- distance to neighbour is known
- and its neighbour can tell (not specific) the distance to destination y
- 当一个节点收到新的值的时候,通知周围节点更新
- 优点:收敛块
- 缺点:缺少弹性
- 断连无法更新或者更新出错或者很慢
- 数字会一直变大
- 优化
- 限制最大跳数
- 限制每次更新的数目
#### Dijastra
#### OSPF
#### BGP
[bgp.he.net](bgp.he.net)
- iBGP: peers
- eBGP: transits
#### IPV6

#### NAT
随机端口映射到主机
#### Mobile
## L4: 传输层
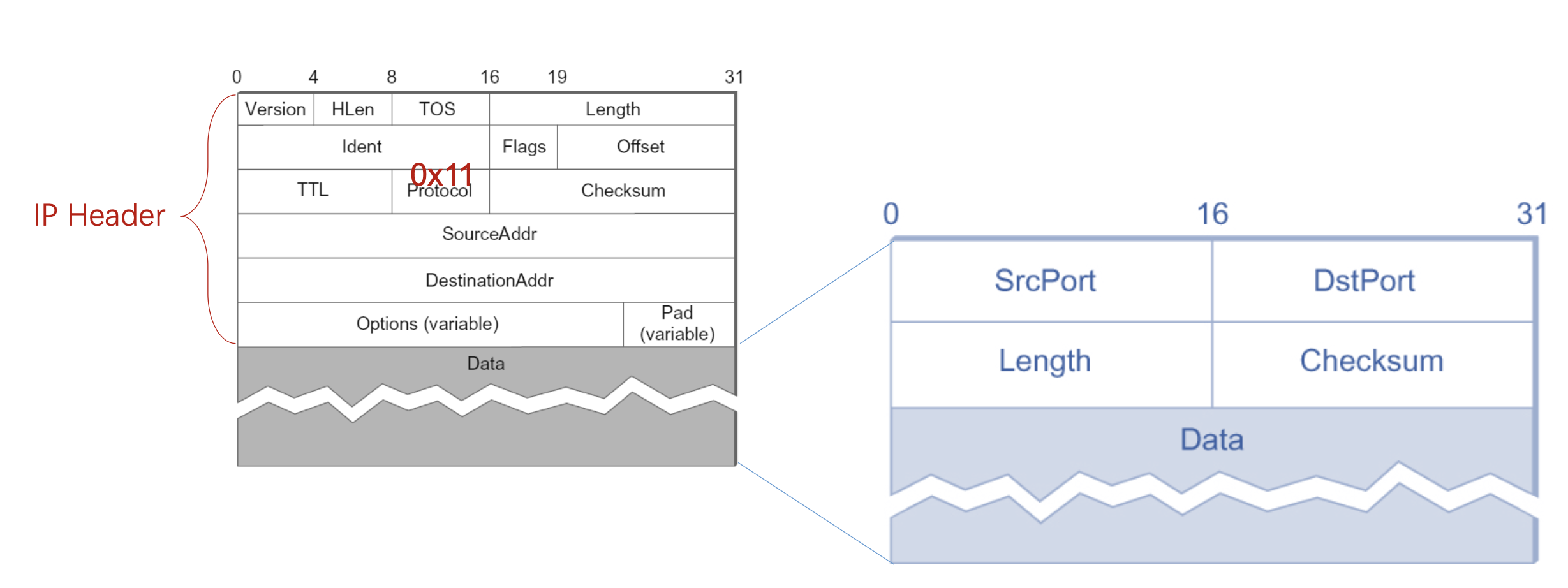
### UDP
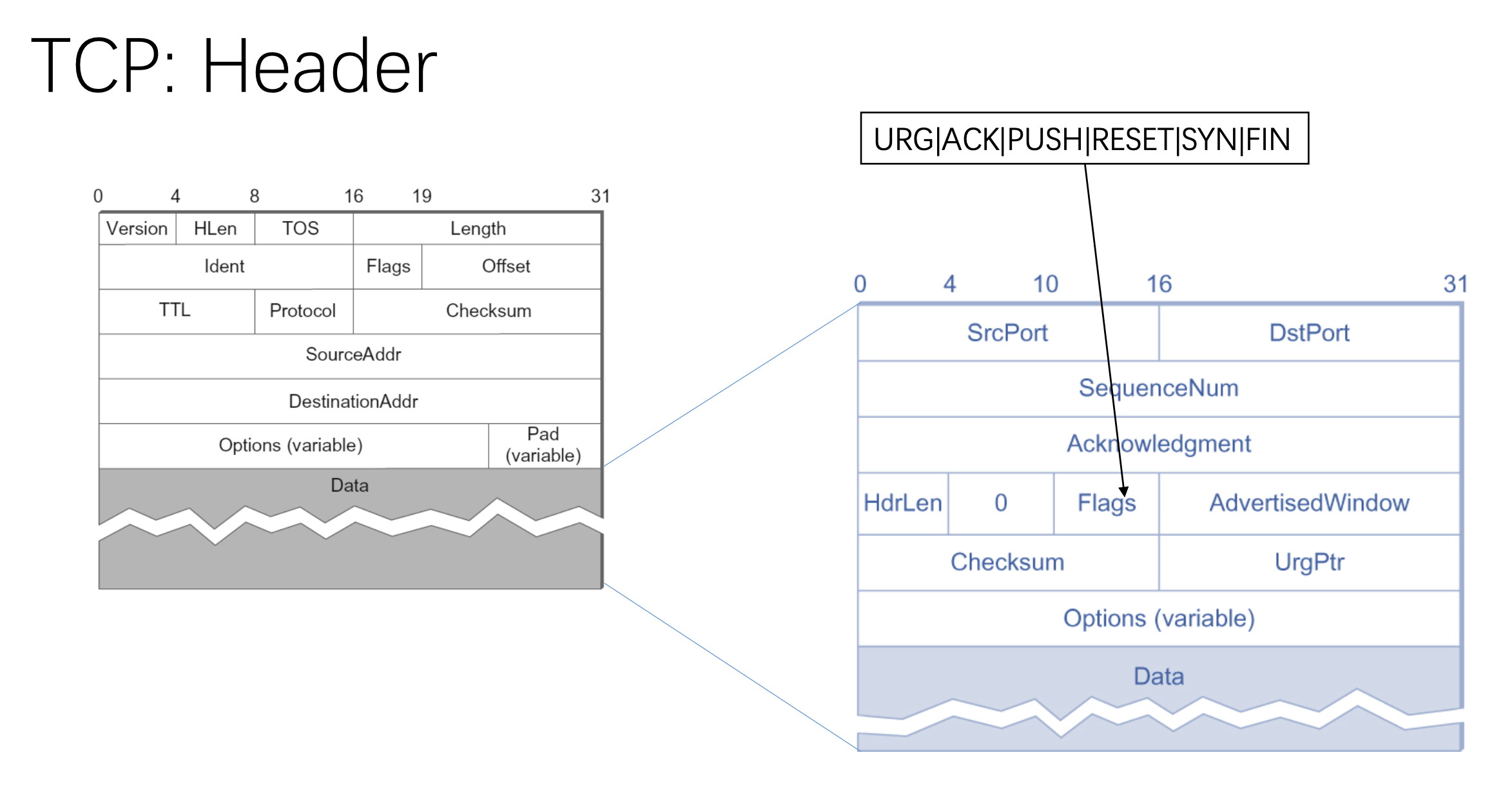
### TCP
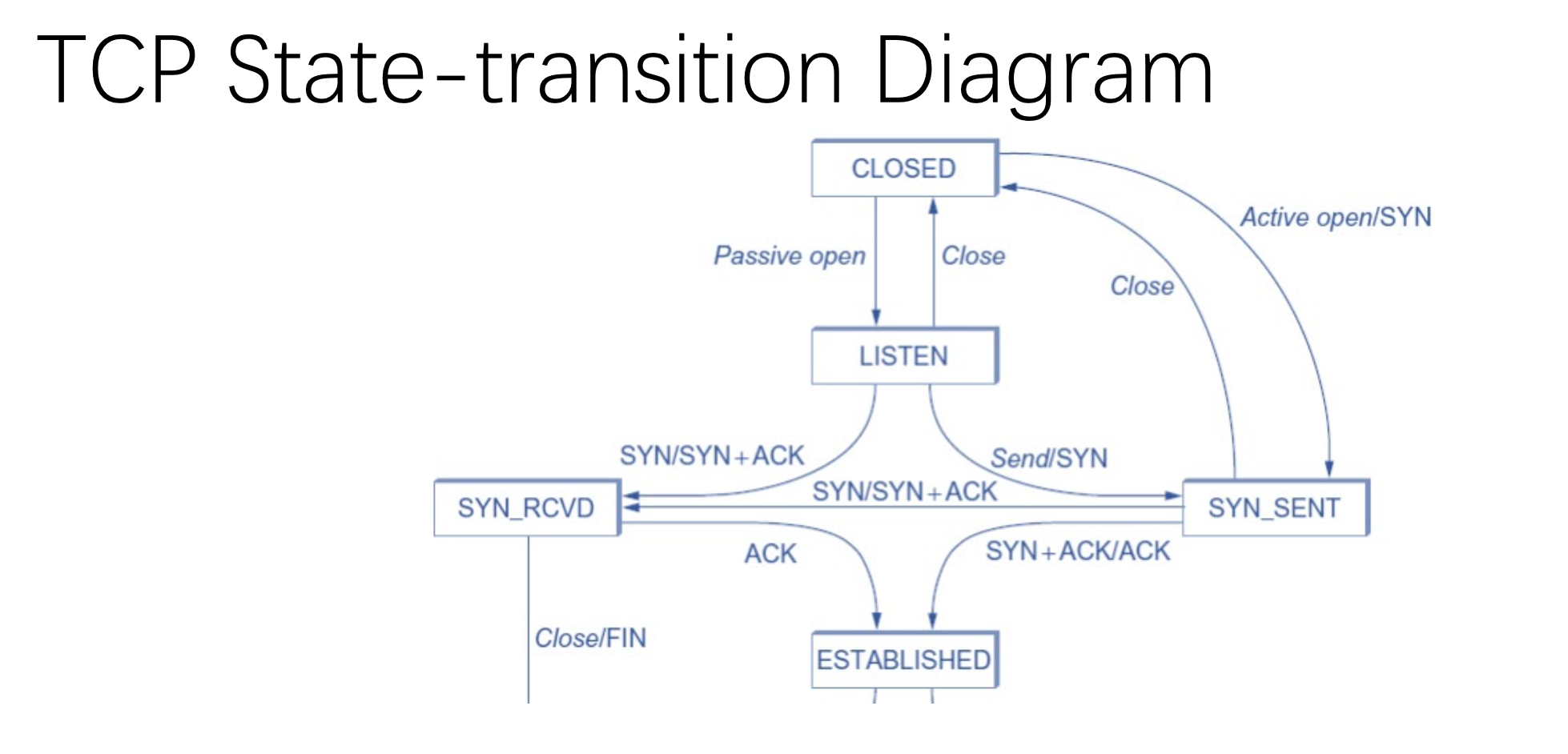
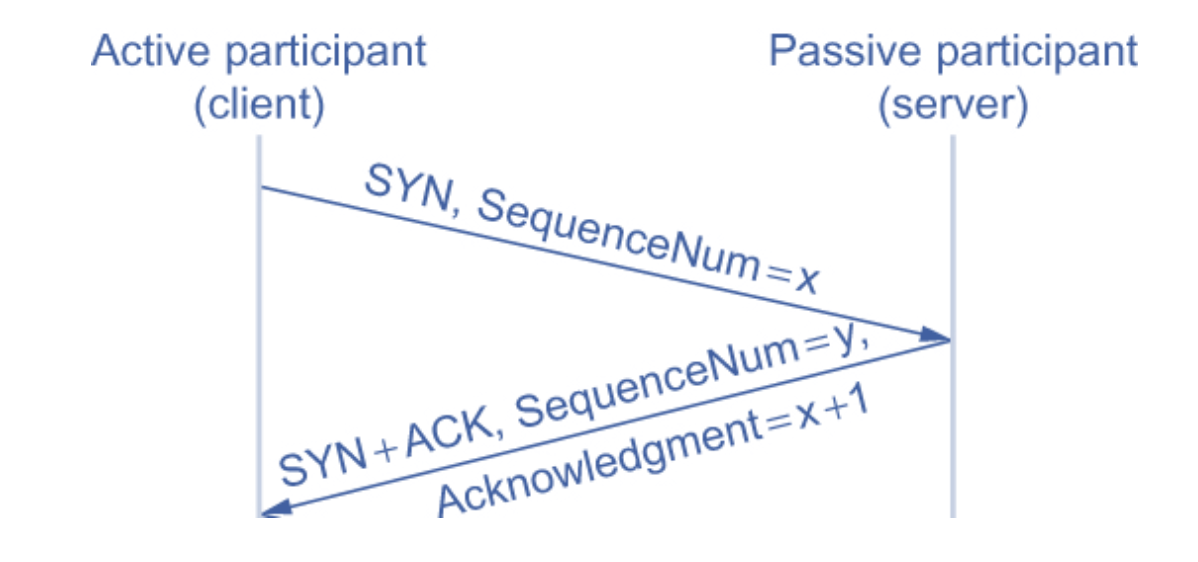
### TCP Congestion in Network
#### Additive Increase/Multiplicative Decrease (AIMD)
- Additive Increase
- Increment = 1/cwnd
- cwnd += Increment
- Multiplicative Decrease
- cwnd = cwnd /2
####
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet