> []# CE - Abitur - Exam - Checklist
## Java:
- ### Terminology:
- Class
- Methods
- Encapsulation/Modifiers
- private
- public
- protected
- Variables
- Abstract
- Interfaces
</br>
- #### UML-Diagram
> 
</br>
- UML: attribute private mit Datentyp dazu schreiben
- Data Types
- Parameters
- Data Structures
- Array
- List
- Stacks
- Queue
- Sorting Algorithms
- Nur SQL - (Order By)
## FX:
- Hyperlinks
- Icons
- Images
- Application Name
- Tableviews
- Observable Lists
- AWT - Nur Paket einbinden nicht nutzen
- Finite State-Machines
## Databases:
- ### Normalization
> ### Student Course (**1NF**)
> | StudentNo | CourseNo | CourseName | InstructorNo | InstructorName | InstructorLocation | Grade |
> | --------- | -------- | ---------- | ------------ | -------------- | ------------------ | ----- |
> | - | - | - | - | -| - | - |
> ### Student (**2NF**)
> | StudentNo | StudentName |
> | --------- | ----------- |
> | - | - | - |
> ### StudentCoruse (**2NF**)
> | StudentNo | CourseNo | Grade |
> | --------- | -------- | ----- |
> | - | - | - |
> ### Course (**2NF**)
> | CourseNo | CourseName | InstructorNo | InstructorName | InstructorLocation |
> | -------- | ---------- | ------------ | -------------- | ------------------ |
> | - | - | - | - | - |
> #### Explanation 2NF
> To achieve the 2NF we need to remove all partial dependencies. This means that every column that is only partially dependend on the compound primary key is to be separated. In this case `CourseName` is only depended on `CourseNo` and thus should be put into a seperate table. Furthermore `InstructorNo` and `InstructorName` are only depended on `CourseNo` and should thereby also be seperated accordingly.
> ### Student (**3NF**)
> | StudentNo | StudentName | CourseNo |
> | --------- | ----------- | -------- |
> | - | - | - |
> ### StudentCourse (**3NF**)
> | StudentNo | CourseNo | Grade |
> | --------- | -------- | ----- |
> | - | - | - |
> ### Course (**3NF**)
> | CourseNo | CourseName | InstructorNo |
> | -------- | ---------- | ------------ |
> | - | - | - |
> ### Instructor (**3NF**)
> | InstructorNo | InstructorName | InstructorLocation |
> | ------------ | -------------- | ------------------ |
> | - | - | - |
> #### Explanation
> In the third normal form we have to remove all transitive dependencies. These are columns which are dependent on other (non primary-key) columns in the same table. In this case these are `InstructorName` and `InstructorLocation` which are dependent on `InstructorNo`. Thus we have to add a new table for them.
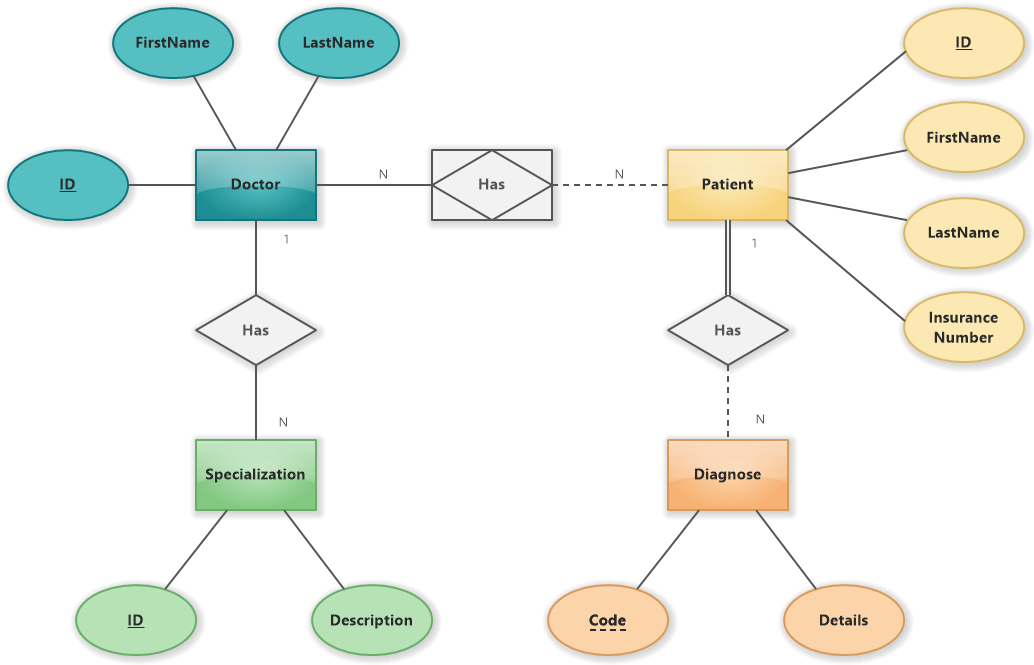
- #### ER-Diagrams
> 
</br>
- ER-Schlüsselattribut unterstreichen (ID)
- ### MySql:
- #### [SQL Statements](https://www.w3schools.com/mysql/mysql_sql.asp)
- `SELECT`
- `INSERT`
- `WHERE` / `LIKE`
- `UPDATE`
- `DELETE` / `DROP`
- `JOIN`
- Keys:
- Foreign
- Primary
## Questions:
- Describe Object Oriented Programming (OOP) and make use of the terms: encapsulation, inheritance, overwriting, overloading, class, object, constructor, modifiers, abstraction. Additionally, explain the concepts of Abstract classes and Interfaces:
- The four main concepts of Object Oriented Programming are encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. Encapsulation describes the process of bundling data into a single unit like an object or a class. A class is a blueprint/ template on how to build an object. Objects are instances of that class that are created with a constructor method. Encapsulated information includes attributes that store information and methods that perform actions. Encapsulation also includes hiding certain information or restricting the access to them. Controlling the access on information can be achieved with the use of modifiers like public, private, or protected that, as the name suggests, specify who can see or access something. Inheritance allows classes to inherit the information and methods of other classes. That way classes that share methods or attributes can all be the subclass or a parent class which provides them with said information. In Java a class can only inherit from one class. This also plays into the next concpet, Polymorphism. Polymorphis means "many forms" and in programming describes how one thing can have multiple meanings. One example of that is overloading a method. Methods can have the same name, but have different actions based on the parameters you pass into them. Different classes can also have methods with the same name and parameters but also do different things. This way you use one method on different objects and achieve different results. Another way to achieve this is by overriding a method which allows you to redefine a method that was already defined. Abstraction means to use simple things to represent complexity, like only having to use a method rather than all the code that it includes, or to hide details from the user. Abstract classes are classes with the abstract modifier. An Interface is a blueprint for a class. Both can't be instantiated, but can include abstract methods. An abstract class can have static and non static fields and both normal and abstract methods. Interfaces can only have static fields and abstract methods. A class can only extend extend one abstract class but multiple interfaces. That way multiple inheritance can be achieved. Abstract methods have to be implemented by classes that inherit or implement them which can be useful to ensure that certain classes have certain methods.
- These are just the terms copied from above not the questions :)
- Just imagine things like: What are the differences between abstract classes and interfaces?:
- Why do we normalize data?
- Reduce redundancy, work more efficiently
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/classes-objects-java/
- What is an Object?:
- In Java an Object is an instance of a class that has a state and a behavior. Its state is represented by fields (variables/attributes) while its behavior is represented by methods. Objects are created from classes that inherit from the Object class. Primitve datatypes like int and float are not objects. In other words, complex datatypes are classes and objects are instances of said classes.
- What is SQL?:
- SQL or Structured Query Language is a language used in programming to communicate with relational databases systems. With it you can access and manipulate databases.
- What are relational databases?:
- Relational Databases are databases that are structured like tables (with rows and columns) to represent connections/relations between the items/information stored in them which makes it easy for humans to understand and use.
- What is a class?:
- In Java a class is a template for the creation of an object that encapsulates fields and methods into one entity.
Deutlich vor 8:30 Uhr Uhr da sein in 2.1.08
## Ablauf
JAVAFX:
- java zip entpacken und in eclipse starten in ordner mit schreibrechten
- einstellungen machen
- gegebene version ausbauen
- 2 Schwerpunkte:
1. JavaFX Componenten: ListView, CheckBox, ChoiceBox, Button, Label, App Name, Icon
- Anordnen nach grafischer Vorlage
- Datentypentwicklung:
Bsp: Complexer Datentyp z.B. Auto, Pkw und SUV sind Fahrzeuge, Fahrrad auch (Angucken: Constructor im UML | UML-Diagram kleine Aufgabe)
2. ähnlich mit weniger komponenten aber dafür mit Listen arbeiten (ArrayList, List, LinkedList, ObservableList)
im Hintergrund (Verladebeispiel) Einfach mit Button events arbeiten (nichts kompliziertes)
(komplett getrennt)
DATENBANKEN:
- zu allen Aufgaben allgemeine Frage: z.B. "Wofür verwendet man eigentlich Datenbanken?"
- aus Text entity relation diagramm erstellen oder oder aus ER Diagram Textuelle Beschreibung
- Was ist sql: SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, HAVING
- In beide Richtung SQL Notation zu Text und zurück (mehr als eine möglichkeit dinge zu beantworten)
- 1. -> 2. -> 3. Normalform von Tabelle erstellen (Datenbank ausgedruckt: Sagen welcher Angestellter ob ein bestimmter Angestellter enthalten ist (SELECT))
- SQL nur theoretisch
- Questions about database systems
- Fragen zu Datenbanken: Was ist eine Datenbank, Relationale Datenbank
Zu beiden Teilen Fragen wie: "Was ist ein Objekt? Weiterführend was ist kein Objekt"
Teile:
1. FX-Projekt mit Aufgaben
2. Datenbanken
## Code für Beispiel FX
### Main
package application;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.fxml.FXMLLoader;
public class Main extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
try {
BorderPane root = (BorderPane)FXMLLoader.load(getClass().getResource("Prepper.fxml"));
Scene scene = new Scene(root,1000,500);
scene.getStylesheets().add(getClass().getResource("application.css").toExternalForm());
primaryStage.setTitle("Another Prepper");
primaryStage.getIcons().add(new Image(getClass().getResourceAsStream("gigachad.jpg")));
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
### Controller
package application;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javafx.beans.InvalidationListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ChangeListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.fxml.FXML;
import javafx.fxml.Initializable;
import javafx.scene.control.CheckBox;
import javafx.scene.control.ChoiceBox;
import javafx.scene.control.Hyperlink;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
public class PrepperController implements Initializable{
@FXML
private Label label;
@FXML
private ChoiceBox<Item> choiceBox;
@FXML
private Hyperlink hyperLink;
@FXML
private ListView<Item> listView;
@FXML
private TableView<Item> tabelView;
@FXML
private TableColumn<Item, Integer> item_ID;
@FXML
private TableColumn<Item, String> item_Name;
ArrayList<Item> items = new ArrayList<Item>(Arrays.asList(
new Item(0,"Ball"),
new Item(1,"Phone"),
new Item(2,"Bottle"),
new Item(3,"Keyboard")
));
ObservableList<Item> itemsOL = FXCollections.observableArrayList();
ObservableList<Item> itemsOL2 = FXCollections.observableArrayList();
private void initTabel() {
itemsOL.addAll(items);
item_ID.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<Item, Integer>("id"));
item_Name.setCellValueFactory(new PropertyValueFactory<Item, String>("name"));
tabelView.getItems().addAll(itemsOL);
tabelView.getSelectionModel().selectedItemProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Item>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Item> arg0, Item arg1, Item arg2) {
label.setText(tabelView.getSelectionModel().getSelectedItem().getName());
}
});
}
@FXML
private void link(ActionEvent event) throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
Desktop.getDesktop().browse(new URI("https://www.youtube.com"));
}
private void initListView() {
//listView.getItems().addAll(items);
itemsOL2.addAll(items);
listView.getItems().addAll(itemsOL2);
listView.getSelectionModel().selectedItemProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Item>() {
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Item> arg0, Item arg1, Item arg2) {
label.setText(listView.getSelectionModel().getSelectedItem().getName());
}
});
}
private void visible(ActionEvent event) {
if(label.isVisible()==true)
label.setVisible(false);
else label.setVisible(true);
}
private void choice(ActionEvent event) {
label.setText(choiceBox.getSelectionModel().getSelectedItem().getName());
}
private void initBox() {
choiceBox.getItems().addAll(items);
choiceBox.setOnAction(this::choice);
}
@Override
public void initialize(URL arg0, ResourceBundle arg1) {
initListView();
initBox();
initTabel();
}
}
### Item
package application;
public class Item {
private int id;
private String name;
//constructor
public Item(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//getter/setter
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

