---
title: AIS3 2020 Collaborative Memo
# some Chinese names will still be present; this is to import the fallback fonts
lang: zh-tw
tags: AIS3
---
{%hackmd By3kXOghU %}
<div class="heading-custom">
Unofficial AIS3 2020 Collaborative Memo
</div>
:::info
- **Official Memo:** [Here](https://hackmd.io/@AIS3-2020/AIS3)
- **Location:** Taiwan Tech IB101
- **Date:** July 27 ~ Aug 2, 2020
:::
# Day 1 - 7/27 Mon.
## Legal Matter - Information Security and Ethicality
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 蘇文傑
- Investigator @ Ministry of Justice Investigation Bureau
- Graduated from NTU, NCTU
- Fields
- Cryptocurrency
- Money laundering
**Contact**
- M44070 @ MJIB.GOV.TW
- 02-27368721#6113
:::
### Recent Trends in Infosec in Taiwan
- Use of cryptocurrency in drug dealing or other illegal activities
- Ransomware attacks in various governmental properties or departments
- How does this relate to us?
- Article 36: #358 ~ #363
- Teenagers and or students are frequently caught in legal troubles (e.g., an underage teenager was caught selling DDoS service via cryptocurrency)
> "Technological progress is like an axe in the hands of a pathological criminal."
> [name=Albert Einstein]
## Critical Infrastructure - Information Security of Industrial Control Systems (Part 1)
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 黃鼎傑
- Chief of Industrial Control Systems Information Security Department @ Taiwan Institute for Information Industry
- Phd. @ Taiwan Tech
- UC Berkeley visiting scholar
- Fields
- Robotics
- Information security
- IoT communication
- Communication protocols
- Industrial IoT
- Sensor network
**Slides**
:::
### Overview of Industrial Control Systems Threats
#### History of Industrial Application
- Various iterations of industrial revolutions led to automation
- Today
- Big Data-driven production
- Connected network to control production
- Smart automation
- Smart production
#### Threats in the Last Decade
- Iraq electricity network
- Stuxnet worm
- Ukraine power plant attack
- ...and many more
Cybersecurity incidents among the industrial industry has been increasing gradually or even exponentially over the years.
- 2010: Iraq stuxnet worm; 60% of the computers in the facilities were affected
- 2014: US power plant attacked by ransomware hidden in a flash drive; the flash drive was brought in by one of the maintenance groups
- 2014: Steel works production plant was attacked by Trojan, lose 50% production
### Analysis of Attack Vectors in Industrial Control
Many insecure networks were and are exposed on the public network, and these services are often caught by services like [shodan.io](https://shodan.io).
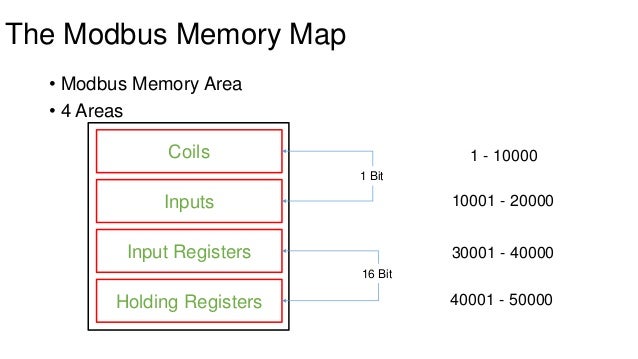
- Modbus protocol
- [Protocol specs](https://www.modbustools.com/modbus.html)
- Port 502
- Plaintext
- 8,221 services were found, and as of 2017, 360 Taiwan-based services are listed
- OPC UA
- [Protocol specs](https://opcfoundation.org/developer-tools/specifications-unified-architecture/part-1-overview-and-concepts/)
- Port 4840
- Can be exploited to control factory devices
- Often placed inside OT
IT vs OT
- Internet - IT Networks - firewall - OT Networks - Remote Management
#### Definition of ICS
> An ICS consists of combinations of control components (e.g., electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic) that act together to achieve an industrial objective (e.g., manufacturing, transportation of matter or energy).
> \- [SP 800-82 Rev. 2](https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-82/rev-2/final)
#### What is SCADA?
- Device level - Control level (PLC) - Supervisory level (HMI; Human Machine Interface)
- Different services are isolated in different layers -> can be used to check malicious applications
#### Quick Overview of PLC
- Controlled via various ICS protocols
- HMI -> Controller > Actuators > Controlled Process > Sensors
- Remote <-> Controller > Actuators > Controlled Process > Sensors
- Attack vectors via protocols like modbus, OPC UA, or other ICS protocols
#### ISA 99 Industrial Automation and Control Systems Security


> via [Cisco Ethernet-to-the-Factory 1.2 Design and Implementation Guide](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Verticals/EttF/EttFDIG/ch2_EttF.html)
> Most factories *probably* don't follow the guidelines due to economical reasons.
> [name=黃鼎傑]
Automation ICS Internet Hierarchical Layout
- Management > Planning > Supervisory > Control > Field
- OSI Model
- 
#### Examples of Attacks
- ICS & HMI servers are frequently targeted
- Threat actor may be familiar with TCP/IP
- HMI server can be used to monitor and control ICS network and infrastructure
- Direct control over various control processes
- How are they targeted?
- Through various entry points in enterprises
- e.g. for convenience-sake, *some* employees might open up the RDP port to the public
### Industrial Control Systems Defense
#### ICS Operating Systems
- Mainframe systems
- Windows XP
- Windows 2000 Workstation
- Windows Server
- Linux
- Redhat
- The biggest concerns are of course... Windows!
- Windows 7 and older Windows Server editions have already reached EoL
- Lack of security patches
- EternalBlue
- REDSIG
- and many more...
- What happens when an OS reaches EoL?
- No security patches
- No services
- How can we reduce the risk?
- System and edge networks should introduce more and more infosec defenses
- Virtualization
#### Backup of ICS
- Disk imaging
- Frequent system backup in case of ransomware or malware attacks
#### Endpoint Protections
- Application whitelisting, sandboxing
- Tripwire
- IP tables
- Log management
- Understand and frequently analyze Windows Event Logs, ACLs, registries, `syslogd`, log aggregation via PowerShell
### Industrial Control Systems Network Protection
#### ICS Communication Protocols
- Complexity and needs
- The protocol has to be immediate, deterministic, reliable, safety critical
- Need for interopability
- Transitioning from serial to network
- through ethernet, TCP/IP, etc.
#### Ethernet in ICS
- Ethernet-based ICS protocols
- Examples
- Goose Messaging
- SAV or Sampled Values
- Pros
- No TCP/IP Overhead
- Nonroutable (secure)
- Low-latency
#### Defending Against ARP and DNS Attacks
- ARP Spoofing
- Empty ARP packets
- IDS/IPS devices can be used to detect this type of attack
- DNS Spoofing (Cache Poisoning)
#### Common ICS Protocols
:::danger
Most of these protocols are not encrypted! This means these protocols are likely susceptible to MiTM attacks.
- Lack thorough protocol and data checks
- Lack any additional security checks
:::
- Universal ICS Protocols
- Modbus
- TCP 502
- OCP UA
- TCP 4840
- OPC UA XML
- TCP 80, 443
- Process Automation Specific Protocols
- EtherCAT
- UDP 34980
- ...and more
- Energy Sector Specific Protocols
- DNP3
- DLMS
- ICCP
:::success
More modern and secure standards are being rolled out, such as `IEC 62351`.
- Packets need to be signed
- VPN encryption protocol
:::
#### Lack of Security-layer Devices
- Traditional WAF will only check for IP and TCP/UDP header
- USB devices are not off-limits in these areas
- Upper-management are often not as concerned; therefore, not willing to invest in this area
- They are often more concerned about other areas such as password, patch, monitoring, encryption management
- Multi-interface devices may even be able to circumvent these protections
- Dial-IP VPN
- Wi-Fi
- Cellular
## Critical Infrastructure - Information Security of Industrial Control Systems (Part 2)
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 李美玲
- Project Manager of Industrial Control Systems Information Security Department @ Taiwan Institute for Information Industry
- Experience
- ICTD Threat Detection Solution
- Fields
- ICS Pentesting
- ICS Threat Detection
**Contact**
- Email
- Joanna @ iii.org.tw
:::
### ICS Network Attack - Case Study
- For example...
- Turkey
- Gasoline delivery pipeline explosion
- Japan
- Oil factory explosion
- Vulnerabilities in critical infrastructures
- Defense in edge servers
- Unable to detect unauthorized activities
- Weak linking among ICS networks and internal networks
- Feature management
- System admins can access industrial system tunneling
- Permission management
- Weak passwords
- System allows for unauthorized access
- Identity identification
- Lack of user activities logging
- Laid off or ex-employee account management
- Privilege management
- Most or many employees have excessive or unnecessary level of permissions
- Resource management
- Lack of human resources may lead to lower incident response and network monitoring efficiency
#### TSMC WannaCry Outbreak
- Threat actor > Bot Domain Random Swift > ransomware activation > dead
- Mishaps during the standard procedures
- Under normal circumstances, USB devices are scanned by a standalone device.
- However, due to an unknown reason, the device was not scanned before being plugged into a mission-critical device.
- WannaCry spread via EternalBlue (port 445)
- Large factories like TSMC practically never stops the production line; security patches cannot be deployed right away
### ICS Network Attack - Pentesting
#### ICS Infrastructure
- Modbus
- Publicly available protocol
- Request-response protocol
- Master-slave implementation
- Packet contains...
- Slave identification
- Function code
- Execution data
- i.e., a master device has to initiate a request and await a response from its slave counterpart
- e.g.,
- IPC (SCADA) -> PLC -> Air Quality Control and/or Water Level Control


#### Attack Workflow
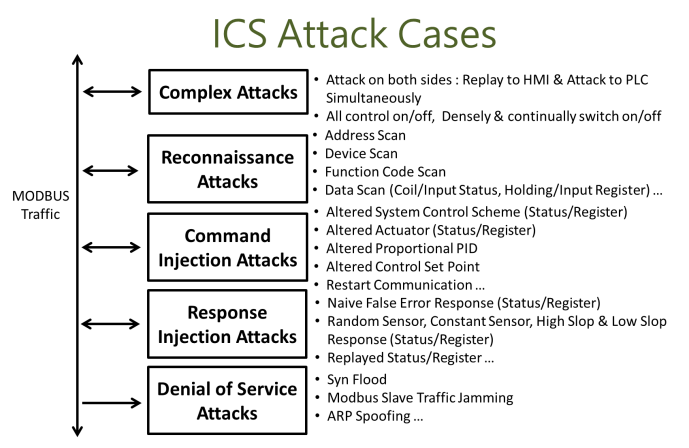
- Recon
- IP scanning
- Obtain device IPs
- Feature scanning
- Obtain device ID and function code
- Address and value scanning
- Obtain various types of data address and values
- Command injection
- Enabling or disabling features
- Coil status: FC 5/15
- Holding register: FC 6/16
- Response injection
- Fore value responses
- Values within or outside of expected value
- Replay
- Regularly, frequently or infrequently replay a series of packets
- Error response
- Respond with a specific error code or even return a random one
- Denial-of-Service
- ARP Spoofing
- Response injection
- Command injection
- Both
- 
- SYN Flooding
### ICS Network Attack - Tools
- Testing & Scanning
- [ModScan/ModSim](https://www.win-tech.com/html/demos.htm)
- [SMOD]()
- Python 2.x ModBus implementation
- ISF
- Industrial Security Exploitation Framework
- Python 2.x
## Digital Forensics - Investigation Report on Chimera APT
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- Chung-Kuan Chen (陳仲寬/Bletchley)
- Senior Security Researcher, Cycarrier Technology
- CHROOT member
- Reviewer of HITCON, HITB
- Discovered several vulns in Synology/QNap
- Field
- Network A&D
- ML
- Software vulnerability
- Malware and program analysis
**Contact**
- Twitter
- @bletchley13
**Materials**
- [Introductory challenges and slides](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1NuZYwnr8izJkn-oG2BpJEEmPPgNDnKg8)
:::
### Network Threat Hunting
#### What is Threat Hunting?
- Cyber threat hunting is the practice of searching iteratively through data to detect advanced threats that evade traditional security solutions.
- Discover hidden attackers that your detection mechanism cannot find
- Firewall
- IDS/IPS
- Anti-virus
- VirusTotal
- Analytics-driven
- Machine-learning and UEBA, used to develop aggregated risk scores that can also serve as hunting hypotheses
- Situational-awareness-driven
- Crown jewel analysis, enterprise risk assessments, company-level or employee-level trends
- Intelligence-driven
- Threat intelligence reports, threat intelligence feeds, malware analysis, vulnerability scans
- Proactive Approach as opposed to Reactive Approach
- Actively looking for incidents without waiting for an alert
- iterative search through data
- using threat intelligence
- using knowledge about attackers' tactics, techniques and procedures
:::warning
Be very careful during incident response.
- During initial assessment or analysis, a rookie may attempt to remove the malware right away, either deleting the malware before the C2 station(s) were found, or the threat actor may be aware of the fact that the IR responder is attempting to get rid of the backdoors.
:::
#### Challenge of Network Forensics
- Network traffic is difficult to detect on gateway machine
- Attacker may use a common service as C2
- Encrypted traffic
- Certs may not be trustworthy
- Lack of abnormal user account
- Investigation scope may be too large
- Threat actor may compromise AD admin priv
- Shouldn't rely on a single investigation to conclude the entire case; multiple investigations or a overview of each incidents may be required
#### Moloch
Moloch is an open-source, large-scale, full packet capturing, indexing, and database system.
- Useful for large datasets
- Support common protocols
- High extensibility
### Endpoint Threat Hunting
#### Tools
- Sysmon
- Free EDR solution (kinda)
- Sysinternals
- Kernel-level monitoring toolkit
- Sysmon + Winlogbeat + ELK
- Windows Audit Log
- 106 - Task Scheduler spawn
- 4688 - Process spawn
- 4104 - PowerShell
- 4624 - Account login
- ELK (Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana)
- neo4j
- Graph database
### Machine Learning for Threat Hunting
:::warning
Machine learning cannot do everything. It is the mapping of human's mind.
:::
### Case Study - APT Chimera
#### Security Incidents in Taiwan
:::warning
Taiwan has the highest wafer production capacity. If a malware successfully bring down a production plant, it could wreak havoc for the entirety of Taiwan's economy.
:::
- ASUS ShadowHammer
- CPC ransomware attack
- TSMC ransomware attack
#### Large-scale APT Attacks in Taiwan
APT "Chimera"
- Vendors in the Hsinchu Science Park were targeted between 2018 to 2019.
- Investigation period: 2018~2019
- An attack on the entire industry service.
- More than 7 vendors worldwide were targeted by the same threat actor.
- Merged various open-source tools into one malicious payload
- Mimikatz
- CobaltStrike
- Dumpert
- C2 is hosted in public cloud
- Google AppEngine
- Azure
- Goal
- Steal documents, source code, SDK of chip-related projects
##### Victim Background
- Codename A: Long-term partner with CyCarrier
- 15 endpoints and 6 user accounts were compromised
- 4 malwares and 8 C2 servers
- Uses disguised Cobalt Strike assembly
- Inject payloads into other processes
- Backdoor was disguised as a Google Update client
- Uses cloud hosting services (i.e., \*.appspot.com; GCP instance)
- Root cause analysis
- Backdoor was delivered via local server to client around 16:00~17:00
- Attack was launched before employees get off their work
- Uses task scheduler and WMIC to deliver persistence and binary payload
- Local server's AD database and registry were archived and collected by the threat actor
- Threat actor delivered the payload from a separate notebook device to the server via task scheduler
- RDP/`net user`/`quser` attempts were detected via hacked VPN credentials
- Codename B: One-time IR service
- IR only occurred well after the attack
- Client was not aware of the attack until Codename C partnered up with Codename B, and Codename C discovered network anomalies from Codename B
- Fileless malware
- Use of PowerShell
- Injects Cobalt Strike backdoor to another process
- At this rate the company was seriously hacked; difficult to analyze
- Threat actor returns on a quarterly basis to collect new data
- Deployed SkeletonKey injector at a later date
- Merged `dumpert` and `mimikatz` tools
- More endpoints were compromised
- Threat actor frequently uses archive software to steal confidential information, such as SDKs, product roadmap, etc.
# Day 2 - 7/28 Tues.
## Critical Infrastructure - Information Security of Industrial Control Systems and Production Systems
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 蔡松廷
- TeamT5 Founder
- Decades of security industry experience
- 15+ years of IR and threat research experience
- Co-founder/cheif director of HITCON
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
### TeamT5 Quick Introduction
Focuses on advanced cyber threats:
- Supply-chain attack
- Cyber espionage
- Long-term targeted attack
- State-sponsored attack
:CN: :ru: 🇰🇵 v.s. :US: :JP: :KR: 🇮🇳
Cyberthreats in Taiwan
- Cyber espionage
- Information operation
- Sabotage
New IR case every 2 weeks
- Government
- Hospital
- NGO
- ...etc.
### OT/ICS Security
Taiwan recent incidents
- Ransom
- Pay in 5 days
- USD $3000/device
- Impact: 1 day shutdown
- Impact: 1 week partial-work
- Only IT was affected
- Malware
- Coldlock
- CobalStrike
- Deployed via Active Directory (DC was compromised)
- Infrastructure
- ProtonMail and Tutanota
- VPS in US
- Investigation
- 10+ companies might be targeted as well
- Chinese APT involved
Lessons learned
- Responsibility and function teams for Incident Handling
- Plan and SOP for incident handling
- Plan and SOP for data/service recovery
- Finding root cause - incident handling command center (coordination)
- High-level support is important
- Don't forget a dedicated person or team for internal/external communication
- Information Sharing is very helpful
Securing critical infrastructures
- Chemical
- Commercial facilities
- ...etc.
:::warning
Availability is king!
- No IPS, WAF, AV, system hardening, anti-exploit, application control, etc.
:::
Complicated environment
- Various vendors, systems, and protocols
- Lifespan of OT system is long
- A device may be running for more than 10 years
- Windows 2000/NT
- Difficult to have a general solution
Patch is not allowed
- Disabling system update is very common
- Impact of system update?
- Sometimes even the supplier doesn't recommend installing update
Trust the supplier (not)
- Most of the critical infras rely on suppliers for cyber-security
- They could *only* trust the supplier
- Some of them worry about what vendor provides
- Security issues? Call the supplier
Silver bullet solution
- Airgapped or isolated from the Internet
- Worry-free and 100% secure
- We don't need a security team
### Group Project
- Startup pitch to investors or customers
- 4 minutes
- Team name
- Problems you want to solve
- Your idea and solutions
- Business opportunities
## National Security - Manipulation of Public Opinion via Social Media
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 簡信昌
- Chief Technology Officer @ Mirror Media
- Software engineer background
- Worked at Yahoo/Verizon Media
:::
### Importance of Public Opinions
- Collection of public opinions
- Study products
- Understand markets
- User feedbacks
- Web 2.0
- Increased interactivities
- Social media
- PTT is a big source of news in Taiwan
- Ployed by algorithms
### Case study
Twitter 2019 Mass Account Removal
- Twitter removed suspicious accounts related to Hong Kong protests
- No particular patterns among these accounts
- Posts seemed inconspicuous
- Used various languages
- Some were obviously bots, while others were difficult to identify
- Followed celebrities and others
- Lack of followers
- Rarely interacted with others
- Twitter published 2 datasets
- Through machine learning, the following discoveries were found:
- Behavior patterns
- Post time
- Bots often post based on a certain pattern (e.g., Asia Pacific work hours)
Facebook removed a number of Facebook Pages
- Facebook usually doesn't intervene
- Unusual
- 2019/12/14 Facebook announced that they deleted 118 Facebook Pages, 99 Groups, and 51 duplicate accounts
- Over 50% of the accounts weren't created until late 2019
- Taiwan Presidential Election
- Similar or identical posts
- Copy paste?
- 2019/12/17 More fake posts started popping up
- Hashtag movements
COVID-19-related Public Opinion Manipulation
- Once again, Twitter has become the warzone for this topic
- Started off with praising of China during February
- ...then these accounts started attacking foreign countries
-
# Day 3 - 7/29 Wed.
## National Security - Data-driven Research on China's Information Manipulation
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 游知澔
- IO Research Laboratory
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
### What is Information Warfare?
- Targeted attacks
- Collaborated effort
- Data engineer
- Organizer
- Researcher
- Community members
### Data Parsing
Tools
- CKIP
- TF-IDF
- Term frequency
- Inverse document frequency
Process
- Sentence -> TF-IDF vectorize corpus -> weighing keywords -> ranking keywords
### Fake News
Spread of fake news have been rampant over the last few years, especially China-related news
- Especially rampant on LINE
#### Case Study
2019/12 ~ 2019/02
- 166404 posts -> 27742 posts about COVID19 -> ~11458 posts about China/US -> 5012 posts unrelated to China propaganda -> 1972 posts about politics
- Spiked on 3/1
## Software Development Security - Development Security and Information Security Unit Testing
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- YSc
- Balsn CTF Team Co-founder
- Security consultant & engineer
:::
:::success
Automation = success!
:::
### DevOps & Security
Deployment pipeline? Software development lifecycle?
- Waterfall dev
- Agile dev
Fast development and release cycle
- Difficult to integrate pentesting or security testing
Solution
- CI/CD!
- Design -> code commit -> CI tests -> code review -> stage deploy -> tests -> prod deploy -> release
### Security Testing
How to pentest a website?
- Aside from XSS/SQLi...
- Preparation
- Business impact
- Standardize
- Vulnerability assessment
- CVSS 3.1
- Threat modeling
- STRIDE
- PASTA
- Security Testing
- Range
- OWASP Testing Guide V4
- OWASP ASVS
- Test automation
- Hardening
- Automated filtering
- Vulnerability analysis and report
- Security testing optimization
- What? - What are we protecting? Keys? Customer data?
- Who? - Who might attack? Script kiddie?
- Where? - From where? From site, feature, or individuals?
- How? - How might the attack be launched? Open-source scanner? Social engineering?
- Static analysis
- Dynamic analysis
#### Information Gathering
- Recon
- Network information
- DNS information
- Domain listing
- Subdomain enumeration
- IP & IP lookup
- Service information
- Software services
- Development tool
- Development framework
- Service version
- Backend language
- Service framework
- Back and frontend framework
- API framework
- ...etc.
- Basic tooling
- dig, curl, whois, nmap, burp, etc.
- OSINT
- Google Hacking, Shodan, Censys
- Configuration and Deployment Testing
- Configuration
- Cloud config
- Server config
- Deployment
- Cert & key management
- ACL & log management
- Basic tooling
- [Gixy](https://github.com/yandex/gixy)
- [kube-hunter](https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-hunter)
- S3 scanner
- OWASP ZAP
- Nikto
- Auth & Session Management Testing
- Role definitions
- Password policy
- Rate-limit & Captcha
- Authorization
- Session lifecycle/cookie flags
- Basic tooling
- dirsearch
- wfuzz
- burp
- Behave
- Data Validation Testing
- SQLi
- NoSQLi
- Code injection
- Command injection
- XML injection
- CRLF injection
- Basic tooling
- sqlmap
- OWASP ZAP
- Require additional tuning
# Day 4 - 7/30 Thurs.
## Web Security - Red Team
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 楊鈞皓
- Information Security Engineer @ CHT Security
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
> Red teaming is not always possible; instead of a team, you may find yourself to be a red loneman.
>
### Introduction
Blue Team vs. Red Team
Blue Team
- Firewall
- DDoS prevention
- IPS/IDA
- WAF
- APT prevention
Red Team
- Attack and discover edge servers, deployment misconfiguration, information from OSINT, social network, darknet, etc.
- Prioritize service stability
- May require knowledge of...
- Hardware
- Information gathering
- Social engineering
- Vulnerability research
- Development ability
- Cryptography
- Reverse engineering
- Requirement evaluation
- Evaluate requirement
- IP range
- Root domain
- Cloud services
- What?
- Wireless network
- Physical and software security
- Target?
- Financial information
- AD server
- Obtain information from upper-management
- Who?
- Outsider
- Employees with malicious intent
- PCs within the network that suffered from phishing attacks
- Recon
- Domain and IP
- Domain range
- IPv4/6
- Subdomain
- Whois
- Toolings
- Google Hacking
- Relevant domains (e.g. `target inurl:example -site:example.com`)
- Shodan
- BuildWith
- Trends
- Domain timeline
- Relevant domain
- SecurityTrails
- DNS History
- Subdomain
- Domain and IP history
- API
- AMASS
- DNS, scraping, cert, API, web archives
- e.g.
- `amass intel -active -adder 140.118.31.99`
- `amass enum -d example.com`
- `masscan`
- IP to domain resolve
- View cert -> cert domain info
- CDN
- Direct IP access may not be allowed depending on the CDN (e.g., Cloudflare)
- CDN bypass
- Bypass CDN sometimes means no WAF
- DDoS?
- Easier to debug
- Easier service discovery on the remote server
- CDN bypass?
- Try to discover the older IP
- Try to find real IP on WAN
- Try to discover subdomains protected by CDN
- Header inspection
- Use different DNS provider
- Service provider
- Information
- Might provide a list of known or prominent clients
- GitHub
- Backend system
- Infosec awareness
- Obtain source code -> code review!
- Weird honeypots
- [Honeypot or Not](https://honeyscore.shodan.io)
- People
- Employee ID
- Email, IP, subdomain discovery via theHarvester
- Email
- Weak password (e.g. `1qaz2wsx#EDC`)
- Employee personal information
- GitHub, Facebook, LinkedIn, PTT, external email provider
- Useful information
- Full name
- Birthdate
- Experience
- SSN
- Personal email address
- Toolings
- GoPhish
- Social engineering
- RLO-based attachment naming
- Phishing email
- OAuth phishing
- Attack without downloading files, account credentials to lower the awareness
- WiFi security
- Wifiphisher
- Aircrack
- DNS hijacking
- WiFi -> intranet
- Business email
- Common accounts
- Password policy
- Facebook, LinkedIn, Yahoo, Gmail
- Service
- Third-party services, frameworks, software supplier
- Known vulnerabilities
- Exploit-db, CVE, HITCON Zeroday
- Toolings
- nikto
- nmap
- OpenVAS
- searchsploit
- ExploitDB
- Vulnerability discovery
- SQLi
- UFU/AFU
- Admin panels with weak passwords
- Persistence
- File naming (e.g. `index1.php`)
- Modify file date
- Encode or encrypt transfer data
- Separate WebShell and the usual IP
- Log removal (not recommended; may disrupt service)
## National Security - War of Public Opinion: Offense, Defense, and the Challenge of Digital Forensics
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 林雨蒼
- CEO @ Doublethink Lab
- 吳銘軒
- Analyst @ Doublethink Lab
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
### China Propaganda 'Infodemic'
False information regarding the pandemic
- Difficult to identify and verify
- Unsustainable journalism
- Political bots and automation
- Foreign influence operations
- Data-driven advertising and campaigning
- Platform blackboxes
How does China influence the global media?
- Propaganda
- Censorship
- Content delivery
How does online information warfare spread?
- Events -> Motivation -> Communication -> Message -> Medium -> Information Operation -> Receiver -> Effect
<missing a chunk here, will add later>
### Prevention
# Day 5 - 7/31 Fri.
## National Security - The Impact of Forged Base Stations on 4G/5G Security
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- 鄭欣明
- Associate Professor @ Department of Information Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
### Cellular Network
#### 5G Radio
- Network slicing
- Software-defined architecture
- Activate different components and functionalities to serve service with specific QoS requirement
- Introduction of virtualization technology
### Security Issues
- Mutual authentication
- Wireless medium is accessible for everyone in the vicinity
- Identifiers can easily be forged
- User authentication from network provider
- Accounting, authorization, and the association of data sessions to a legal person
- Network authentication from user
- Network authentication for traffic confidentiality
- GSM: By faking the identity of a legitimate network
### Rogue Base Station Attacks
Implementation of Rogue Base Station Attacks
- Software Defined Radio with GNU Radio
- A free software development toolkit
- Provides signal processing blocks
- Low-cost external RF hardware
- USRP by Ettus Research
- Open-source Software
- OpenBTS, OpenBTS-UMTS, Osmocon, OAI,srsLTE, NextEPC, free5GC
- Very possible
- Cheap compared to commercial products
- Free software
- ~50,000 TWD
#### Classifications of Attacks
- Isolated rogue BS attacks
- The rogue BS cannot connect to the operational core network
- Leverage the procedure before AKA
- Leverage the unencrypted message
### Conclusion
- Rogue base station attack is possible for academic researchers and of course for the adversary
- Cheap
- Easy to deploy
- Portable
- Detection and prevention or attack is necessary
- Modification on protocols
- Protocol in 5G is similar to 4G
- Lots of vulnerabilities exist
## Software Development Security - Head First Product Security
### 👨🏫 Author Background & Other Info
:::success
**Presenter(s)**
- Ken Lee
- Former Product Developer
- Chief Security Officer
- Head of Synology Inc. Security Team
**Contact**
**Slides**
:::
### Synology PSIRT
#### Scale of Synology Inc.
- Over 6M servers up and running
- Running 57M apps
- Managing 870K connections to Synology
- Securing tens of EB of data and peace of mind
#### What is PSIRT?
The Synology Product Security Incident Response Team (PSIRT) is dedicated to managing the receipt, investigation, coordination and public reporting of security vulnerability information related to Synology products.
Product Security
- Security infra
- Cryptography
- Certification and compliance
- Anti-piracy
- Strategy
- Discovery -> Triage -> Remediation -> Disclosure
- Record timeline
- Security advisory
#### The Phantom Menance (2013)
- Started working in 2013/01
- No developers responded to vulnerabilties
- Lacked a sense of cybersecurity
- High-profile CVEs were notified by customers
#### Attack of the Clones (2014-Q1-2)
- Heartbleed struck
- Helped IT team patch services
- Immature security advisories
#### Revenge of the Sith (2014-Q3-4)
- Severely affected by Synolocker
<!-- Need confirmation for above -->
- Built a working group for security
- Deployed security mitigations to DSM 5
#### A New Hope (2015)
- Approved cybersecurity act for DSM 6.0
- Rebuilt core DSM infrastructure
- Created a build farm for security releases
#### The Empire Strikes Back (2016)
- Built vulnerability response program
- Built invitation-only bounty program
- Reported critical flows of Photo Station
- Disclosed vulnerabilties w/o confirmation
#### Return of the Jedi (2017)
- Authorized as the CNA
- Built incident response program
- Announced security bug bounty program
- Built product security assurance program
#### The Force Awakens (2018)
- Built PSIRT
- Authorized as a member of [FIRST](https://www.first.org/)
- Actively join international communities
#### The Rise of Skywalker (2019)
- Built CSIRT and reorganized SIRT
- Responded to high-profile vulnerabilities
- Connected with CISA & DHS
#### Community Engagement
- MITRE
- CVE ecosystem
- CVE CNA Summit
- Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST)
- Annual conference
- Special interest group
- CERT/CC
- Precaution against upcoming vulnerabilties
- CERT vendor meeting
:::warning
Do not make getting a CVE of your own as a goal. It's about how you can help the community.
:::
### Vulnerability Response
- MITRE Template
- [VULNTYPE] in [COMPONENT] in [VENDOR] [PRODUCT] [VERSION] allows [ATTACKER] to [IMPACT] via [VECTOR].
- [COMPONENT] in [VENDOT] [PRODUCT] [VERSION] [ROOTCAUSE], which allows [ATTACK] to [IMPACT] via [VECTOR].]
- e.g.,
- Directory traversal vulnerability in PixlrEditorHandler.php in Synology Photo Station before 6.7.3-3432 and 6.3-2967 allows remote attackers to write arbitrary files via the path parameter.
- CPE
- List vulnerable version
- Earlier versions are affected
- 1.2.3 and earlier
- 1.2.3 and 1.3.4
- Fixed or updated version
- before 1.2.3
- Type of users
- Remote attackers
- Remote authenticated users
- Local Users
- Physically proximate attackers
- Man-in-the-middle attackers
- CAPEC
- Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification
#### What counts as a CVE?
* CNT1 | Independently Fixable
* CNT2 | Vulnerability
- CNT 2.1 | Vendor Acknowledgment
- CNT 2.2A | Claim-Based
- CNT 2.2B | Security Model-Based
* CNT3
- Shared Codebase
- Libraries, Protocols, or Standards
Inlcusion Decisions
- INC1 | In Scope of Authority
- INC2 | Intended to be Public
- INC3 | Installable / Customer-Controlled Software
- INC4 | Generally Available and Licensed Product
- INC5 | Duplicate
Edge Cases
- MD5 / SHA-1
- Default credentials
- Cloudbleed
- End-of-life products
Update CVE Entries
- Reject
- Not a vulnerability
- Not GA
- Merge
- Split
- Dispute
- Partial dispute
Assumptions
- Scoring should assume detailed knowledge
- Assume vulnerable configurations
- Score based on privileges gained, not attained
- Allows multiple CVSS scores for a single vuln
### Secure Coding
Code Review
- Ensure code quality and maintainability
- Share knowledge and make everyone better
- Find defects or trivial logic errors
### TLP
### TLP:RED
Cyber Kill Chain
- Recon
- Weaponization
- Delivery
- Exploitation
- Installation
- Command and Control
- Actions on Objective
Lessons learned
- Never trust inputs w/o sanitization
- RTFM before committing patches
- Security-by-design and by-default are required
- Security is as important as UX
- Supply-chain security
Analysis
- Relative path traversal
- Missing authentication for critical function
- Permissions, privileges and access controls
- Insufficient verification of data authenticity
- Information exposure
Improvement
- Confined runtime privileges
- Revised the authentication and authorization for CGI and WebAPI
- Introduced self-check for system integrity
- Reviewed Synology-made protocols
### Lab
<style>
.markdown-body ul > li > p {
display: inline-block;
margin-top: 0;
}
</style>
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet

