# RH415 "Red Hat Security: Linux in Physical, Virtual, and Cloud" notes in the margin
###### tags: `red hat, rhel`
> You will find here notes and links to official docs with information on products and technologies that described on RedHat Training.
> THIS DOCUMENT DOES NOT REPRINT ANY COPYRIGHTED CONTENT FROM REDHAT TRAINING.
> You will find here only public accessible outline.
[Course description: RH415 "Red Hat Security: Linux in Physical, Virtual, and Cloud"](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/rh415-red-hat-security-linux-physical-virtual-and-cloud)
## :memo: Table of contents
[ToC]
### 1. Managing Security and Risk
[RHEL 8 Docs: Managing and monitoring security updates](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/managing_and_monitoring_security_updates)
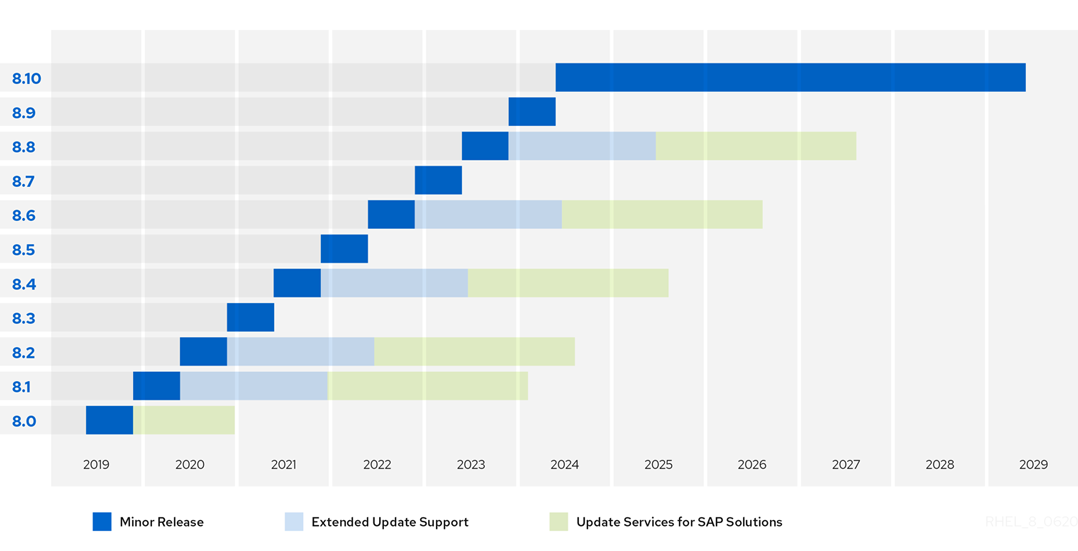
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux Life Cycle](https://access.redhat.com/support/policy/updates/errata)

[Product Security Center](https://access.redhat.com/security/)
[Notifications and Advisories](https://access.redhat.com/security/updates/advisory)
[Red Hat CVE Database](https://access.redhat.com/security/security-updates/#/cve)
[Red Hat Security Blog](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/channel/security)
[Red Hat Security Blog (old place)](https://access.redhat.com/blogs/product-security)
[Understanding Red Hat security ratings](https://access.redhat.com/security/updates/classification)
[Backporting Security Fixes](https://access.redhat.com/security/updates/backporting)
[Red Hat Product Security Center](https://access.redhat.com/security)
[Red Hat Security Data Changelog](https://access.redhat.com/articles/5554431)
[Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures](https://cve.mitre.org/cve/search_cve_list.html)
[CVE-2014-3670 php buffer overflow bug](https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2014-3670)
[Red Hat Log4Shell cve](https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/cve-2021-44228)
[Log4Shell Wiki Ru](https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log4Shell)
[Using daysofrisk.pl with the Red Hat Security Data API](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/using-daysofriskpl-red-hat-security-data-api)
[Days of Risk Report (automatically generated) sample report](https://access.redhat.com/security/data/metrics/summary-rhel8-critical.html)
[Determining Common Platform Enumeration (CPE)](https://redhat-connect.gitbook.io/partner-guide-for-adopting-red-hat-oval-v2/determining-common-platform-enumeration-cpe)
Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) is a standardized method of describing and identifying classes of applications, operating systems, and hardware devices present among an enterprise's computing assets

[What is Clair?](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/containers/what-is-clair)
Clair is an open source project which provides a tool to monitor the security of your containers through the static analysis of vulnerabilities in appc and docker containers.
[Red Hat Blog: Scanning container image vulnerabilities with Clair](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/scanning-container-image-vulnerabilities-clair)
[RHEL 8 Docs: Security hardening](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/security_hardening/index)
[RHEL 8 Docs: Securing Networks](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/securing_networks/index)
[Install OpenVAS (GVM) on Kali Linux](https://spy-soft.net/openvas-gvm-kali-linux/)
[Kali Linux: Дистрибутив для пентестинга](https://www.kali.org/get-kali/)
[Список инструментов Kali Linux](https://kali.tools/)
[OpenVAS wiki](https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenVAS)
OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System, Открытая система оценки уязвимости, первоначальное название GNessUs) — фреймворк, состоящий из нескольких сервисов и утилит, позволяющий производить сканирование узлов сети на наличие уязвимостей и управление уязвимостями.
Все продукты OpenVAS являются свободным ПО. Большая часть компонентов выпускается под лицензией GPL
[Установка и использование OpenVAS (GVM) на Kali Linux](https://spy-soft.net/openvas-gvm-kali-linux/)
[Использование сканера уязвимостей OpenVAS](https://habr.com/ru/articles/203766/)
[Nikto](https://github.com/sullo/nikto) – это сканер с открытым исходным кодом (GPL) для веб-серверов
```bash
git clone https://github.com/sullo/nikto
# Main script is in program/
cd nikto/program
# Run using the shebang interpreter
./nikto.pl -h http://www.example.com
# Run using perl (if you forget to chmod)
perl nikto.pl -h http://www.example.com
```
[Проверяем на уязвимости любой сайт с помощью Nikto](https://habr.com/ru/companies/otus/articles/492546/)
[Инструкция по использованию сканера веб-серверов Nikto](https://hackware.ru/?p=3443)
[Vul - Agentless Vulnerability Scanner for Linux/FreeBSD](https://vuls.io/en/)
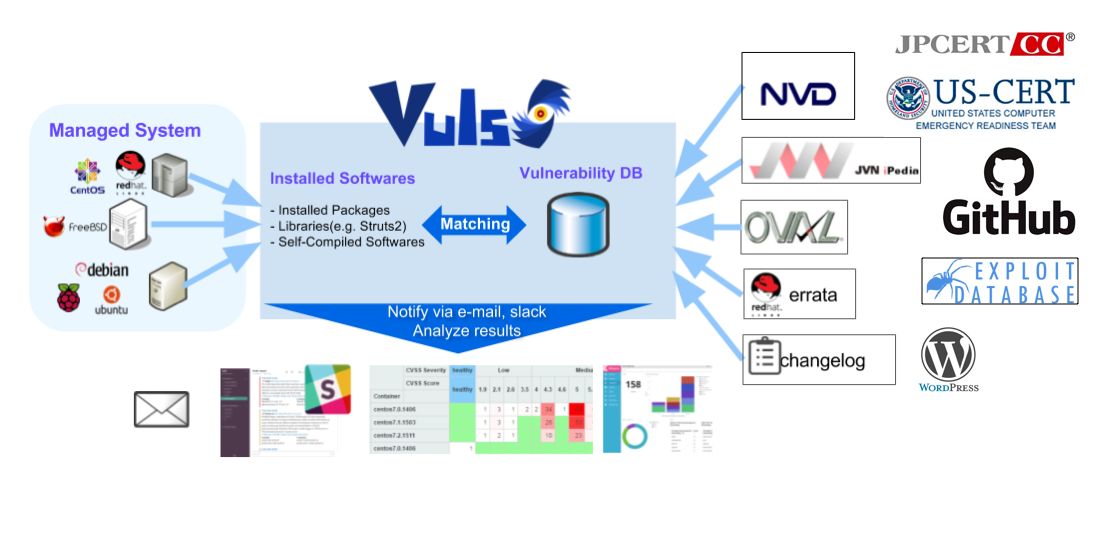
[Tutorial - Local Scan Mode](https://vuls.io/docs/en/tutorial-local-scan.html)
[examples of config.toml for local and remote scan](https://github.com/vulsio/vulsctl)
[How to install and setup Docker on RHEL 7/CentOS 7](https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/install-use-setup-docker-on-rhel7-centos7-linux/)
### 2. Automating Configuration and Remediation with Ansible
[Ansible.com](https://www.ansible.com/)
[Red Hat blog: Channel: Red Hat Ansible Automation](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/channel/red-hat-ansible-automation)
[Red Hat kb: How to download and install Red Hat Ansible Engine](https://access.redhat.com/articles/3174981)
[Red Hat kb: Using Ansible in RHEL 8.6 and later](https://access.redhat.com/articles/6393361)
[Learn Linux TV Tutorial: Using Ansible "Pull" Mode to Dynamically Automate Server/Workstation Builds ](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sn1HQq_GFNE)
[Linux System Roles](https://linux-system-roles.github.io/)
### 3. Protecting Data with LUKS and NBDE
[Cryptsetup and LUKS - open-source disk encryption](https://gitlab.com/cryptsetup/cryptsetup)
Cryptsetup is a utility used to conveniently set up disk encryption based
on the DMCrypt kernel module.
These include plain dm-crypt volumes, LUKS volumes, loop-AES,
TrueCrypt (including VeraCrypt extension), BitLocker and FileVault2 formats.
Why LUKS?
- compatibility via standardization,
- secure against low entropy attacks,
- support for multiple keys,
- effective passphrase revocation,
- free.
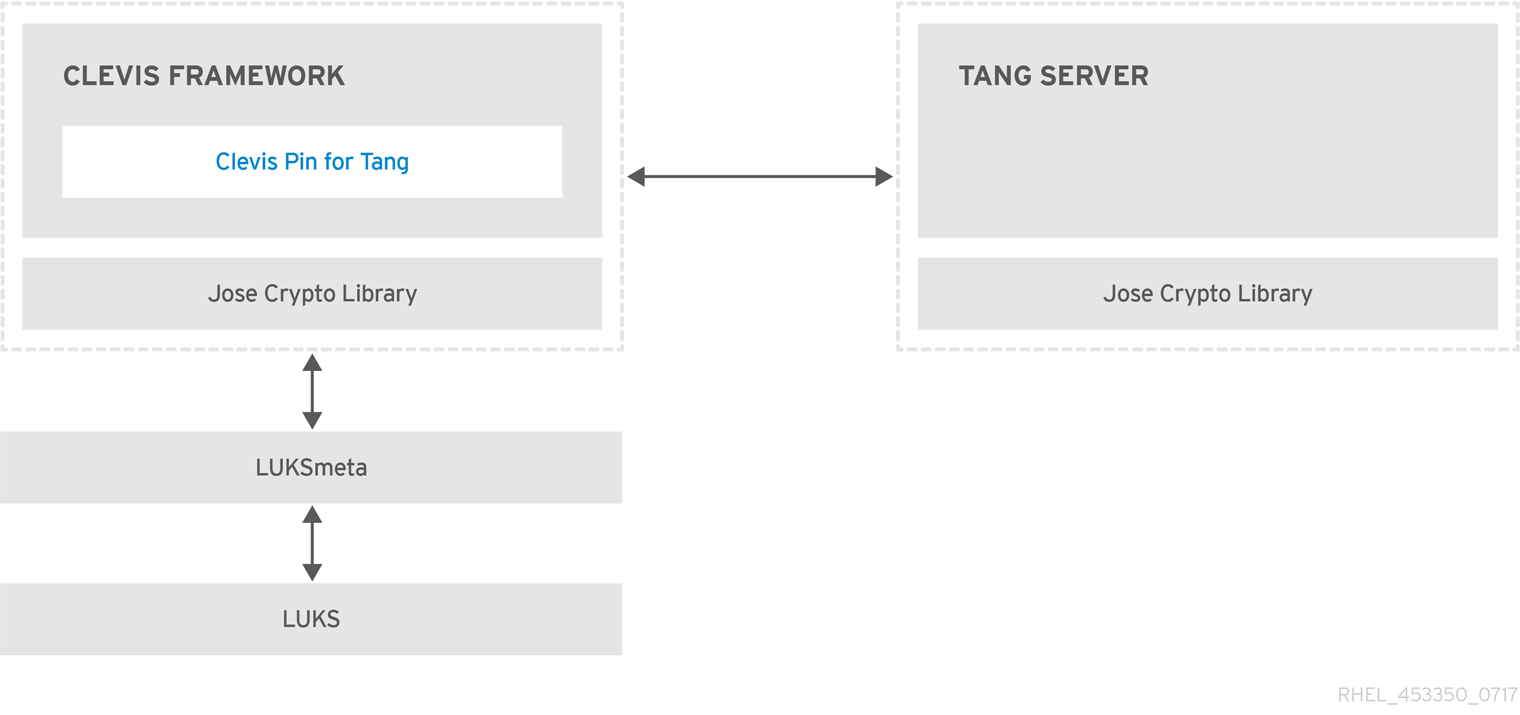
[Clevis is a pluggable framework for automated decryption. ](https://github.com/latchset/clevis)
[Tang is a server for binding data to network presence.](https://github.com/latchset/tang)
[RHEL8 Docs: Security Hardering: Configuring automated unlocking of encrypted volumes using policy-based decryption](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/security_hardening/configuring-automated-unlocking-of-encrypted-volumes-using-policy-based-decryption_security-hardening)
### 4. Restricting USB Device Access
[home | USBGuard ](https://usbguard.github.io/)
The USBGuard software framework helps to protect your computer against rogue USB devices (a.k.a. BadUSB) by implementing basic whitelisting and blacklisting capabilities based on device attributes.
Features
- Rule language for writting USB device authorization policies
- Daemon component with an IPC interface for dynamic interaction and policy enforcement
- Command line and GUI interface to interact with a running USBGuard instance
- C++ API for interacting with the daemon component implemented in a shared library
[RHEL8 Docs: Security Hardering: Protecting systems against intrusive USB devices](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/security_hardening/protecting-systems-against-intrusive-usb-devices_security-hardening)
[Using USBGuard vs. UDev rules for USB device authorization](https://usbguard.github.io/blog/2015/USBGuard-vs-UDev)
### 5. Controlling Authentication with PAM
[FreeBSD article: Подключаемые Модули Аутентификации (PAM)](https://docs.freebsd.org/doc/13.0-RELEASE/usr/local/share/doc/freebsd/ru/articles/pam/article.html)
[Red Hat KB: What should go in password-auth vs system-auth in RHEL6 and RHEL 7](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/45492)
- The problem with /etc/pam.d/system-auth is that it contains modules that are not usable in remote configurations so remote services such as sshd, vsftpd now use /etc/pam.d/password-auth.
```bash=
$ cat /etc/pam.d/sshd |grep system-auth
$ cat /etc/pam.d/sshd |grep password
auth substack password-auth
account include password-auth
password include password-auth
session include password-auth
$ cat /etc/pam.d/login |grep password
password include system-auth
$ cat /etc/pam.d/login |grep system-auth
auth substack system-auth
account include system-auth
password include system-auth
session include system-auth
```
[pam_pwquality(8) PAM module to perform password quality checking](https://manpages.org/pam_pwquality/8)
[Создание политики паролей в Linux](https://habr.com/ru/company/otus/blog/448996/)
[RedHat KB: The meaning of the Valid field in the faillock(8) command output](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/6962920)
[SSSD Open Source Client for Enterprise Identity Management](https://sssd.io/)

[SSSD on github](https://github.com/SSSD/sssd)
### 6. Recording System Events with Audit
[Linux Audit](https://people.redhat.com/sgrubb/audit/)
https://github.com/threathunters-io/laurel
[The Linux Audit Project](https://github.com/linux-audit)
[RHEL7 Security Guide: System Auditing](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/chap-system_auditing#sec-audit_system_architecture)
[RHEL Audit System Reference](https://access.redhat.com/articles/4409591)
[Настройка auditd для обнаружения и расследования инцидентов информационной безопасности](https://habr.com/ru/articles/553036/)
### 7. Monitoring File System Changes
[AIDE (Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment, \[eyd\]) is a file and directory integrity checker.](https://aide.github.io/)
### 8. Mitigating Risk with SELinux
[GitHub: SELinux Project](https://github.com/SELinuxProject)
[Dan Walsh Blog](https://danwalsh.livejournal.com/)
[YouTube: Red Hat Summit: Are you listening to what SELinux is telling you?](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wv9kwlabdlo)
[b374k PHP webshell 3.2](https://github.com/b374k/b374k)
[Dan Walsh's Blog: How do I tell what would be allowed by a boolean?](https://danwalsh.livejournal.com/64779.html)
[GitHub Blog: Introduction to SELinux](https://github.blog/2023-07-05-introduction-to-selinux/)
[Kaspersky Web Traffic Security installation guide: Disable SELinux](https://support.kaspersky.com/KWTS/6.1/ru-RU/165993.htm)
[Seriously, stop disabling SELinux.](https://stopdisablingselinux.com/)
[CertDepot: RHEL7: How to deploy SELinux man pages](https://www.certdepot.net/rhel7-deploy-selinux-man-pages/)
[Gentoo Wiki: SELinux/ru ](https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/SELinux/ru)
[SELinux Coloring Book](https://developers.redhat.com/books/selinux-coloring-book)

[Github book: SELinux Notebook](https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux-notebook)
[Книга: Свен Вермейлен: Администрирование системы защиты SELinux](https://dmkpress.com/catalog/computer/securuty/978-5-97060-557-8/)
[RHEL8 Docs Using SELinux: Writing a custom SELinux policy](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/ru-ru/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/using_selinux/writing-a-custom-selinux-policy_using-selinux)
[RedHat KB: Basic SELinux Troubleshooting in CLI](https://access.redhat.com/articles/2191331)
### 9. Managing Compliance with OpenSCAP
The [Security Content Automation Protocol SCAP](https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/security-content-automation-protocol) is a synthesis of interoperable specifications derived from community ideas. Community participation is a great strength for SCAP, because the security automation community ensures the broadest possible range of use cases is reflected in SCAP functionality. This Web site is provided to support continued community involvement. From this site, you will find information about both existing SCAP specifications and emerging specifications relevant to NIST's security automation agenda. You are invited to participate, whether monitoring community dialog or leading more substantive activities like specification authorship.
[SCAP Security Guide is a security policy written in a form of SCAP documents](https://www.open-scap.org/security-policies/scap-security-guide/)
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 STIG](https://cyber.trackr.live/stig/RHEL_8_STIG/1/7)
Tailoring Files
It may sometimes be required to adjust the security policy to your specific needs.
In Satellite, tailoring_files represent the custom modifications to default XCCDF profiles and they can be applied to hosts via compliance policies
[OpenSCAP User Manual](https://static.open-scap.org/openscap-1.3/oscap_user_manual.html)
[Аудит информационной безопасности. XCCDF и OVAL](https://habr.com/ru/post/538764/)
### 10. Automating Compliance with Red Hat Satellite
https://opensource.com/article/21/9/centos-stream-foreman
### 11. Analyzing and Remediating Issues with Red Hat Insights
### 12. Comprehensive Review