# openai-using-the-realitime-API
Realtime API
Beta
====================
Build low-latency, multi-modal experiences with the Realtime API.
The OpenAI Realtime API enables low-latency, multimodal interactions including speech-to-speech conversational experiences and real-time transcription.
This API works with natively multimodal models such as [GPT-4o](/docs/models/gpt-4o-realtime) and [GPT-4o mini](/docs/models/gpt-4o-mini-realtime), offering capabilities such as real-time text and audio processing, function calling, and speech generation, and with the latest transcription models [GPT-4o Transcribe](/docs/models/gpt-4o-transcribe) and [GPT-4o mini Transcribe](/docs/models/gpt-4o-mini-transcribe).
Get started with the Realtime API
---------------------------------
You can connect to the Realtime API in two ways:
* Using [WebRTC](#connect-with-webrtc), which is ideal for client-side applications (for example, a web app)
* Using [WebSockets](#connect-with-websockets), which is great for server-to-server applications (from your backend or if you're building a voice agent over phone for example)
Start by exploring examples and partner integrations below, or learn how to connect to the Realtime API using the most relevant method for your use case below.
### Example applications
Check out one of the example applications below to see the Realtime API in action.
[
Realtime Console
To get started quickly, download and configure the Realtime console demo. See events flowing back and forth, and inspect their contents. Learn how to execute custom logic with function calling.
](https://github.com/openai/openai-realtime-console)[
Realtime Solar System demo
A demo of the Realtime API with the WebRTC integration, navigating the solar system through voice thanks to function calling.
](https://github.com/openai/openai-realtime-solar-system)[
Twilio Integration Demo
A demo combining the Realtime API with Twilio to build an AI calling assistant.
](https://github.com/openai/openai-realtime-twilio-demo)[
Realtime API Agents Demo
A demonstration of handoffs between Realtime API voice agents with reasoning model validation.
](https://github.com/openai/openai-realtime-agents)
### Partner integrations
Check out these partner integrations, which use the Realtime API in frontend applications and telephony use cases.
[
LiveKit integration guide
How to use the Realtime API with LiveKit's WebRTC infrastructure.
](https://docs.livekit.io/agents/openai/overview/)[
Twilio integration guide
Build Realtime apps using Twilio's powerful voice APIs.
](https://www.twilio.com/en-us/blog/twilio-openai-realtime-api-launch-integration)[
Agora integration quickstart
How to integrate Agora's real-time audio communication capabilities with the Realtime API.
](https://docs.agora.io/en/open-ai-integration/get-started/quickstart)[
Pipecat integration guide
Create voice agents with OpenAI audio models and Pipecat orchestration framework.
](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/features/openai-audio-models-and-apis)[](https://github.com/craigsdennis/talk-to-javascript-openai-workers)
[
](https://github.com/craigsdennis/talk-to-javascript-openai-workers)
[
Client-side tool calling
](https://github.com/craigsdennis/talk-to-javascript-openai-workers)
[](https://github.com/craigsdennis/talk-to-javascript-openai-workers)
[Built with Cloudflare Workers, an example application showcasing client-side tool calling. Also check out the](https://github.com/craigsdennis/talk-to-javascript-openai-workers) [tutorial on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TcOytsfva0o).
Use cases
---------
The most common use case for the Realtime API is to build a real-time, speech-to-speech, conversational experience. This is great for building [voice agents](/docs/guides/voice-agents) and other voice-enabled applications.
The Realtime API can also be used independently for transcription and turn detection use cases. A client can stream audio in and have Realtime API produce streaming transcripts when speech is detected.
Both use-cases benefit from built-in [voice activity detection (VAD)](/docs/guides/realtime-vad) to automatically detect when a user is done speaking. This can be helpful to seamlessly handle conversation turns, or to analyze transcriptions one phrase at a time.
Learn more about these use cases in the dedicated guides.
[
Realtime Speech-to-Speech
Learn to use the Realtime API for streaming speech-to-speech conversations.
](/docs/guides/realtime-conversations)[
Realtime Transcription
Learn to use the Realtime API for transcription-only use cases.
](/docs/guides/realtime-transcription)
Depending on your use case (conversation or transcription), you should initialize a session in different ways. Use the switcher below to see the details for each case.
Connect with WebRTC
-------------------
[WebRTC](https://webrtc.org/) is a powerful set of standard interfaces for building real-time applications. The OpenAI Realtime API supports connecting to realtime models through a WebRTC peer connection. Follow this guide to learn how to configure a WebRTC connection to the Realtime API.
### Overview
In scenarios where you would like to connect to a Realtime model from an insecure client over the network (like a web browser), we recommend using the WebRTC connection method. WebRTC is better equipped to handle variable connection states, and provides a number of convenient APIs for capturing user audio inputs and playing remote audio streams from the model.
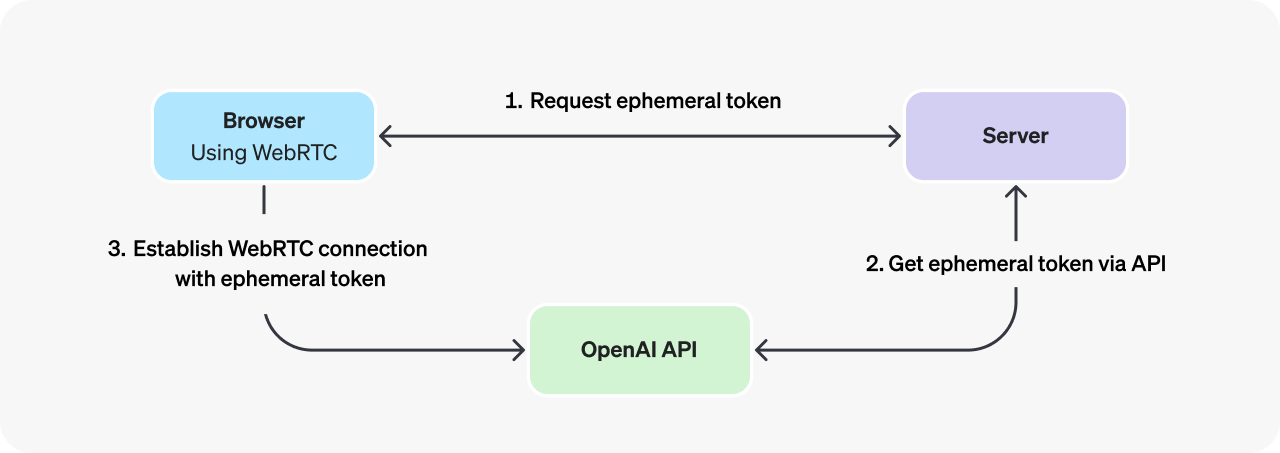
Connecting to the Realtime API from the browser should be done with an ephemeral API key, [generated via the OpenAI REST API](/docs/api-reference/realtime-sessions). The process for initializing a WebRTC connection is as follows (assuming a web browser client):
1. A browser makes a request to a developer-controlled server to mint an ephemeral API key.
2. The developer's server uses a [standard API key](/settings/organization/api-keys) to request an ephemeral key from the [OpenAI REST API](/docs/api-reference/realtime-sessions), and returns that new key to the browser. Note that ephemeral keys currently expire one minute after being issued.
3. The browser uses the ephemeral key to authenticate a session directly with the OpenAI Realtime API as a [WebRTC peer connection](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/RTCPeerConnection).
While it is technically possible to use a [standard API key](/settings/organization/api-keys) to authenticate client-side WebRTC sessions, **this is a dangerous and insecure practice** because it leaks your secret key. Standard API keys grant access to your full OpenAI API account, and should only be used in secure server-side environments. We recommend ephemeral keys in client-side applications whenever possible.
### Connection details
Connecting via WebRTC requires the following connection information:
|URL|https://api.openai.com/v1/realtime|
|Query Parameters|modelRealtime model ID to connect to, like gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17|
|Headers|Authorization: Bearer EPHEMERAL_KEYSubstitute EPHEMERAL_KEY with an ephemeral API token - see below for details on how to generate one.|
The following example shows how to initialize a [WebRTC session](https://webrtc.org/getting-started/overview) (including the data channel to send and receive Realtime API events). It assumes you have already fetched an ephemeral API token (example server code for this can be found in the [next section](#creating-an-ephemeral-token)).
```javascript
async function init() {
// Get an ephemeral key from your server - see server code below
const tokenResponse = await fetch("/session");
const data = await tokenResponse.json();
const EPHEMERAL_KEY = data.client_secret.value;
// Create a peer connection
const pc = new RTCPeerConnection();
// Set up to play remote audio from the model
const audioEl = document.createElement("audio");
audioEl.autoplay = true;
pc.ontrack = e => audioEl.srcObject = e.streams[0];
// Add local audio track for microphone input in the browser
const ms = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({
audio: true
});
pc.addTrack(ms.getTracks()[0]);
// Set up data channel for sending and receiving events
const dc = pc.createDataChannel("oai-events");
dc.addEventListener("message", (e) => {
// Realtime server events appear here!
console.log(e);
});
// Start the session using the Session Description Protocol (SDP)
const offer = await pc.createOffer();
await pc.setLocalDescription(offer);
const baseUrl = "https://api.openai.com/v1/realtime";
const model = "gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17";
const sdpResponse = await fetch(`${baseUrl}?model=${model}`, {
method: "POST",
body: offer.sdp,
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${EPHEMERAL_KEY}`,
"Content-Type": "application/sdp"
},
});
const answer = {
type: "answer",
sdp: await sdpResponse.text(),
};
await pc.setRemoteDescription(answer);
}
init();
```
The WebRTC APIs provide rich controls for handling media streams and input devices. For more guidance on building user interfaces on top of WebRTC, [refer to the docs on MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebRTC_API).
### Creating an ephemeral token
To create an ephemeral token to use on the client-side, you will need to build a small server-side application (or integrate with an existing one) to make an [OpenAI REST API](/docs/api-reference/realtime-sessions) request for an ephemeral key. You will use a [standard API key](/settings/organization/api-keys) to authenticate this request on your backend server.
Below is an example of a simple Node.js [express](https://expressjs.com/) server which mints an ephemeral API key using the REST API:
```javascript
import express from "express";
const app = express();
// An endpoint which would work with the client code above - it returns
// the contents of a REST API request to this protected endpoint
app.get("/session", async (req, res) => {
const r = await fetch("https://api.openai.com/v1/realtime/sessions", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Authorization": `Bearer ${process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
model: "gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17",
voice: "verse",
}),
});
const data = await r.json();
// Send back the JSON we received from the OpenAI REST API
res.send(data);
});
app.listen(3000);
```
You can create a server endpoint like this one on any platform that can send and receive HTTP requests. Just ensure that **you only use standard OpenAI API keys on the server, not in the browser.**
### Sending and receiving events
To learn how to send and receive events over the WebRTC data channel, refer to the [Realtime conversations guide](/docs/guides/realtime-conversations#handling-audio-with-webrtc).
Connect with WebSockets
-----------------------
[WebSockets](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebSockets_API) are a broadly supported API for realtime data transfer, and a great choice for connecting to the OpenAI Realtime API in server-to-server applications. For browser and mobile clients, we recommend connecting via [WebRTC](#connect-with-webrtc).
### Overview
In a server-to-server integration with Realtime, your backend system will connect via WebSocket directly to the Realtime API. You can use a [standard API key](/settings/organization/api-keys) to authenticate this connection, since the token will only be available on your secure backend server.

WebSocket connections can also be authenticated with an ephemeral client token ([as shown above in the WebRTC section](#creating-an-ephemeral-token)) if you choose to connect to the Realtime API via WebSocket on a client device.
Standard OpenAI API tokens **should only be used in secure server-side environments**.
### Connection details
Speech-to-Speech
Connecting via WebSocket requires the following connection information:
|URL|wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime|
|Query Parameters|modelRealtime model ID to connect to, like gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17|
|Headers|Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEYSubstitute YOUR_API_KEY with a standard API key on the server, or an ephemeral token on insecure clients (note that WebRTC is recommended for this use case).OpenAI-Beta: realtime=v1This header is required during the beta period.|
Below are several examples of using these connection details to initialize a WebSocket connection to the Realtime API.
ws module (Node.js)
Connect using the ws module (Node.js)
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
const url = "wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17";
const ws = new WebSocket(url, {
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
"OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1",
},
});
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(JSON.parse(message.toString()));
});
```
websocket-client (Python)
Connect with websocket-client (Python)
```python
# example requires websocket-client library:
# pip install websocket-client
import os
import json
import websocket
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
url = "wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17"
headers = [
"Authorization: Bearer " + OPENAI_API_KEY,
"OpenAI-Beta: realtime=v1"
]
def on_open(ws):
print("Connected to server.")
def on_message(ws, message):
data = json.loads(message)
print("Received event:", json.dumps(data, indent=2))
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
url,
header=headers,
on_open=on_open,
on_message=on_message,
)
ws.run_forever()
```
WebSocket (browsers)
Connect with standard WebSocket (browsers)
```javascript
/*
Note that in client-side environments like web browsers, we recommend
using WebRTC instead. It is possible, however, to use the standard
WebSocket interface in browser-like environments like Deno and
Cloudflare Workers.
*/
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17",
[
"realtime",
// Auth
"openai-insecure-api-key." + OPENAI_API_KEY,
// Optional
"openai-organization." + OPENAI_ORG_ID,
"openai-project." + OPENAI_PROJECT_ID,
// Beta protocol, required
"openai-beta.realtime-v1"
]
);
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.data);
});
```
### Sending and receiving events
To learn how to send and receive events over Websockets, refer to the [Realtime conversations guide](/docs/guides/realtime-conversations#handling-audio-with-websockets).
Transcription
Connecting via WebSocket requires the following connection information:
|URL|wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime|
|Query Parameters|intentThe intent of the connection: transcription|
|Headers|Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEYSubstitute YOUR_API_KEY with a standard API key on the server, or an ephemeral token on insecure clients (note that WebRTC is recommended for this use case).OpenAI-Beta: realtime=v1This header is required during the beta period.|
Below are several examples of using these connection details to initialize a WebSocket connection to the Realtime API.
ws module (Node.js)
Connect using the ws module (Node.js)
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
const url = "wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?intent=transcription";
const ws = new WebSocket(url, {
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
"OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1",
},
});
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(JSON.parse(message.toString()));
});
```
websocket-client (Python)
Connect with websocket-client (Python)
```python
import os
import json
import websocket
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
url = "wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?intent=transcription"
headers = [
"Authorization: Bearer " + OPENAI_API_KEY,
"OpenAI-Beta: realtime=v1"
]
def on_open(ws):
print("Connected to server.")
def on_message(ws, message):
data = json.loads(message)
print("Received event:", json.dumps(data, indent=2))
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
url,
header=headers,
on_open=on_open,
on_message=on_message,
)
ws.run_forever()
```
WebSocket (browsers)
Connect with standard WebSocket (browsers)
```javascript
/*
Note that in client-side environments like web browsers, we recommend
using WebRTC instead. It is possible, however, to use the standard
WebSocket interface in browser-like environments like Deno and
Cloudflare Workers.
*/
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?intent=transcription",
[
"realtime",
// Auth
"openai-insecure-api-key." + OPENAI_API_KEY,
// Optional
"openai-organization." + OPENAI_ORG_ID,
"openai-project." + OPENAI_PROJECT_ID,
// Beta protocol, required
"openai-beta.realtime-v1"
]
);
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.data);
});
```
### Sending and receiving events
To learn how to send and receive events over Websockets, refer to the [Realtime transcription guide](/docs/guides/realtime-transcription#handling-transcriptions).
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

