1372.Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree
===
###### tags: `Medium`,`Tree`,`DP`,`DFS`
[1372. Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-zigzag-path-in-a-binary-tree/)
### 題目描述
You are given the `root` of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
* Choose **any** node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
* If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
* Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
* Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return *the longest **ZigZag** path contained in that tree.*
### 範例
**Example 1:**
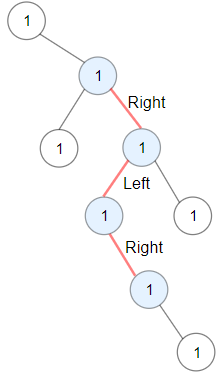
```
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
```
**Example 2:**
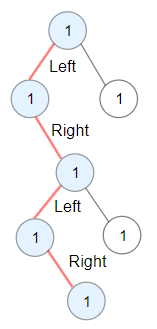
```
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
```
**Example 3:**
```
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
```
**Constraints**:
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 5 * 10^4^].
* 1 <= `Node.val` <= 100
### 解答
#### Javascript
```javascript=
function longestZigZag(root) {
let longest = 0;
const stack = [[root, 0, 0]];
while (stack.length) {
const [node, left, right] = stack.pop();
if (node === null) continue;
longest = Math.max(longest, left, right);
stack.push([node.left, right + 1, 0]);
stack.push([node.right, 0, left + 1]);
}
return longest;
}
```
> [name=Marsgoat][time=Apr 19, 2023]
#### Python
```python=
class Solution:
def longestZigZag(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.pathLength = 0
# goLeft: Next step go left or not
def dfs(node, goLeft, steps):
if node:
self.pathLength = max(self.pathLength, steps)
if goLeft:
dfs(node.left, False, steps + 1) # Continue to the left
dfs(node.right, True, 1) # Restart to the right
else:
dfs(node.left, False, 1) # Restart to the left
dfs(node.right, True, steps + 1) # Continue to the right
dfs(root, False, 0) # Left start
dfs(root, True, 0) # Right start
return self.pathLength
```
> [name=Ron Chen][time=Wed, Apr 19, 2023]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)