2090.K Radius Subarray Averages
===
###### tags: `Medium`,`Array`,`Sliding Window`
[2090. K Radius Subarray Averages](https://leetcode.com/problems/k-radius-subarray-averages/description/)
### 題目描述
You are given a **0-indexed** array `nums` of `n` integers, and an integer `k`.
The **k-radius average** for a subarray of `nums` **centered** at some index `i` with the **radius** `k` is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return *an array* `avgs` *of length* `n` *where* `avgs[i]` *is the **k-radius average** for the subarray centered at index* `i`.
The **average** of `x` elements is the sum of the `x` elements divided by `x`, using **integer division**. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
* For example, the average of four elements `2`, `3`, `1`, and `5` is `(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75`, which truncates to `2`.
### 範例
**Example 1:**
```
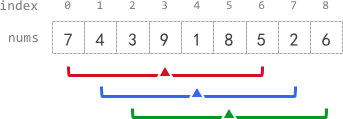
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3
Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1]
Explanation:
- avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index.
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37.
Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5.
- For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4.
- For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4.
- avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
```
**Example 2:**
```
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0
Output: [100000]
Explanation:
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000.
avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
```
**Example 3:**
```
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000
Output: [-1]
Explanation:
- avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
```
**Constraints**:
* `n` == `nums.length`
* 1 <= `n` <= 10^5^
* 0 <= `nums[i]`, `k` <= 10^5^
### 解答
#### Javascript
```javascript=
function getAverages(nums, k) {
const result = Array(nums.length).fill(-1);
const length = 2 * k + 1;
let sum = 0;
let left = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
if (i >= length - 1) {
result[i - k] = Math.floor(sum / length);
sum -= nums[left];
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
```
> 記錄一下第一次使用leetcode的計時功能,從讀題到AC共花15分3秒。
> [name=Marsgoat][time=Tue, Jun 20, 2023]
#### C++
``` cpp
using LL = long long int;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
if (k == 0) {
return nums;
}
int n = nums.size();
vector<LL> prefixSum(n + 1, 0);
prefixSum[1] = nums[0];
for (int i = 2; i < n + 1; i ++) {
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
vector<int> ans(n, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (i - k < 0 or i + k >= n) {
continue;
}
ans[i] = (prefixSum[i + k + 1] - prefixSum[i - k]) / (2 * k + 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|:--------- | --- | --- | --- | --- |:--- | --- | --- |:--- |:--- |:--- |
| nums | 7 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 6 | |
| prefixSum | 0 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 23 | 24 | 32 | 37 | 39 | 45 |
> [name=Jerry Wu][time=20 June, 2023]
#### C#
```csharp=
public class Solution {
public int[] GetAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
if (k == 0) return nums;
int n = nums.Length;
int slide = k * 2 + 1;
int[] ans = new int[n];
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans[i] = -1;
sum += nums[i];
if (i >= slide - 1) {
ans[i - k] = (int)(sum / slide);
sum -= nums[i - slide + 1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
> [name=Jim][time=Jun 20, 2023]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)