# XV6 Ch3 Trap,中斷及驅動程式
>CPU 執行一個 porcess 時,是不斷的進行:讀取指令、增加程式計數器、執行指令的迴圈;但有時候一個程式需要進入 kernel,而不是執行下一行指令;包括:設備信號的發出、使用者程式做一些非法的事或是呼叫一個 system call。
- 處理上述情況有三大挑戰:
1. Kernel 需使處理器能夠從 user mode 轉至 kernel mode(再轉回來)。
2. Kernel 及設備須協調好他們平行的活動。
3. Kernel 需了解設備的介面。
---
## System call,例外及中斷
- 有三種情況須從 user 轉至 kernel:
1. system call:使用者程式要求 OS 服務。
2. 例外 exception:程式執行非法動作(如除零)。
3. 中斷 interrupt:設備發出一個信號來引起 OS 注意。
- 所有中斷由 kernel 管理。
- OS 必須在此三種情況保證以下事情:
1. 保存暫存器以備將來的狀態回復。p
2. 系統需準備好在 kernel 中執行。
3. 選擇一個 kernel 開始的位置。
4. Kernel 能夠取得此事件的資訊。
5. 保證安全性(獨立)。
- Xv6 使用的方法概述:
1. 一個中斷停止了處理器的迴圈,並開始執行 interrupt handler。
2. 在開始執行 interrupt handler 之前,處理器儲存他的暫存器。
- Trap:當前 process 引起
- 中斷:由設備引起
:::warning
xv6 用 trap 來表示中斷,這是因為此術語被 PDP11/40 使用,也是 UNIX 的傳統術語。
:::
## X86 的保護機制
- x86 有 4 個 protection level,0(最高)至 3(最低)。
- 實際上大部分只使用兩個層級:0(kernel mode)及 3(user mode);當前的層級儲存在 `%cs` 的 CPL 中。
- Interrupt handler 在 IDT 中被定義。
- IDT interrupt descriptor table:有 256 格,每一格都提供了相對應的 `%cs` 及 `%eip`。
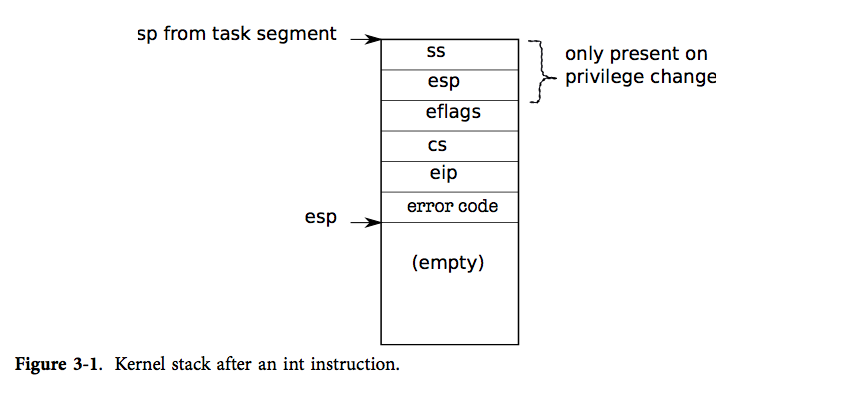
- 呼叫一個 system call 需要呼叫一個 `int n` 指令,n 為 IDT 的索引;`int n` 進行下面步驟:
1. 從 IDT 獲得第 n 個描述符
2. 檢查 `%cs` 中的 CPL 是否 <= DPL,DPL 為描述符的層級
3. 如果目標的段選擇器的 PL < CPL,儲存 CPU 內部的 `%esp` 及 `%ss`
4. 讀取 task segment descriptor 的 `%ss` 及 `%esp`
5. Push `%ss`、`%esp`、`%eflags`、`%cs` 及 `%eip`
6. 清除 `%eflags` 的 IF bit
---
## Code: 第一個 system call
### File: initcode.S
```c=8
.globl start
start:
pushl $argv
pushl $init
pushl $0 // where caller pc would be
movl $SYS_exec, %eax
int $T_SYSCALL
```
- Process 將`exec` 的參數 push 進堆疊,並將 system call number 放進 `%eax`。
- `SYS_exec` 即為 system call number,對應到 syscalls 的陣列索引(syscall.c 中),一個函數指標陣列。
#### `syscalls[]`
:::success
**File:** syscall.c
:::
```c=102
static int (*syscalls[])(void) = {
[SYS_fork] sys_fork,
[SYS_exit] sys_exit,
[SYS_wait] sys_wait,
[SYS_pipe] sys_pipe,
[SYS_read] sys_read,
[SYS_kill] sys_kill,
[SYS_exec] sys_exec,
[SYS_fstat] sys_fstat,
[SYS_chdir] sys_chdir,
[SYS_dup] sys_dup,
[SYS_getpid] sys_getpid,
[SYS_sbrk] sys_sbrk,
[SYS_sleep] sys_sleep,
[SYS_uptime] sys_uptime,
[SYS_open] sys_open,
[SYS_write] sys_write,
[SYS_mknod] sys_mknod,
[SYS_unlink] sys_unlink,
[SYS_link] sys_link,
[SYS_mkdir] sys_mkdir,
[SYS_close] sys_close,
};
```
---
## Code: Assembly trap handler
- x86 提供 256 種中斷,0-31 為軟體異常。
- xv6 將 32-63 給硬體中斷,64 作為 system call。
- Main 呼叫 `tvinit`。
### `tvinit()`
:::success
**File:** trap.c
:::
```c=
// file: trap.c
void
tvinit(void)
{
int i;
```
- `Tvinit` 設置 `idt` 表的 256 項。
```c=+
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++)
SETGATE(idt[i], 0, SEG_KCODE<<3, vectors[i], 0);
```
- 接著執行 `T_SYSCALL`,user 會呼叫 `trap`(將 `1` 傳入 `SETGATE` 的第二變數來指定為 trap gate)。
- Trap gate 不會清除 IF bit。
- 並將 system call 的權限設為 `DPL_USER`,允許使用者程式使用 `int` 指令產生 `trap`;xv6 不允許 process 用 `int` 產生其他中斷,如果這麼做會拋出錯誤並產生 13 號中斷。
```c=+
SETGATE(idt[T_SYSCALL], 1, SEG_KCODE<<3, vectors[T_SYSCALL], DPL_USER);
initlock(&tickslock, "time");
}
```
#### `SETGATE()`
:::success
**File:** mmu.h
:::
```c=213
#define SETGATE(gate, istrap, sel, off, d) \
{ \
(gate).off_15_0 = (uint)(off) & 0xffff; \
(gate).cs = (sel); \
(gate).args = 0; \
(gate).rsv1 = 0; \
(gate).type = (istrap) ? STS_TG32 : STS_IG32; \
(gate).s = 0; \
(gate).dpl = (d); \
(gate).p = 1; \
(gate).off_31_16 = (uint)(off) >> 16; \
}
```
```c
#define STS_IG32 0xE // 32-bit Interrupt Gate
#define STS_TG32 0xF // 32-bit Trap Gate
```
---
### Trap 發生時
- user mode:從 task segment descriptor 讀取 `%esp`、`%ss`, 接著 push 舊的 `%ss`、`%esp` 進新的堆疊。
- kernel mode:不用上述動作。
- 接著 push `%eflags`、`%cs`、`%eip`。
- 從對應的 IDT 讀取 `%eip`、`%cs`。
#### File: vector.pl
```perl=
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
# Generate vectors.S, the trap/interrupt entry points.
# There has to be one entry point per interrupt number
# since otherwise there's no way for trap() to discover
# the interrupt number.
print "# generated by vectors.pl - do not edit\n";
print "# handlers\n";
print ".globl alltraps\n";
for(my $i = 0; $i < 256; $i++){
print ".globl vector$i\n";
print "vector$i:\n";
if(!($i == 8 || ($i >= 10 && $i <= 14) || $i == 17)){
print " pushl \$0\n";
}
print " pushl \$$i\n";
print " jmp alltraps\n";
}
print "\n# vector table\n";
print ".data\n";
print ".globl vectors\n";
print "vectors:\n";
for(my $i = 0; $i < 256; $i++){
print " .long vector$i\n";
}
```
- xv6 用 Perl 腳本來生成 IDT 的進入點(`vector[]`)。
- 如果處理器沒有 push 錯誤碼,則在其項 push。
- Push 中斷號碼,跳至 `alltraps`。
#### File: trapret.S
```c=
#include "mmu.h"
# vectors.S sends all traps here.
.globl alltraps
alltraps:
# Build trap frame.
pushl %ds
pushl %es
pushl %fs
pushl %gs
pushal
```
- 接著繼續 push `%ds`、`%es`、`%fs`、`%gs` 及通用暫存器,現在 kernel stack 包含一個 `struct traprframe`。

##### `struct trapframe`
```c
// file: x86.h (150)
struct trapframe {
// registers as pushed by pusha
uint edi;
uint esi;
uint ebp;
uint oesp; // useless & ignored
uint ebx;
uint edx;
uint ecx;
uint eax;
// rest of trap frame
ushort gs;
ushort padding1;
ushort fs;
ushort padding2;
ushort es;
ushort padding3;
ushort ds;
ushort padding4;
uint trapno;
// below here defined by x86 hardware
uint err;
uint eip;
ushort cs;
ushort padding5;
uint eflags;
// below here only when crossing rings, such as from user to kernel
uint esp;
ushort ss;
ushort padding6;
};
```
```c=+
# Set up data and per-cpu segments.
movw $(SEG_KDATA<<3), %ax
movw %ax, %ds
movw %ax, %es
movw $(SEG_KCPU<<3), %ax
movw %ax, %fs
movw %ax, %gs
# Call trap(tf), where tf=%esp
pushl %esp
call trap
addl $4, %esp
```
- push `%esp`(trap frame),呼叫 *trap*。
```c=+
# Return falls through to trapret...
.globl trapret
trapret:
popal
popl %gs
popl %fs
popl %es
popl %ds
addl $0x8, %esp # trapno and errcode
iret
```
- trap return 後跳回 user space。
---
## Code: C trap handler
:::success
**File:** trap.c
:::
#### `trap()`
```c=36
void
trap(struct trapframe *tf)
{
if(tf->trapno == T_SYSCALL){
if(proc->killed)
exit();
proc->tf = tf;
syscall();
if(proc->killed)
exit();
return;
}
```
- 如果是 `TY_SYSCALL`,呼叫 syscall()。
```c=+
switch(tf->trapno){
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_TIMER:
if(cpu->id == 0){
acquire(&tickslock);
ticks++;
wakeup(&ticks);
release(&tickslock);
}
lapiceoi();
break;
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_IDE:
ideintr();
lapiceoi();
break;
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_IDE+1:
// Bochs generates spurious IDE1 interrupts.
break;
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_KBD:
kbdintr();
lapiceoi();
break;
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_COM1:
uartintr();
lapiceoi();
break;
case T_IRQ0 + 7:
case T_IRQ0 + IRQ_SPURIOUS:
cprintf("cpu%d: spurious interrupt at %x:%x\n",
cpu->id, tf->cs, tf->eip);
lapiceoi();
break;
```
- 檢查是否為硬體中斷
```c=+
//PAGEBREAK: 13
default:
if(proc == 0 || (tf->cs&3) == 0){
// In kernel, it must be our mistake.
cprintf("unexpected trap %d from cpu %d eip %x (cr2=0x%x)\n",
tf->trapno, cpu->id, tf->eip, rcr2());
panic("trap");
}
// In user space, assume process misbehaved.
cprintf("pid %d %s: trap %d err %d on cpu %d "
"eip 0x%x addr 0x%x--kill proc\n",
proc->pid, proc->name, tf->trapno, tf->err, cpu->id, tf->eip,
rcr2());
proc->killed = 1;
}
// Force process exit if it has been killed and is in user space.
// (If it is still executing in the kernel, let it keep running
// until it gets to the regular system call return.)
if(proc && proc->killed && (tf->cs&3) == DPL_USER)
exit();
// Force process to give up CPU on clock tick.
// If interrupts were on while locks held, would need to check nlock.
if(proc && proc->state == RUNNING && tf->trapno == T_IRQ0+IRQ_TIMER)
yield();
// Check if the process has been killed since we yielded
if(proc && proc->killed && (tf->cs&3) == DPL_USER)
exit();
}
```
- 如果非 system call 或硬體中斷,trap 就認定為一個錯誤:
- user:cp->killed (ch5)
- kernel:panic
---
## Code: System calls(機制)
:::success
**File:** syscall.c
:::
### `syscall()`
- 從 trap frame 中的 `%eax` 讀取 system call 號碼,及對應 syscall table 的索引。
- 如果 system call 號碼是非法的,`return -1`。
```c=126
void
syscall(void)
{
int num;
num = proc->tf->eax;
if(num > 0 && num < NELEM(syscalls) && syscalls[num]) {
proc->tf->eax = syscalls[num]();
} else {
cprintf("%d %s: unknown sys call %d\n",
proc->pid, proc->name, num);
proc->tf->eax = -1;
}
}
```
### `syscalls[]`
```c=102
static int (*syscalls[])(void) = {
[SYS_fork] sys_fork,
[SYS_exit] sys_exit,
[SYS_wait] sys_wait,
[SYS_pipe] sys_pipe,
[SYS_read] sys_read,
[SYS_kill] sys_kill,
[SYS_exec] sys_exec,
[SYS_fstat] sys_fstat,
[SYS_chdir] sys_chdir,
[SYS_dup] sys_dup,
[SYS_getpid] sys_getpid,
[SYS_sbrk] sys_sbrk,
[SYS_sleep] sys_sleep,
[SYS_uptime] sys_uptime,
[SYS_open] sys_open,
[SYS_write] sys_write,
[SYS_mknod] sys_mknod,
[SYS_unlink] sys_unlink,
[SYS_link] sys_link,
[SYS_mkdir] sys_mkdir,
[SYS_close] sys_close,
};
```
### File: syscall.h
```c=
// System call numbers
#define SYS_fork 1
#define SYS_exit 2
#define SYS_wait 3
#define SYS_pipe 4
#define SYS_read 5
#define SYS_kill 6
#define SYS_exec 7
#define SYS_fstat 8
#define SYS_chdir 9
#define SYS_dup 10
#define SYS_getpid 11
#define SYS_sbrk 12
#define SYS_sleep 13
#define SYS_uptime 14
#define SYS_open 15
#define SYS_write 16
#define SYS_mknod 17
#define SYS_unlink 18
#define SYS_link 19
#define SYS_mkdir 20
#define SYS_close 21
```
- 取得 system call 參數:
- `argint`:整數
- `argptr`:指標
- `argstr`:字串
- `argfd`:檔案描述符
---
## Code: interrupts
### Programmable Interrupt Controler **PIC**
- 早期主機板(單核心)上有一塊 PIC,code: picirq.c
- 多核心主機板的每顆 CPU 都需要一個 PIC,需要一個方法來分發中斷,操作方式分為兩部份:
- IO APIC (ioapic.c):於 I/O 系統上
- Local APIC (lapic.c):與每個 CPU 有關
- IO APIC 包含一張表,處理器可以通過記憶體映射 I/O 來寫其中的一項。
- 在初始化時,xv6 將 0 中斷映射到 CR0,以此類推,但將其關閉。
- 不同的設備自己開啟自己的中斷,同時指定接收中斷的處理器。
- `%eflags` 的 IF bit 是處理器用來控制是否要接收中斷,`cli` 清除 IF 來關閉中斷,`sti` 打開。
---
## Code: 硬碟驅動程式
- 硬碟驅動程式用 `struct buf` 來表示一個磁碟區
### File: buf.h
```c=
struct buf {
int flags;
uint dev; // device number
uint sector; // sector number
struct buf *prev; // LRU cache list
struct buf *next;
struct buf *qnext; // disk queue
uchar data[512]; // copy of the disk sector
};
#define B_BUSY 0x1 // buffer is locked by some process
#define B_VALID 0x2 // buffer has been read from disk
#define B_DIRTY 0x4 // buffer needs to be written to disk
```
- `flags` 紀錄記憶體與硬碟的關係:
- `B_VALID` 表示已被讀入
- `B_DIRTY` 表示資料須被寫出
- `B_BUSY` 為一個鎖,代表別的 process 正在使用此 buf
- main 呼叫 ideinit 初始化硬碟驅動程式
:::success
**File:** ide.c
:::
### `ideinit()`
```c=45
// file: ide.c (45)
void
ideinit(void)
{
int i;
initlock(&idelock, "ide");
picenable(IRQ_IDE);
ioapicenable(IRQ_IDE, ncpu - 1);
```
- 呼叫 `picenable` 打開單處理器的中斷
- 呼叫 `ioapicenable` 打開多處理器的中斷(只打開最後一個 CPU)
```c=+
idewait(0);
```
- `idewait` 等待硬碟接受命令,直到 busy 位(`IDE_BUSY`)被清除,ready 位(`IDE_DRDY`)被設置。
#### `idewait()`
```c
static int
idewait(int checkerr)
{
int r;
while(((r = inb(0x1f7)) & (IDE_BSY|IDE_DRDY)) != IDE_DRDY)
;
if(checkerr && (r & (IDE_DF|IDE_ERR)) != 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
```
```c=+
// Check if disk 1 is present
outb(0x1f6, 0xe0 | (1<<4));
for(i=0; i<1000; i++){
if(inb(0x1f7) != 0){
havedisk1 = 1;
break;
}
}
// Switch back to disk 0.
outb(0x1f6, 0xe0 | (0<<4));
}
```
- 設置完成後,只能通過 buffer cache 調用 `iderw`,`iderw` 根據 `flags` 值更新一個鎖著的 buf:
- B_DIRTY:將 buf 寫回硬碟
- 若 B_VALID 未設置:從硬碟讀資料進 buf
### `iderw()`
```c=126
void
iderw(struct buf *b)
{
struct buf **pp;
if(!(b->flags & B_BUSY))
panic("iderw: buf not busy");
if((b->flags & (B_VALID|B_DIRTY)) == B_VALID)
panic("iderw: nothing to do");
if(b->dev != 0 && !havedisk1)
panic("iderw: ide disk 1 not present");
acquire(&idelock); //DOC:acquire-lock
// Append b to idequeue.
b->qnext = 0;
for(pp=&idequeue; *pp; pp=&(*pp)->qnext) //DOC:insert-queue
;
*pp = b;
```
- 把 buf b 放置隊伍的末端
```c=+
// Start disk if necessary.
if(idequeue == b)
idestart(b);
```
- 如果此 buf 在隊首,呼叫 `idestart` 將其送到硬碟。
- 其他情況需等上一個處理完畢時才處理。
```c=+
// Wait for request to finish.
while((b->flags & (B_VALID|B_DIRTY)) != B_VALID){
sleep(b, &idelock);
}
release(&idelock);
}
```
- `iderw` 將請求加入的隊伍裡,並睡眠,等待 interrupt handler 處理完後更新其 flags。
- 最後,硬碟完成其工作並觸發一個中斷,trap 呼叫 `ideintr` 來處理。
### `ideintr()`
```c=91
void
ideintr(void)
{
struct buf *b;
// First queued buffer is the active request.
acquire(&idelock);
if((b = idequeue) == 0){
release(&idelock);
// cprintf("spurious IDE interrupt\n");
return;
}
idequeue = b->qnext;
// Read data if needed.
if(!(b->flags & B_DIRTY) && idewait(1) >= 0)
insl(0x1f0, b->data, 512/4);
```
- 查詢隊首的 buf,如果正在被寫入,且 IDE 有資料在等待,呼叫 `insl` 將資料寫入。
```c=+
// Wake process waiting for this buf.
b->flags |= B_VALID;
b->flags &= ~B_DIRTY;
wakeup(b);
```
- 設置 `B_VALID`,清除 `B_DIRTY`。
- 喚醒 `b`
```c=+
// Start disk on next buf in queue.
if(idequeue != 0)
idestart(idequeue);
release(&idelock);
}
```
- 最後將下一個 buf 傳給硬碟。
###### tags: `xv6` `kernel` `interrupt`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet