662.Maximum Width of Binary Tree
===
###### tags: `Medium`,`Tree`,`BFS`,`DFS`
[662. Maximum Width of Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/)
### 題目描述
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return *the **maximum width** of the given tree.*
The **maximum width** of a tree is the maximum **width** among all levels.
The **width** of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is **guaranteed** that the answer will in the range of a **32-bit** signed integer.
### 範例
**Example 1:**
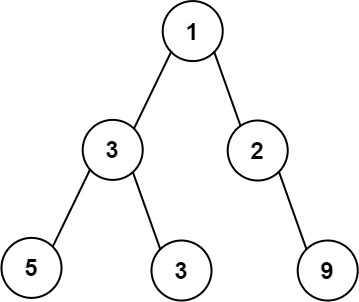
```
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output: 4
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
```
**Example 2:**
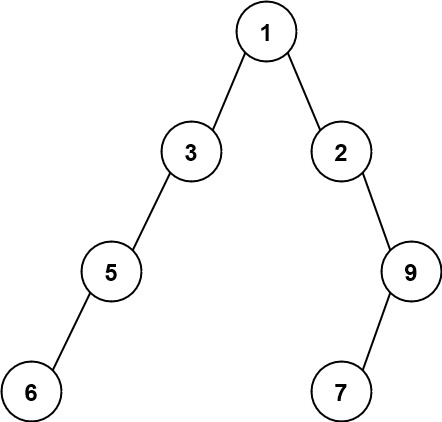
```
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7]
Output: 7
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
```
**Example 3:**
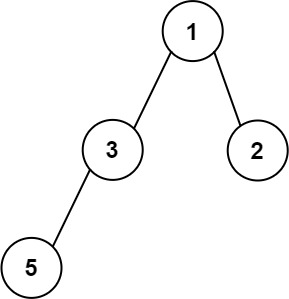
```
Input: root = [1,3,2,5]
Output: 2
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
```
**Constraints**:
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[1, 3000]`.
* -100 <= `Node.val` <= 100
### 解答
#### Python
```python=
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
q = deque([(root, 0, 0)])
dic = defaultdict(list)
while q:
node, level, idx = q.popleft()
dic[level].append(idx)
if node.left:
q.append((node.left, level + 1, 2 * idx))
if node.right:
q.append((node.right, level + 1, 2 * idx + 1))
max_width = 0
for nodes in dic.values():
width = nodes[-1] - nodes[0] + 1
max_width = max(max_width, width)
return max_width
```
> [name=Ron Chen][time=Thu, Apr 20, 2023]
#### Javascript
```javascript=
function widthOfBinaryTree(root) {
let max = 1;
const queue = [[root, 0]];
while (queue.length) {
const n = queue.length;
if (n === 1) queue[0][1] = 1;
const [left, right] = [queue[0][1], queue[n - 1][1]];
max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const [node, index] = queue.shift();
if (node.left) queue.push([node.left, index * 2]);
if (node.right) queue.push([node.right, index * 2 + 1]);
}
}
return max;
}
```
> [name=Marsgoat][time=Thu, Apr 20, 2023]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)