1572.Matrix Diagonal Sum
===
###### tags: `Easy`,`Array`,`Matrix`
[1572. Matrix Diagonal Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/matrix-diagonal-sum/)
### 題目描述
Given a square matrix `mat`, return the sum of the matrix diagonals.
Only include the sum of all the elements on the primary diagonal and all the elements on the secondary diagonal that are not part of the primary diagonal.
### 範例
**Example 1:**
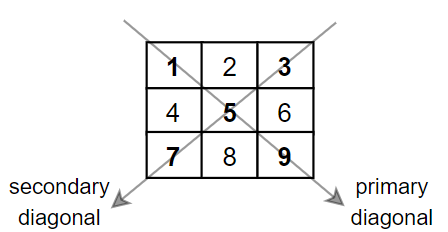
```
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]]
Output: 25
Explanation: Diagonals sum: 1 + 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 25
Notice that element mat[1][1] = 5 is counted only once.
```
**Example 2:**
```
Input: mat = [[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1]]
Output: 8
```
**Example 3:**
```
Input: mat = [[5]]
Output: 5
```
**Constraints**:
* `n` == `mat.length` == `mat[i].length`
* 1 <= `n` <= 100
* 1 <= `mat[i][j]` <= 100
### 解答
#### Python
```python=
class Solution:
def diagonalSum(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(mat)
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
ans += mat[i][i] + mat[i][n - i - 1]
if n & 1:
ans -= mat[n // 2][n // 2]
return ans
```
> [name=Yen-Chi Chen][time=Mon, May 8, 2023]
```python=
class Solution:
def diagonalSum(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int:
return sum([mat[i][i] + mat[i][len(mat) - i - 1] if i != len(mat) - i - 1 else mat[i][i] for i in range(len(mat))])
```
> [name=Ron Chen][time=Mon, May 8, 2023]
#### Javascript
```javascript=
function diagonalSum(mat) {
let sum = 0;
const n = mat.length - 1;
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
if (i === j || n - i === j || n - j === i) {
sum += mat[i][j];
}
}
}
return sum;
}
```
> [name=Marsgoat][time=Mon, May 8, 2023]
#### TypeScript
```typescript=
function diagonalSum(mat: number[][]): number {
const matLength = mat.length;
const midIndex = ~~(matLength / 2);
let primarySum = 0;
let secondarySum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < matLength; i++) {
primarySum += mat[i][i];
secondarySum += mat[i][matLength - 1 - i];
}
return matLength % 2
? primarySum + secondarySum - mat[midIndex][midIndex]
: primarySum + secondarySum;
}
```
> [name=Sheep][time=Mon, May 8, 2023]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)