# Introduction
Efficient project management holds immense importance in today’s business landscape for achieving successful outcomes. Project Management Application empowers users with comprehensive oversight.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a Project Management Application by utilizing various AWS services, including:
- [AWS DynamoDB](https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/) as the database
- [AWS Lambda](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/) for creating interactive functions with the database
- [AWS API Gateway](https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/) for establishing a `REST API` for the web application
- [AWS S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/) for hosting the web application
- [AWS Amplify](https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/amplify/home?region=us-east-1) for web application hosting.
# Prerequisites
To fully grasp the concepts presented in this tutorial, the following are required:
- An AWS account – [Sign up](https://portal.aws.amazon.com/billing/signup).
- AWS Identity and Access Management user with console access
- Basic understanding of JavaScript
- [A GitHub account](https://github.com/)
# The Architecture

# Overview of AWS services used in the application.
The application uses the following AWS services:
- [AWS S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/): For storing and retrieving assets like images and files.
- [AWS DynamoDB](https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/): As the `NoSQL` database for efficient data storage and retrieval.
- [AWS Lambda](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/): To create serverless functions for data manipulation and business logic implementation.
- [AWS API Gateway](https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/): For managing `APIs` and enabling seamless communication between frontend and backend components.
These AWS services provide scalable storage, serverless computing, efficient `API` management, and a powerful frontend framework, resulting in a robust project management solution.
# Purpose of the project management application.
The Project Management Application aims to streamline and enhance project management processes, providing users with an efficient tool to track and maintain projects from start to finish. By leveraging AWS services like `S3`, `Lambda`, `DynamoDB`, `API Gateway`, and `Next.js`, the application offers a scalable solution that caters to the diverse needs of project managers and teams.
# Importance of effective project management for individuals.
Individuals greatly benefit from effective project management as it enables them to prioritize tasks, allocate resources efficiently, and meet deadlines. Individuals can achieve desired outcomes, enhance productivity, and experience personal growth by honing their project management skills.
# Concept of project management and its benefits.
Project management involves systematically planning, organizing, and executing projects to achieve specific goals within defined constraints. Key points regarding the benefits of project management include:
- Provides clear direction, structure, and efficient execution of projects.
- Fosters effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Enables proactive risk management and issue resolution.
- Optimizes resource allocation, improving productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Ensures successful project outcomes, delivering high-quality results within set parameters.
# Key features and functionalities of the application.
The project management application offers the following key features and functionalities:
- Create: Users can create new projects, tasks, and milestones within the application.
- Read: Users can view and access project details, task statuses, and progress.
- Update: Users can update project information, task assignments, and milestone dates.
- Delete: Users can delete projects, tasks, and milestones when necessary.
- Comprehensive project tracking and management capabilities.
Integration with AWS services like `DynamoDB`, `S3`, `Lambda`, and `API Gateway`.
- User-friendly interface for easy navigation and usage.
# Role and workflow of AWS S3, Lambda, DynamoDB, API Gateway, and Next.js in the project.
This tutorial shows you how to create a serverless `API` that performs `CRUD` operations on AWS services such as `DynamoDB`, `S3`, `Lambda functions`, and `API Gateway`. The workflow for building this `API` involves the following steps:
`API Gateway:` Configure an `HTTP API` in `API Gateway` to serve as the entry point for client requests. Define routes and methods (`GET`, `POST`, `PUT`, `DELETE`) for the desired `CRUD` operations.
`Lambda Function:` Create `AWS Lambda functions` that implement the business logic for each `CRUD` operation. For example, a `Lambda function` can handle a `POST` request to create an item, a `GET` request to retrieve an item, a `PUT` request to update an item, and a `DELETE` request to remove an item.
`DynamoDB:` Utilize `DynamoDB` as the `NoSQL` database for storing and retrieving data. The Lambda functions to interact with `DynamoDB` to perform the necessary `CRUD` operations. For instance, when creating an item, the `Lambda function` writes the data to a `DynamoDB` table, and when retrieving an item, the `Lambda function` fetches the data from the table.
`S3:` Storage for assets like images or files. `S3` provides a scalable and durable object storage service for storing and retrieving these assets.
Following this tutorial, you will build a serverless API that effectively performs `CRUD` operations using `DynamoDB`, `S3`, `Lambda functions`, and `API Gateway`.
# Steps to set up the development environment for the application.
Here are the steps to set up the development environment for the application:
- Create a `DynamoDB` Table: you begin by configuring a `DynamoDB` table (Project and Client Table) with the necessary attributes and primary key.
- Set Up AWS `S3` for Assets Storage: Create an `S3` bucket to store and manage assets like images or files.
- Create a `Lambda Function:` Develop a function (Project and Client Lambda functions) to handle `CRUD` operations on the `DynamoDB` table.
- Create an `HTTP API:` Use the `API` Gateway Console to create an `HTTP API` for Project and Client with endpoints for `CRUD` operations.
- Create Routes: Define routes in the `API Gateway` for Project and Client to match your application’s functionality.
- Create an Integration: Connect the `API Gateway` for Project and Client to the `Lambda function` through an integration.
- Attach Your Integration to Routes: Associate the integration with the appropriate routes for Project and Client in the `API Gateway`.
- Test Your `API`: Use testing tools like the `API Gateway` or Postman to validate the `API’s` functionality.
# Implementation of the Application's Backend
## Create a DynamoDB table
To store data for your `API`, you will utilize a `DynamoDB` table. Each item in the table will have a unique ID, which will serve as the partition key.
To create the Project DynamoDB table, follow these steps:
- Go to [https://console.aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/](https://console.aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/) to access the DynamoDB console.
- Select the option to create a table.
- Enter `http-project-management-items` as the table name.
- Set id as the partition key.
- Proceed to create the table.
Next, create the Client's `DynamoDB` table by following the same steps above but change the table name to `http-client-management-items`.
By following these steps, you will create a `DynamoDB table` to store data for your `API`, ensuring efficient and effective data management.
## Create S3 Bucket
Amazon Simple Storage Service (`Amazon S3`) is a highly scalable and cost-effective storage service provided by AWS. It offers low-latency access to store a virtually unlimited number of objects.
To create S3 Bucket, follow these steps:
- Go to [https://console.aws.amazon.com/S3/](https://console.aws.amazon.com/S3/) to access the `S3` console.
- Select the option to create a bucket
- Enter `http-project-management-items-bucket` as the bucket name.
- Choose the AWS region closest to you or where you would like your data to reside. In this case, it is [**US-east-1**]
- In Block Public Access settings for this bucket category, Uncheck the BLOCK ALL PUBLIC ACCESS
-In the Bucket Versioning category, choose Disabled.
- Click on the Create Bucket.
Upon successfully creating the bucket, you will receive a confirmation message at the top of the page.

### Set S3 bucket permissions:
- Open the Amazon `S3` console.
- Select the bucket you want to set permissions for.
- Edit the `Bucket Policy` tab and paste the code below:
```javaScript
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "PublicReadWriteAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::http-project-management-items-bucket",
"arn:aws:s3:::http-project-management-items-bucket/*"
]
}
]
}
```
- Click on the Save changes
## Create a Lambda function
You will create `Lambda functions` for the `API` backend to handle `CRUD` operations for the Project and Client details `DynamoDB`. The functions use `API Gateway` events to interact with `DynamoDB`, determining the appropriate actions.
To create a Lambda function for the Project details, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Lambda console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/lambda](https://console.aws.amazon.com/lambda).
- Choose Create function.
- Enter `http-project-management-lambda-function` as the function name.
- Under Permissions, select Change default execution role.
- Choose Create a new role from AWS policy templates.
- Enter `http-crud-tutorial-role` as the role name.
- Choose Simple microservice permissions,
- Choose Create function.
- Open the console's code editor and replace the contents of `index.mjs` with the provided code.
- Choose Deploy to update your function.
```javaScript
import { DynamoDBClient } from "@aws-sdk/client-dynamodb";
import {
DynamoDBDocumentClient,
PutCommand,
UpdateCommand,
GetCommand,
DeleteCommand,
ScanCommand,
} from "@aws-sdk/lib-dynamodb";
const dynamoDBClient = new DynamoDBClient({});
const client = new DynamoDBClient({});
const dynamoDBDocumentClient = DynamoDBDocumentClient.from(dynamoDBClient);
const dynamo = DynamoDBDocumentClient.from(client);
const tableName = "http-project-management-items";
export const handler = async (event, context) => {
let body;
let statusCode = 200;
const headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
};
try {
switch (event.routeKey) {
case "PUT /items":
if (!event.body) {
throw new Error("Request body is missing.");
}
const requestJSON = JSON.parse(event.body);
await dynamoDBDocumentClient.send(
new PutCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Item: {
id: requestJSON.id,
projectName: requestJSON.projectName,
projectStatus: requestJSON.projectStatus,
},
})
);
body = "Item added successfully";
break;
case "PUT /items/{id}":
if (!event.body) {
throw new Error("Request body is missing.");
}
const id = event.pathParameters.id;
const updateRequestJSON = JSON.parse(event.body);
await dynamoDBDocumentClient.send(
new UpdateCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: { id },
UpdateExpression:
"SET projectName = :projectName, projectStatus = :projectStatus",
ExpressionAttributeValues: {
":projectName": updateRequestJSON.projectName,
":id": updateRequestJSON.id,
":projectStatus": updateRequestJSON.projectStatus,
},
})
);
body = "Item updated successfully";
break;
case "GET /items":
body = await dynamo.send(new ScanCommand({ TableName: tableName }));
body = body.Items;
break;
case "GET /items/{id}":
body = await dynamo.send(
new GetCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: {
id: event.pathParameters.id,
},
})
);
body = body.Item;
break;
case "DELETE /items/{id}":
await dynamo.send(
new DeleteCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: {
id: event.pathParameters.id,
},
})
);
body = `Deleted item ${event.pathParameters.id}`;
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Unsupported route: "${event.routeKey}"`);
}
} catch (err) {
statusCode = 400;
body = err.message;
} finally {
if (typeof body !== "string") {
body = JSON.stringify(body);
}
}
return {
statusCode,
body,
headers,
};
};
```
Next, create a `Lambda function` for the Client's details by following the same steps above but change the function name to `http-client-management-lambda-function` and use the Client's table name you created above. Also, write the `CRUD` logic for `PUT /clients`, `GET /clients`, `PUT /clients/{id}`, and `DELETE /clients/{id}`.
## Create an HTTP API
To create an `HTTP API`, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the `API Gateway` console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway).
- Choose Create `API` and select Build for `HTTP API`.
- Enter `http-project-management-api` as the `API` name.
- Proceed to the next step without configuring routes.
- Review the automatically created stage by `API Gateway` and proceed to the next step.
- Choose `Create` to create the `HTTP API`.
Next, create an `HTTP API` for the Client details by following the same steps above but change the API name to `http-client-management-api`
## Create routes
To create routes for your `API`, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the `API Gateway` console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway).
- Select your `API` from the available options.
- Navigate to the Routes section.
- Choose Create to add a new route.
- For the method, select `GET.`
- Enter ``/items/{id}`` as the path. The `{id}` is a path parameter `API` Gateway extracts from the request path.
- Click Create to create the route.
- Repeat steps 4-7 for the routes: `GET /items,` `DELETE /items/{id},` and `PUT /items.`
Next, Follow the same steps to create routes for the Client's API.

## Create an integration
To create integrations for your `API` routes, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the `API Gateway` console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigatew).
- Select your `API` from the available options.
- Go to the `Integrations` section.
- Choose Manage integrations and Create to create a new integration.
- Skip the step to attach the integration to a route for now. You will complete that in a later step.
- For the integration type, select `Lambda function.`
- Enter `http-project-management-lambda-function` as the Lambda function.
Click Create to create the integration.
Next, Follow the same steps to create Integrations for the Client’s `API`, but remember to use the correct function name you created earlier.

## Attach your integration to routes
To attach integrations to your `API` routes, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the `API Gateway` console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway).
- Select your `API` from the available options.
- Go to the Integrations section.
- Choose a specific route you want to attach an integration to.
- Under Choose an existing integration, select `http-project-management-lambda-function.`
- Click Attach integration to link the integration to the route.
- Repeat steps 4-6 for all the routes in your `API`.
- Verify that all routes indicate an attached `AWS Lambda` integration.
Next, Follow the same steps to attach Integrations for the Client’s `API`, but remember to use the correct function name you created earlier.
## Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
CORS allows resources from different domains to be loaded by browsers.
To configure CORS, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the `API Gateway` console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway).
- Select your `API` from the available options.
- Go to the `CORS` section.
- Specify the following parameters in a `CORS` configuration:
```javaScript
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *, http://localhost:3000
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Authorization, *
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, DELETE, PUT, *
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: Date, x-api-id
Access-Control-Max-Age: 300
```
- Click Save to configure your `CORS`.

## Test your API
To ensure the functionality of your `API`, you can use the following professional steps:
- Sign in to the API Gateway console at [https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway).
- Select your `API` from the available options.
- Note your API's invoke URL, which can be found under `Invoke URL` on the Details page.
- Copy the entire invoke URL, such as [https://abcdef123.execute-api.us-east-2.amazonaws.com](https://abcdef123.execute-api.us-east-2.amazonaws.com).
**To create or update an item:** Execute the following command to create or update an item. The command includes a request body that contains the `item's ID`, `project name`, `client name`, `gender`, `client image`, and `project status`.
```javaScript
curl --location --request PUT 'https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"id": "1",
"projectName": "Project one",
"clientName": "Dami",
"gender": "male",
"ClientImage": "base_64_image",
"projectStatus": "Pending"
}'
```
**To get all items:**
Use the following command to list all items.
```javaScript
curl --location 'https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items' \
--data ''
```
To delete an item
Use the following command to list all items.
```javaScript
curl --location --request DELETE 'https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items/1' \
--data ''
```
# Building the Application Frontend
To build the Application Frontend, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the desired directory in your terminal.
- Run the following command to create a `Next.js` starter project:
```javaScript
npx create-next-app project-mgt-app && cd project-mgt-app
```
The command creates a `Next.js` project called `project-mgt-app` and navigates into the project directory.
## Installing dependencies
### Installing React Icons
[React-icon](https://react-icons.github.io/react-icons/) is a powerful library that enables you to effortlessly incorporate icons from various icon libraries into your React applications.
To use it in your application, run the command below in your terminal.
```javaScript
npm i react-icons
```
## Utility Directory
In the `src/app directory`, create a folder with the name `util`. This directory will contain the functions to add client Projects and Client detail.
### Adding and editing client functions
In the `src/app/util` directory, create the file `src/app/util/Add&editClientfunctions.js` and add the following code:
```javascript
export const handleClientSubmit = async ({
event,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
}) => {
event.preventDefault();
// ...
fetch("/addclient", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => {
setAdd(false);
// ...
})
.catch((error) => console.log("error", error));
};
export const handleClientEdit = async ({
event,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
searchParams,
}) => {
event.preventDefault();
// ...
fetch(`/editclient/${searchParams.get("cid")}`, requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => {
setAdd(false);
// ...
})
.catch((error) => console.log("error", error));
};
```
This code above consists of two functions, `handleClientSubmit` and `handleClientEdit`. Client submission is handled by handleClientSubmit, and client editing is handled by `handleClientEdit`.
### Adding and editing Project functions
In the `src/app/util` directory, create the file `src/app/util/Add&editProjectfunction.js` and add the following code:
```javaScript
export const handleProjectSubmit = async ({
event,
formData,
setFormData,
setAdd,
router,
}) => {
event.preventDefault();
// ...
fetch("/additem", requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => {
setAdd(false);
// ...
})
.catch((error) => console.log("error", error));
};
export const handleProjectEdit = async ({
event,
formData,
setFormData,
router,
setEdit,
}) => {
event.preventDefault();
// ...
fetch(`/editproject`, requestOptions)
.then((response) => response.text())
.then((result) => {
// ...
})
.catch((error) => console.log("error", error));
};
```
This code above consists of two functions, `handleProjectSubmit` and `handleProjectEdit`. Client submission is handled by `handleProjectSubmit`, and client editing is handled by `handleProjectEdit`.
## Components Directory
In the `src/app` directory, create a folder with the name `components`. It is the directory that will contain all the reusable components for the projects.
### Form Component
In the `src/app/Forms` directory, create the file `src/app/Forms/ClientForm.js` and add the following code:
```javascript
{/* ... */}
<form
className="max-w-lg mx-auto"
onSubmit={searchParams.get("q") ? handleEdit : handleSubmit}
>
<div className="grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 mt-4 sm:grid-cols-2">
<div>
<label
htmlFor="emailAddress"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Client Name
</label>
<input
required
id="clientName"
type="text"
name="clientName"
value={formData.clientName}
onChange={handleChange}
className="block w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 text-gray-700 bg-white border border-gray-200
rounded-md dark:bg-gray-800 "
/>
</div>
<div>
<label
htmlFor="clientimage"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Client Logo
</label>
<input
required
id="clientimage"
type="file"
accept="image/*"
name="clientImage"
onChange={(e) => {
convertToBase64(e.target.files[0]);
}}
className="block w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 text-gray-700 bg-white border border-gray-200"
/>
</div>
<div className="mb-4">
<label
htmlFor="gender"
className="block mb-2 text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Client Gender:
</label>
<div className="flex flex-wrap items-center">
<label
htmlFor="male"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200 mr-4 mb-2 sm:mb-0 sm:flex-grow"
>
<input
type="checkbox"
id="male"
name="gender"
value="male"
checked={formData.gender.includes("male")}
onChange={handleChange}
className="mr-2 text-blue-500"
/>{" "}
Male
</label>
<label
htmlFor="female"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200 sm:flex-grow"
>
<input
type="checkbox"
id="female"
name="gender"
value="female"
checked={formData.gender.includes("female")}
onChange={handleChange}
className="mr-2 text-blue-500"
/>{" "}
Female
</label>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<label
htmlFor="clientId"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Client ID
</label>
<input
required
id="clientId"
type="number"
name="clientId"
value={
searchParams.get("q")
? Number(searchParams.get("cid"))
: formData.clientId
}
onChange={handleChange}
className="block w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 text-gray-700 bg-white border border-gray-200
rounded-md dark:bg-gray-800 "
/>
</div>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-end mt-6">
<button
type="submit"
className="flex items-center justify-center px-4 py-2 bg-blue-200 text-blue-800
rounded-md hover:bg-blue-300 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-300"
>
{searchParams.get("q")
? `${Edit ? "loading..." : "Update"}`
: `${Add ? "loading..." : "Save"}`}
</button>
</div>
</form>
{/* ... */}
```
The code above is a component (`ClientForm`) that renders a form for adding or editing client information. It includes input fields for client name, logo, gender, and client ID and handles form submission using `handleSubmit` or `handleEdit` functions based on query parameters. It also displays a back button and loading state during the submit action.
Next, In the `src/app/Forms` directory, create the file `src/app/Forms/ProjectForm.js` and add the following code:
```javascript
{/* /... */}
<form
className="max-w-lg mx-auto"
onSubmit={localStorage.getItem("id") ? handleEdit : handleSubmit}
>
<div className="grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 mt-4 sm:grid-cols-2">
<div>
<label
htmlFor="username"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Project Name
</label>
<input
required
id="username"
type="text"
name="projectName"
value={formData?.projectName}
onChange={handleChange}
className="block w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 text-gray-700 bg-white border border-gray-200 rounded-md dark:bg-gray-800 "
/>
</div>
<div className="mb-4">
<label
htmlFor="projectStatus"
className="block mb-2 text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Project Status:
</label>
<div className="flex flex-wrap items-center">
<label
htmlFor="pending"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200 mr-4 mb-2 sm:mb-0 sm:flex-grow"
>
<input
type="checkbox"
id="pending"
name="projectStatus"
value="pending"
checked={formData.projectStatus.includes("pending")}
onChange={handleChange}
className="mr-2 text-blue-500"
/>
Pending
</label>
<label
htmlFor="active"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200 mr-4 mb-2 sm:mb-0 sm:flex-grow"
>
<input
type="checkbox"
id="active"
name="projectStatus"
value="active"
checked={formData.projectStatus.includes("active")}
onChange={handleChange}
className="mr-2 text-blue-500"
/>
Active
</label>
<label
htmlFor="completed"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200 sm:flex-grow"
>
<input
type="checkbox"
id="completed"
name="projectStatus"
value="completed"
checked={formData.projectStatus.includes("completed")}
onChange={handleChange}
className="mr-2 text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
/>
Completed
</label>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<label
htmlFor="projectid"
className="text-gray-700 dark:text-gray-200"
>
Project ID
</label>
<input
required
id="projectid"
type="number"
name="projectId"
value={
localStorage.getItem("id") ? Number(id_) : formData.projectId
}
onChange={handleChange}
className="block w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 text-gray-700 bg-white border border-gray-200 rounded-md dark:bg-gray-800 "
/>
</div>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-end mt-6">
<button
type="submit"
className="flex items-center justify-center px-4 py-2 bg-blue-200 text-blue-800 rounded-md hover:bg-blue-300 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-300"
>
{localStorage.getItem("id")
? `${Edit ? "loading..." : "Update"}`
: `${Add ? "loading..." : "Save"}`}
</button>
</div>
</form>
{/* /... */}
```
The code above is a component (`ProjectForm`) that renders a form for adding or editing project information. It includes input fields for project name, status, and ID and handles form submission using `handleSubmit` or `handleEdit` functions based on the presence of a value in local storage.
### Table Component
In the `src/app` directory, create the file `src/app/components/Tables/TableBody.js` and add the following code:
```javascript
function TableBody({ data, handleDelete }) {
return (
<tbody className="bg-white divide-y divide-gray-200 dark:divide-gray-700 dark:bg-gray-900">
{data?.map((item, id) => {
return (
<tr className="hover:bg-[#97D8C4] hover:bg-blue-50 " key={id}>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-300 whitespace-nowrap">
{Number(item?.id)}
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-300 whitespace-nowrap">
{item?.projectName}
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm font-medium text-gray-700 whitespace-nowrap">
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-2">
<div>
<h2 className="font-medium text-gray-800 dark:text-white ">
{item?.clientName}
</h2>
<p className="text-sm font-normal text-gray-600 dark:text-gray-400">
@{item?.clientName?.replace(/\s/g, "")?.toLowerCase()}
</p>
</div>
</div>
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm font-medium text-gray-700 whitespace-nowrap">
<div
className={`inline-flex items-center px-3 py-1 rounded-full gap-x-2 ${
item.projectStatus === "Completed" ||
item.projectStatus === "completed"
? "bg-emerald-100/60 dark:bg-gray-800"
: item.projectStatus === "Active" ||
item.projectStatus === "active"
? "dark:bg-gray-800 bg-blue-100/60"
: "dark:bg-gray-800 bg-pink-100/60"
}`}
>
<span
className={`h-1.5 w-1.5 rounded-full ${
item.projectStatus === "Completed" ||
item.projectStatus === "completed"
? "bg-emerald-500"
: item.projectStatus === "Active" ||
item.projectStatus === "active"
? "bg-blue-500 "
: " bg-pink-500 "
} `}
></span>
<h2
className={`text-sm font-normal ${
item.projectStatus === "Completed" ||
item.projectStatus === "completed"
? "text-emerald-500"
: item.projectStatus === "Active" ||
item.projectStatus === "active"
? "text-blue-500"
: "text-pink-500"
}`}
>
{item?.projectStatus?.charAt(0)?.toUpperCase() +
item?.projectStatus?.slice(1)}
</h2>
</div>
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-300 whitespace-nowrap">
{item?.gender?.charAt(0)?.toUpperCase() + item?.gender?.slice(1)}
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm font-medium text-gray-700 whitespace-nowrap">
<img
className="object-cover w-10 h-10 rounded-full"
src={`https://http-project-management-items-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com/${item?.ClientImage}`}
alt=""
/>
</td>
<td className="px-4 py-4 text-sm whitespace-nowrap">
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-6">
<Link
href={{
pathname: "/newclient",
query: { q: `${item?.id}`, cid: `${item?.client_id}` },
}}
className="text-gray-500 transition-colors duration-200 dark:hover:text-yellow-500 dark:text-gray-300 hover:text-yellow-500 focus:outline-none"
>
<LuEdit className="text-blue-700" />
</Link>
<button
onClick={() => handleDelete(item)}
className="text-gray-500 transition-colors duration-200 dark:hover:text-red-500 dark:text-gray-300 hover:text-red-500 focus:outline-none"
>
<RiDeleteBin5Line className="text-blue-700" />
</button>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
);
})}
</tbody>
);
}
export default TableBody;
```
The code above is a `TableBody` component that renders a table's body section. It receives data and a handleDelete function as props and maps over the data array to generate table rows with specific information. It includes editing and deleting buttons for each row.
Next, In the `src/app` directory, create the file `src/app/components/Tables/TableComponent.js` and add the following code:
```javaScript
import React from "react";
import TableBody from "./TableBody";
function TableComponent({ data, handleDelete }) {
return (
<div className="flex flex-col mt-6">
<table className="min-w-full divide-y divide-gray-200 dark:divide-gray-700">
<thead className="bg-gray-50 dark:bg-gray-800">
<tr>
<th
scope="col"
className="py-3.5 px-4 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-3">
<span>ID</span>
</div>
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-4 py-3.5 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
Project Name
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="py-3.5 px-4 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-3">
<span>Client Name</span>
</div>
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-6 py-3.5 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
<button className="flex items-center gap-x-2">
<span>Project Status</span>
</button>
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="px-4 py-3.5 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
Gender
</th>
<th
scope="col"
className="py-3.5 px-4 text-sm font-normal text-left rtl:text-right text-gray-500 "
>
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-3">
<span>Client Logo</span>
</div>
</th>
<th scope="col" className="relative py-3.5 px-4">
<span className="sr-only">Edit</span>
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<TableBody data={data} handleDelete={handleDelete} />
</table>
</div>
);
}
export default TableComponent;
```
The code above is a `TableComponent` that renders a table with a header and body section. It receives data and a handleDelete function as props. The table header includes columns for ID, Project Name, Client Name, Project Status, Gender, Client Logo, and an empty column for editing. The body section is rendered using the `TableBody` component, passing the data and handleDelete props.
Next, In the `src/app directory`, create the file `src/app/components/Tables/Index.jsx` and add the following code:
```javaScript
"use client";
import { RiAddLine } from "react-icons/ri";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
import TableComponent from "./TableComponent";
function Table({ data }) {
const router = useRouter();
const handleClick = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
router.push("/newclient");
};
const handleDelete = async (data) => {
try {
const requestOptions = {
method: "DELETE",
redirect: "follow",
};
const deleteProjectPromise = fetch(
`/deleteproject/${data?.id}`,
requestOptions
);
const deleteClientPromise = fetch(
`/deleteclient/${data?.client_id}`,
requestOptions
);
await Promise.all([deleteProjectPromise, deleteClientPromise]);
window.location.reload();
} catch (error) {
console.log("error", error);
}
};
return (
<div>
<section className="container px-4 mx-auto ">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center ">
<div className="flex items-center gap-x-3">
<h2 className="text-lg font-medium text-gray-800 dark:text-white">
Total projects
</h2>
<span className="px-3 py-1 text-xs text-blue-600 bg-blue-100 rounded-full dark:bg-gray-800 dark:text-blue-400">
{data?.length}
</span>
</div>
<div>
<button
onClick={handleClick}
className="flex items-center justify-center px-4 py-2 bg-blue-200 text-blue-800
rounded-md hover:bg-blue-300 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-300"
>
<RiAddLine className="mr-2" />
New Project
</button>
</div>
</div>
<TableComponent handleDelete={handleDelete} data={data} />
</section>
</div>
);
}
export default Table;
```
The `Table` component renders a table section with project data. It provides functionality to add new projects and delete existing ones. It also causes the `TableComponent` component to pass the `handleDelete` function and the data array as props.
## Project Pages
In the `src/app` directory, create a folder with the name `newproject`. The folder will contain the page to add a new project.
### Add project page
In the `src/app/addproject` directory, create the file `src/app/addproject/page.js` and add the following code:
```javaScript
"use client";
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { useSearchParams } from "next/navigation";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
import ProjectForm from "../../components/Forms/ProjectForm";
import {
handleProjectSubmit,
handleProjectEdit,
} from "../../util/Add&editProjectfunction";
function Index() {
const router = useRouter();
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
const [attachment, setattachment] = useState("");
const [add, setAdd] = useState(false);
const [edit, setEdit] = useState(false);
const [file, setfile] = useState("");
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({
projectName: "",
projectStatus: [],
projectId: 0,
});
const handleChange = (event) => {
const { name, value, type, checked } = event.target;
if (type === "checkbox") {
const updatedValues = [...formData[name]];
if (checked) {
updatedValues.push(value);
} else {
const index = updatedValues.indexOf(value);
if (index > -1) {
updatedValues.splice(index, 1);
}
}
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: updatedValues }));
} else if (type === "file") {
const file = event.target.files[0];
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: file }));
} else {
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: value }));
}
};
const convert_to_base64 = async (file) => {
setfile(file);
const file_reader = new FileReader();
file_reader.readAsDataURL(file);
file_reader.onload = () => {
setattachment(file_reader?.result?.split(",")[1]);
};
};
return (
<>
<div className="text-center mb-8 bg-[#DBEAFE] py-4">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold text-blue-700 mb-4">
Project Management System
</h1>
</div>
<ProjectForm
id_={localStorage.getItem("id")}
searchParams={searchParams}
handleEdit={(event) =>
handleProjectEdit({
event,
setEdit,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
})
}
handleChange={handleChange}
handleSubmit={(event) =>
handleProjectSubmit({
event,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
})
}
Add={add}
formData={formData}
convertToBase64={convert_to_base64}
Edit={edit}
Router={() => router.back()}
/>
</>
);
}
export default Index;
```
The `Index` component represents the main page of a Project Management System. It includes a project form for adding and editing projects, as well as functionality for handling form submissions and file attachments.
### Add client page
In the `src/app/newclient directory`, create the file `src/app/newclient/page.js` and add the following code:
```javascript
"use client";
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { useSearchParams } from "next/navigation";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
import ClientForm from "../../components/Forms/ClientForm";
import {
handleClientSubmit,
handleClientEdit,
} from "../../util/Add&editClientfunctions";
function NewClient() {
const router = useRouter();
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
const [attachment, setattachment] = useState("");
const [add, setAdd] = useState(false);
const [file, setfile] = useState("");
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({
clientName: "",
gender: [],
clientId: 0,
clientImage: null,
});
const handleChange = (event) => {
const { name, value, type, checked } = event.target;
if (type === "checkbox") {
const updatedValues = [...formData[name]];
if (checked) {
updatedValues.push(value);
} else {
const index = updatedValues.indexOf(value);
if (index > -1) {
updatedValues.splice(index, 1);
}
}
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: updatedValues }));
} else if (type === "file") {
const file = event.target.files[0];
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: file }));
} else {
setFormData((prevData) => ({ ...prevData, [name]: value }));
}
};
const convert_to_base64 = async (file) => {
setfile(file);
const file_reader = new FileReader();
file_reader.readAsDataURL(file);
file_reader.onload = () => {
setattachment(file_reader?.result?.split(",")[1]);
};
};
return (
<>
<div className="text-center mb-8 bg-[#DBEAFE] py-4">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold text-blue-700 mb-4">
Project Management System
</h1>
</div>
<ClientForm
searchParams={searchParams}
handleEdit={() =>
handleClientEdit({
event,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
searchParams,
})
}
Edit={add}
handleChange={handleChange}
handleSubmit={(event) =>
handleClientSubmit({
event,
setFormData,
formData,
setAdd,
attachment,
router,
})
}
Add={add}
formData={formData}
convertToBase64={convert_to_base64}
Router={() => router.back()}
/>
</>
);
}
export default NewClient;
```
### URL Rewrites for API Integration
In the `next.config.js` file, add the following code:
```javaScript
module.exports = () => {
const rewrites = () => {
return [
{
source: "/additem",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items",
},
{
source: "/getproject",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items",
},
{
source: "/editproject",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items",
},
{
source: "/deleteproject/:id",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/items/:id",
},
{
source: "/deleteclient/:id",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/clients/:id",
},
{
source: "/addclient",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/clients",
},
{
source: "/editclient/:id",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/clients/:id",
},
{
source: "/getclient",
destination:
"https://xxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/clients",
},
];
};
return {
rewrites,
};
};
```
>**Note**: Be sure to use your actual endpoint in the destination.
The provided code above snippet showcases a solution for handling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) in a Next.js application. CORS is a security mechanism that restricts cross-origin HTTP requests. By configuring URL rewrites, the code enables communication with an external API by rewriting the request URLs and addressing the CORS issue.
### Home Page
In the `src/app/page.js` file, add the following code:
```javaScript
"use client";
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import Table from "./components/Tables/Index";
export default function page() {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
localStorage.clear();
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response1 = await fetch("/getproject", { method: "GET" });
const response2 = await fetch("/getclient", { method: "GET" });
if (!response1.ok || !response2.ok) {
throw new Error("Failed to fetch data");
}
const data1 = await response1.json();
const data2 = await response2.json();
const combinedData = data1.map((item1, index) => {
const item2 = data2[index];
return {
projectName: item1?.projectName,
projectStatus: item1?.projectStatus,
id: item1?.id,
clientName: item2?.clientName,
ClientImage: item2?.ClientImage,
gender: item2?.gender,
client_id: item2?.id,
};
});
setData(combinedData);
setLoading(false);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
setLoading(false);
}
};
fetchData();
}, []);
return (
<>
<div className="text-center mb-8 bg-[#DBEAFE] py-4">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold text-blue-700 mb-4">
Project Management System
</h1>
</div>
<main className="flex min-h-screen flex-col items-center justify-between p-24">
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : (
<div>
<Table data={data} />
</div>
)}
</main>
</>
);
}
```
# Testing and Deployment
Follow the steps below to test your Project Management Application:
Navigate into your `project-mgt-app` directory and run:
```javaScript
npm run dev
```
Your Project Management Application is now running at localhost:8000
To view your homepage, visit localhost:8000 in your browser. You should see the homepage.
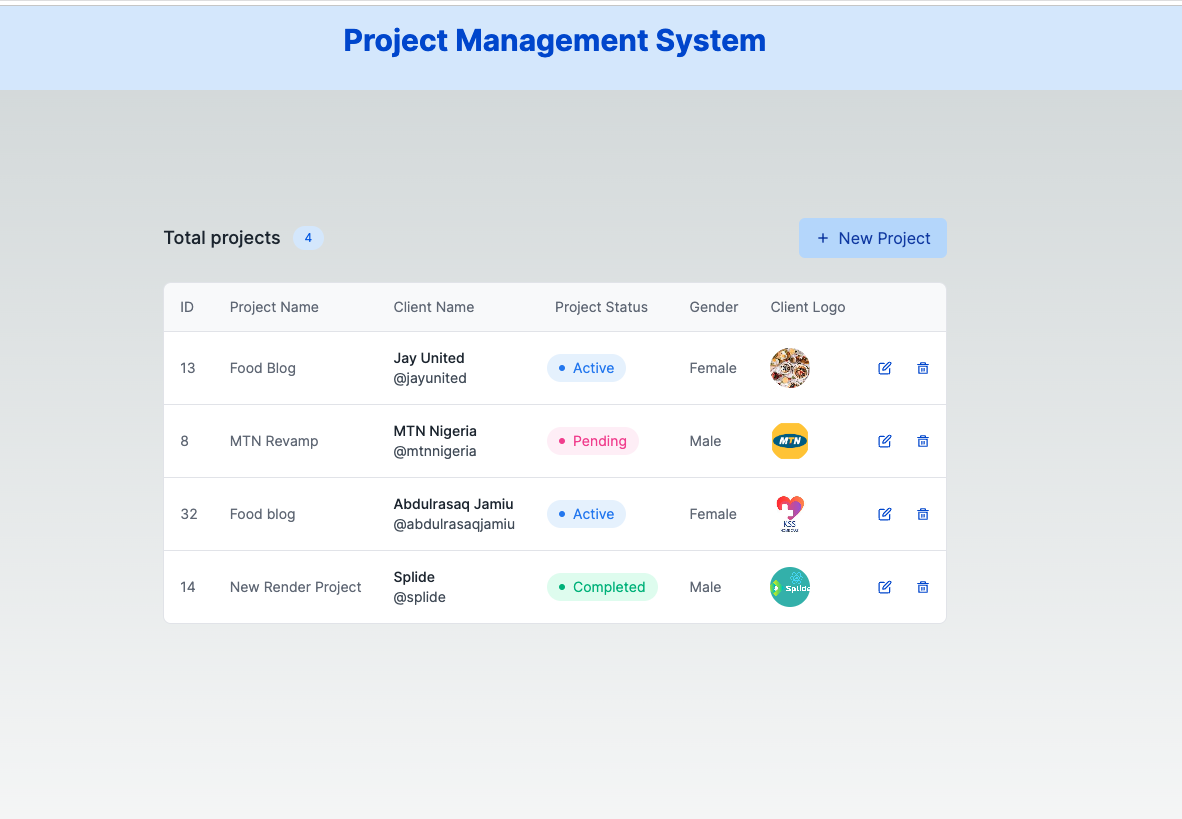
You can click on the **New Client** Button to add a new project.


Also, you can click on the edit and delete icons to make changes to your project.
## Deployment
To deploy your application, you will use `AWS Amplify` Hosting.
[AWS Amplify Hosting](https://aws.amazon.com/amplify/hosting/) - the ultimate solution for fast, secure, and scalable web app deployment. Whether you're building a static or server-side rendered app, a mobile app landing page, or a web app, Amplify Hosting's fully managed Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment `(CI/CD)` service has everything you need.
You can quickly deploy web content with support for modern web frameworks like `React`, `Angular`, `Vue`, `Next.js`, `Gatsby`, `Hugo`, `Jekyll`, and more.
Follow the steps below to deploy your Project Management Application:
- Push your application to a `Git` provider
- In the [AWS Amplify Hosting](https://aws.amazon.com/amplify/hosting/), click the Host web app button
- Choose your Git provider (in this case, Github) and click on the `Connect branch` button.
- Authorize and install AWS Amplify to access your repositories.
- Click the `Next` button to redirect you to a page where you can configure your build settings.
- Click on Next. On the `Review` page, select Save and deploy
Your app will be created, and you will be taken to the app's page in the Amplify Console.
After the deployment phase is marked complete, you can now view your app.

# Conclusion
Serverless applications have gained popularity due to their appealing benefits:
- No server management is required.
- Automatic scalability and high availability.
- Cost optimization by paying only for utilized resources and usage duration.
In this tutorial, you learned how to use `AWS's API Gateway` and `Lambda functions` to build a `REST API` that performs `CRUD` operations on an `AWS DynamoDB` database and utilizes `AWS S3` Storage. Furthermore, you discovered how to host the `API` on `AWS Amplify` Hosting.
If you find AWS fascinating, there are other captivating projects you can explore, such as:
- Implementing user authentication with `Amazon Cognito`.
- Simplifying the management and deployment of serverless applications using frameworks like Serverless or services like `AWS CloudFormation`.
# References
- [Building a Serverless Web App on AWS Services](https://www.pluralsight.com/guides/building-a-serverless-web-app-on-aws-services)
- [Tutorial: Build a CRUD API with Lambda and DynamoDB](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/http-api-dynamo-db.html)
- [How to use a proxy in Next.js](https://blog.logrocket.com/how-to-use-proxy-next-js/)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

