328.Odd Even Linked List
===
###### tags: `Medium`,`Linked List`
[328. Odd Even Linked List](https://leetcode.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/)
### 題目描述
Given the `head` of a singly linked list, group all the nodes with odd indices together followed by the nodes with even indices, and return the reordered list.
The **first** node is considered **odd**, and the **second** node is **even**, and so on.
Note that the relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
You must solve the problem in $O(1)$ extra space complexity and $O(n)$ time complexity.
### 範例
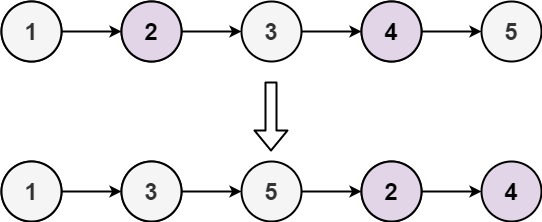
**Example 1:**
```
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,3,5,2,4]
```
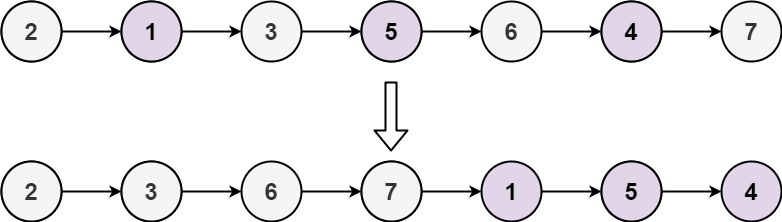
**Example 2:**
```
Input: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
Output: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
```
**Constraints**:
* The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range [0, 10^4^].
* -10^6^ <= `Node.val` <= 10^6^
### 解答
#### Javascript
```javascript=
function oddEvenList(head) {
if (head === null) return null;
let odd = head;
let even = head.next;
const evenHead = even;
while (even && even.next) {
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
```
> [name=Marsgoat][time= Dec 6, 2022]
#### Python
```python=
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return head
odd, even = head, head.next
evenHead = even
while even and even.next:
odd.next = odd.next.next
even.next = even.next.next
odd = odd.next
even = even.next
odd.next = evenHead
return head
```
> [name=Kobe][time= Dec 6, 2022]
#### C#
```csharp=
public class Solution {
public ListNode OddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode odd = head;
ListNode even = head.next;
ListNode evenHead = even;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd = odd.next = even.next;
even = even.next = even.next.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}
```
> [name=Jim][time= Dec 6, 2022]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)