```md
Authors: Dhruv Kanthaliya, Animesh Chaturvedi
Date: 18/08/2022
Message: this is the first of the end of my life
```
# Networks
# Class 1 - 18th Aug 2022

<b>Definition</b> : connection of devices for transfering data, communication.
## Introduction to networks
### Benifits of network
* Workgroup Network - Schools, Colleges
- everyone is admin
- no specific sytem like a server
- Server based networks are secure than this type.
* Server based Network - Diff dept or branches in offices
- has protocols thus making the system more secure
- server receives all the requests
### Roles of computer in network
* File & print server
* secure - only accessible if shared
* file sharing & printing

* Database Server
* used for database management in backend
* mysql, oracle, etc.
* also handles NoSQL i.e. handles both relational and non relational data.

* Mail server
* Diff servers for diff locations & companies
* can have different accesses for different users
* softwares for internal mail server
* MS Exchange
* Unix/redhat linux - send mail server
* Domino Lotus Notes
* Google - also has its own email server
* Fax server
* multiple fax machines can be managed for same or diff branches
* similar to a print file server, only the printer is replaces by a fax machine
* Directory Services Server
* has the securtiy protocols
* most imp server - all other servers are managed by this server.
* centralize, store, protect and locate in a single location of every employee's data in each dept. on their own branch folder. Centralised in a single server, that server is called the <strong>directory service server</strong>.
* It's like a database server but it limits itself to what kind of information it contains
## Classification of a network
Resource - <a href = "https://data-flair.training/blogs/types-of-computer-networks/"> some website </a>
* Based on OS / types of network operating systems
* peer to peer
* any host can act as server or client
* NetwareLite, windows 95/98/XP/7, etc.
* network operating systems allow users to share network resources saved in a common, accessible network location. In this architecture, all devices are treated equally in terms of functionality. Peer-to-peer usually works best for small to medium LANs and is cheaper to set up.
* client server
* clients contact the server for resources. Both have diff OS.
* Novell NetWare, windows NT/2000/2003/2008, MacCatalina etc.
* Server used as a backup to maintain each system's data backup or each user's data.
* In this architecture, all functions and applications are unified under one file server that can be used to execute individual client actions regardless of physical location. Client/server tends to be most expensive to implement and requires a large amount of technical maintenance. An advantage to the client/server model is that the network is controlled centrally, makes changes or additions to technology easier to incorporate.
* Based on processing
* centralized processing
* processing, data storage centralized
* distributed processing
* processing, data storage distributed
* Based on size/distance
* PAN - Personal Area Network
* USB, hotspot, bluetooth, IrDA
* max 10 ft or 3 m
* HAN - Home Area Network, chromecast.
* LAN - Local Area Network
* max 500 m
* inside a building
* also see *VLAN* : A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical overlay network that groups together a subset of devices that share a physical LAN, isolating the traffic for each group.
* CAN - Campus Area Network
* on a college campus or a millitary base
* MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
* company with different branches connected
* 64 kbps to 2 mbps
* min 50 km
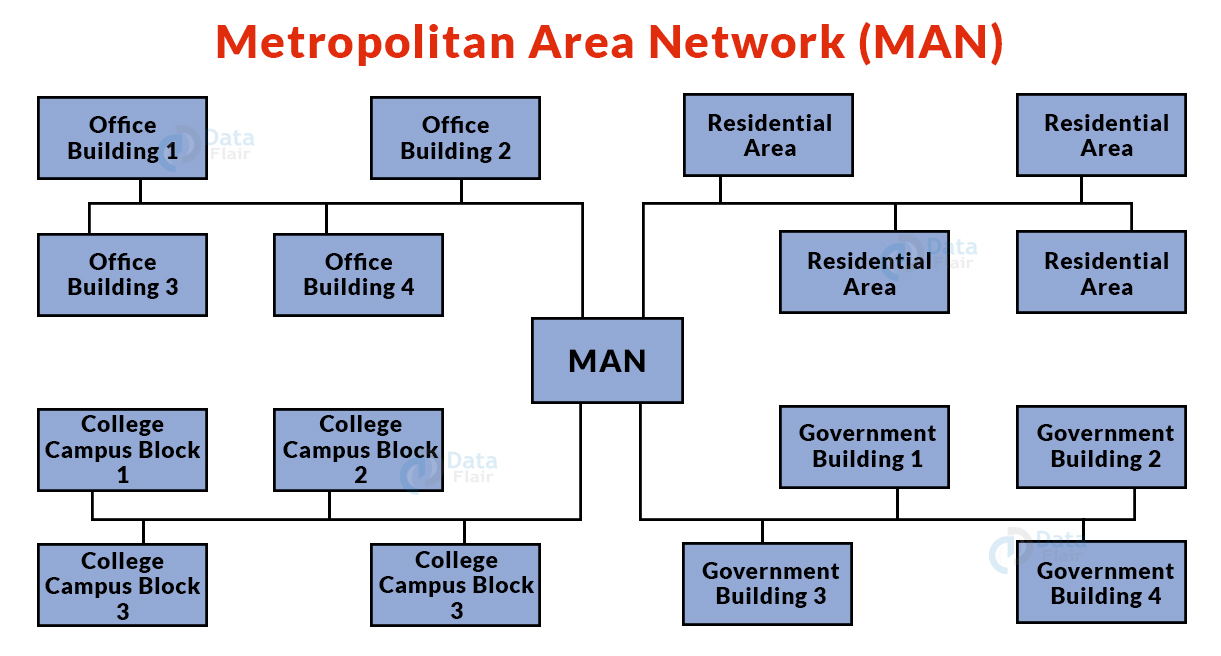
* WAN - Wide Area Network
* multiple MANs connected here
* Transcontinenetal and global are reach
* speed and distance together match very the cost variable
* very expensive for high speed and longer distance
* multiple routers are used
* mac vs ip address
[Resource](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-mac-address-and-ip-address/)
* mac address is like your real name(hardware oriented) whereas IP address is like your nick name(Network oriented).
* IP changes with time and environment.
* MAC - 48 (6 bytes) bit hexadecimal notation
* eg . 00:FF:FF:AB:BB:AA
* IP address is of 4 bytes or 32 bits
* eg. 192.48.1.1
* types of cables :question:
* switch vs router
* What is a Switch?
Switches facilitate the sharing of resources by connecting together all the devices, including computers, printers, and servers, in a small business network. Thanks to the switch, these connected devices can share information and talk to each other, regardless of where they are in a building or on a campus. Building a small business network is not possible without switches to tie devices together.
* What is a router?
Just as a switch connects multiple devices to create a network, a router connects multiple switches, and their respective networks, to form an even larger network. These networks may be in a single location or across multiple locations. When building a small business network, you will need one or more routers. In addition to connecting multiple networks together, the router also allows networked devices and multiple users to access the Internet.
Ultimately, a router works as a dispatcher, directing traffic and choosing the most efficient route for information, in the form of data packets, to travel across a network. A router connects your business to the world, protects information from security threats, and even decides which devices have priority over others.
* osi networking layers :question:
## Network Infrastructure
### Network - bits and pieces
* Network Interface Card
* amplifies electronic signals
* packages data for transmission
* physcially connects computer to transmission media (cable)
* manufacturers - intel, dlink, cisco
* use - data serialization - parallel data stream converted to serial data stream
* contains MAC address
* it is a hexadecimal code of 48 bits
* 24 bits of vendor code and other for seial number
* it is burned into the ROM on a network interface card
* When the network interface card initializes, the address is copied into RAM.
* to check the MAC address use the below command
```shell=
ipconfig /all
```
#### Why do we need the OSI MODEL?
Detailed Version - <a href="https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/this-is-exactly-why-we-still-use-the-osi-model-when-we-have-tcp-ip-model/"> Some website </a>
To address the problem of networks inceasing in size and in numbers the international organization for standardization(ISO).
OSI is an acronym for Open Systems Interconnection. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) created the OSI model (ISO). It’s a model for how applications communicate over the internet. In order to facilitate interoperability between diverse devices and applications, the OSI model describes computing functions into a universal set of rules and standards.
The OSI model can be thought of as a universal computer networking language. It is built on the divide-and-conquer concept, and it divides the communication system into seven abstract layers, each of which is layered on top of the previous layer.
OSI - Open System Interconnection
IOS - Internetwork Operating System
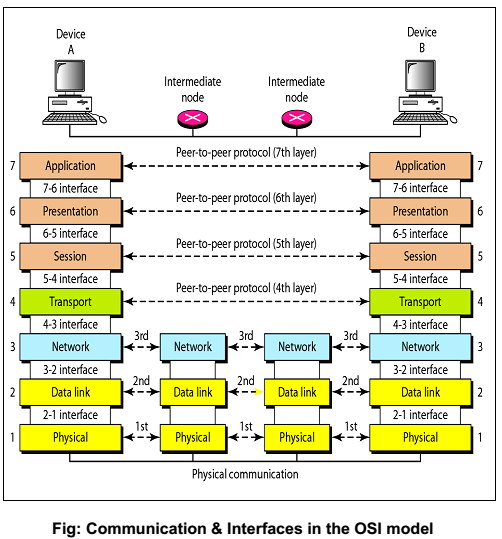
<Strong>OSI MODEL</Strong>
7- Application Layer
6- Presentation Layer
5- Session Layer
4- Transport Layer
3- Network Layer
2- Data Link Layer
1- Physical Layer
4,5,6,7 are the host layers
1,2,3 are the the media layers. they manage the info out/in the LAN or WAN between the surce and destination hosts.
OSI model analogy - bicycle example
#### The OSI layers Communication
#### Encapsulation Process

#### Data Flow through a Network

TRACERT (Trace Route), a command-line utility that you can use to trace the path that an Internet Protocol (IP) packet takes to its destination.
The ping command sends packets of data to a specific IP address on a network, and then lets you know how long it took to transmit that data and get a response. It’s a handy tool that you can use to quickly test various points of your network.
```shell=
tracert yahoo.com
ping google.com
netstat // to check network statistcis
ipconfig // to do something
arp -a // address resolution protocol - ip to mac
rarp -a // reverse arp - mac to ip
```
<!-- tracer visualisation https://gsuite.tools/traceroute
-->
The most commonly used IP address on the loopback network is 127.0.0.1 for IPv4 and ::1 for IPv6. The standard domain name for the address is localhost.
#### Network Protocols
* netbeui (Network basic extended user interface) protocol win 3.11/win95/98
* small network, not for domain, used for work group
* ipx/spx - inter packet exchange protocol, sequence packet xchange - novel
* small, medium and large networks
* Apple Talk
* by apple inc.
* for apple macintosh
* small, medium and large networks
* TCP/IP
* supports all platforms
* reliable and faster than other protocols
* used in small, medium and large networks
* internet uses this protocol
#### Based on tcp/ip
* ftp - port 21
* file tranfer protocol
* http - port 80
* hypertext transfer protocol
* telnet - port 23
* smtp - port 110
* simple mail transfer protocol
* for outgoing mails
* pop3 - port 25
* post office protocol
* for incoming mails
* IMAP
* internet message access protocol
* for incoming mails from different servers
* SSL: secure shell layer
* port 443
* authentication protocol
* RAS - remote access - port 3389
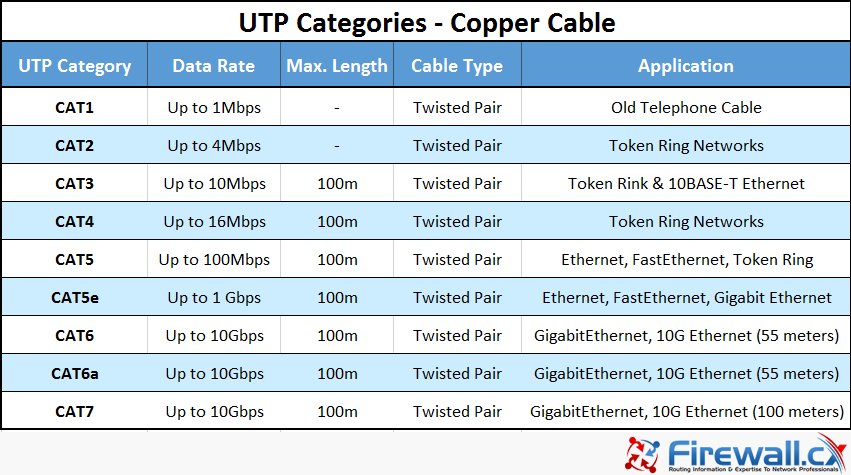
## Network Cables
### Coaxial cable
Only benifit is that it is cheap, otherwise has a lower bandwidth, slow speed and requires maintainance.
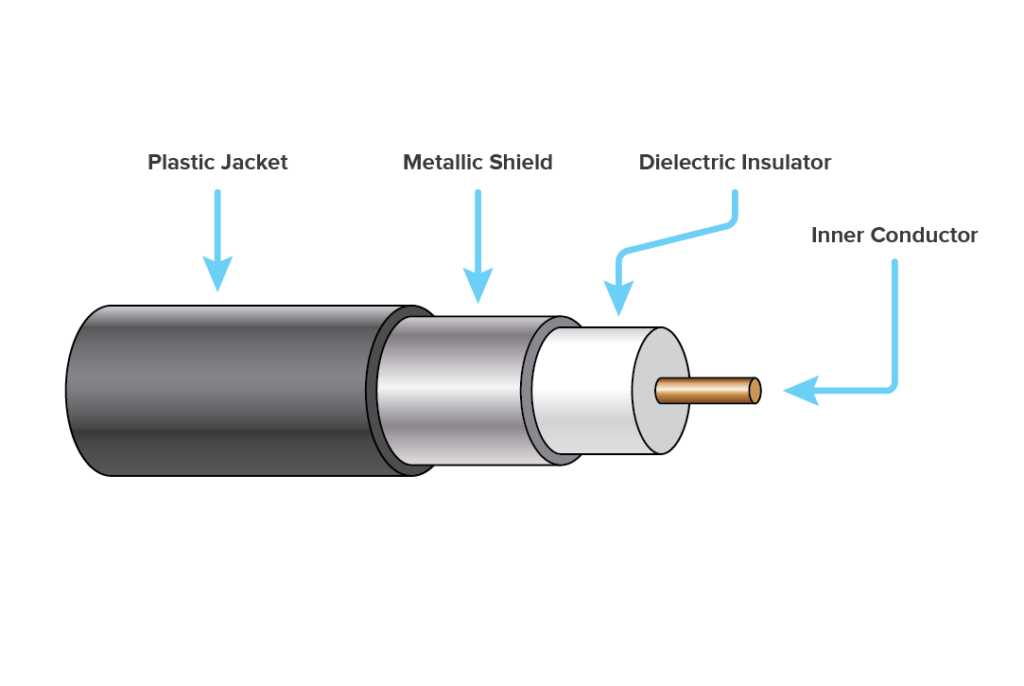
* thinnet
* 10 base 2
* 10 - default bandwidth base stands base band transmission
* max dist bw two systems 180-200 meter
* small coaxial cable
* thicknet
* 10 base 5
* 10 is the default bandwidth
* max dist = 500m
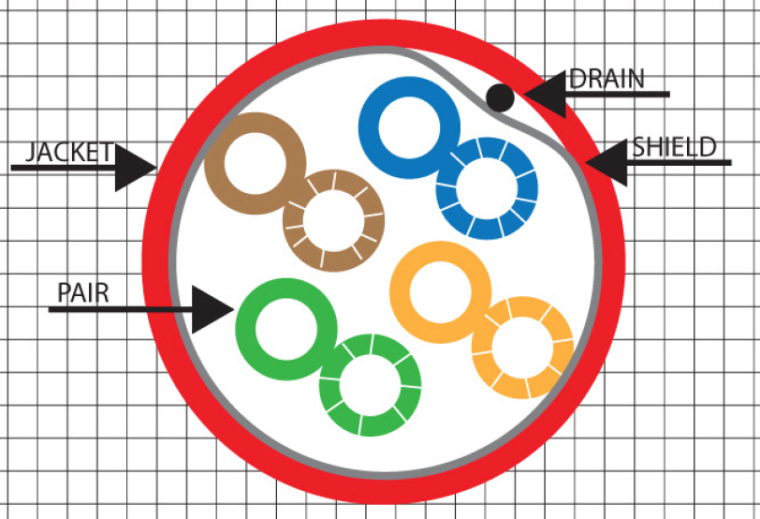
* Twisted pair cable
* 4 colours - orange, green, white, blue
* stp
* shielded
* ISPs usually use this type of cable
* reduces EMI (electromagnetic interference)
* utp
* unshielded
* S/STP
* screen shielded twisted pair
* more twists to reduce crosstalk (interference) among cables

#### Stranded and solid core cat5e utp cable cross section
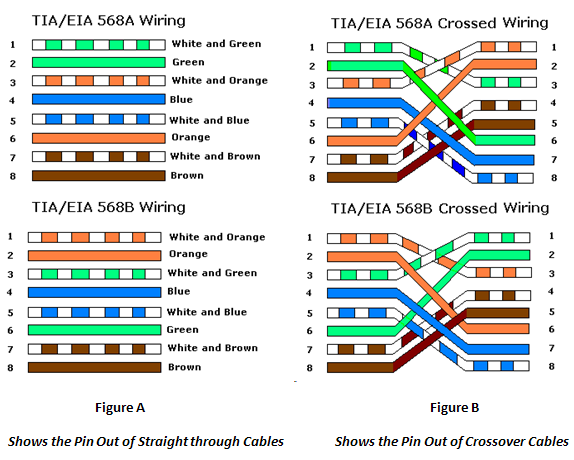
* Straight Through Cable
used for the following connections:
* switch to router
* switch to pc or server
* hub to pc or server
use this only when only 1 port is designated with an "X".
* Crossover Cable
used for following connections:
* swith to switch
* swith to hub
* hub to hub
* router to router
* router to pc
* pc to pc
In the case of crossover cable, pin 1 & pin 2 in one connector connect with pin 3 & pin 6 on the other.
Green & orange pairs change places on one end.
* Fiber Optic Cables
* Single
* Multimode
### Cabel connectors
* BNC
* 15 pin attachment unit interface
* thicknet backbone wirh attached transciever & cable
* RJ45
* register jack
* can be used for pc-to-pc or pc-to-switch connection
* standards -
* EIA/TIA-T568-A OR T568-B
* 568-A -- pair 1 - blue white blue, owo, gwg, brown white brown - owo split
* 568-B -- pair 1 - blue white blue, owo, gwg, brown white brown - gwg split

Using these cables and connectors different topologies are implemented.
#### TCP vs UDP
<a href = "https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/differences-between-tcp-and-udp/"> Website </a>
<!--- embed video links
<iframe
width="640"
height="480"
src=""
frameborder="0"
allow="autoplay; encrypted-media"
allowfullscreen
>
</iframe>
--->
___
# Class 2 - 19th Aug '22
<a href="https://slidetodoc.com/connecting-to-an-ethernet-lan-building-a-simple/"> Presentation </a>
### Fiber Optic Cable Connectors

## Network Topologies
* Common types
* bus
* star
* ring
* hybrid
### Bus topolgy

* tough to troubleshoot
* terminators are at the end to absorb the overcoming signal
* faster than all the other topologies
* can be implemented with coaxial cables too!
### Ring Topology

* clockwise unidirectional data transfer.
* closed loop
* repeaters at each component
* typically used in FDDI networks
* slower transmission
* every pc has 2 network cards
* if one of the system goes down the entire system goes down
* data is quickly transfered without a bottle neck.
* data packets must pass through every computer bw the sender & receiver
### Star Topology

* Failure of a node will not affect other nodes
* Security can be implemented easily
* Failure of the switch/hub can bring down the entire network
* No problem with collisions of data, when each station is connected to the switch with full duplex.
* It consists of one central switch or hub, typically used in ethernet & token ring
* Limited cable length & number of stations
### Hybrid Topology
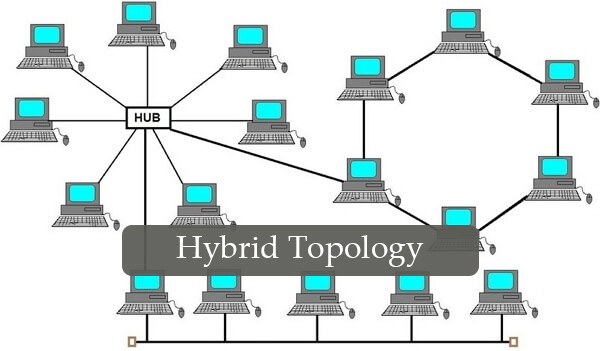
* mix of any of the topologies such as bus, star or ring
* partial mesh, full mesh are purely hybrid topologies
* Tree (Star Bus)
* Star Ring
Comparision
* ease
* troubleshooting
* wiring
### Mesh topology

* expensive
## Types of Data Transmission
some thing to pad

* Unicast - one to one
* Multicast - one to many
* Broadcast - one to all
## Basic Communication- Modes of Operation

* simplex - one way communication. eg - megaphone
* half duplex - two way communication but one at a time. eg - transmission through hub
* full duplex - two way simultaneous communication. eg - mobile phone
## Networking Devices
Resource - <a href ="https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/network-devices-hub-repeater-bridge-switch-router-gateways/"> some link </a>
* Repeater
* regenerate weak signals
* works in transport layer (both tcp and udp)
* obsolete
* Hub
* default bandwidth - 10
* centralised sharing device
* always broadcasts
* divides the bandwidth
* commonly used in ethernet 10baseT or 100baseT networks
* works in physical layer
* drawback - single collision route
* Bridges
* connects network segments
* works in the data link layer
* ability to make decisions about whether to pass signals in to the next segment of a network.
* max 6 ports
* <b> Application :</b> bridge can be used to segment a network to reduce traffic
* Switch
* works in data link layer
* it's a multi port bridge
* stores mac addresses in an internal lookup table
* can be configured to use VLANs
* support spanning tree protocol to create resilient networks - switch having lowest mac address will be considered as route bridge by spanning tree protocol (STP).
* types
* managable
* advantages - VLANs, port security, VTP (VLAN Trunk protocol)
* it's expensive
* works like a computer
* unmanagable
* worthless
* Routers
* it connects multiple VLANs
* works in the network layer
* controls broadcasts to network
* interconnects LANs and WANs
* provide path determination using metrics
* forwards packets from one netork to another
* routers are slower than bridges and swtiches, but make "smart" decisions on how to route packets received on one port to a netwrok or another port.
* routers contain tables of netwoek addresses aling wtih optimal destination routes to other networks i.e. routing table.

## Application Layer
* Computer applications
* word processor
* presentation graphics
* spreadsheets
* database
* design/manufacturing
* project planning
* others
* Network application
* e-mail
* file transfer
* remote access
* clint-server process
* information location
* network management
* others
* Internetwork application
* electronic data interchange
* WWW
* e-mail gateways
* special intrest bulletin boards
* financial transactions
* internet navigation utilities
* conferences (video, voice, data)
## Session Layer
* netwrok file system
* SQL
* Remote procedure call
* X window system
* apple talk session protocol (ASP)
* DEC session control protocol (SCP)
## TCP
* IP
* ICMP
* internet control message protocol
* IGMP
* Intergroup message protocol
* ARP
* address routing protocol
## Transport Layer
<a href="https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/transport-layer-responsibilities">some website</a>
<a href="https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/tcp-3-way-handshake-process/">3 way handshake</a>
<iframe
width="640"
height="480"
src="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LnbvhoxHn8M"
frameborder="0"
allow="autoplay; encrypted-media"
allowfullscreen
>
</iframe>
<a href="https://madpackets.com/2018/04/25/tcp-sequence-and-acknowledgement-numbers-explained/">Sequence and Acknowlwdgement Numbers</a>
[Segmenet Format](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/services-and-segment-structure-in-tcp/)
## ARP - Address Resolution Protocol
Something...Something
## UDP - tcp's rival
* user data protocol
* UDP segment format
## Why IP address?
The purpose of an IP address is to handle the connection between devices that send and receive information across a network. The IP address uniquely identifies every device on the internet; without one, there's no way to contact them.
* every host ( computer, metworking , device, peripheral) must have a unique address to identify themselves in a network.
* host Id:
* identifies the individual host
* is assigned by organizations to individual devices
```
ip address = net id + host id
```
* An IP address has 2 parts:
* the network portion
* found on the left side of ip address
* the host portion
* found on the right side of ip address

### IP header fields

Resource : <a href="https://www.computernetworkingnotes.com/networking-tutorials/ipv4-header-structure-and-fields-explained.html">some website</a>
* Version:
Version of the internet protocol. Standard is IPv4. (4 bit)
* IHL:
internet header length indicates the lenght of the IP header, min length is 5 x 32 bit(4 bit)
* ToS
type of service indicates the quality of the requested serbice in reality this entry gets ignored.
* Total Length:
contains the complete length of the packet.
* Identification:
* Flags:
* Fragments offset:
* TTL: Time to Life
* Protocol: this enty conrtains a identification number of the higher ranking
* Header checksum:
* Source IP address:
* Destnation IP address:
* Options:
## IP Adressing
<a href="https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-classful-ip-addressing/">some other link</a>
### Private IP address range
Class A - 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B - 172.16.0.0 to 172.16.31.254
Class C - 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.254
### Public IP range -
Class A - 1.0.0.0 to 9.255.255.255
Class B - 128.0.0.0 to 171.255.255.255
Class C - 191.0.0.0 to 192.167.255.255
[IP address resource link](https://www.avast.com/c-what-is-an-ip-address)
### Default Subnet Masks
<a href="https://sourcedaddy.com/networking/default-subnets.html"> Resource </a>
## What is a subnet?
A subnet, or subnetwork, is a segmented piece of a larger network. More specifically, subnets are a logical partition of an IP network into multiple, smaller network segments. The Internet Protocol (IP) is the method for sending data from one computer to another over the internet.
* tells the router the number of bits to look at when routing
* defines the number of bits that are significant
* used as a measuring tool, not to hide anything
Subnetting is used to minimize the wasteage of IP addresses.
<b>CIDR</b> - classless inter domain routing - the value is denoted by '/' it allows to manage the subnetting for any class a or b or c
It is also defined as how many number of bits are ON or reserved.
The attributes of subnetting:
1. Network ID
2. Broadcast IP
3. First Host IP - Ip address after the Network ID
5. Last Host IP - IP address before the Broadcast IP
6. Next Network - IP address after the broadcast IP
7. # IP Addresses - no. of IPs in each network
8. CIDR/Subnet - Converting between CIDR/Subnet Mask
Subnet bits can be borrowed from the host part only and not from the network part.
for eg. :-
/8 - 255.0.0.0 - 1111111.0000000.00000000.00000000
/9 - 255.128.0.0 - 11111111.100000000.00000000.00000000
/10 - 255.192.0.0 - 11111111.11000000.00000000.00000000
/11 - 255.224.0.0 - 111111111.11100000.00000000.00000000
/12 - 255.240.0.0 - 11111111.11110000.00000000.00000000
/13 - 255.248.0.0 - 11111111.11111000.00000000.00000000
/14 - 255.252.0.0 - 11111111.11111100.00000000.00000000
/15 - 255.254.0.0 - 11111111.11111110.00000000.00000000
/16 - 255.255.0.0 - 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
/17 - 255.255.128.0 - 11111111.11111111.10000000.00000000
/18 - 255.255.192.0 - 11111111.11111111.11000000.00000000
/19 - 255.255.224.0 - 11111111.11111111.11100000.00000000
/20 - 255.255.240.0 - 11111111.11111111.11110000.00000000
/21 - 255.255.248.0 - 11111111.11111111.11111000.00000000
/22 - 255.255.252.0 - 11111111.11111111.11111100.00000000
/23 - 255.255.254.0 - 11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000
Class C
/24 - 255.255.255.0 - 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
```
the teacher guy(Zakir Hussain) did this thing till /32
all the 0 or OFF bits are used by the host.
```
<iframe
width="640"
height="480"
src="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-wlfAdcmFQ"
frameborder="0"
allow="autoplay; encrypted-media"
allowfullscreen
>
</iframe>
eg. find the starting subnet id of the first nerwoek, starting ip address of the first pc, ip address last pc ip address, then find broadcast id used by the switch, and find number of networks?
given: 192.23.4.5 /26
Sol.
Starting subnet
multiplying(AND) 192.23.4.5 by default subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
ans: 192.23.4.0
Ending Subnet ID
192.23.4.11000000 /26
192.23.4.192
Number of subnets that can be created
we need to put in host part given slash value i.e. /26
192.23.4.11000000(/26)
192.23.4.192
1 subnet, 0 host
no of subnets=2^n = 2^2 (2 bits from 26)=4 subnets
Number of PCs that can be connected in each subnet= 2^h-2 = 2^6-2 = 62
Broadcast ID: 192.23.4.63 (since numbers of machines is 62)
Next subnet ID: 192.23.4.64
Next subnet ID: 192.23.4.128
Next subnet ID: 192.23.4.192
| Subnet Id | Start pc ip of subnet | End pc ip of subnet | Broadcast Id |
| -------- | -------- | -------- | ------- |
| 192.23.4.0 | 192.23.4.1| 192.23.4.62 |192.23.4.63 |
| 192.23.4.64 | 192.23.4.65 | 192.23.4.126 | 192.23.4.127 |
| 192.23.4.128 | 192.23.4.129 | 192.23.4.190 | 192.23.4.191 |
| 192.23.4.192 | 192.23.4.193 | 192.23.4.254 | 192.23.4.255 |
Eg. 223.3.4.0 /28
sol. first subnet is already given
28 in binary is 11100
somehow got 240 i.e. 11110000
no of subnets = 2^4 = 16
no of hosts = 2^(4+8) - 2= 4094
# Class 3 - 22nd Aug '22
### VLSM
* Variable Length Subnet Mask
* eg - /27, /26, /25, /24
* Highest number of networks would be given priority
* Classless Subnetting
* Diff class IP range & diff class subnet
## IPv6 Advanced Features
[Intro and format](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/internet-protocol-version-6-ipv6/)
* larger address space
* IPv4 vs IPv6 [Resource](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/differences-between-ipv4-and-ipv6/)
* represented in hex code
* checksum field is not available
* no classes
* does not support VLSM
* inbuilt security by IPSEC
In IPv6 representation, we have three addressing methods :
Unicast
Multicast
Anycast
1. Unicast Address –
Unicast Address identifies a single network interface. A packet sent to a unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that address.
2. Multicast Address –
Multicast Address is used by multiple hosts, called as Group, acquires a multicast destination address. These hosts need not be geographically together. If any packet is sent to this multicast address, it will be distributed to all interfaces corresponding to that multicast address.
3. Anycast Address –
Anycast Address is assigned to a group of interfaces. Any packet sent to an anycast address will be delivered to only one member interface (mostly nearest host possible).
## IPv6 addressing
[resource](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/ipv6/ipv6_address_types.htm)
## Network File Service
NFS enable computers attached to the network to access files stored on other computers or servers in the saame way that access files on their own diskes.
* same file can be accessed by multiple clients at the same time
* the clients may different priviliges
## Web Server and Service
A software or hardware that accepts requests via HTTP or HTTPS.
A web service is a methodd of communication berween two electronic devices over the Web(Internet). The W3C defines a "web service" as "a softwarre system designed to support interoperable machine to machine interaction over a network"
Advantages of cho
ng a web service:
- The web is an inexpensive means to publish and distribute information
Disadvantages of choosing a web service:
- Increase in the consumption of bandwidth on the network
- Often requires additional services to place les on the web server (i.e. FTP)
## Remote Access Service
Using special server-based software the administrator can quite literally possess
or control the mouse and keyboard of the other computer to do troubleshooting
and maintenance tasks, thus saving much time and potential expense.
Eg. anydesk, teamViewer.

## Web Hosting
A web host, or web hosting service provider, is a business that provides the technologies and services needed for the website or webpage to be viewed in the Internet. Websites are hosted, or stored, on special computers called servers.
## VPN
A virtual private network extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.
Virtual: Information within a private network is transported over a public network.
Private: The traffic is encrypted / integrity checked to keep the data condential.
### Creating a VLAN
In config mode
```
vlan 10 // some number
name sales // dept name
exi //exit
do wr // do write
do sh vlan // showing the created vlans
// CONFIGURING MACHINES IN A VLAN
INT RANGE FA0/1-2 //
SWITCHPORT MODE ACCESS
SWITCHPORT ACCESS VLAN 10
// configuring single machine in a vlan
INT FA0/1 //
SWITCHPORT MODE ACCESS
SWITCHPORT ACCESS VLAN 10
```
## Routing
Forwarding data packets from one location to another remote location.
[Types of Routing](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-of-routing/)
### Default Routing
All traffic will be forwarded to the single source router with destination interface.
### Static Routing
Network admin decides the path.
### Dynamic Routing
#### Routing Protocols
* Distance Vector Protocol
* Bellman Ford Algorithm
* Link State Protocol
* Djikstra or SPF (Shortest Path First) Algorithm
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

