1235.Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
===
###### tags: `Hard`,`Array`,`DP`,`Sorting`,`Binary Search`
[1235. Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/)
### 題目描述
We have `n` jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from `startTime[i]` to `endTime[i]`, obtaining a profit of `profit[i]`.
You're given the `startTime`, `endTime` and `profit` arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time `X` you will be able to start another job that starts at time `X`.
### 範例
**Example 1:**
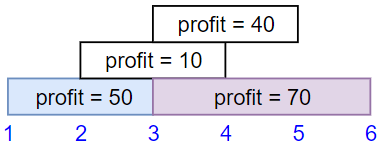
```
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70]
Output: 120
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job.
Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
```
**Example 2:**
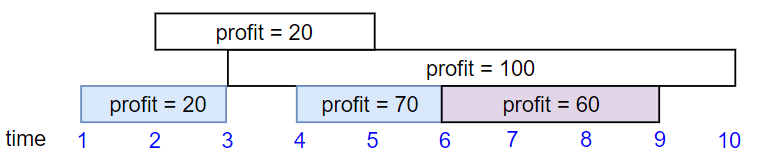
```
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60]
Output: 150
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job.
Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
```
**Example 3:**
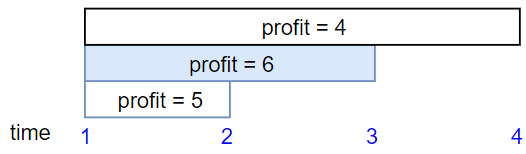
```
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4]
Output: 6
```
**Constraints**:
* `1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <=` $5 * 10^4$
* `1 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <=` $10^9$
* `1 <= profit[i] <=` $10^4$
### 解答
#### C++
```cpp=
struct Job {
int start, end, profit;
bool operator<(const Job &rhs) const {return end < rhs.end;}
};
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int n = startTime.size();
vector<Job> jobs(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
jobs[i].start = startTime[i];
jobs[i].end = endTime[i];
jobs[i].profit = profit[i];
}
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
vector<int> dp(n+1, 0);
int best = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
auto job = jobs[i];
Job fake;
fake.end = job.start + 1;
int k = lower_bound(jobs.begin(), jobs.end(), fake) - jobs.begin();
int value = dp[k] + job.profit;
if (value > best) {
dp[i+1] = value;
best = value;
} else {
dp[i+1] = best;
}
}
return best;
}
};
```
> [name=Yen-Chi Chen][time=Sun, Nov 26, 2022 10:08 PM]
#### Python
```python=
class Solution:
def jobScheduling(self, startTime: List[int], endTime: List[int], profit: List[int]) -> int:
jobs = sorted(zip(startTime, endTime, profit), key=lambda job: job[1])
best = 0
dp = [[0, best]]
for start, end, profit in jobs:
k = bisect.bisect(dp, [start+1])
v = dp[k-1][1] + profit
if v > best:
best = v
dp.append([end, best])
return best
```
> [name=Yen-Chi Chen][time=Sun, Nov 26, 2022 10:08 PM]
Time: $O(n\log n)$
Extra Space: $O(n)$
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)