# RH354 "RHEL 8 New Features..." notes in the margin
##### tags: `red hat, rhel`
[Course description: RH354 RHEL 8 New Features for Experienced Linux Administrators](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/rh354-red-hat-enterprise-linux-8-new-features-experienced-linux-administrators)
## :memo: Table of contents
[ToC]
### 1. Previewing Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html-single/8.0_release_notes/index)
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/8.1_release_notes/index)
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.2](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/8.2_release_notes/index)
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.3](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/8.3_release_notes/index)
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/8.4_release_notes/index)
[Release notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.5](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/8.5_release_notes/index)
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux Presents 24: What's New in RHEL 8.5](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ws1SjGZ6b_U)
[RED HAT BLOG SERIES: What's New in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/latest-rhel-series)
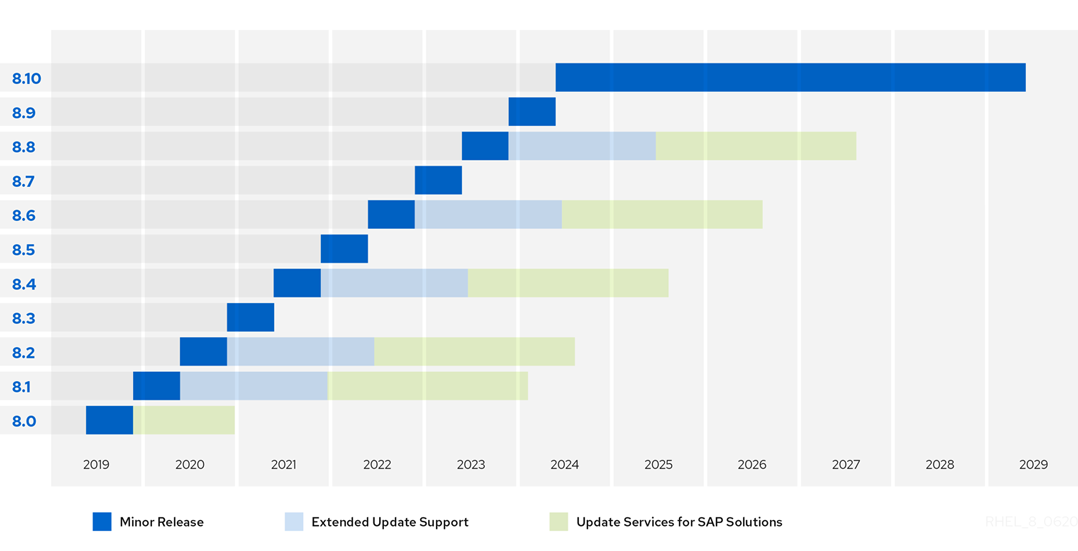
[Red Hat KB: Red Hat Enterprise Linux Release Dates](https://access.redhat.com/articles/3078)
| Release | General Availability Date | redhat-release Errata Date* | Kernel Version |
| ------- | ------------------------- | --------------------------- | -------------- |
| RHEL 8.5 | 2021-11-09 | 2021-11-09 RHSA-2021:4356 | 4.18.0-348 |
| RHEL 8.4 | 2021-05-18 | 2021-05-18 RHSA-2021:1578 | 4.18.0-305 |
| RHEL 8.3 | 2020-11-03 | 2020-11-03 RHBA-2020:4495 | 4.18.0-240 |
| RHEL 8.2 | 2020-04-28 | 2020-04-28 RHBA-2020:1758 | 4.18.0-193 |
| RHEL 8.1 | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 RHBA-2019:3543 | 4.18.0-147 |
| RHEL 8 | 2019-05-07 | - | 4.18.0-80 |
To find your Red Hat Enterprise Linux release please:
``
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
``
To find your kernel version please:
``
$ uname -a
``
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Life Cycle](https://access.redhat.com/support/policy/updates/errata/#RHEL8_Life_Cycle)
[WEBINAR on-demand recording from May 12, 2021: Expanded tools for containers and cloud workload management - what's new in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4](https://www.redhat.com/en/events/webinar/expanded-tools-for-containers-and-cloud-workload-management-what-new-red-hat-enterprise-linux#ondemand-form)
[Red Hat Developer Article: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 now generally available](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2019/05/07/red-hat-enterprise-linux-8-now-generally-available)
### 2. Installing or Upgrading to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8
[Supported in-place upgrade paths for Red Hat Enterprise Linux](https://access.redhat.com/articles/4263361)
[Red Hat Customer Portal Labs:](https://access.redhat.com/labs/) [Red Hat Enterprise Linux Upgrade Helper](https://access.redhat.com/labs/rhelupgradehelper/8/)
[Why does subscription-manager list return: "No Installed Products found" ?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/100423)
[Upgrading from RHEL 7 to RHEL 8: Known issues](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/upgrading_from_rhel_7_to_rhel_8/troubleshooting_upgrading-from-rhel-7-to-rhel-8#known-issues_troubleshooting)
[YouTube Video: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 to 8 In-Place Upgrade Using Leapp](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4nG2X_pmxv4)
[Developer documentation for Leapp](https://leapp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html)
[Leapp utility metadata in-place upgrades of RHEL for disconnected upgrades](https://access.redhat.com/articles/3664871#instructions-on-how-to-use-this-metadata-4)
[Red Hat Blog: Boom! Booting RHEL from LVM snapshots](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/boom-booting-rhel-lvm-snapshots)
[Upgrading from RHEL 7 to RHEL 8 with Leapp and BOOM](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/upgrading-rhel-7-rhel-8-leapp-and-boom)
[Migrate to and certify on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 with LEAPP](https://connect.redhat.com/en/partner-with-us/red-hat-enterprise-linux-certification/upgrade-red-hat-enterprise-linux)
[YouTube Video: Upgrade to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 with LEAPP](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yqSHL31R42E)
[github: Leapp Framework actors: el7toel8 ](https://github.com/oamg/leapp-repository)
[Convert2RHEL: How to convert from CentOS Linux and Oracle Linux to Red Hat Enterprise Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux/migration-process/convert2rhel-how-to-convert-from-centos-linux-to-red-hat-enterprise-linux):
* [Red Hat Blog: An Introduction to Convert2RHEL: Now officially supported to convert RHEL-like systems to RHEL](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/introduction-convert2rhel-now-officially-supported-convert-rhel-systems-rhel)
* [YouTube Video: Converting From CentOS to RHEL With Convert2RHEL and Satellite](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ui7nPUovUq0)
* [YouTube Video: Convert from Oracle Linux with Convert2RHEL](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TyjH0cdZc-8)
* [YouTube Video: Convert from CentOS Linux with Convert2RHEL](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xX7P4BzOcNg)
* [Red Hat Enterprise Linux Presents (E19): In-Place Upgrades with Leapp](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hmBSjAcedkM)
* [Red Hat Enterprise Linux Presents (E20): Convert2RHEL](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Git-6uAz1t4)
[YouTube Video: RHEL 8 Beta - Using Leapp and Boom to Upgrade to the RHEL 8 Beta](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y6v3JIIYpGA)
[RedHat Developer Article: Getting Red Hat Developer Subscription: What RHEL users need to know](https://developers.redhat.com/articles/getting-red-hat-developer-subscription-what-rhel-users-need-know)
Get the software
1. Join the Red Hat Developer Program and register at developers.redhat.com to get a subscription. Each system that runs Red Hat Enterprise Linux will need a subscription.
2. [Download](https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/download/) Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server
3. [Install](https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/hello-world) Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server using one of our guides. For Microsoft Windows, Apple Mac OS, or other Linux users, our guides cover creating a virtual machine (VM) with VirtualBox, Hyper-V, or installing on a physical system.
4. After installation, you will be prompted to register your system with the Red Hat Customer Portal. This will attach your system to your subscription, which enables the system to download updates and additional software from Red Hat.
[No-cost Red Hat Enterprise Linux Individual Developer Subscription: FAQs](https://developers.redhat.com/articles/faqs-no-cost-red-hat-enterprise-linux)
[RedHat KB: As a customer how does Red Hat support me when I use third party components?](https://access.redhat.com/third-party-software-support)
[Production Support Scope of Coverage](https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/production/soc)
If we ship it, we...
| Support | Do not support |
| ------- | -------------- |
| Installation | Modified RPMs
| Usage | Third-party software/drivers and uncertified hardware/hypervisors
| Configuration | Community projects upon which enterprise releases are based
| Diagnosis | Code development
| Bug reports (dependent on product life cycle)| System and network design
| Bug fixes | Implementation and development of security rules and policies
| Red Hat Extras channel | Red Hat Supplementary / Optional channels
| | Technology preview features
| | Packages included to satisfy dependencies or "incidental inclusions" when deployed as standalone items
[Creating a Local Repository and Sharing With Offline Systems](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JAIjTpXwpuI)
[Red Hat Insights Get started](https://access.redhat.com/products/red-hat-insights#getstarted)
### 3. Provisioning and Configuring Servers
[www.server-world.info website with many simple step-by-step instructions how to configure RHEL/CentOS Server](https://www.server-world.info/en/)
[Red Hat Developer Blog: Introducing Application Streams in RHEL 8](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2018/11/15/rhel8-introducing-appstreams/)
[RHEL 8 Docs: Installing, managing, and removing user-space components](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/installing_managing_and_removing_user-space_components/index)
[RHEL 8 yum cheat sheet](https://developers.redhat.com/cheat-sheets/red-hat-enterprise-linux-8)
RHEL 8 Repositories:
* BaseOS - primarily core operating system packages with support for the lifetime of the OS
* Appstream - user-space applications and components, including numerous Application Streams
* CodeReady Builder- additional libraries and tools for developers
* Supplementary - 3rd party support only
Terms and terminology:
For even more information about Application Streams and modules, see
Introducing Application Streams in RHEL 8.
* Application Stream (or simply stream) - refers to content. PHP 7.2 is an application stream. PHP 7.3 is an application stream.
* Module - is the packaging format. PHP is packaged as a module.
* Module Stream - different versions of a component packaged as a module. PHP 7.2 is an application stream packaged in a module stream.
* appstream - is the name of the RHEL 8 repo where you can find Application Streams.
FINDING AND EXPLORING MODULES
| Command | Explanation |
| ------- | ----------- |
| yum module list | list all modules |
| yum module list installed | list installed modules |
| yum module provides package | find which module provides a package |
| yum module info module | examine details of a module |
| yum module info --profile module:stream | list packages installed by profiles of a module |
| yum module list module | display the current status of a module |
WORKING WITH MODULES
| Command | Explanation |
| ------- | ----------- |
| yum module enable module:stream | enable a specific stream without installing packages |
| yum module install module:stream/profile | install a specific stream |
| yum module remove module && yum module disable module | disable a module stream and remove all packages provided by it |
[dnf docs: Changes in DNF CLI compared to YUM](https://dnf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cli_vs_yum.html)
[What is the difference between DNF and YUM?](https://www.2daygeek.com/comparison-difference-between-dnf-vs-yum/)
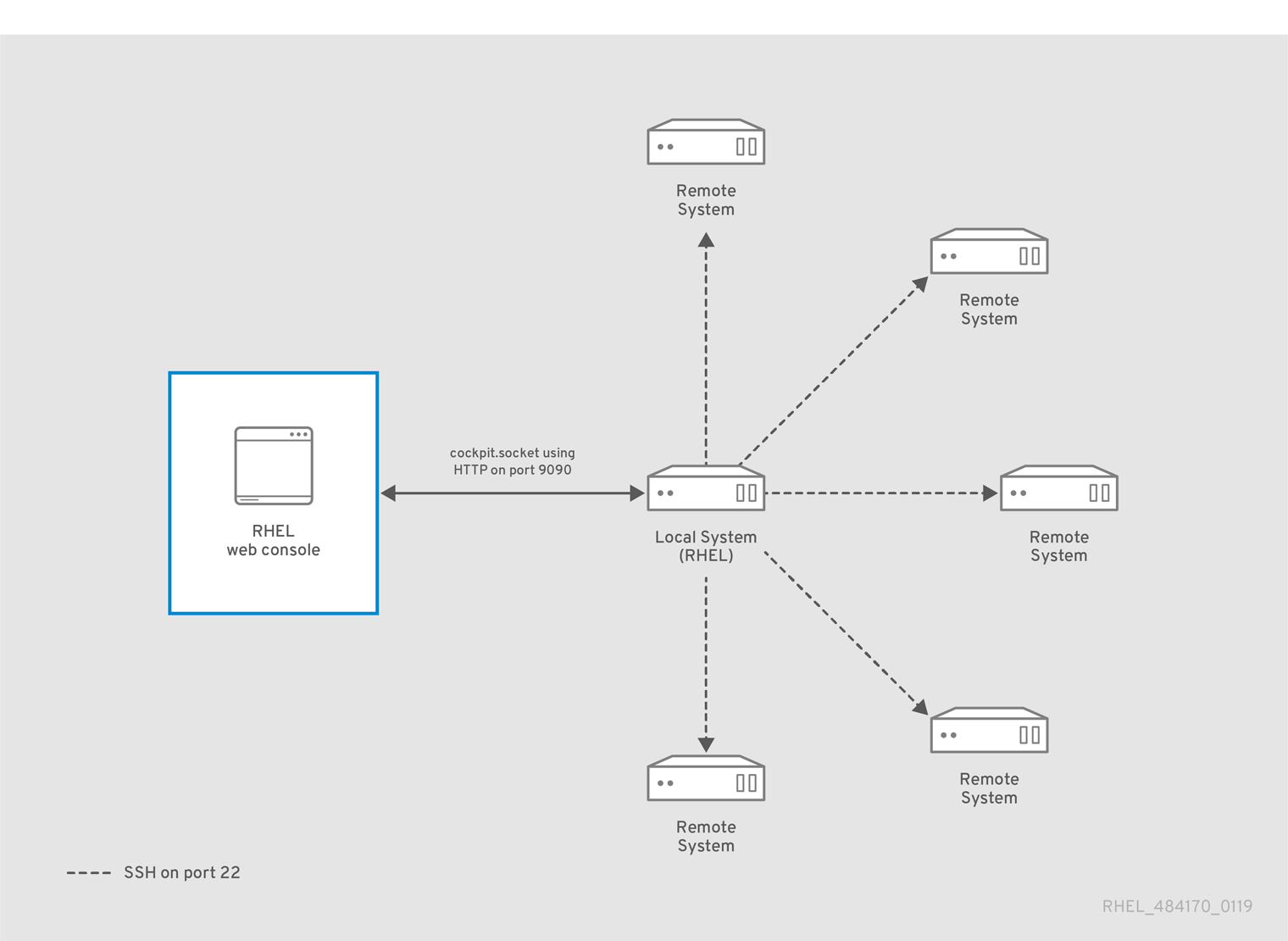
https://cockpit-project.org/
[Fedora Magazine: Cockpit and the evolution of the Web User Interface](https://fedoramagazine.org/cockpit-and-the-evolution-of-the-web-user-interface/)
[Managing user accounts with Cockpit](https://fedoramagazine.org/managing-user-accounts-with-cockpit/)

[RHEL 8 Docs: Managing systems using the RHEL 8 web console](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/managing_systems_using_the_rhel_8_web_console/index)
[RHEL 8 Docs: Composing a customized RHEL system image](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/composing_a_customized_rhel_system_image/index)
[Lorax is used to build the Anaconda Installer boot.iso](https://weldr.io/lorax/rhel8-branch/intro.html)
[Using Composer on RHEL 7.5 with mirrored repositories](https://weldr.io/Running-Composer-on-RHEL/)
[RedHat KB: Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) System Roles](https://access.redhat.com/articles/3050101)
[](https://linux-system-roles.github.io/)
[GitHub project: linux-system-roles ](https://github.com/linux-system-roles)
[Ansible Galaxy: Linux System Roles](https://galaxy.ansible.com/linux-system-roles)
[Ansible Doc: Roles](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_reuse_roles.html)
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux Presents... automation with RHEL System Roles](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=voRx1uqSvf4)
### 4. Adapting to Core System Changes
https://wayland.freedesktop.org/
| X11 | Wayland |
| --- | --- |
| 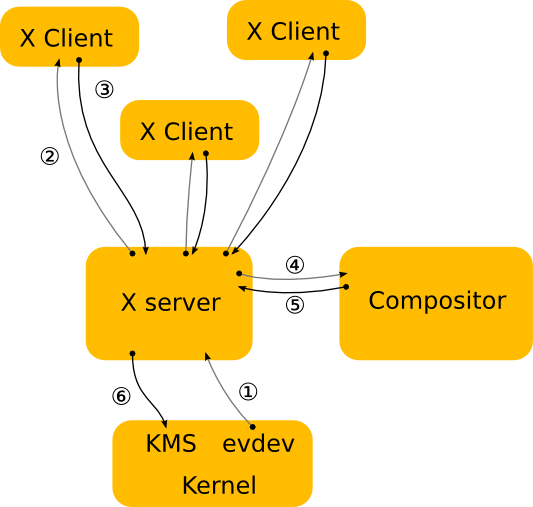| 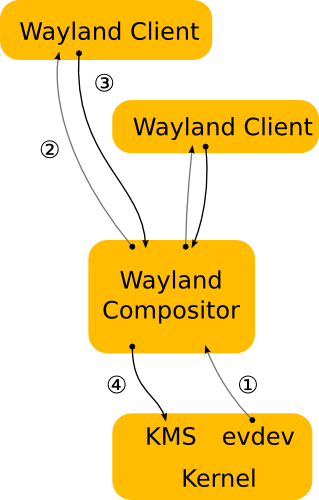 |
https://wiki.gnome.org/Initiatives/Wayland
[Habr: Что придет на замену X Window System?](https://habr.com/ru/post/321470/)
[Habr: Wayland на замену X Window System](https://habr.com/ru/post/322580/)
[Youtube Video: My name is Wayland](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ykC__9E34_s)
[Сказ о том, как Mir превратился в Wayland-композитор](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XlAkLx3UQPA)
[How to debug Wayland problems: Known issues, frequent complaints, fundamental changes](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/How_to_debug_Wayland_problems#Known_issues.2C_frequent_complaints.2C_fundamental_changes)
[FedoraProject Wiki: Wayland features Wayland Desktop features progress](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Wayland_features)
[Boycott Wayland! It breaks everything! BIG discussion about Wayland new features and unsolved issues](https://gist.github.com/probonopd/9feb7c20257af5dd915e3a9f2d1f2277)
[Reference wayland-server and standard desktop APIs](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/wayland/wayland/-/issues/233)
[tigerVNC github issue: TiverVNC do not support Wayland till now since 2015](https://github.com/TigerVNC/tigervnc/issues/158)
[RedHat KB: How to configure Virtual Network Computing (VNC) in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7/8 - 8.2?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/966063)
[Are there any changes to the default vncserver configuration in RHEL8.3?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/5544351)
Enable GNOME 3 [Looking Glass](https://wiki.gnome.org/Projects/GnomeShell/LookingGlass).
Looking Glass is GNOME Shell's integrated debugger and inspector tool
``
gsettings set org.gnome.shell development-tools true
``
[RHEL8 Docs: chronyc sources -v explained](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/system_administrators_guide/ch-configuring_ntp_using_the_chrony_suite#sect-Checking_chrony_sources)
[RHEL8 Docs: ](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html-single/configuring_authentication_and_authorization_in_rhel/index#configuring-user-authentication-using-authselect_configuring-authentication-and-authorization-in-rhel)
```
[student@workstation ~]$ python
bash: python: command not found...
```
[Red Hat Blogs: What, no Python in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8?](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2019/05/07/what-no-python-in-red-hat-enterprise-linux-8/)
[Python Developer Guide: The "python" Command on Unix-Like Systems](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0394/)
[Red Hat Blogs: Python in RHEL 8](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2018/11/14/python-in-rhel-8-3)
[Sunsetting Python 2. PSF support end date: 1 January 2020 ](https://www.python.org/doc/sunset-python-2/)
[Porting Python 2 Code to Python 3](https://docs.python.org/3/howto/pyporting.html)
[Python 3 support on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/2353081)
"Python 2.7 package in RHEL 8 support end at June 2024"
[RedHat KB: How is Python 2 supported in RHEL after 2020?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/4455511)
Optional (and not required for ansible) way to enable python command
```
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --list
python auto /usr/libexec/no-python
python3 auto /usr/bin/python3.6
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --display python
python - status is auto.
link currently points to /usr/libexec/no-python
/usr/libexec/no-python - priority 404
slave unversioned-python: (null)
slave unversioned-python-man: /usr/share/man/man1/unversioned-python.1.gz
/usr/bin/python3 - priority 300
slave unversioned-python: /usr/bin/python3
slave unversioned-python-man: /usr/share/man/man1/python3.1.gz
Current `best' version is /usr/libexec/no-python.
[student@workstation ~]$ file /usr/libexec/no-python
/usr/libexec/no-python: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable
[student@workstation ~]$ man unversioned-python
## Select one option
# Interactively select what the `python` command runs.
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --config python
# Configure the `python` command to run Python 3
# Note: this is non-standard behavior according to [PEP 394].
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --set python /usr/bin/python3
# Configure the `python` command to run Python 2
# Note: please review the support lifecycle of python2 before relying on it
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --set python /usr/bin/python2
# Undo configuration changes and revert to the default (missing `python` command)
[student@workstation ~]$ alternatives --auto python
```
[Python2 vs Python3 | Syntax and performance Comparison](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python2-vs-python3-syntax-and-performance-comparison/)

[Python in RHEL 8](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2018/11/14/python-in-rhel-8-3)
### 5. Implementing Storage Using New Features
Manage storage using the Stratis local storage management system and use VDO volumes to optimize storage space in use.
[Stratis Project ](https://stratis-storage.github.io/)
https://opensource.com/article/18/4/stratis-easy-use-local-storage-management-linux
https://opensource.com/article/18/4/stratis-lessons-learned
[RHEL8 Docs: Managing file systems: Chapter 17. Managing layered local storage with Stratis](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/managing_file_systems/managing-layered-local-storage-with-stratis_managing-file-systems)
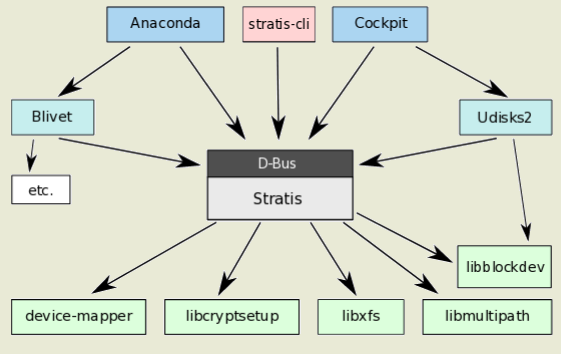
[Red hat Interactive Lab: Stratis](https://lab.redhat.com/stratis)
[RHEL8 Docs: Deduplicating and Compressing storage](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html-single/deduplicating_and_compressing_storage/index)


https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/introducing-virtual-data-optimizer-reduce-cloud-and-premise-storage-costs
[Red hat Interactive Lab: VDO](https://lab.redhat.com/vdo-configure)
https://www.opennet.ru/opennews/art.shtml?num=51828
### 6. Managing Containers with the New Runtime
[Open Container Initiative](https://opencontainers.org/)
[Expanded tools for containers and cloud workload management - what's new in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4](https://www.redhat.com/en/events/webinar/expanded-tools-for-containers-and-cloud-workload-management-what-new-red-hat-enterprise-linux)

[Getting Started with Podman](https://podman.io/getting-started/)

[Getting started with Buildah](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2021/01/11/getting-started-with-buildah)
image build example using Buildah commands
```bash
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -o errexit
# Create a container
container=$(buildah from fedora:28)
# Labels are part of the "buildah config" command
buildah config --label maintainer="Chris Collins <collins.christopher@gmail.com>" $container
# Grab the source code outside of the container
curl -sSL http://ftpmirror.gnu.org/hello/hello-2.10.tar.gz -o hello-2.10.tar.gz
buildah copy $container hello-2.10.tar.gz /tmp/hello-2.10.tar.gz
buildah run $container dnf install -y tar gzip gcc make
Buildah run $container dnf clean all
buildah run $container tar xvzf /tmp/hello-2.10.tar.gz -C /opt
# Workingdir is also a "buildah config" command
buildah config --workingdir /opt/hello-2.10 $container
buildah run $container ./configure
buildah run $container make
buildah run $container make install
buildah run $container hello -v
# Entrypoint, too, is a “buildah config” command
buildah config --entrypoint /usr/local/bin/hello $container
# Finally saves the running container to an image
buildah commit --format docker $container hello:latest
```
[cri-o lightweight container runtime for kubernetes](https://cri-o.io/)
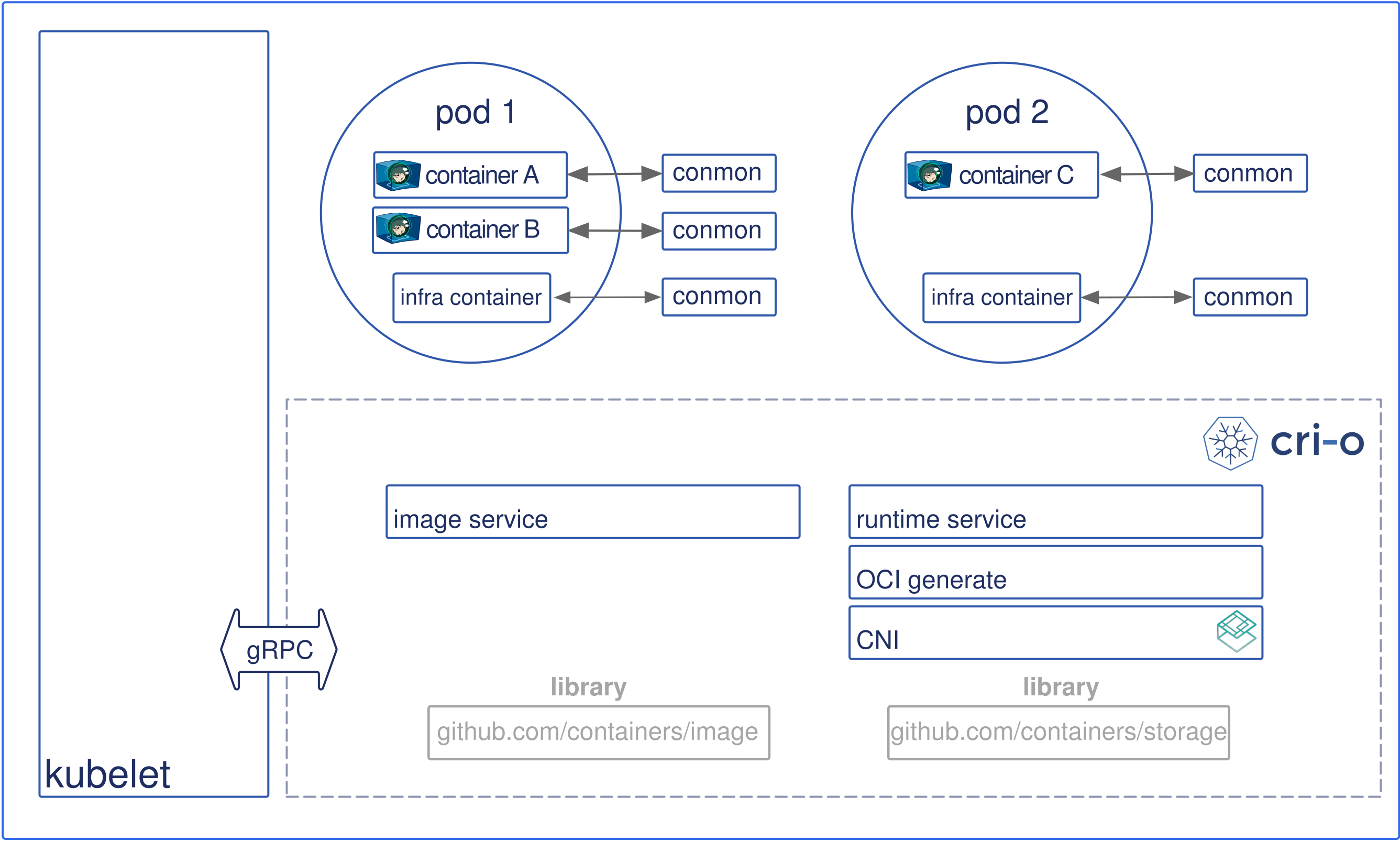
### 7. Implementing Enhanced Networking Features
[RedHat Developer Blog: iptables: The two variants and their relationship with nftables](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/08/18/iptables-the-two-variants-and-their-relationship-with-nftables)

[firewalld: A service daemon with D-Bus interface](https://firewalld.org/)
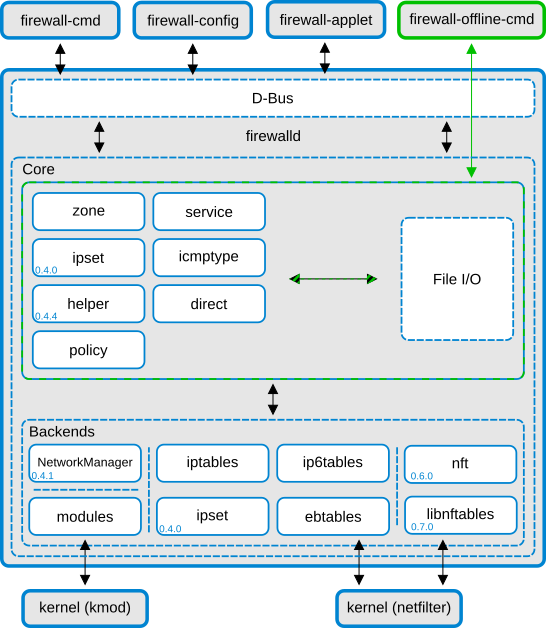
--- firewalld structure ---
[RedHat Developer Blog: If You Like Bonding, You Will Love Teaming](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/if-you-bonding-you-will-love-teaming)
[RHEL7 Docs: Comparison between bonding and teaming](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/networking_guide/sec-comparison_of_network_teaming_to_bonding)
### 8. Adapting to Virtualization Improvements
[What Is the Difference between QEMU and KVM?](https://www.packetcoders.io/what-is-the-difference-between-qemu-and-kvm/)
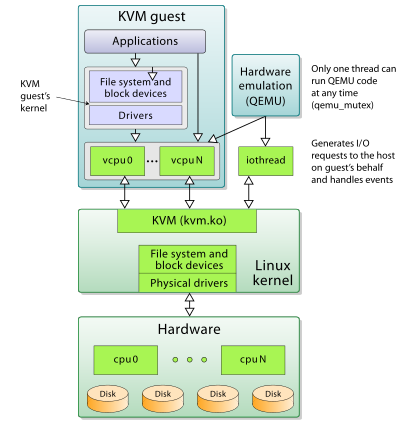
[KVM & Qemu](http://saravananlinux.blogspot.com/2015/07/kvm-qemu.html)
[www.linux-kvm.org FAQ](https://www.linux-kvm.org/)
- [What is the difference between KVM and QEMU?](https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/FAQ#What_is_the_difference_between_KVM_and_QEMU.3F)
QEMU uses emulation; KVM uses processor extensions (HVM) for virtualization.
[RedHat KB: How can I view, create, and remove SCSI persistent reservations and keys?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/43402)
[Intel® 82Q35 Graphics and Memory Controller chipset](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/31918/intel-82q35-graphics-and-memory-controller.html)
Windows inside RHEL 8 KVM
[Github Repo: KVM/QEMU Windows guest drivers (virtio-win)](https://github.com/virtio-win/kvm-guest-drivers-windows)
[RHEL8 CHAPTER 17. INSTALLING AND MANAGING WINDOWS VIRTUAL MACHINES](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_virtualization/installing-and-managing-windows-virtual-machines-on-rhel_configuring-and-managing-virtualization)
RHEL 8 inside Hyper-V
[поддерживаемые CentOS и Red Hat Enterprise Linux виртуальные машины в Hyper-V](https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows-server/virtualization/hyper-v/Supported-Linux-and-FreeBSD-virtual-machines-for-Hyper-V-on-Windows)
KVM GPU Passthrough:
* [GitLab Project: Single GPU Passthrough Community Guide](https://gitlab.com/risingprismtv/single-gpu-passthrough/-/wikis/home)
* [Don't Dual Boot, Do this instead | MacOS Big Sur and Windows 10 KVM SINGLE GPU OVMF Passthrough](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_JTEsQufSx4)
[RHEL 8 WorkShop](http://redhatgov.io/workshops/rhel_8/)
Workshop Description
This workshop will cover the features, specifications and improvements that comprise the release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux Version 8 (RHEL 8).
* Exercise 1.0 - Welcome to RHEL!
* Exercise 1.1 - What's New in RHEL 8
* Exercise 1.2 - Tour of the Web Console
* Exercise 1.3 - Managing Updates Using the Web Console
* Exercise 1.4 - Configuring Terminal Session Recording
* Exercise 1.5 - Managing Cryptographic Policies
* Exercise 1.6 - Managing Software in an Application Stream
* Exercise 1.7 - OpenSCAP Security Compliance Scanning
* Exercise 1.8 - Introduction to using buildah, podman and skopeo to work on containers
* Exercise 1.9 - System Roles with Ansible