---
tags: coding
---
# 競賽筆記
> 個人的筆記與經驗與學習過程
+ 目錄:
- [預備知識](#預備知識)
- [C++ STL](#STL)
- [解題策略與演算法](#解題策略與演算法)
- [解題紀錄](#解題紀錄)
------------------------
# 預備知識
### cin & cout的優化
關掉和 stdin 及 stdout 的同步,但記得關掉後,一律只能用
cout 及 cin 了,就不要混用 printf 及 scanf
```cpp=
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
```
關掉 cout 及 cin 的互相綁定
之後的程式碼,都不要用 endl,改用 \n
---
### 數學知識
**前幾個**比較重要

#### 等差級數和
(a+b)*n/2
a:首項 b:末項 n:總共幾項
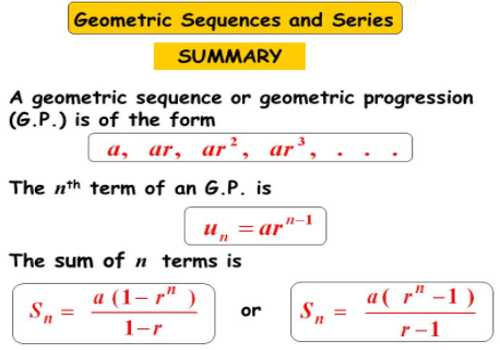
#### 等比級數和
---
### 時間複雜度

---
### 資料溢位
```cpp=
int a = 123456789;
long long b = a*a; //a*a時還是int 乘完才會轉成long long
cout << b << "\n"; // -1757895751
```
---
### 浮點數問題
some numbers cannot be represented accurately as floating point numbers, and there will be rounding errors.
A better way to compare floating point numbers is to assume that two numbers are equal if the difference between them is less than x, where x
is a small number.
In practice, the numbers can be compared as follows (x = 10^-9):
```cpp=
if (abs(a-b) < 1e-9) {
// a and b are equal
}
```
---
### 大數mod
```cpp=
(a+b) mod m = (a mod m + b mod m) mod m
(a-b) mod m = (a mod m - b mod m) mod m
(a*b) mod m = (a mod m * b mod m) mod m
```
在C++or其他語言,負數的餘數會是**0或負數**
```cpp=
x = x%m;
if (x < 0) x += m;
```
this is only needed when there are subtractions in the code and the remainder may become negative.
---
### 二項式係數

---
### GCD

---
# STL
### Dynamic Array
#### Vector
vector<***datatype***> ***name***
**實作原理**:
從記憶體找出一塊符合size的連續位址來存放
當push_back超過這塊size就找塊新的大小夠的來存放
**盡量在初始宣告需要的大小,避免常常重新分配記憶體空間**
[STL-Vector](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/)
```cpp=
// Constructor
vector<int> first; //空白
vector<int> second (4,100);//size=4 , all value is 100
vector<int> third (second.begin(),second.end());//copy second by iterator
vector<int> fourth (third); //copy third(throw in)
//operator=
vector<int> foo (3,0);
vector<int> bar (5,0);
bar = foo;//size=3
foo = std::vector<int>();//size=0
//member function
```
---
#### String(lib:string)
***Strings can be combined using the + symbol***
[STL-String](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/)
```cpp=
string a = "hatti";
string b = a+a;
cout << b << "\n"; // hattihatti
b[5] = ’v’;
cout << b << "\n"; // hattivatti
string c = b.substr(3,4);
cout << c << "\n"; // tiva
```
---
### Set
set is based on a balanced binary tree and its operations work in O(logn) time.
[STL-Set](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/set/)
```cpp=
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(5);
cout << s.count(3) << "\n"; // 1
cout << s.count(4) << "\n"; // 0
s.erase(3);
s.insert(4);
cout << s.count(3) << "\n"; // 0
cout << s.count(4) << "\n"; // 1
set<int> s2 = {2,5,6,8};
cout << s2.size() << "\n"; // 4
for (auto x : s2) {
cout << x << "\n";
}
```
---
### Bitset
A bitset is an array whose each value is either 0 or 1(like bool array).
[STL-Bitset](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/bitset/bitset/)
---
### Map
A map is a generalized array that consists of key-value-pairs.
[STL-Map](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/)
```cpp=
map<string,int> m;
m["monkey"] = 4;//m.insert(pair<string,int>('monkey',4))and so on
m["banana"] = 3;
m["harpsichord"] = 9;
cout << m["banana"] << "\n"; // 3
cout << m["aybabtu"] << "\n"; // 0
```
---
### Binary Search in C++ lib(Algorithm)
Time Complexity:**log(n)**
binary_search:
```cpp=
binary_search(arr,arr+n,x);//array
binary_search(vec.begin(),vec.end(),x);//vector
```
**lower_bound**:
returns a pointer to the first array element whose value is at
least x.
```cpp=
lower_bound(arr,arr+n,x);
```
**upper_bound**:
returns a pointer to the first array element whose value is
larger than x.
```cpp=
upper_bound(arr,arr+n,x);
```
**equal_range**:
returns both above pointers.
```cpp=
auto r=equal_range(arr,arr+n,x);
//auto is created on C++11
```
---
### Sort in C++
```cpp=
#include<algorithm> //sort function in this lib
#include<vector>
//version of vector
vector<int> x;
sort(x.begin(),x.end());
sort(x.rbegin(),x.rend());//reverse version of vector
//version of array
int arr[n];
sort(arr,arr+n);
//version of string
string x="monkey";
sort(x.begin(),x.end());//依照字母順序排列:ekmnoy
```
---
### Priority queue
```cpp=
//queue的一種
//會自動把push進去的數字變成decreasing order
//可用來排序或heap
priority_queue<int> q;
q.push(3);
q.push(5);
q.push(7);
q.push(2);
cout << q.top() << "\n"; // 7
q.pop();
cout << q.top() << "\n"; // 5
q.pop();
q.push(6);
cout << q.top() << "\n"; // 6
q.pop();
```
---
### Increasing order 的 priority queue
```cpp=
//讓top出來的順序變成由小到大(increasing order)
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q;
```
---
# 解題策略與演算法
以下內容需思考,**別死背**
---
### Tower of Hanoi(Recursive)

---
### Logic calculation
#### To multiply/divide an integer by 2
```cpp=
S = 34 //(base 10) = 100010 (base 2)
S = S << 1 //= S * 2 = 68 (base 10) = 1000100 (base 2)
S = S >> 2 //= S / 4 = 17 (base 10) = 10001 (base 2)
S = S >> 1 //= S / 2 = 8 (base 10) = 1000 (base 2)
```
---
#### To set/turn on the j-th item (0-based indexing) of the set
use the bitwise OR operation S |= (1 << j).
```cpp=
S = 34 //(base 10) = 100010 (base 2)
j = 3,//= 001000 (base 2)
S |= (1 << j)
S = 42 //(base 10) = 101010 (base 2)
```
---
#### To check if the j-th item of the set is on
use the bitwise AND operation T = S & (1 << j).
```cpp=
S = 42 //(base 10) = 101010 (base 2)
j = 3,//= 001000
T = S & (1 << j)
T = 8 //(base 10) = 001000 (base 2)
```
---
#### To clear/turn off the j-th item of the set
use the bitwise AND operation S &= ∼(1 << j).
```cpp=
S = 42 //(base 10) = 101010 (base 2)
j = 1,
S &= ~(1<<j)
S = 40 //(base 10) = 101000 (base 2)
```
---
### 保留小數點後幾位(不四捨五入)
```cpp=
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double pi=3.1415926;
double num;
double fi=5.0;
double div=10;
cin>>num;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)div*=10;
//小數後3位就減掉0.0005 以此推類
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(num)<<pi-fi/div<<endl;
cout.unsetf(ios::fixed) //關掉fixed
//後面的輸出就不會被fixed限制住
return 0;
}
```
---
### 最大子序列總和(continuous sequence)
best紀錄最大的總和
sum+array[k]和array[k]比較
較大的再跟best比較
```cpp=
int best = 0, sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
sum = max(array[k],sum+array[k]);
best = max(best,sum);
}
cout << best << "\n";
```
---
### Counting Sort
當輸入的資料數字**範圍小但大量**時可用
用法:使用陣列紀錄出現的次數
Time Complexity:O(n)
---
### Binary Search
O(logn)
```cpp=
int a = 0, b = n-1;
while (a <= b) {
int k = (a+b)/2;
if (array[k] == x) {
// x found at index k
}
if (array[k] > x) b = k-1;
else a = k+1;
}
```
---
### Knapsack problems(DP)
Describe:
Given a list of weights [w1,w2,...,wn], determine all sums that can be constructed using the weights.
```cpp=
possible(x,k)=possible(x-wk,k-1)|possible(x,k-1)
//recursive relation
//end condition:
possible(x,0)=(true if x = 0;false if x!= 0)
//DP program as following(easy)
possible[0][0] = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for (int x = 0; x <= W; x++) {
if (x-w[k] >= 0)
possible[x][k] |=possible[x-w[k]][k-1];
possible[x][k] |= possible[x][k-1];
}
}
//one-dimensional array DP implementation(difficult)
possible[0] = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for (int x = W; x >= 0; x--) {
if (possible[x]) possible[x+w[k]] = true;
}
}
```
---
### 子集合
```cpp=
//湊出0~n-1所有可能的子集合
vector<int>subset;
void search(int k) {
if (k == n)
{
// process subset
}
else
{
search(k+1);
subset.push_back(k);
search(k+1);
subset.pop_back();
}
}
//下面的圖為n=3時
```

---
### 排列組合
```cpp=
//number version of permutation
#define n 3
vector<int>chosen(n);
void search() {
if (permutation.size() == n)
{
// process permutation ex: print
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (chosen[i]) continue;
permutation.push_back(i);
chosen[i] = true;
search();
chosen[i] = false;
permutation.pop_back();
}
}
}
```
---
# 解題紀錄
## LeetCode
#### 1108. Defanging an IP Address(Easy)
很簡單的字串處理,把原本字串有dot的地方加上中括弧即可
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
string defangIPaddr(string address) {
string ans = "";
for(int i=0;i<address.size();i++)
{
if(address[i] == '.')
ans += "[.]";
else
ans += address[i];
}
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### 807. Max Increase to Keep City Skyline(Medium)
先把從左至右以及從上到下看過去的高度記錄下來
範例
從左往右看,各棟高度為[8,7,9,3]
從上往下看,各棟高度為[9,4,8,7]
再取交會處的較小數字,然後減掉原本大樓的高度
再加總,就是最多可以增加的高度。
過程:
紀錄兩方向看過去最高點:n^2
算最多可增加高度:n^2
複雜度:**O(n^2)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int maxIncreaseKeepingSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<int>a(grid.size(), 0),b(grid.size(), 0);
int len = grid.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++)
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < len ; j++)
{
if(a[i] < grid[i][j])a[i] = grid[i][j];
if(b[i] < grid[j][i])b[i] = grid[j][i];
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++)
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < len ; j++)
{
ans += min(a[i], b[j]) - grid[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### 1221. Split a String in Balanced Strings(Easy)
用一個變數來計數,遇到R就+1,遇到L就-1
如果stack跑到0就ans+1,代表有對稱的組合出現
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int balancedStringSplit(string s) {
int ans = 0;
int stack = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i++)
{
if(s[i] == 'R')
stack++;
else
stack--;
if(stack == 0)
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### 938. Range Sum of BST(Easy)
沒啥好說的,用遞迴解決
複雜度:**O(n)**
```cpp=
code:
class Solution {
public:
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode* now, int L, int R) {
if (now == NULL)return 0;
if (now->val >= L && now->val <= R)
{
return now->val + rangeSumBST(now->left,L,R) + rangeSumBST(now->right,L,R);
}
else if(now->val <= L)
{
return (now->val == L ? now->val : 0) + rangeSumBST(now->right,L,R);
}
else if(now->val >= R)
{
return (now->val == R ? now->val : 0) + rangeSumBST(now->left,L,R);
}
return 0;
}
};
```
#### 26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array(Easy)
使用vector.erase()來解決
不過每次的erase最大可能會需要到O(n)複雜度
如果用另外的陣列儲存的話可以降低空間複雜度
複雜度:**O(n^2)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i] == nums[i-1]) nums.erase(nums.begin()+(i--));
}
return nums.size();
}
};
```
---
#### 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II(Easy)
ex:[1 , 3 , 5 , 6]
第一種算法:6 - 1 = 5
第二種算法:(3 - 1) + (5 - 3) + (6 - 5) = 2 + 2 + 1 = 5
通常我們在思考都是用第一種
不過第一種還要多判斷大於或小於
第二種算法則簡潔易懂
我們使用第二種算法
為了避免小於0也被加進去
使用 **max(0 , 差值)** 來避免這種情況發生
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i < prices.size() ; i++)
{
ans += max(0 , prices[i] - prices[i-1]);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### **136. Single Number(Easy)**
很燒腦的題目,有很多方法能做
一開始想了幾種解法
後來看解答才發現
可以使用**Bit Manipulation**
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
ans ^= nums[i];
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### 189. Rotate Array(Easy)
s:space complexity
t:time complexity
Leetcode提供幾個解法:
1.Brute Force(TLE)
2.extra memory(array) -> s:O(n), t:O(n)
3.rotate dependency -> s:O(1), t:O(n)
4.**reverse** -> s:O(1), t:O(n)
difficulity:
2最簡單
3.4其次(可以call c++ algorithm裡面的reverse的話4就很簡單)
題外話:c++也有提供rotate,不過是向左rotate
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
k = k % nums.size();
reverse(nums.begin(),nums.end());
reverse(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+k);
reverse(nums.begin()+k,nums.end());
}
};
```
---
#### 217. Contains Duplicate(Easy)
最簡單的作法
先排序再從第二個開始往前一個比較
複雜度:**O(nlogn)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i] == nums[i-1])return true;
}
return false;
}
};
```
---
#### 350. Intersection of Two Arrays II(Easy)
兩個array先排序
再用two pointers 解決
複雜度:**O(2*nlogn + n) = O(nlogn)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
sort(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());
sort(nums2.begin(),nums2.end());
vector<int> ans_arr;
int one=0,two=0;
while(one != nums1.size() && two != nums2.size())
{
if(nums1[one] == nums2[two])
{
ans_arr.push_back(nums1[one]);
one++;
two++;
}
else if(nums1[one] > nums2[two])two++;
else one++;
}
return ans_arr;
}
};
```
---
#### 66. Plus One(Easy)
類大數運算
檢查有無進位
無進位就跳出迴圈
避免9999這種 edge case 發生
所以迴圈外還要檢查to 是否為1
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {
int to = 1;
for(int i=digits.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
digits[i] += to;
to = digits[i] / 10;
digits[i] %= 10;
if(!to)break;
}
if(to) digits.insert(digits.begin(),to);
return digits;
}
};
```
---
#### 283. Move Zeroes(Easy)
用pos表示要被交換的位置
如果nums[i]不為0則跟pos交換
交換後表示pos是不為0,pos就++
如果整個陣列都不為0則程式則一直跟自己(因為pos會++)交換
如果有0的話pos會留在那個位置直到nums[i]不為0然後做交換
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int pos=0;//零的位置
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i])
{
int tmp = nums[pos];
nums[pos++] = nums[i];
nums[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
};
```
---
#### 1. Two Sum(Easy)
這題比較麻煩的點是在不能對原陣列排序
所以我另外宣告一個陣列,用它來排序
找到sum後再回去原陣列找他的index
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int>b(nums);
sort(b.begin(),b.end());
vector<int>ans;
int f=0,t=nums.size()-1;
while(1)
{
if(b[f]+b[t]>target)t--;
else if(b[f]+b[t]<target)f++;
else
{
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i]==b[f])ans.push_back(i);
else if(nums[i]==b[t])ans.push_back(i);
}
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
---
#### 36. Valid Sudoku(Medium)
這題其實不難
就依照其規則檢查陣列內數字是否符合規則
複雜度:**O(n^2)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int len = board[0].size();
vector<int>ori(10,1);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
vector<int>pos(ori);
for(int j=0;j<len;j++)
{
if(board[i][j]=='.')continue;
if(pos[board[i][j]-48])pos[board[i][j]-48]--;
else return false;
}
pos=ori;
for(int j=0;j<len;j++)
{
if(board[j][i]=='.')continue;
if(pos[board[j][i]-48])pos[board[j][i]-48]--;
else return false;
}
}
int x=0,y=0;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
vector<int>pos(ori);
for(int a=x;a<x+3;a++)
{
for(int b=y;b<y+3;b++)
{
if(board[a][b]=='.')continue;
if(pos[board[a][b]-48])pos[board[a][b]-48]--;
else return false;
}
}
y = (y+3)%9;
if(i && i%3==2)x+=3;
}
return true;
}
};
```
---
#### 48. Rotate Image(Medium)
這題的解法是亂想的
先做垂直翻轉再對角翻轉(從左下到右上)
Transpose
複雜度:**O(n^2)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public://先做垂直翻轉,再做對角翻轉(左下to右上)
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
for(int i=0,j=matrix.size()-1;i<=j;i++,j--)
{
for(int k=0;k<matrix.size();k++)
{
int tmp=matrix[i][k];
matrix[i][k]=matrix[j][k];
matrix[j][k]=tmp;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)
{
for(int j=i;j<matrix.size();j++)
{
int tmp=matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i]=tmp;
}
}
}
};
```
---
#### 55. Jump Game(Medium)
這題的解法是參考網路上的
用Greedy解
思路是:如果ith可以走到終點 就從ith往回找
可以到ith的點就代表他可以到終點
一樣從那個點開始往前找,以此類推
最後如果找到index = 0就代表有路
複雜度:**O(n)**
code:
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
int init = nums.size()-1;
for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(i + nums[i] >= init)
{
init = i;
}
}
return init == 0;
}
};
```
___
#### 915. Partition Array into Disjoint Intervals(Medium)
解法:
參考網路上的,有空多看幾次
用Greedy解
ex:[5,0,3,8,6]
=>[5,5,5,8,6]正確解法
=>[5,5,5,8,8]錯誤解法
目前遇到的最大值(cur_max)每回合更新
當前一個最大值(pre_max)比現在第i個值(A[i])要大時才更新
用樓上的為例子,當i=4時:
A[i] = 6, cur_max = 8,pre_max = 5
雖然6 < 8,但是6 > 5 所以不用把pre_max更新成cur_max
複雜度:**O(n)**
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
int partitionDisjoint(vector<int>& A) {
int cur_max = A[0];
int pre_max = A[0];
int pos = 0;
for(int i=1;i<A.size();i++)
{
cur_max = max(A[i],cur_max);
if(pre_max > A[i])
{
pre_max = cur_max;
pos = i;
}
}
return pos+1;
}
};
```
---
[LeetCode-1365. How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number(Easy)](https://medium.com/%E7%B2%89%E8%82%9D%E7%9A%84coding%E7%88%86%E8%82%9D%E9%9B%9C%E8%A8%98/%E8%A7%A3%E9%A1%8C-leetcode-1365-how-many-numbers-are-smaller-than-the-current-number-easy-cf509fb95c38)
---
#### 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator(Medium)
```cpp=
class BSTIterator {
public:
queue<int>q;
void travel(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)return ;
travel(root->left);
q.push(root->val);
travel(root->right);
}
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
travel(root);
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {
int ans = q.front();
q.pop();
return ans;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
return !q.empty();
}
TreeNode* rt;
};
```
---
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

