# DO380 "Red Hat OpenShift Administration III : Scaling Kubernetes Deployments in the Enterprise" notes in the margin
###### tags: `red hat, openshift, kubernetes, containers`
[Course description: Red Hat OpenShift Administration III: Scaling Kubernetes Deployments in the Enterprise](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/do380-red-hat-openshift-administration-III-scaling-kubernetes-deployments-enterprise?section=Outline)
## :memo: Table of contents
[ToC]
### Chapter 1. Moving From Kubernetes to OpenShift
[Kubernetes Docs: Organizing Cluster Access Using kubeconfig Files](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/organize-cluster-access-kubeconfig/)
[Kubernetes Docs: Configure Access to Multiple Clusters](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/configure-access-multiple-clusters/)
[Reference Docs for Kustomize](https://kubectl.docs.kubernetes.io/references/kustomize/)
[Kubernetes Docs: The Kustomization File An overview of the content of a kustomization file.](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/manage-kubernetes-objects/kustomization/)
[DC vs deployment: CAP theorem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP_theorem)
[Latest Openshift Clients and installer](https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/x86_64/clients/ocp/latest/)
[https://kustomize.io/](https://kustomize.io/)
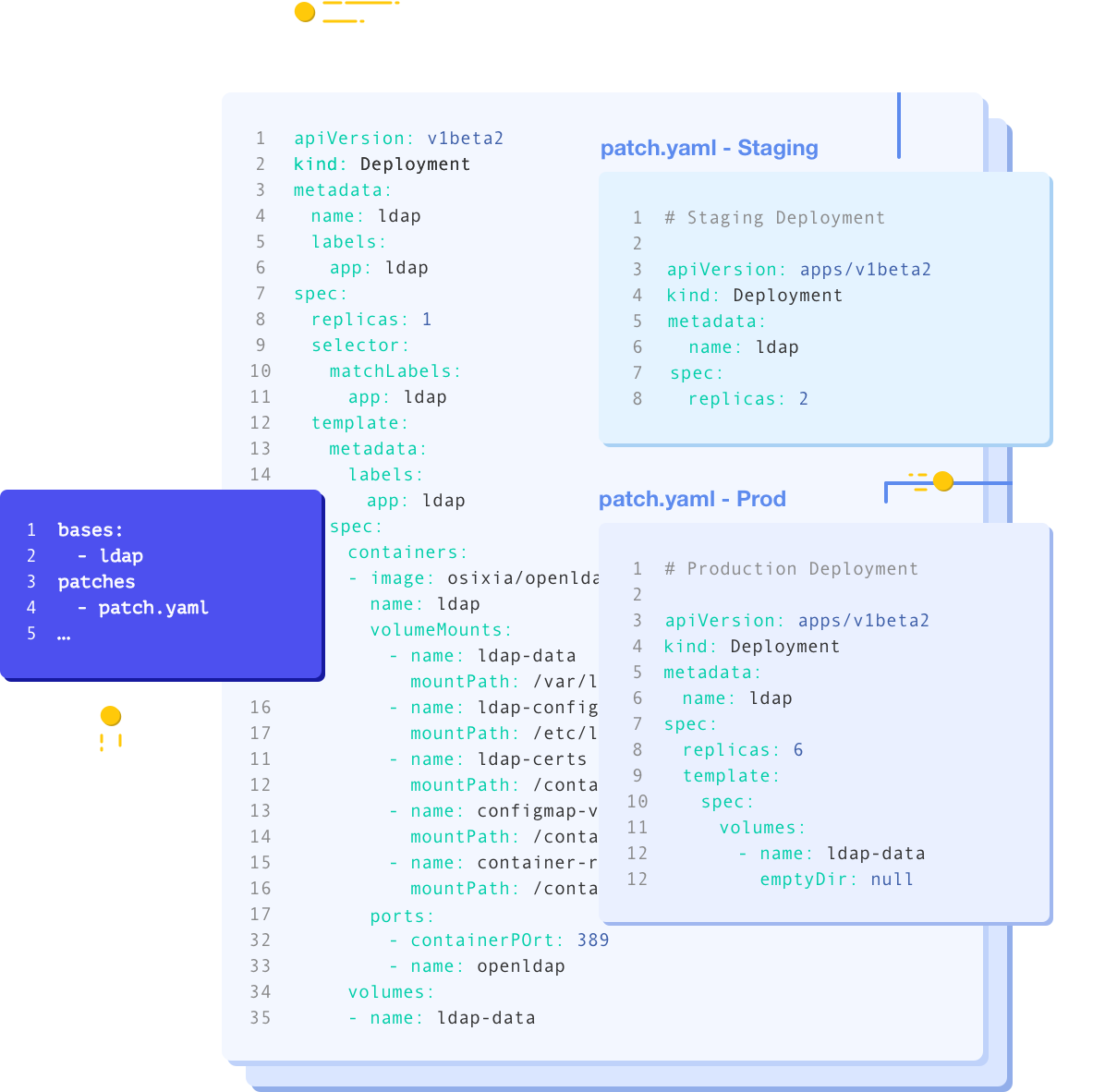
[https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize)
kustomize lets you customize raw, template-free YAML files for multiple purposes, leaving the original YAML untouched and usable as is.
kustomize targets kubernetes; it understands and can patch kubernetes style API objects. It's like make, in that what it does is declared in a file, and it's like sed, in that it emits edited text.
[An Introduction to Kustomize](https://blog.scottlowe.org/2019/09/13/an-introduction-to-kustomize/)
[Southbridge blog post](https://habr.com/ru/company/flant/blog/469179/)
[Kustomize cfg: Configuration Basics](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/blob/master/cmd/config/docs/tutorials/configuration-basics.md)
[The Kubernetes Resource Model (KRM)](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/architecture/resource-management.md)

[Kubernetes docs: Изучение объектов Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/ru/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/kubernetes-objects/)
[Using Admission Controllers](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/)
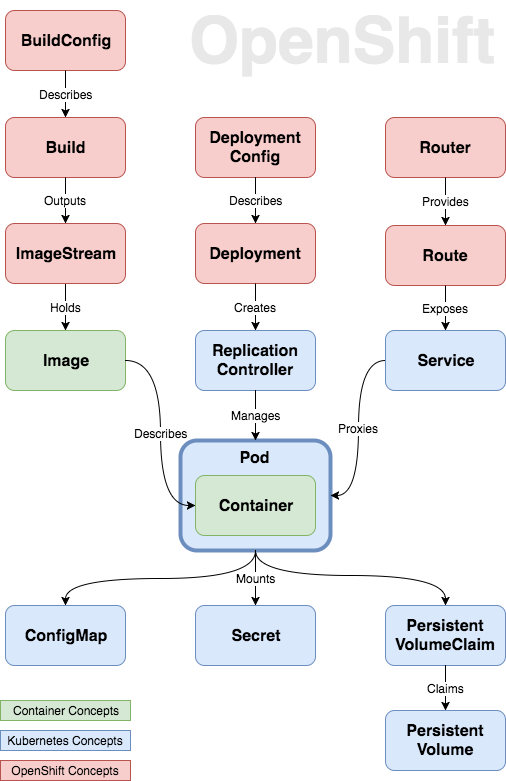
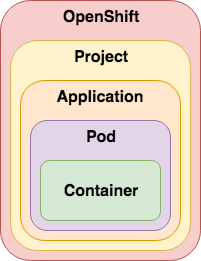
[OpenShift 3 Demystified. For Developers](https://platform.deloitte.com.au/articles/2017/openshift-3-demystified-for-developers/)
[Using Red Hat OpenShift image streams with Kubernetes deployments](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2019/09/20/using-red-hat-openshift-image-streams-with-kubernetes-deployments/)
[How to Simplify Container Image Management in Kubernetes with OpenShift Image Streams](https://www.openshift.com/blog/image-streams-faq)

### Chapter 2. Introduce automation on OpenShift
https://kubernetes.io/ru/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/kubernetes-objects/
https://docs.okd.io/latest/rest_api/index.html
[jq is a lightweight and flexible command-line JSON processor.](https://stedolan.github.io/jq/)
```
curl -s http://api.ocp4.domain.com:6443/apis/project.openshift.io/v1/projects \
|jq '.items[].metadata.name'
```
[FX : Command-line tool and terminal JSON viewer](https://github.com/antonmedv/fx)

Automate OpenShift administration tasks using bash scripts and Ansible playbooks.
https://www.ansibleforkubernetes.com/
[Youtube Video: Jeff Geerlings Kubernetes 101](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IcslsH7OoYo&list=PL2_OBreMn7FoYmfx27iSwocotjiikS5BD)
### Chapter 3. Manage operators with OpenShift
[Openshift Docs: What Operators are?](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/operators/understanding/olm-what-operators-are.html)

[Openshift Docs: Understanding Operator Lifecycle Manager](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/operators/understanding/olm/olm-understanding-olm.html)
| Resource | Short name | Description | looks like |
|--------- | ---------- | ----------- | ---------- |
| ClusterServiceVersion (CSV)| csv | Primary metadata resource describes operator. For example: name, version, icon, required resources. | rpm package
| CatalogSource | catsrc | Information for accessing repository of CSVs (Operators), CRDs, and packages that define an application. (packagemanifests from catalogsource) | yum repository
| Subscription | sub | Keeps CSVs up to date by tracking a channel in a package. (channel,approval mode) | yum install
| InstallPlan | ip | Calculated list of resources to be created to automatically install or upgrade a CSV. | file list and scriptlets that runs to install rpm
| OperatorGroup | og | Configures all Operators deployed in the same namespace as the OperatorGroup object to watch for their custom resource (CR) in a list of namespaces or cluster-wide.
| OperatorConditions | - | Creates a communication channel between OLM and an Operator it manages. Operators can write to the Status.Conditions array to communicate complex states to OLM.
[OpenShift Commons Briefing: Operator Lifecycle Management with Evan Cordell (Red Hat)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rlXJDrNJVpQ)
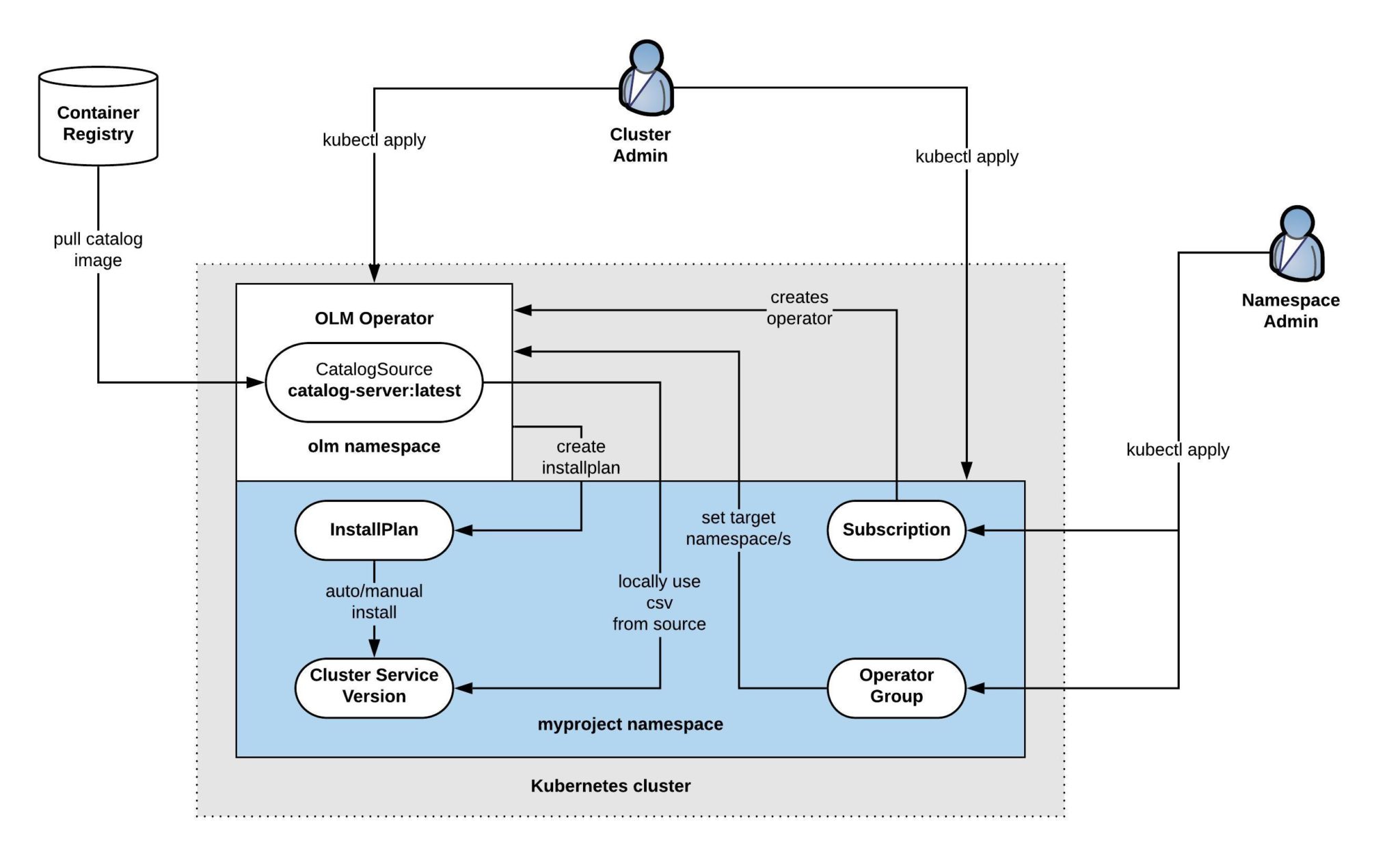
[techbloc.net blog post: Using Operator Lifecycle Manager and create custom Operator Catalog for Kubernetes](https://techbloc.net/archives/4372)
[Demystifying Operator deployment in OpenShift](https://medium.com/@vbudidarmawan/demystifying-operator-deployment-in-openshift-2ac7f24ad487)
[Делаем понятным развёртывание оператора в OpenShift](https://habr.com/ru/company/nixys/blog/574924/)
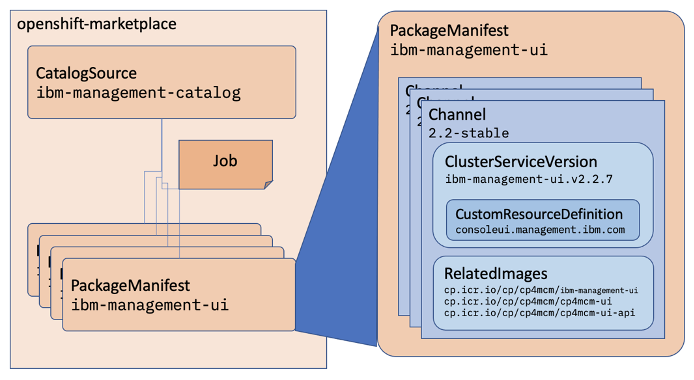
CatalogSource and PackageManifest
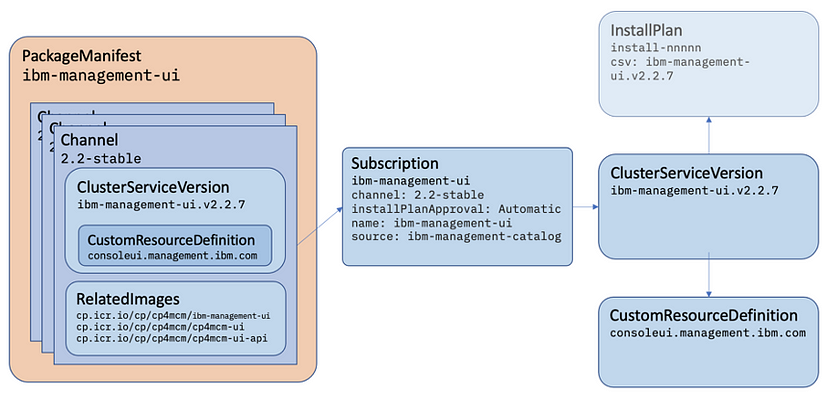
Channel and Subscription
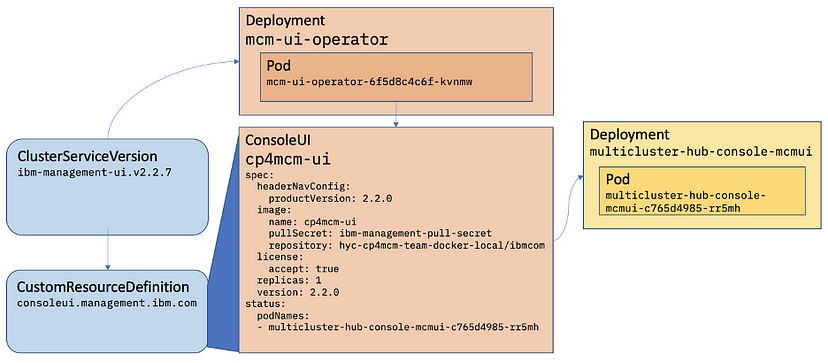
Installed operator
[O'Reilly free e-book: Kubernetes Operators: Automating the Container Orchestration Platform](https://developers.redhat.com/download-manager/file/cl-oreilly-kubernetes-operators-ebook-f21452-202001-en_2.pdf)
### Chapter 4. Implementing GitOps with Jenkins
https://www.prolinux.org/post/2017/09/vstuplenie-v-declarative-jenkins-pipelines/
[Continuous integration vs. continuous delivery vs. continuous deployment](https://www.atlassian.com/continuous-delivery/principles/continuous-integration-vs-delivery-vs-deployment)
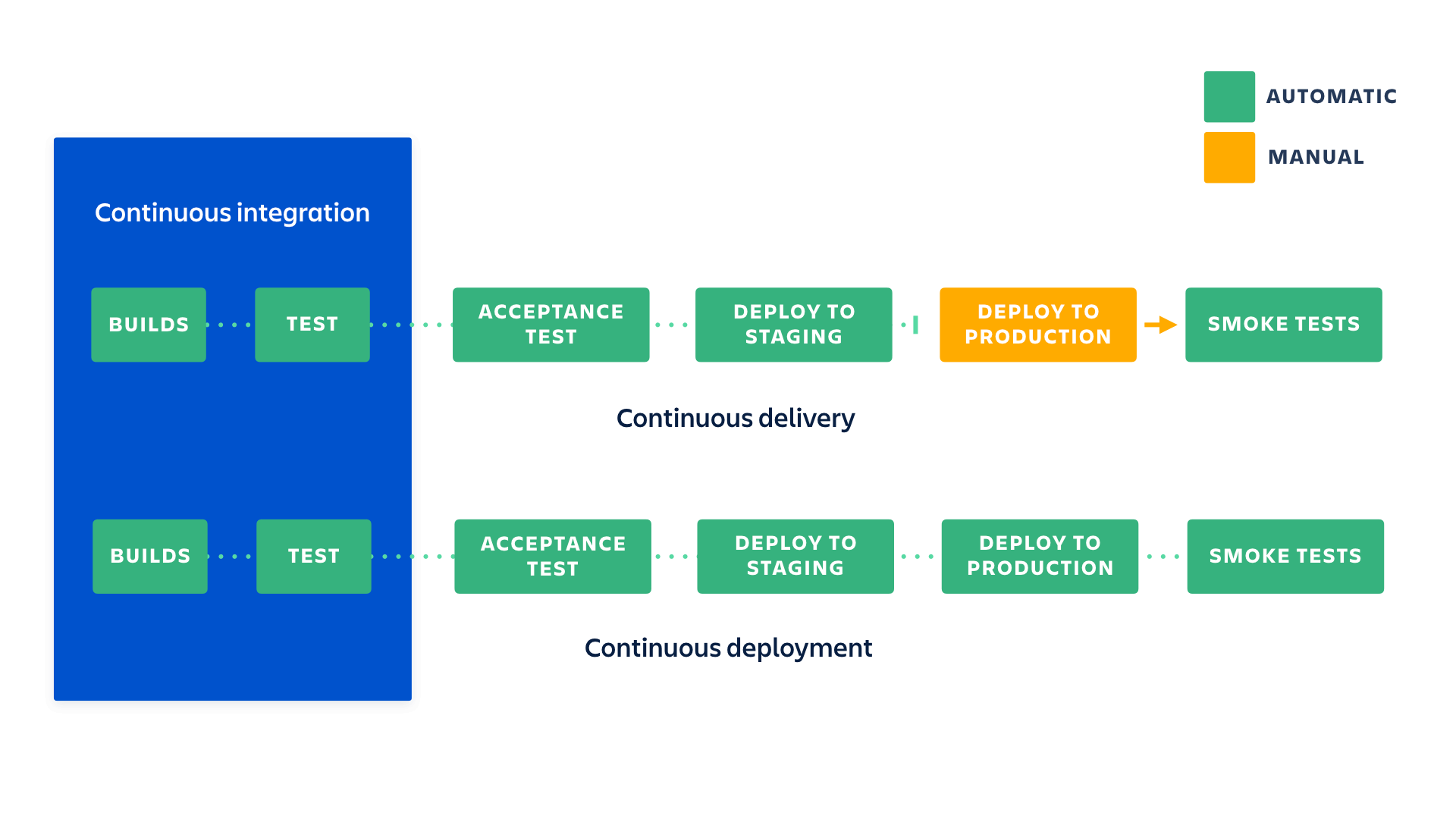
[RedHat Developers Blogs: Building modern CI/CD workflows for serverless applications with Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines and Argo CD, Part 1](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/10/01/building-modern-ci-cd-workflows-for-serverless-applications-with-red-hat-openshift-pipelines-and-argo-cd-part-1#)
[RedHat Developers Blogs: Building modern CI/CD workflows for serverless applications with Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines and Argo CD, Part 2](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/10/14/building-modern-ci-cd-workflows-for-serverless-applications-with-red-hat-openshift-pipelines-and-argo-cd-part-2#)
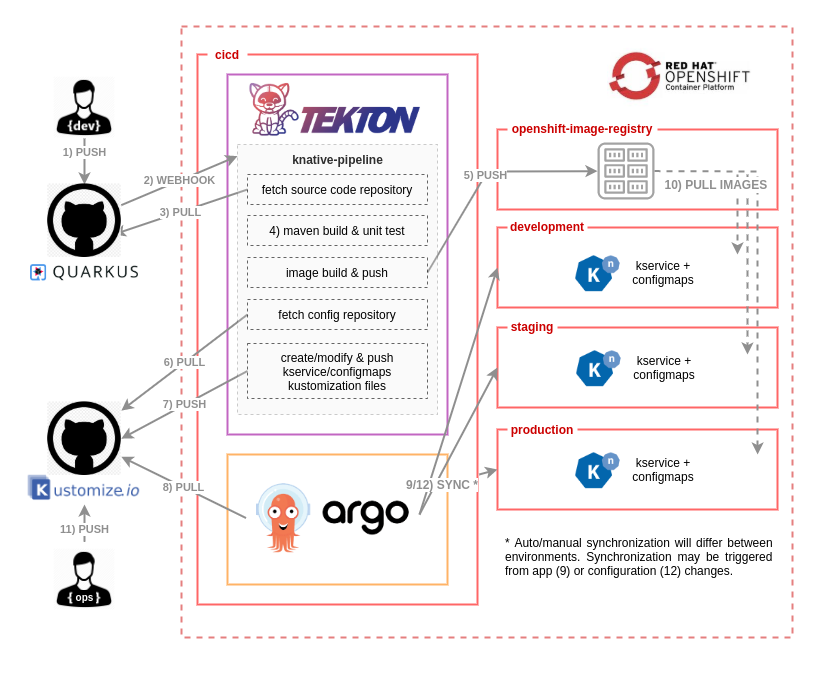
[Youtube video: Что же такое GitOps? Его свойства и недостатки](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n12xQNWhRdw)
Implement a GitOps workflow using containerized Jenkins to administer an OpenShift cluster.
https://habr.com/ru/company/southbridge/blog/535954/
https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/11/03/argo-cd-and-tekton-match-made-in-kubernetes-heaven
[E-books The Path to GitOps Christian Hernandez](https://developers.redhat.com/e-books/path-gitops)
### Chapter 5. Configuring Enterprise Authentication
Kubernetes Documentation | Reference | API Access Control | [Authenticating](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/authentication/#user-impersonation)
[Openshift Docs: Supported Identity Providers](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/authentication/understanding-identity-provider.html#supported-identity-providers)
[arctiq.ca blog post: OpenShift 4 Authentication via Azure AD](https://www.arctiq.ca/our-blog/2020/1/30/ocp4-auth-with-azure-ad/)
### Chapter 6. Configuring Trusted TLS certificates
[Openshift Docs: Adding API server certificates](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.6/security/certificates/api-server.html)
1. Create a secret that contains the certificate chain and private key in the openshift-config namespace.
```bash
oc create secret tls <secret> --cert=</path/to/cert.crt> \
--key=</path/to/cert.key> \
-n openshift-config
```
- secret is the name of the secret that will contain the certificate chain and private key.
- /path/to/cert.crt is the path to the certificate chain on your local file system.
- /path/to/cert.key is the path to the private key associated with this certificate.
2. Update the API server to reference the created secret.
```
oc patch apiserver cluster \
--type=merge -p \
'{"spec":{"servingCerts": {"namedCertificates":
[{"names": ["<FQDN>"],
"servingCertificate": {"name": "<secret>"}}]}}}'
```
- Replace FQDN with the FQDN that the API server should provide the certificate for
- Replace secret with the name used for the secret in the previous step.
3. Examine the apiserver/cluster object and confirm the secret is now referenced.
```
oc get apiserver cluster -o yaml
...
spec:
servingCerts:
namedCertificates:
- names:
- <FQDN>
servingCertificate:
name: <secret>
...
```
[Ingress Operator in OpenShift Container Platform](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/networking/ingress-operator.html#nw-ingress-controller-configuration-parameters_configuring-ingress)
[Openshift Docs: Ingress Operator: Setting a custom default certificate](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/networking/ingress-operator.html#nw-ingress-setting-a-custom-default-certificate_configuring-ingress)
1. Create a Secret resource containing the custom certificate in the openshift-ingress namespace using the tls.crt and tls.key files.
```bash
oc --namespace openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers
NAME AGE
default 10m
```
2. Update the IngressController CR to reference the new certificate secret.
```bash
oc --namespace openshift-ingress create secret tls custom-certs-default --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key
oc patch --type=merge --namespace openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default --patch '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate":{"name":"custom-certs-default"}}}'
```
3. Verify the update was effective:
```bash
oc get --namespace openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default --output jsonpath='{.spec.defaultCertificate}'
```
Configure OpenShift with trusted TLS certificates for external access to cluster services and applications.
### Chapter 7. Configure Dedicated Node Pools
[RedHat KB: How to add OpenShift 4 RHCOS Worker Nodes in UPI in new installations (< 24 hours)](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/4246261)
[Adding worker nodes to the OCP 4 UPI cluster existing 24+ hours](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/4799921)
[Adding new nodes to UPI cluster fails after upgrading to OpenShift 4.6+](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/5514051)
[OCP 4.6 Release notes: Ignition Spec updated to v3 ](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.6/release_notes/ocp-4-6-release-notes.html#ocp-4-6-ignition-spect-updated-v3)
[Recommended cluster scaling practices](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/scalability_and_performance/recommended-cluster-scaling-practices.html)
[GitHub repo openshift/machine-config-operator: MachineConfigDaemon docs](https://github.com/openshift/machine-config-operator/blob/master/docs/MachineConfigDaemon.md)
[GitHub repo openshift/machine-config-operator: Custom pool docs](https://github.com/openshift/machine-config-operator/blob/master/docs/custom-pools.md)
[Openshift docs: Red Hat CoreOS Server: Architecture](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/architecture/architecture-rhcos.html)
[github openshift-installer docs: Troubleshooting Bootstrap Failures](https://github.com/openshift/installer/blob/master/docs/user/troubleshootingbootstrap.md)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zQ7QfUY5Ulk
### Chapter 8. Configure persistent storage
[Understanding ephemeral storage](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/storage/understanding-ephemeral-storage.html)
Pods use ephemeral local storage for scratch space, caching, and logs. Issues related to the lack of local storage accounting and isolation include the following:
- Pods do not know how much local storage is available to them.
- Pods cannot request guaranteed local storage.
- Local storage is a best effort resource.
- Pods can be evicted due to other pods filling the local storage, after which new pods are not admitted until sufficient storage has been reclaimed.
Unlike persistent volumes, ephemeral storage is unstructured and the space is shared between all pods running on a node, in addition to other uses by the system, the container runtime, and OpenShift Container Platform. The ephemeral storage framework allows pods to specify their transient local storage needs. It also allows OpenShift Container Platform to schedule pods where appropriate, and to protect the node against excessive use of local storage.
[Kubernetes Docs: Volumes](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes/)
[Openshift Docs: Understanding persistent storage](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.7/storage/understanding-persistent-storage.html)
[Openshift Docs: Available storage options](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.10/scaling_performance/optimizing_storage.html#general-storage-guidelines)
[Kubernetes Blog: Kubernetes 1.14: Local Persistent Volumes GA](https://kubernetes.io/blog/2019/04/04/kubernetes-1.14-local-persistent-volumes-ga/)
### Chapter 9. Manage cluster monitoring and metrics
Configure and manage the OpenShift monitoring stack.
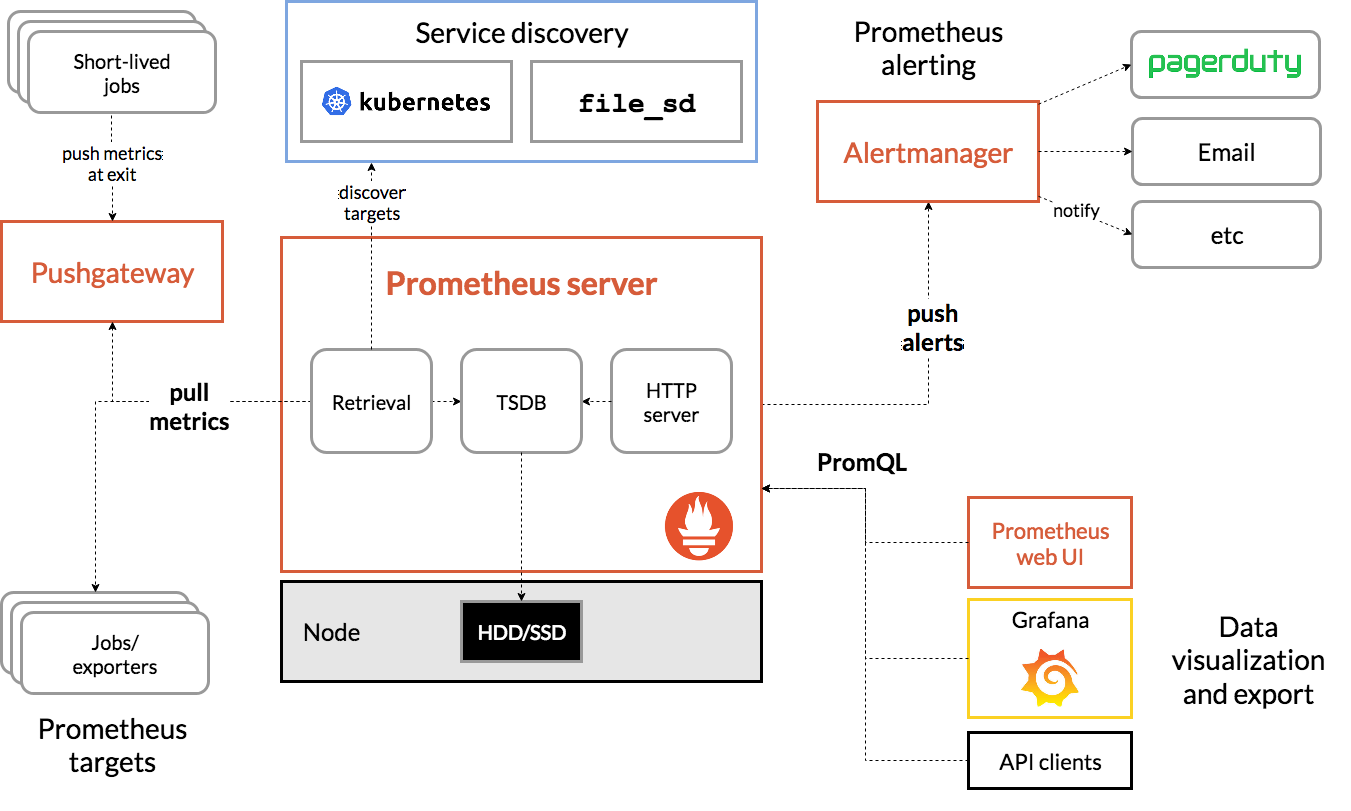
[https://prometheus.io/docs/: QUERYING PROMETHEUS](https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/querying/basics/)
)
PromQL examples:
* sum(container_memory_usage_bytes) / 1024 / 1024
* sum(container_memory_usage_bytes{image!='',node="master0.domain.tld"}/1024/1024) by (node)
* rate(apiserver_request_total{code!~"2.*"}[2m])
* 100 - avg by (instance) (rate(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="idle"}[5m]) * 100)
* node_load5
[Мониторинг и Kubernetes (Дмитрий Столяров, Флант, RootConf 2018)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zj6SlzzBRaA)
[Полное руководство по Prometheus в 2019 году](https://habr.com/ru/company/southbridge/blog/455290/)
[RedHat KB: Is it possible to add custom dashboards to OpenShift web console?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/6076431)
[RedHat KB: Custom Grafana Dashboard for custom metrics](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/5335491)
[RedHat KB: Is it possible to add custom dashboards to OpenShift web console?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/4874091)
[Ask an OpenShift Admin (Ep 31): Alertmanager configuration and customization](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TRSy6G3y9aY)
[Полное руководство по Prometheus в 2019 году](https://habr.com/ru/company/southbridge/blog/455290/)
### Chapter 10. Provision and inspect cluster logging
[Kubernetes Documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/) |
[Concepts](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/) | [Cluster Administration](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/) | [Logging Architecture](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/logging/)
### Chapter 10. Recover failed worker nodes
Inspect, troubleshoot, and remediate worker nodes in a variety of failure scenarios.
[Openshift Docs: Replacing an unhealthy etcd member](https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.11/backup_and_restore/control_plane_backup_and_restore/replacing-unhealthy-etcd-member.html#restore-replace-stopped-etcd-member_replacing-unhealthy-etcd-member)
https://cloud.redhat.com/blog/ocp-disaster-recovery-part-1-how-to-create-automated-etcd-backup-in-openshift-4.x
https://cloud.redhat.com/blog/ocp-disaster-recovery-part-2-recovering-an-openshift-4-ipi-cluster-with-the-loss-of-one-master-node
> Disclaimer: You will find here notes and links to official docs with additional information on products and technologies that described on RedHat training.
> THIS DOCUMENT DOES NOT REPRINT ANY COPYRIGHTED CONTENT FROM REDHAT TRAINING. You will find here only public accessible outline.