---
tags: cs231n, computer vision, deep learning
---
# cs231n Lecture 1 - Image Classification
## What is image classification
* Motivation: Human->easy, Machine->hard
* To know the vision Machine sees
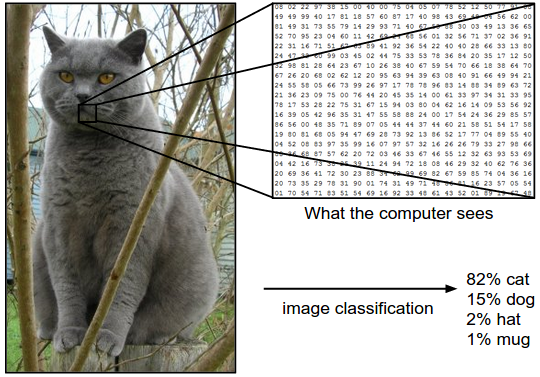
* Pseudo (What we want to do!!):
```
def classifier(image)
# Do some magic here!!
return class_label
```
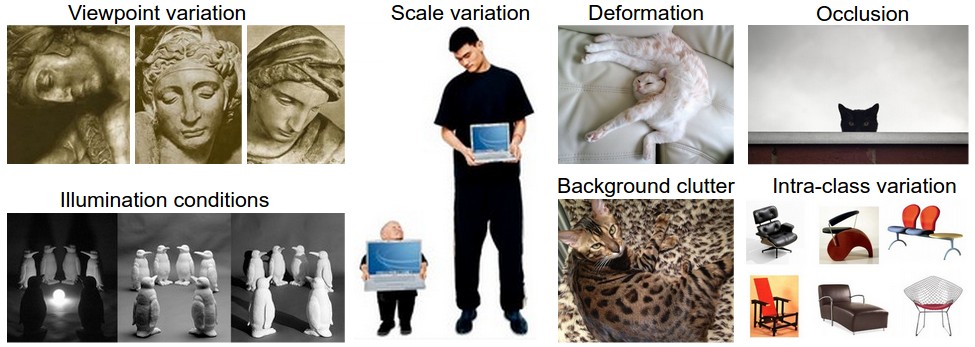
## Challenge to do image classification
* Type:
* Viewpoint variation
* Scale variation
* Deformation
* Occlusion
* Illumination conditions
* Background clutter
* Intra-class variation
* edge detection -> data driven approach
* reason: since edge detection varies according to the target we want to classify
* edge detection

* data driven

* Way the machine learning do:
```
def training(train_image,label)
# Train our model
return model
```
```
def testing(model, test_image)
# Model classify the test_image
return class_label
```
* Tricky tip to train a model:
* take whole dataset to training -> **BAD**
* split whole dataset to training & testing set -> **BAD**
* split whole dataset into training, validation, and testing set -> **BETTER**
* Cross Validation -> Good but impractical on large dataset (**expensive!!**)
## What is KNN (K Nearest Neighbors)
* L1 distance & L2 distance & Linf distance


* How to define a KNN class
```
import numpy as np
class NearestNeighbor(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def train(self, X, y):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example. Y is 1-dimension of size N """
# the nearest neighbor classifier simply remembers all the training data
self.Xtr = X
self.ytr = y
def predict(self, X):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example we wish to predict label for """
num_test = X.shape[0]
# lets make sure that the output type matches the input type
Ypred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype = self.ytr.dtype)
# loop over all test rows
for i in xrange(num_test):
# find the nearest training image to the i'th test image
# using the L1 distance (sum of absolute value differences)
distances = np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1)
min_index = np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance
Ypred[i] = self.ytr[min_index] # predict the label of the nearest example
return Ypred
```
* The result
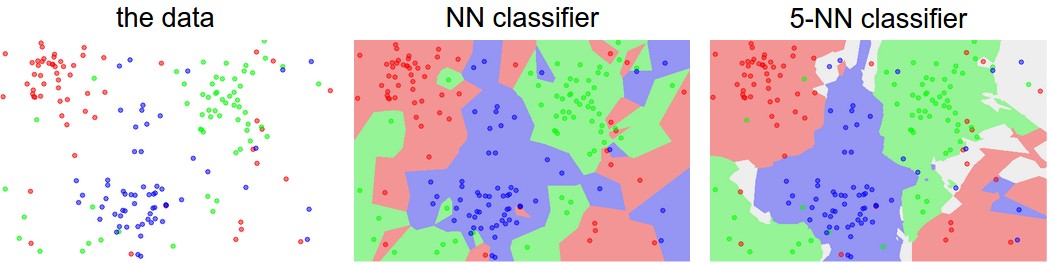
* The hyperparameter
In this case, K & the chosen distance all need to ADJUST to find the best result
* Evaluation:
**BAD, NEVER BEEN USED**
-> train: O(1), test: O(n) = slow test
-> metrice distance not informative

-> the feature exponentially grow

## What is Linear Classification
* Like LEGO...

* The linear classifier model


* Hard Cases

* Question: How to determine whether weight W is good?
