[1514. Path with Maximum Probability](https://leetcode.com/problems/path-with-maximum-probability/)
### 題目描述
You are given an undirected weighted graph of `n` nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where `edges[i] = [a, b]` is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge `succProb[i]`.
Given two nodes `start` and `end`, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from `start` to `end` and return its success probability.
If there is no path from `start` to `end`, **return 0**. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most **1e-5**.
### 範例
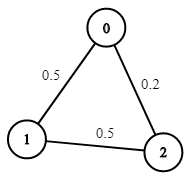
**Example 1:**
```
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.25000
Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
```
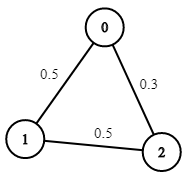
**Example 2:**
```
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.30000
```
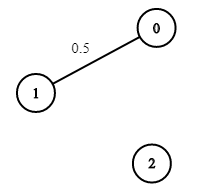
**Example 3:**
```
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.00000
Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
```
**Constraints**:
* 2 <= `n` <= 10^4^
* 0 <= `start`, `end` < `n`
* `start` != `end`
* 0 <= `a`, `b` < `n`
* `a` != `b`
* 0 <= `succProb.length` == `edges.length` <= 2*10^4^
* 0 <= `succProb[i]` <= 1
* There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
### 解答
#### C++
``` cpp=
class Solution {
public:
const double INF = numeric_limits<double>::max();
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
vector<double> distance(n, INF);
vector<int> adj[n];
vector<vector<double>> logProb(n, vector<double>(n, INF));
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i ++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
logProb[u][v] = -log2(succProb[i]);
logProb[v][u] = -log2(succProb[i]);
}
auto cmp = [&distance](const int u, const int v) {
return distance[u] < distance[v];
};
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> frontier(cmp);
distance[start] = 0.;
frontier.push(start);
while (not frontier.empty()) {
int u = frontier.top();
frontier.pop();
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (distance[u] + logProb[u][v] < distance[v]) {
distance[v] = distance[u] + logProb[u][v];
frontier.push(v);
}
}
}
return pow(2, -distance[end]);
}
};
```
Dijkstra's algorithm, TLE when `n=10000`
---
``` cpp=
class Solution {
public:
const double INF = numeric_limits<double>::max();
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
vector<vector<pair<int, double>>> adj(n);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i ++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
adj[u].push_back({v, succProb[i]});
adj[v].push_back({u, succProb[i]});
}
vector<double> distance(n, 0.);
distance[start] = 1.;
queue<int> frontier;
frontier.push(start);
while (not frontier.empty()) {
int u = frontier.front();
frontier.pop();
for (const auto [v, prob] : adj[u]) {
if (distance[u] * prob > distance[v]) {
distance[v] = distance[u] * prob;
frontier.push(v);
}
}
}
return distance[end];
}
};
```
BFS, Beats 93.16%
> [name=Jerry][time=28 June, 2023]
### Reference
[回到題目列表](https://hackmd.io/@Marsgoat/leetcode_every_day)